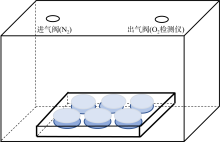
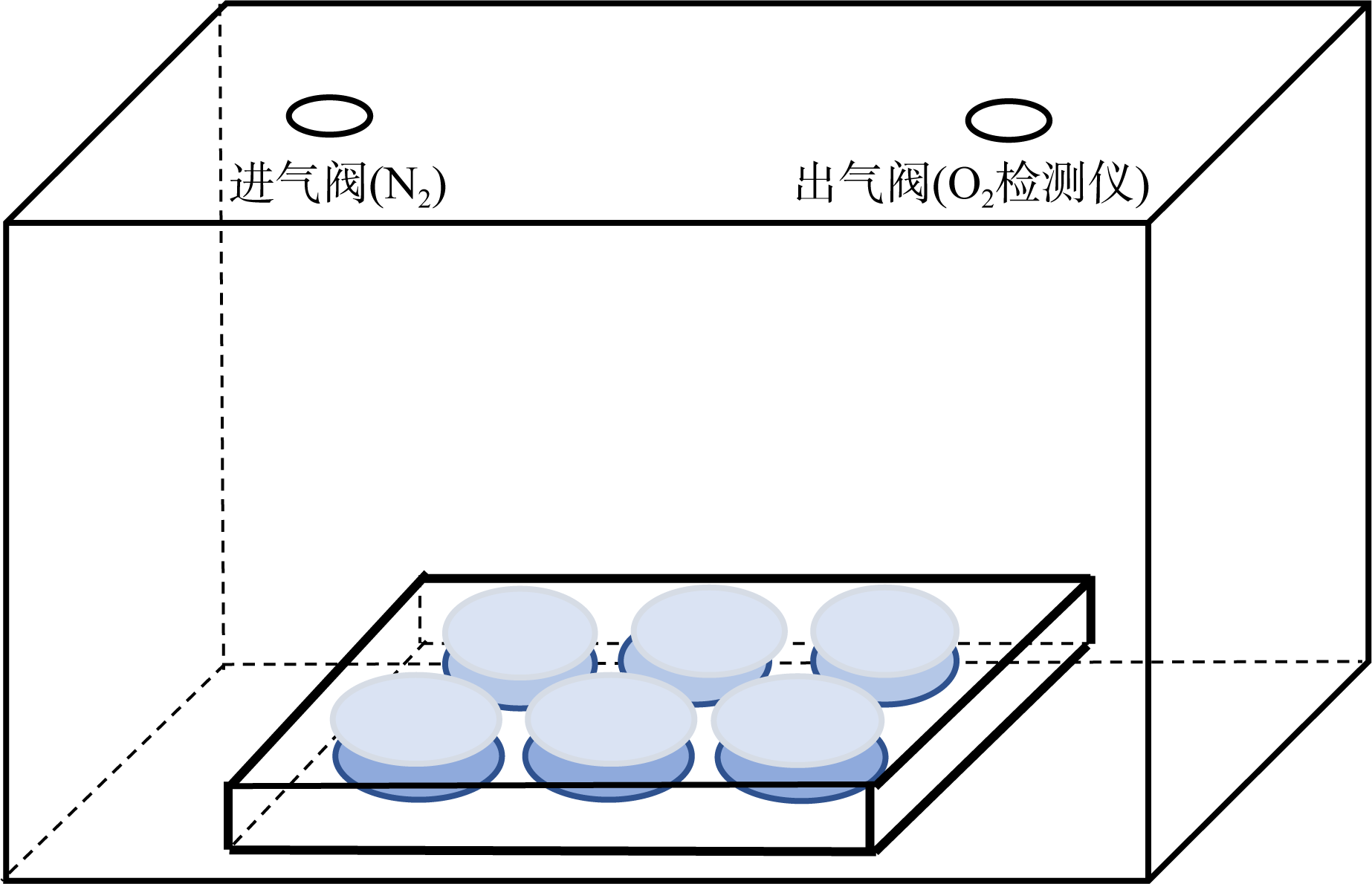
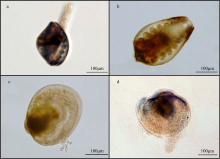
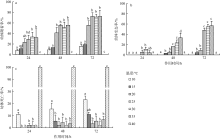
| [1] |
蔡立哲, 高阳, 刘炜明, 等, 2006. 外来物种沙筛贝对厦门马銮湾大型底栖动物的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 28(5): 83-89.
