Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 135-146.doi: 10.11978/2021125CSTR: 32234.14.2021125
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
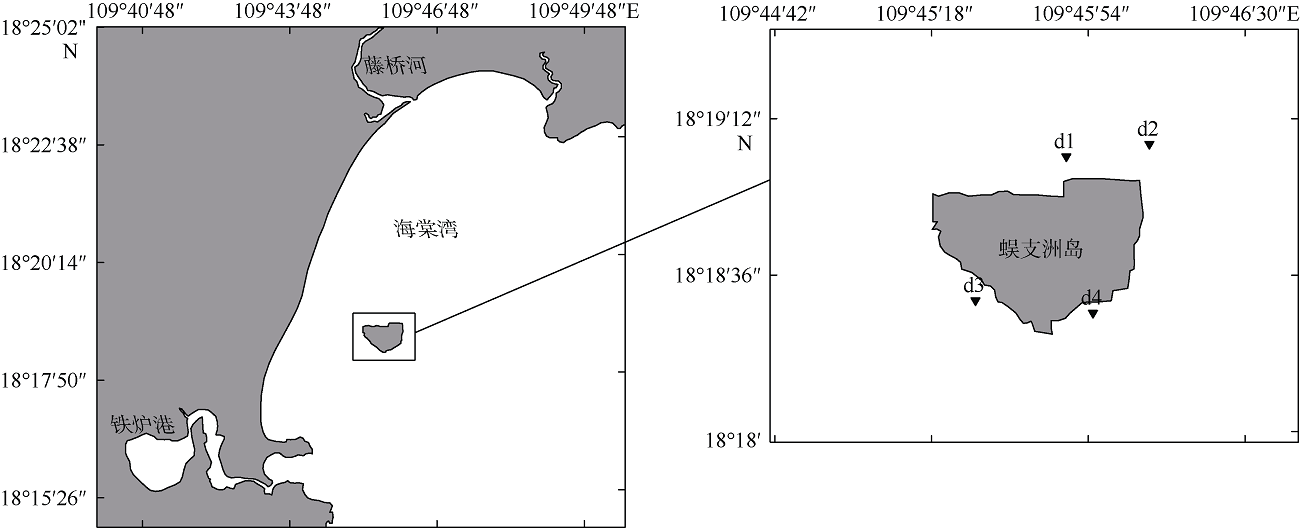
Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya
MA Wengang( ), XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang(
), XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang( ), LI Xiubao(
), LI Xiubao( ), WANG Aimin
), WANG Aimin
- College of Marine Science, Hainan University, State Key Laboratory of Marine Resources Utilization in South China Sea, Haikou 570228, China
-
Received:2021-09-15Revised:2021-11-23Published:2021-11-29 -
Contact:XU Qiang,LI Xiubao E-mail:956497289@qq.com;xuqianghnu@hainanu.edu.cn;xiubaoli@163.com -
Supported by:National Key R&D Program of China(2019YFD0901304);National Natural Science Foundation of China(42076097);Hainan Natural Science Foundation(2019RC070)
CLC Number:
- Q958
Cite this article
MA Wengang, XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang, LI Xiubao, WANG Aimin. Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 135-146.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
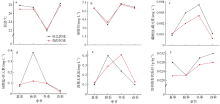
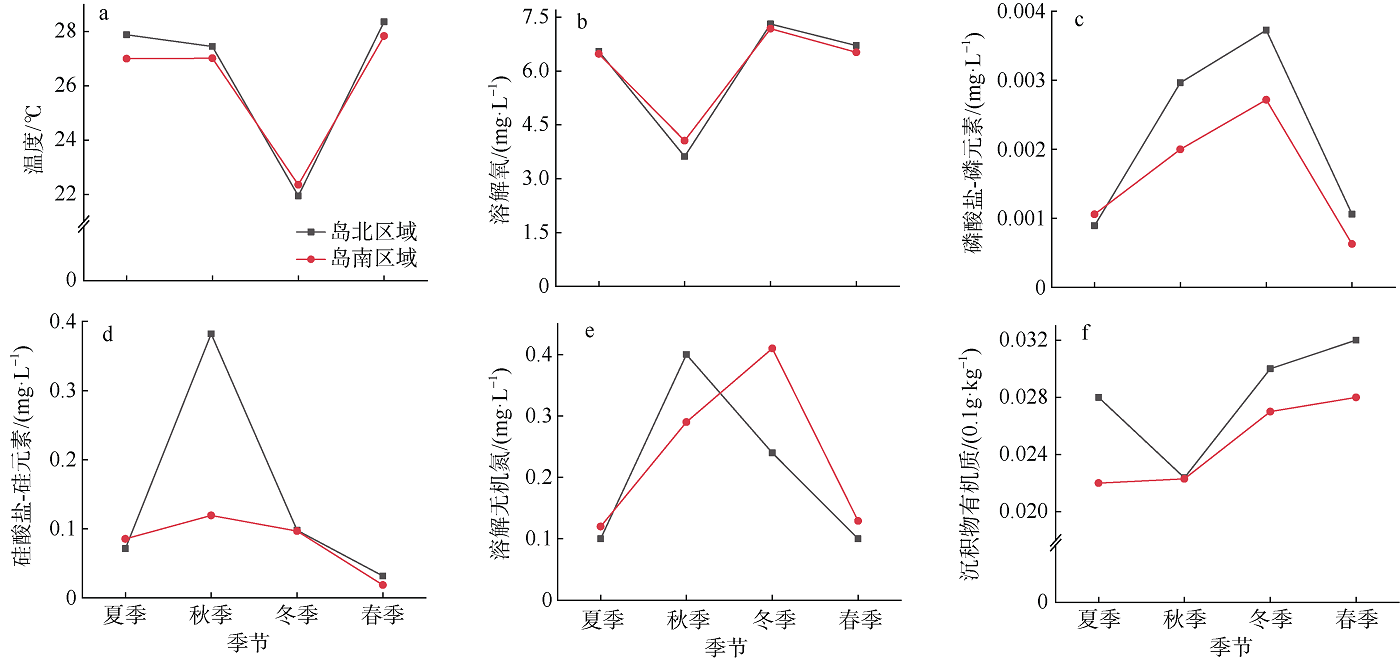
Seasonal variation of water environmental factors in coastal area of Wuzhizhou Island"
| 季节 | T/℃ | DO/(mg·L-1) | Chl a/(μg·L-1) | P/(mg·L-1) | Si/(mg·L-1) | DIN/(mg·L-1) | Md | Org/(0.1g·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 夏季 | 27.44±0.70ab | 6.51±0.07b | 0.37±0.08ab | 0.001±0.0002b | 0.075±0.011ab | 0.112±0.011b | 1.89±1.31a | 2.60±0.94a |
