Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 72-86.doi: 10.11978/2023081CSTR: 32234.14.2023081
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
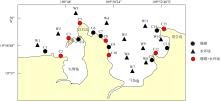
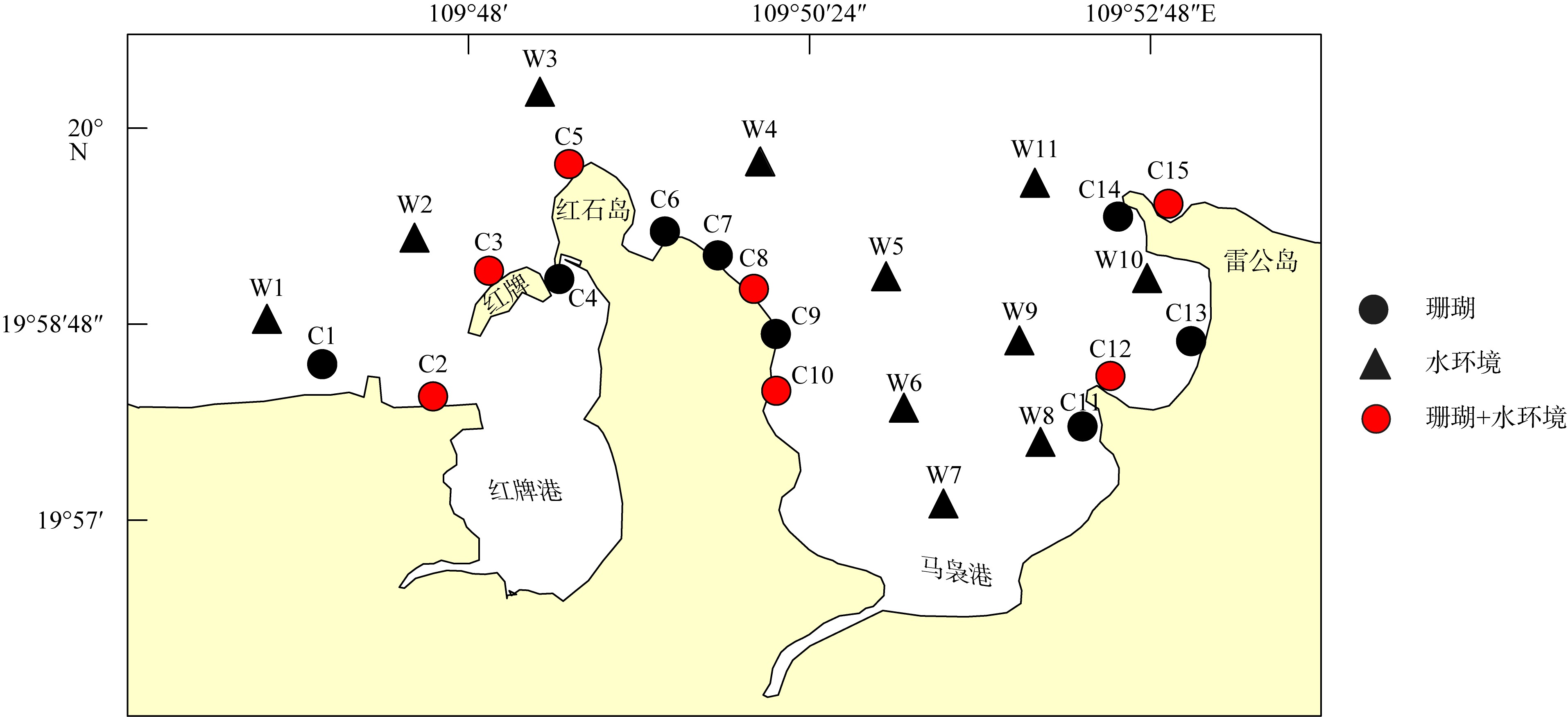
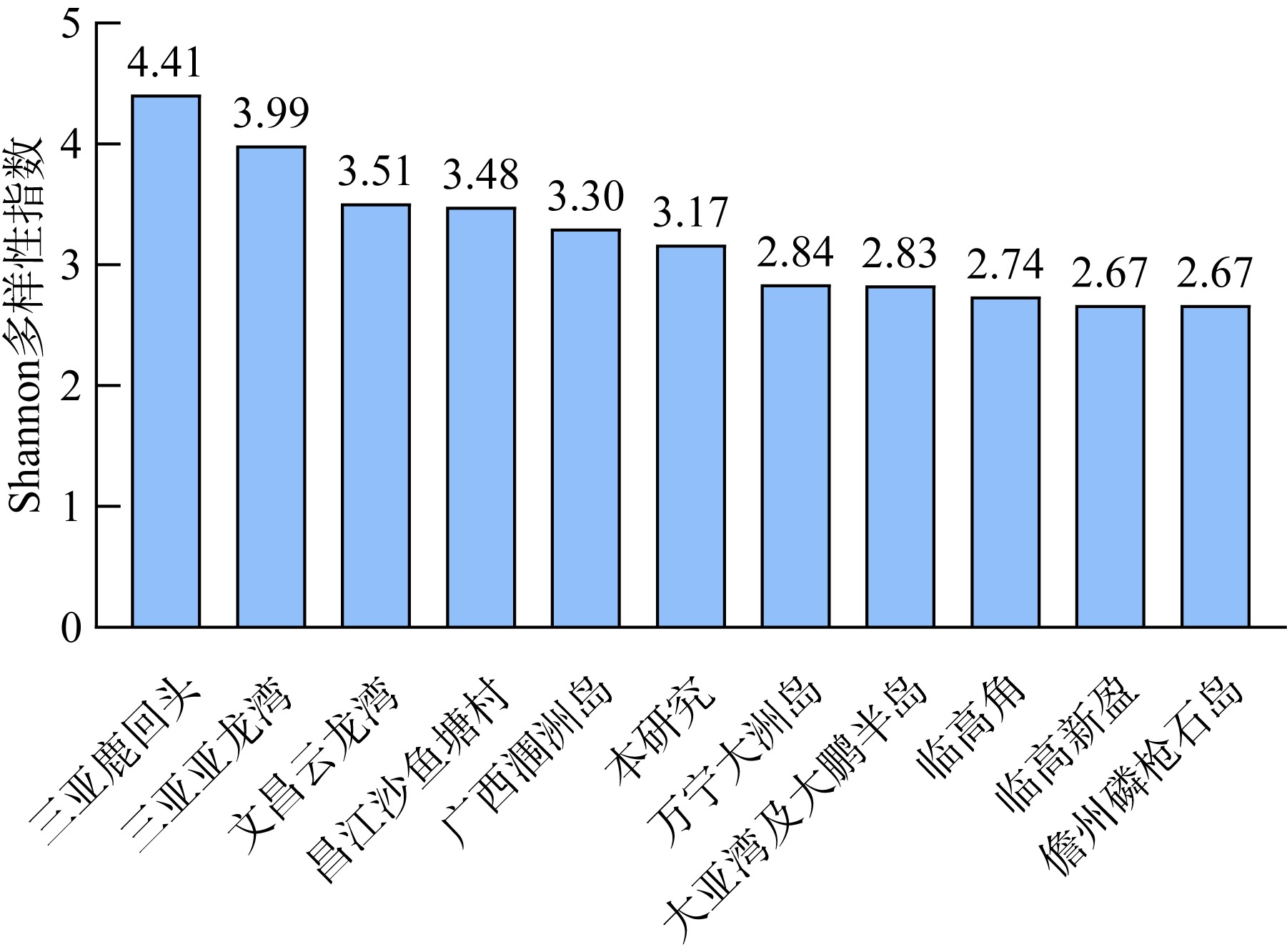
Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan
LUO Yong1,2,3( ), HUANG Lintao1,4, YANG Jianhui1, LIAN Jiansheng1,2,3, LIU Chengyue1,2,3, JIANG Lei1,2,3, LIANG Yuxian1, CHEN Lunju1, LEI Xinming1,2,3, LIU Sheng1,2,3, HUANG Hui1,2,3(
), HUANG Lintao1,4, YANG Jianhui1, LIAN Jiansheng1,2,3, LIU Chengyue1,2,3, JIANG Lei1,2,3, LIANG Yuxian1, CHEN Lunju1, LEI Xinming1,2,3, LIU Sheng1,2,3, HUANG Hui1,2,3( )
)
- 1. Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. CAS-HKUST Sanya Joint Laboratory of Marine Science Research, Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Biotechnology of Hainan Province, Sanya Institute of Ocean Eco-Environmental Engineering, SCSIO, Sanya 572000, China
3. Sanya National Marine Ecosystem Research Station; Tropical Marine Biological Research Station in Hainan, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sanya 572000, China
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2023-06-15Revised:2023-07-22Online:2024-05-10Published:2024-06-04 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976120); National Natural Science Foundation of China(42276124); National Key Research and Development Program(2021YFC31005001); Natural Science Foundation of Hainan Province(423MS130)
Cite this article
LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
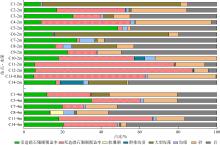
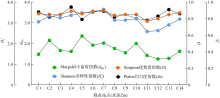
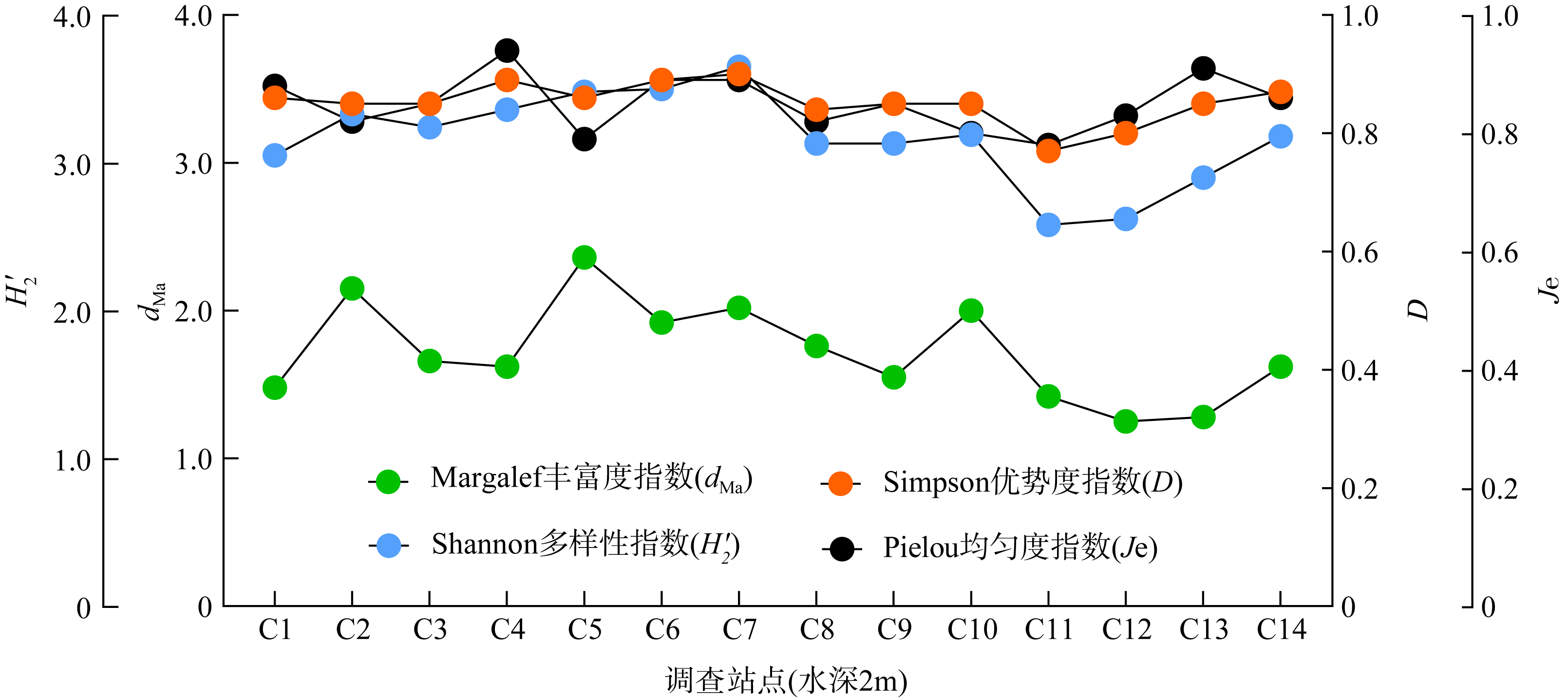
Tab. 1
Distribution range and dominant species of reef-building corals"
| 站点 | 分布水深/m | 样带布设水深/m | 活造礁石珊瑚覆盖率/% | 造礁石珊瑚物种数 | 优势种 | 优势种占活珊瑚覆盖率比例/% | 生长类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 1.0~5.0 | 2 | 8.67 | 11 | 澄黄滨珊瑚 Porites lutea | 26.92 | 团块状(massive) |