|
|
CAI LIZHE, GAO YANG, LIU WEIMING, et al, 2006. Effect of exotic species Mytilopsis sallei on macrozoobenthos in the Maluan Bay, Xiamen in China[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 28(5): 83-89 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
蒋湘, 魏亦彤, 许乐乐, 等, 2021. 光照强度、温度及海水类型对卤虫(Artemia saline)卵孵化率和幼体存活率的影响[J]. 水产科技情报, 48(4): 197-202.
|
|
JIANG XIANG, WEI YITONG, XU LELE, et al, 2021. Effects of light intensity, temperature and seawater type on hatchability and survival rate of Artemia saline[J]. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 48(4): 197-202 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
孔宁, 2016. 温度、盐度对皱纹盘鲍“97”选群生长发育的影响[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所).
|
|
KONG NING, 2016. Effects of temperature and salinity on growth and development of “97” selective breeding population of Haliotis discus hannai Ino[D]. Qingdao: Institute of Oceanology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [4] |
马鸿梅, 秦传新, 王兴强, 等, 2020. 应用Maxent建立沙筛贝潜在生境模型[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(4): 1357-1364.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202004.038
|
|
MA HONGMEI, QIN CHUANXIN, WANG XINGQIANG, et al, 2020. Establishing potential habitats of Mytilopsis sallei with Maxent niche model[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 31(4): 1357-1364 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [5] |
牛东红, 王宏蕾, 李家乐, 2024. 海洋贝类对盐度胁迫适应机制的研究进展[J]. 水产学报, 48(4): 049104.
|
|
NIU DONGHONG, WANG HONGLEI, LI JIALE, 2024. Research progress on adaptation mechanism of marine shellfish to salinity stress[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 48(4): 049104 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
王建军, 黄宗国, 郑成兴, 等, 1999. 厦门和东山外来物种沙筛贝的种群动态和结构[J]. 台湾海峡, 18(4): 372-377.
|
|
WANG JIANJUN, HUANG ZONGGUO, ZHENG CHENGXING, et al, 1999. Population dynamics and structure of alien species Mytilopsis sallei in Fujian, China[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 18(4): 372-377 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [7] |
张兴志, 何苹萍, 官俊良, 等, 2024. 低氧胁迫及复氧对香港牡蛎抗氧化和能量代谢相关酶活性的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 44(2): 32-38.
|
|
ZHANG XINGZHI, HE PINGPING, GUAN JUNLIANG, et al, 2024. Effects of Hypoxia-reoxygenation on antioxidant capacity and enzyme activities related to energy metabolism of Crassostrea hongkongensis[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 44(2): 32-38 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
张悦, 许道艳, 廖国祥, 等, 2024. 我国海洋外来生物入侵现状、监管问题及建议[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 41(1): 37-44.
|
|
ZHANG YUE, XU DAOYAN, LIAO GUOXIANG, et al, 2024. The present situation, supervision problems and suggestions of Marine alien biological invasion in China[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 41(1): 37-44 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
ASTUDILLO J C, BONEBRAKE T C, LEUNG K M Y, 2017. The recently introduced bivalve Xenostrobus securis has higher thermal and salinity tolerance than the native Brachidontes variabilis and established Mytilopsis sallei[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 118(1-2): 229-236.
|
| [10] |
CAI LIZHE, HWANG J S, DAHMS H U, et al, 2014. Effect of the invasive bivalve Mytilopsis sallei on the macrofaunal fouling community and the environment of Yundang Lagoon, Xiamen, China[J]. Hydrobiologia, 741(1): 101-111.
|
| [11] |
DONG HAO, LIU JIE, ZHAO LINLIN, et al, 2023. Applying an ensemble of small models in predicting habitat suitability of invasive M. sallei along the southern coast of China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 197: 115777.
|
| [12] |
DOROPOULOS C, THOMSON D P, TRAPON M, et al, 2020. Depth gradients drive changes in early successional community composition and associated coral larvae settlement interactions[J]. Marine Biology, 167(5): 59.
|
| [13] |
FENG DANQING, KE CAIHUAN, LU CHANGYI, et al, 2010. The influence of temperature and light on larval pre-settlement metamorphosis: a study of the effects of environmental factors on pre-settlement metamorphosis of the solitary ascidian Styela canopus[J]. Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology, 43(1): 11-24.