| 秋季 | 27.24 ±0.30b | 3.84±0.68c | 2.03±0.34a | 0.003±0.0009ab | 0.379±0.278a | 0.347±0.068a | — | 2.23±0.28a |
| 冬季 | 22.16±0.24c | 7.25±0.08a | 0.49±0.29b | 0.003±0.0014a | 0.095±0.013ab | 0.324±0.120a | 2.26±2.47a | 2.87±0.43a |
| 春季 | 28.10±0.31a | 6.62±0.17b | 0.57±0.14ab | 0.001±0.0005b | 0.030±0.013b | 0.112±0.027b | 2.37±1.48a | 3.10±0.36a |
Tab. 2
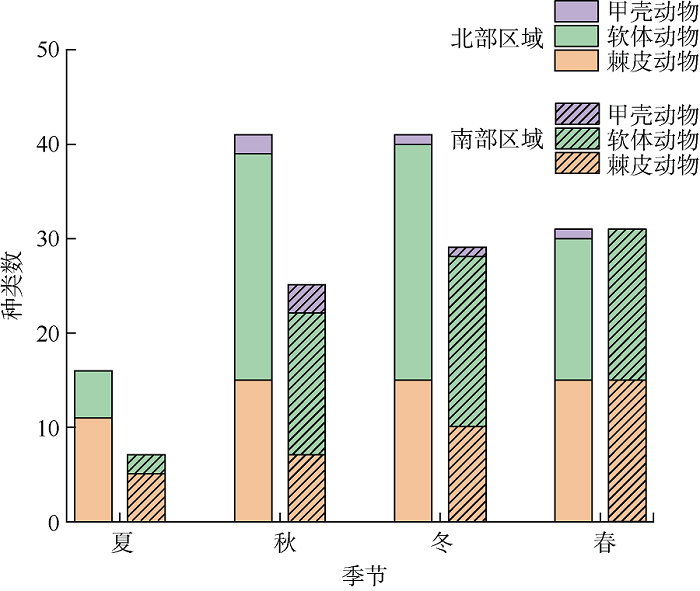
Dominant species in each season"
| 优势种 | 优势度 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 种名 | 学名 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 春季 |
| 吕宋棘海星 | Echinaster luzonicus | 0.046 | 0.042 | 0.038 | 0.037 |
| 蓝指海星 | Linckia laevigata | 0.060 | 0.032 | 0.043 | 0.039 |
| 蓝环冠海胆 | Diadema savignyi | — | — | 0.038 | 0.078 |
| 刺冠海胆 | Diadema setosum | — | 0.049 | — | — |
| 冠刺棘海胆 | Echinothrix diadema | — | — | 0.029 | — |
| 红腹海参 | Holothuria eduils | 0.114 | 0.225 | 0.057 | 0.191 |
| 黑海参 | Holothuria atra | 0.305 | 0.121 | 0.060 | 0.106 |
| 绿刺参 | Stichopus chloronotus | 0.101 | — | 0.034 | 0.055 |
| 金口蝾螺 | Turbo argyrostomus | 0.050 | 0.028 | 0.047 | 0.028 |
| 塔形扭柱螺 | Tectus pyramis | — | — | 0.038 | — |
| 角小核果螺 | Drupella cornus | 0.146 | — | 0.107 | 0.028 |
| 紫栖珊瑚螺 | Coralliophila violacea | — | — | 0.023 | — |
| 焦棘螺 | Chicoreus torrefactus | — | — | 0.036 | — |
| 秉氏海齿花 | Comanthus bennetti | — | 0.048 | 0.047 | 0.094 |
| 许氏大羽花 | Comanthina schlegeli | — | — | 0.023 | 0.049 |
| 小足真寄居蟹 | Dardanus pedunculatus | — | 0.084 | — | — |
Tab. 3
Biodiversity index and M-AMBI in four seasons"