| 4 | 12.00 | 13 | 斯氏伯孔珊瑚 Bernardpora stutchburyi | 26.39 | 皮壳状(encrusting) | ||
| C2 | 0.5~3.5 | 2 | 17.17 | 17 | 斯氏伯孔珊瑚 Bernardpora stutchburyi | 32.04 | 皮壳状(encrusting) |
| C3 | 0.5~3.5 | 2 | 9.00 | 12 | 十字牡丹珊瑚 Pavona decussata | 16.67 | 指状(digitate) |
| C4 | 0.5~3.5 | 2 | 25.50 | 14 | 粗糙腔星珊瑚 Coelastrea aspera | 30.07 | 团块状(massive) |
| C5 | 0.5~6.5 | 2 | 48.67 | 21 | 角孔珊瑚 Goniopora sp. | 30.48 | 皮壳状(encrusting) |
| 4 | 35.00 | 26 | 多孔同星珊瑚 Plesiastrea versipora | 33.81 | 团块状(massive) | ||
| C6 | 1.5~7.0 | 2 | 14.83 | 15 | 斯托科斯角孔珊瑚 Goniopora stokesi | 20.22 | 柱状(columnar) |
| C7 | 0.5~9.0 | 2 | 27.50 | 17 | 多孔同星珊瑚 Plesiastrea versipora | 17.58 | 团块状(massive) |
| 4 | 20.00 | 18 | 多孔同星珊瑚 Plesiastrea versipora | 37.50 | 团块状(massive) | ||
| C8 | 0.5~5.0 | 2 | 16.33 | 14 | 盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea sp. | 28.57 | 团块状(massive) |
| 4 | 13.50 | 11 | 多孔同星珊瑚 Plesiastrea versipora | 50.62 | 团块状(massive) | ||
| C9 | 0.5~4.0 | 2 | 22.67 | 13 | 多孔同星珊瑚 Plesiastrea versipora | 28.68 | 团块状(massive) |
| C10 | 0.5~3.0 | 2 | 18.00 | 16 | 大盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea maxima | 25.00 | 团块状(massive) |
| C11 | 0.5~5.0 | 2 | 5.67 | 10 | 板叶角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites complanata | 38.24 | 团块状(massive) |
| 4 | 18.17 | 12 | 秘密角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites abdita | 54.13 | 团块状(massive) | ||
| C12 | 0.5~3.5 | 2 | 6.00 | 9 | 海洋盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea maritima | 33.33 | 团块状(massive) |
| C13 | 0.5~6.0 | 2 | 16.67 | 13 | 澄黄滨珊瑚 Porites lutea | 23.00 | 团块状(massive) |
| 4 | 20.50 | 13 | 紫小星珊瑚 Leptastrea purpurea | 33.33 | 皮壳状(encrusting) | ||
| C14 | 0.5~1.5 | 0.8 | 5.17 | 10 | 斯托科斯角孔珊瑚 Goniopora stokesi | 25.81 | 柱状(columnar) |
Tab. 2
List of reef-building coral species in the coastal waters of Lingao’s Hongpai-Maniao and their comparison with surrounding waters"