|
| [14] |
GURR S J, GOLESKI J, LIMA F P, et al, 2018. Cardiac responses of the bay scallop Argopecten irradians to diel-cycling hypoxia[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 500: 18-29.
|
| [15] |
HASSELL K L, COUTIN P C, NUGEGODA D, 2009. A novel approach to controlling dissolved oxygen levels in laboratory experiments[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 371(2): 147-154.
|
| [16] |
HE JIAN, QI JIANFEI, FENG DANQING, et al, 2016. Embryonic and larval development of the invasive biofouler Mytilopsis sallei (Récluz, 1849) (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae)[J]. Journal of Molluscan Studies, 82(1): 23-30.
|
| [17] |
LIM C S, TAY T S, TAN K S, et al, 2020. Removal of larvae of two marine invasive bivalves, Mytilopsis sallei (Récluz, 1849) and Mytella strigata (Hanley, 1843), by water treatment processes[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 155: 111154.
|
| [18] |
LOUREIRO T G, PETERS K, ROBINSON T B, 2021. Light, shade and predation: who wins and who loses in sessile fouling communities?[J]. Marine Biodiversity, 51(6): 94.
|
| [19] |
MORTON B, LEUNG K F, 2015. Introduction of the alien Xenostrobus securis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) into Hong Kong, China: interactions with and impacts upon native species and the earlier introduced Mytilopsis sallei (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 92(1-2): 134-142.
|
| [20] |
MUHTADI A, LEIDONALD R, RAHMAWATI A, et al, 2024. New record and population dynamics of the invasive bivalve Mytilopsis sallei (Récluz, 1849) in a tropical coastal lake from Indonesia[J]. BioInvasions Records, 13(2): 453-467.
|
| [21] |
NADA M A L, BAQUIRAN J I P, CABAITAN P C, et al, 2020. Behavior and development of larvae in the sponge Haliclona amboinensis[J]. Invertebrate Biology, 139(3): e12296.
|
| [22] |
NOZAWA Y, Harrison P L, 2007. Effects of elevated temperature on larval settlement and post-settlement survival in scleractinian corals, Acropora solitaryensis and Favites chinensis[J]. Marine Biology, 152(5): 1181-1185.
|
| [23] |
PYŠEK P, HULME P E, SIMBERLOFF D, et al, 2020. Scientists' warning on invasive alien species[J]. Biological Reviews, 95(6): 1511-1534.
|
| [24] |
QUEIROZ R N M, DA SILVA P M, DESOUZA A M, et al, 2020. Effects of environmental factors on the distribution of the exotic species Mytilopsis sallei (Récluz, 1849) (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) on the Northeast coast of Brazil[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 165: 101954.
|
| [25] |
RAO XIAOZHEN, LIN GANG, 2020. Effects of age, salinity and temperature on the metamorphosis and survival of Capitulum mitella cyprids (Cirripedia: Thoracica: Scalpellomorpha)[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 100(1): 55-62.
|
| [26] |
SA-NGUANSIL S, WANGKULANGKUL K, 2020. Salinity tolerance in different life history stages of an invasive false mussel Mytilopsis sallei Recluz, 1849: implications for its restricted distribution[J]. Molluscan Research, 40(3): 214-222.
|
| [27] |
VAN DER GAAG M, VAN DER VELDE G, LEUVEN R S E W, 2017. Settlement, seasonal size distribution, and growth of the invasive bivalve Mytilopsis leucophaeata (Conrad, 1831) (Dreissenidae) in relation to environmental factors[J]. Journal of Shellfish Research, 36(2): 417-426.
|
| [28] |
WEI QINSHENG, XUE LIANG, YAO QINGZHEN, et al, 2021. Oxygen decline in a temperate marginal sea: contribution of warming and eutrophication[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 757: 143227.
|
| [29] |
WELLS F E, 2019. Environmental emergency: why did the false mussel Mytilopsis sallei not invade Darwin Harbour, Australia?[J]. Malacologia, 62(2): 247-256.
|
| [30] |
WHALAN S, 2023. The role of photobehaviour in sponge larval dispersal and settlement[J]. PLoS One, 18(7): e0287989.
|
 ), PAN Huakang2, LIU Liyang2, HE Jian2, ZHAO Ke3, QI Jianfei4, ZHANG Zhen1, SU Pei2(
), PAN Huakang2, LIU Liyang2, HE Jian2, ZHAO Ke3, QI Jianfei4, ZHANG Zhen1, SU Pei2( ), FENG Danqing2
), FENG Danqing2