| d | J | H′ | 水体状况 | M-AMBI | 水体环境状况 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 夏季 | 1.26±0.53b | 0.70±0.10a | 2.14±0.41b | 轻度污染 | 0.59±0.06b | 优良 |
| 秋季 | 3.11±1.24ab | 0.74±0.13a | 3.21±0.93a | 无污染 | 0.77±0.16a | 高等 |
| 冬季 | 3.40±0.26a | 0.81±0.09a | 3.71±0.52a | 无污染 | 0.85±0.07a | 高等 |
| 春季 | 3.04±0.99ab | 0.79±0.13a | 3.52±0.75a | 无污染 | 0.82±0.09a | 高等 |
| [1] | 蔡立哲, 马丽, 高阳, 等, 2002. 海洋底栖动物多样性指数污染程度评价标准的分析[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 41(5): 641-646. |
| CAI LIZHE, MA LI, GAO YANG, et al, 2002. Analysis on assessing criterion for polluted situation using species diversity index of marine macrofauna[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 41(5): 641-646. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 陈晨, 焦海峰, 王一农, 等, 2016. 象山港海洋牧场示范区大型底栖生物的时空变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(1): 130-139. |
| JIAO HAIFENG, WANG YINONG, et al, 2016. Temporal and spatial changes of macrobenthos in marine pasture demonstration area in Xiangshan Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 47(1): 130-139. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 董栋, 李新正, 王洪法, 等, 2015. 海南岛三亚珊瑚礁区大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 海洋科学, 39(3): 83-91. |
| ONG DONG, LI XINZHENG, WANG HONGFA, et al, 2015. Macrobenthic community characters of coral reef at Sanya, Hainan[J]. Marine Sciences, 39(3): 83-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 黄丁勇, 王建佳, 陈甘霖, 等, 2021. 亚龙湾珊瑚礁大型礁栖生物的群落结构及生态警示[J]. 生态学杂志, 40(2): 412-426. |