| 类群 | 科 | 属 | 种 | 临高新盈 和临高角 | 儋州磷 枪石岛Ⅰ | 昌江 海尾 | 儋州磷 枪石岛Ⅱ | 儋州白马井、南华墟和磷枪石岛 | 临高红牌-马袅海域(本研究) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 复杂 类群 | 鹿角 珊瑚科 | 鹿角珊瑚属 | 指形鹿角珊瑚 Acropora digitifera | + | + | |||||||
| 粗野鹿角珊瑚 Acropora humilis | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 风信子鹿角珊瑚 Acropora hyacinthus | + | + | ||||||||||
| 多孔鹿角珊瑚 Acropora millepora | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 美丽鹿角珊瑚 Acropora muricata | + | + | ||||||||||
| 鼻形鹿角珊瑚 Acropora nasuta | + | + | ||||||||||
| 霜鹿角珊瑚 Acropora pruinosa | + | + | ||||||||||
| 佳丽鹿角珊瑚 Acropora pulchra | + | + | ||||||||||
| 单独鹿角珊瑚 Acropora solitaryensis | + | |||||||||||
| 鹿角珊瑚 Acropora sp. | + | + | ||||||||||
| 隆起鹿角珊瑚 Acropora tumida | + | |||||||||||
| 壮实鹿角珊瑚 Acropora valida | + | + | ||||||||||
| 星孔珊瑚属 | 多星孔珊瑚 Astreopora myriophthalma | + | ||||||||||
| 蔷薇珊瑚属 | 繁锦蔷薇珊瑚 Montipora efflorescens | + | ||||||||||
| 横错蔷薇珊瑚 Montipora gaimardi | + | |||||||||||
| 弯柔蔷薇珊瑚 Montipora mollis | + | |||||||||||
| 单星蔷薇珊瑚 Montipora monasteriat | + | |||||||||||
| 翼形蔷薇珊瑚 Montipora peltiformis | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 蔷薇珊瑚 Montipora sp. | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 膨胀蔷薇珊瑚 Montipora turgescens | + | + | ||||||||||
| 滨珊瑚科 | 角孔珊瑚属 | 柱形角孔珊瑚 Goniopora columna | + | + | + | |||||||
| 大角孔珊瑚 Goniopora djiboutiensis | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 小角孔珊瑚 Goniopora minor | + | |||||||||||
| 诺福克角孔珊瑚 Goniopora norfolkensis | + | |||||||||||
| 潘朵拉角孔珊瑚 Goniopora pandoraensis | + | |||||||||||
| 扁平角孔珊瑚 Goniopora planulata | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 角孔珊瑚 Goniopora sp. | + | + | ||||||||||
| 斯托科斯角孔珊瑚 Goniopora stokesi | + | |||||||||||
| 伯孔珊瑚属 | 斯氏伯孔珊瑚 Bernardpora stutchburyi | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 滨珊瑚属 | 亚氏滨珊瑚 Porites aranetai | + | ||||||||||
| 团块滨珊瑚 Porites lobata | + | + | ||||||||||
| 澄黄滨珊瑚 Porites lutea | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 普哥滨珊瑚 Porites pukoensis | + | + | ||||||||||