| HUANG DINGYONG, WANG JIANJIA, CHEN GANLIN, et al, 2021. Community structure and ecological warning of reef-associated fish and macrobenthos in the Yalong Bay[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 40(2): 412-426. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 黄端杰, 许强, 李秀保, 等, 2020. 三亚蜈支洲岛珊瑚礁-沙质底复合区棘皮动物群落结构[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(1): 103-113. |
| HUANG DUANJIE, XU QIANG, LI XIUBAO, et al, 2020. The community structure of echinoderms in sandy coral reef area in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya, China[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 51(1): 103-113. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 黄晖, 张浴阳, 刘骋跃, 2020. 热带岛礁型海洋牧场中珊瑚礁生境与资源的修复[J]. 科技促进发展, 16(2): 225-230. |
| HUANG HUI, ZHANG YUYANG, LIU CHENGYUE, 2020. Coral reef habitat and resources restoration in tropical island marine ranching[J]. Science and Technology for Development, 16(2): 225-230. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [7] | 李秀保, 李元超, 许强, 2019. 三亚蜈支洲岛珊瑚礁的现状、生态修复及保护对策[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 14-84. (in Chinese) |
| [8] | 李元超, 杨毅, 郑新庆, 等, 2015. 海南三亚后海海域珊瑚礁生态系统的健康状况及其影响因素[J]. 生态学杂志, 34(4): 1105-1112. |
| LI YUANCHAO, YANG YI, ZHENG XINQING, et al, 2015. Health status and influencing factors of coral reef ecosystems in Houhai waters, Sanya, Hainan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 34(4): 1105-1112. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] |
林和山, 俞炜炜, 刘坤, 等, 2015. 基于AMBI和M-AMBI法的底栖生态环境质量评价-以厦门五缘湾海域为例[J]. 海洋学报, 37(8): 76-87.
doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1164-x |
|
LIN HESHAN, YU WEIWEI, LIU KUN, et al, 2015. Assessing benthic ecological status in stressed Wuyuan Bay (Xiamen, China) using AMBI and M-AMBI[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 37(8): 76-87. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.1007/s13131-018-1164-x |
|
| [10] | 刘帅磊, 王赛, 崔永德, 等, 2018. 亚热带城市河流底栖动物完整性评价--以流溪河为例[J]. 生态学报, 38(1): 342-357. |
| LIU SHUAILEI, WANG SAI, CUI YONGDE, et al, 2018. Ecological assessment of a subtropical urban river based on the Benthic-Index of Biotic Integrity-Liuxi River[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(1): 342-357. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 罗章凤, 方展强, 2017. 珠海横琴岛芒洲湿地红树林人工恢复期大型底栖动物群落结构研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(3): 61-72. |
| LUO ZHANGFENG, FANG ZHANQIANG, 2017. A study on the community structure of macrobenthos during the period of artificial mangrove restoration in Mangzhou wetland of Hengqin Island, Zhuhai[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(3): 61-72. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] | 全秋梅, 肖雅元, 徐姗楠, 等, 2020. 胶州湾大型底栖动物群落结构季节变化及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 39(12): 4110-4120. |
| QUAN QIUMEI, XIAO YAYUAN, XU SHANNAN, et al, 2020. Seasonal variation in macrozoobenthos community structure and its relation to environmental factors in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 39(12): 4110-4120. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [13] |
孙有方, 雷新明, 练健生, 等, 2018. 三亚珊瑚礁保护区珊瑚礁生态系统现状及其健康状况评价[J]. 生物多样性, 26(3): 258-265.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2017312 |
|
SUN YOUFANG, LEI XINMING, LIAN JIANSHENG, et al, 2018. Ecosystem status and health assessment of Sanya Coral Reef National Nature Reserve[J]. Biodiversity Science, 26(3): 258-265. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.17520/biods.2017312 |
|
| [14] | 田胜艳, 于子山, 刘晓收, 等, 2006. 丰度/生物量比较曲线法监测大型底栖动物群落受污染扰动的研究[J]. 海洋通报, 25(1): 92-96. |
| TIAN SHENGYAN, YU ZISHAN, LIU XIAOSHOU, et al, 2006. Abundance/biomass curves for detecting pollution effects on marine macrobenthic communities[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 25(1): 92-96. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 田胜艳, 张文亮, 张锐, 2009. 大型底栖动物在海洋生态系统中的作用[J]. 盐业与化工, 38(2): 50-54. |
| TIAN SHENGYAN, ZHANG WENLIANG, ZHANG RUI, 2009. Role of macrobenthos in marine ecosystem[J]. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry, 38(2): 50-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 王言丰, 胡启伟, 余景, 等, 2019. 粤东柘林湾海洋牧场渔业资源增殖效果评估[J]. 南方水产科学, 15(2): 12-19. |
| WANG YANFENG, HU QIWEI, YU JING, et al, 2019. Effect assessment of fishery resources proliferation in Zhelin Bay marine ranching in eastern Guangdong[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 15(2): 12-19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 吴莹莹, 雷新明, 黄晖, 等, 2021. 南海典型珊瑚礁生态系统健康评价方法研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(4): 84-97. |
| WU YINGYING, LEI XINMING, HUANG HUI, et al, 2021. Study on the health assessment method of typical coral reef ecosystem in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 40(4): 84-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 吴钟解, 张光星, 陈石泉, 等, 2015. 海南西瑁洲岛周边海域造礁石珊瑚空间分布及其生态系统健康评价[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 34(1): 133-140. |
| WU ZHONGJIE, ZHANG GUANGXING, CHEN SHIQUAN, et al, 2015. Spatial distribution and ecosystem health assessment of hermatypic corals in surrounding waters of Ximaozhou Island, Hainan[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 34(1): 133-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 夏景全, 贾志宇, 张国豪, 等, 2020. 火山石对破碎化珊瑚礁的修复效果研究[J]. 浙江海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 39(3): 237-244. |
| XIA JINGQUAN, JIA ZHIYU, ZHANG GUOHAO, et al, 2020. Study on effect of basalt on restoration of damaged coral reef[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 39(3): 237-244. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 夏景全, 2021. 火山石生境重构与珊瑚移植在修复三亚破碎化珊瑚礁上的作用[D]. 海南: 海南大学. |
| XIA JINGQUAN, 2021. The role of volcanic habitat reconstruction and coral transplantation in the restoration of fragmented coral reefs in Sanya[D]. Hainan: Hainan University. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [21] | 许惠丽, 冯博轩, 谢敏睿, 等, 2020. 三亚蜈支洲岛两种造礁石珊瑚的生理特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 39(2): 181-188. |
| XU HUILI, FENG BOXUAN, XIE MINRUI, et al, 2020. Physiological characteristics of two reef-building corals in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 39(2): 181-188. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [22] | 许强, 刘维, 高菲, 等, 2018. 发展中国南海热带岛礁海洋牧场--机遇、现状与展望[J]. 渔业科学进展, 39(5): 173-180. |
| XU QIANG, LIU WEI, GAO FEI, et al, 2018. Development of marine ranching at tropical island area in South China Sea-advantages, status and prospects[J]. Progress in Fishery Sciences, 39(5): 173-180. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [23] |
徐帅帅, 邸宝平, 王玉珏, 等, 2017. 我国典型潮间带底栖硅藻群落空间分布特征[J]. 海洋学报, 39(6): 95-113.
doi: 10.1007/s13131-020-1693-y |
|
XU SHUAISHUAI, DI BAOPING, WANG YUJUE, et al, 2017. Spatial distribution of benthic diatom in the typical intertidal zones in China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 39(6): 95-113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.1007/s13131-020-1693-y |
|
| [24] | 徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿, 1989. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 8(4): 13-15, 19. |
| XU ZHAOLI, CHEN YAQU, 1989. Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Ecology, 8(4): 13-15, 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [25] | 杨东, 周政权, 张建设, 等, 2017. 烟台牟平海洋牧场夏季大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 海洋科学, 41(5): 134-143. |
| YANG DONG, ZHOU ZHENGQUAN, ZHANG JIANSHE, et al, 2017. Characteristics of macrobenthic communities at the Muping marine ranch of Yantai in summer[J]. Marine Sciences, 41(5): 134-143. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [26] | 袁涛萍, 李恒翔, 李路, 等, 2017. 夏季大亚湾大型底栖动物群落结构[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(1): 41-47. |
| YUAN TAOPING, LI HENGXIANG, LI LU, et al, 2017. Community structure of macrobenthos in summer in Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(1): 41-47. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [27] | 张志南, 2000. 水层-底栖耦合生态动力学研究的某些进展[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 30(1): 115-122. |
| ZHANG ZHINAN, 2000. Some progress of the study on the ecosystem dynamics for benthic -pelagic coupling[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao, 30(1): 115-122. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [28] |
AZOVSKY A I, KOKAREV V N, 2019. Stable but fragile: long-term dynamics of arctic benthic macrofauna in Baydaratskaya Bay (the Kara Sea)[J]. Polar Biology, 42(7): 1307-1322.
doi: 10.1007/s00300-019-02519-y |
| [29] |
BOUTOUMIT S, BOUOUAROUR O, KAMCHA R E, et al, 2021. Spatial patterns of macrozoobenthos assemblages in a sentinel coastal lagoon: biodiversity and environmental drivers[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(5): 461.
doi: 10.3390/jmse9050461 |
| [30] |
GERASIMOVA A V, FILIPPOVA N A, LISITSYNA K N, et al, 2021. Current state of macrobenthos in the southwestern Kara Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 224: 104452.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2021.104452 |
| [31] |
HUANG JIANZHONG, WANG FENGXIA, ZHAO HONGWEI, et al, 2020. Reef benthic composition and coral communities at the Wuzhizhou Island in the south China sea: the impacts of anthropogenic disturbance[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 243: 106863.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106863 |
| [32] |
HUTCHINGS P, 1990. Review of the effects of trawling on macrobenthic epifaunal communities[J]. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 41(1): 111-120.
doi: 10.1071/MF9900111 |
| [33] |
KOLYUCHKINA G A, SYOMIN V L, GRIGORENKO K S, et al, 2020. The role of abiotic environmental factors in the vertical distribution of macrozoobenthos at the northeastern black sea coast[J]. Biology Bulletin, 47(9): 1126-1141.