| 坚实滨珊瑚 Porites solida | + | |||||||||||
| 滨珊瑚 Porites sp. | + | + | ||||||||||
| 菌珊瑚科 | 厚丝珊瑚属 | 标准厚丝珊瑚 Pachyseris speciosa | + | |||||||||
| 牡丹珊瑚属 | 十字牡丹珊瑚 Pavona decussata | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 叶形牡丹珊瑚 Pavona frondifera | + | |||||||||||
| 真叶珊瑚科 | 真叶珊瑚属 | 联合真叶珊瑚 Euphyllia cristata | + | |||||||||
| 复杂 类群 | 真叶 珊瑚科 | 真叶珊瑚属 | 缨真叶珊瑚 Euphyllia fimbriata | + | ||||||||
| 盔形珊瑚属 | 稀杯盔形珊瑚 Galaxea astreata | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 丛生盔形珊瑚 Galaxea fascicularis | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 铁星 珊瑚科 | 假铁星珊瑚属 | 假铁星珊瑚 Pseudosiderastrea tayamai | + | |||||||||
| 木珊瑚科 | 陀螺珊瑚属 | 皱折陀螺珊瑚 Turbinaria mesenterina | + | + | + | |||||||
| 盾形陀螺珊瑚 Turbinaria peltata | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 坚实类群 | 星群 珊瑚科 | 柱群珊瑚属 | 罩柱群珊瑚 Stylocoeniella guentheri | + | + | + | ||||||
| 杯形珊瑚科 | 杯形珊瑚属 | 鹿角杯形珊瑚 Pocillopora damicornis | + | + | ||||||||
| 埃氏杯形珊瑚 Pocillopora eydouxi | + | |||||||||||
| 多曲杯形珊瑚 Pocillopora meandrina | + | |||||||||||
| 疣状杯形珊瑚 Pocillopora verrucosa | + | |||||||||||
| 石芝珊瑚科 | 石芝珊瑚属 | 石芝珊瑚 Fungia fungites | + | |||||||||
| 足柄珊瑚属 | 壳形足柄珊瑚 Podabacia crustacea | + | ||||||||||
| 沙珊瑚科 | 沙珊瑚属 | 深室沙珊瑚 Psammocora contigua | + | + | + | |||||||
| 沙珊瑚 Psammocora sp. | + | |||||||||||
| 筛珊瑚科 | 筛珊瑚属 | 吞蚀筛珊瑚 Coscinaraea exesa | + | + | ||||||||
| 筛珊瑚 Coscinaraea sp. | + | |||||||||||
| 黑星 珊瑚科 | 黑星珊瑚属 | 黑星珊瑚 Oulastrea crispata | + | + | ||||||||
| 叶状 珊瑚科 | 棘星珊瑚属 | 棘星珊瑚 Acanthastrea echinata | + | + | ||||||||
| 联合棘星珊瑚 Acanthastrea hemprichii | + | |||||||||||
| 刺叶珊瑚属 | 粗糙刺叶珊瑚 Echinophyllia aspera | + | ||||||||||
| 叶状珊瑚属 | 菌形叶状珊瑚 Lobophyllia agaricia | + | ||||||||||
| 伞房叶状珊瑚 Lobophyllia corymbosa | + | + | ||||||||||
| 褶曲叶状珊瑚 Lobophyllia flabelliformis | + | |||||||||||
| 赫氏叶状珊瑚 Lobophyllia hemprichii | + | |||||||||||
| 辐射叶状珊瑚 Lobophyllia radians | + | |||||||||||
| 裸肋 珊瑚科 | 刺孔珊瑚属 | 宝石刺孔珊瑚 Echinopora gemmacea | + | |||||||||
| 刺星珊瑚属 | 小叶刺星珊瑚 Cyphastrea microphthalma | + | ||||||||||
| 日本刺星珊瑚 Cyphastrea japonica | + | |||||||||||
| 锯齿刺星珊瑚 Cyphastrea serailia | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 菊花珊瑚属 | 粗糙菊花珊瑚 Goniastrea aspera | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 梳状菊花珊瑚 Goniastrea pectinata | + | + | ||||||||||
| 网状菊花珊瑚 Goniastrea retiformis | + | + | ||||||||||
| 菊花珊瑚 Goniastrea sp. | + | + | ||||||||||
| 刺柄珊瑚属 | 腐蚀刺柄珊瑚 Hydnophora exesa | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 圆星珊瑚属 | 曲圆星珊瑚 Astrea curta | + | + | |||||||||
| 腔星珊瑚属 | 粗糙腔星珊瑚 Coelastrea aspera | + | ||||||||||
| 帛琉腔星珊瑚 Coelastrea palauensis | + | + | ||||||||||
| 盘星珊瑚属 | 黄癣盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea favus | + | + | |||||||||
| 蜥岛盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea lizardensis | + | |||||||||||
| 海洋盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea maritima | + | + | ||||||||||
| 大盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea maxima | + | |||||||||||
| 罗图马盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea rotumana | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 标准盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea speciosa | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 坚实类群 | 裸肋 珊瑚科 | 盘星珊瑚属 | 盘星珊瑚 Dipsastraea sp. | + | ||||||||
| 扁脑珊瑚属 | 尖边扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra acuta | + | ||||||||||
| 肉质扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra carnosa | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 交替扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra crosslandi | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 精巧扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra daedalea | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 小扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra pini | + | |||||||||||
| 中华扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra sinensis | + | |||||||||||