doi: 10.1134/S1062359020090071 |
| [34] | LI XIUBAO, LIU SHENG, HUANG HUI, et al, 2012. Coral bleaching caused by an abnormal water temperature rise at Luhuitou fringing reef, Sanya Bay, China[J]. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 15(2): 227-233. |
| [35] |
LI XIUBAO, WANG DAORU, HUANG HUI, et al, 2015. Linking benthic community structure to terrestrial runoff and upwelling in the coral reefs of northeastern Hainan Island[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 156: 92-102.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2014.09.021 |
| [36] |
LUNT J, SMEE D L, 2014. Turbidity influences trophic interactions in estuaries[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 59(6): 2002-2012.
doi: 10.4319/lo.2014.59.6.2002 |
| [37] |
RAJAN R S P, JYOTHIBABU R, ARUNPANDI N, et al, 2021. Macrobenthos community response to the seasonal hypoxia associated with coastal upwelling off Kochi, along the Southwest coast of India[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 224: 104450.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2021.104450 |
| [38] |
RODRÍGUEZ-TRONCOSO A P, RODRÍGUEZ-ZARAGOZA F A, MAYFIELD A B, et al, 2019. Temporal variation in invertebrate recruitment on an Eastern Pacific coral reef[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 145: 8-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2018.12.007 |
| [39] |
ROJAS-MONTIEL B, REYES-BONILLA H, CALDERON- AGUILERA L E, et al, 2020. Echinoderm functional diversity does not correlate with the protection level of marine protected areas in the Mexican Pacific[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 29(6): 1871-1896.
doi: 10.1007/s10531-020-01952-4 |
| [40] | SOARES M O, ROSSI S, GURGEL A R, et al, 2021. Impacts of a changing environment on marginal coral reefs in the Tropical Southwestern Atlantic[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 210: 105692. |
| [41] |
VON DER OHE P C, GOEDKOOP W, 2013. Distinguishing the effects of habitat degradation and pesticide stress on benthic invertebrates using stressor-specific metrics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 444: 480-490.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.001 |
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | MO Danyang, NING Zhiming, YANG Bin, XIA Ronglin, LIU Zhijin. Response of dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in coral reef sediments of the Weizhou island to temperature changes [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [3] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [4] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [5] | JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [6] | JIA Nan, ZHOU Tiancheng, HU Simin, ZHANG Chen, HUANG Hui, LIU Sheng. Difference in the feeding contents of three hermit crabs in the coral reefs of the Nansha Islands, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 109-121. |
| [7] | PENG Erman, YAO Yu, LI Zhuangzhi, XU Conghao. Numerical study of the hydrodynamic characteristics of reef coast under the combined effects of waves and currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 187-194. |
| [8] | LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [9] | HUANG Hui, YUAN Xiangcheng, SONG Yan, LI Yingxin, ZHOU Weihua, LONG Aimin. Carbon sequestration process and carbon storage mechanism of reef ecosystem in South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 13-21. |
| [10] | HUANG Hui, YU Xiaolei, HUANG Lintao, JIANG Lei. Current status and prospects of coral reef ecology research [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 3-12. |
| [11] | GAO Jie, YU Kefu, XU Shendong, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Biao, WANG Yonggang. Content and source analysis of organic carbon in the outer slope sediments of the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [12] | ZHANG Yuyang, LIU Chengyue, YU Xiaolei, LUO Yong, ZHOU Tiancheng, LIAN Jiansheng, HUANG Hui. Study on relocation effect of scleractinian coral in the Fenghuang Island, Sanya* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 177-186. |
| [13] | LEI Mingfeng, YU Kefu, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Biao, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Xiaoyan. The rapid ecological degradation and its impact on fish of the Yinyu Island in the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [14] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [15] | LIANG Yuxian, LIU Chengyue, YU Xiaolei, ZHANG Yuyang, LIAN Wenke, CHEN Lunju, HUANG Hui. Focusing on supplementing and restoring degraded coral reefs with key groups of reef-building coral - paradigms in the restoration of Xidao Island’s coral reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 166-176. |
|
||