| 扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra sp. | + | + | ||||||||||
| 琉球扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra ryukyuensis | + | |||||||||||
| 八重山扁脑珊瑚 Platygyra yaeyamaensis | + | |||||||||||
| 角蜂巢珊瑚属 | 秘密角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites abdita | + | + | + | + | + | ||||||
| 尖丘角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites acuticollis | + | |||||||||||
| 中华角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites chinensis | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 板叶角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites complanata | + | + | ||||||||||
| 多弯角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites flexuosa | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 小五边角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites micropentagonus | + | |||||||||||
| 五边角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites pentagona | + | + | + | + | ||||||||
| 角蜂巢珊瑚 Favites sp. | + | + | + | |||||||||
| 同星珊瑚科 | 同星珊瑚属 | 多孔同星珊瑚 Plesiastrea versipora | + | + | + | |||||||
| 未定类群 | 未定 | 小星珊瑚属 | 白斑小星珊瑚 Leptastrea pruinosa | + | ||||||||
| 紫小星珊瑚 Leptastrea purpurea | + | + | ||||||||||
| 总计 | 15 | 33 | 104 | 19 | 45 | 29 | 19 | 55 | 49 | |||
| [1] |
高勤峰, 张恭, 董双林, 2019. 网箱养殖生态学研究进展[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 49(3): 7-17.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
郭峰, 肖家光, 田鹏, 等, 2022. 大亚湾及大鹏半岛沿岸造礁石珊瑚现状与生态脆弱性评价[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 41(4): 568-582.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
胡文佳, 张典, 廖宝林, 等, 2021. 中国大陆沿岸造礁石珊瑚适生区及保护空缺分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(1): 401-411.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
黄丁勇, 李元超, 王建佳, 等, 2020. 亚龙湾西岸造礁石珊瑚种类多样性及恢复潜力分析[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(3): 444-455.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
黄晖, 尤丰, 练健生, 等, 2012. 海南岛西北部海域珊瑚礁造礁石珊瑚种类组成与分布[J]. 海洋科学, 36(9): 64-74.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
黄建中, 魏宇衡, 顾志峰, 等, 2020. 海南西岛珊瑚群落变化及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(6): 103-113.
doi: 10.11978/2020020 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020020 |
|
| [7] |
黄林韬, 黄晖, 江雷, 2020. 中国造礁石珊瑚分类厘定[J]. 生物多样性, 28(4): 515-523.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2019384 |
|
doi: 10.17520/biods.2019384 |
|
| [8] |
孔凡洲, 于仁成, 徐子钧, 等, 2012. 应用Excel软件计算生物多样性指数[J]. 海洋科学, 36(4): 57-62.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李长青, 夏利栋, 沈贝祺, 等, 2022. 海南三亚珊瑚礁国家级自然保护区珊瑚群落近年的动态变化[J]. 海南热带海洋学院学报, 29(5): 61-72.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
廖宝林, 肖宝华, 覃业曼, 等, 2020. 海南儋州海域造礁石珊瑚种类组成及动态变化研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 37(7): 55-61.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
刘丽, 李泽鹏, 申玉春, 等, 2013. 四种环境因子对澄黄滨珊瑚和斯氏角孔珊瑚胁迫作用研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(3): 72-77.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.03.011 |
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.03.011 |
|
| [12] |
刘苗苗, 沈建伟, 王月, 等, 2011. 雷州半岛徐闻西岸珊瑚岸礁造礁珊瑚群落结构及其演变[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 31(6): 37-45.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
牛文涛, 张潇娴, 林荣澄, 等, 2010. 海南昌江沿岸海域石珊瑚的物种多样性及其分布[J]. 台湾海峡, 29(3): 389-393.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
施祺, 严宏强, 张会领, 等, 2011. 西沙群岛永兴岛礁坡石珊瑚覆盖率的空间变化[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(2): 10-17.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
王道儒, 王华接, 李元超, 等, 2011. 雷州半岛珊瑚幼虫补充来源初步研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(2): 26-32.
|
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.02.026 |
|
| [16] |
吴川良, 李长青, 张文勇, 等, 2019. 三亚国家级珊瑚礁自然保护区珊瑚礁资源的多样性[J]. 热带生物学报, 10(1): 14-21.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
吴钟解, 陈石泉, 陈敏, 等, 2013. 海南岛造礁石珊瑚资源初步调查与分析[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 35(2): 44-50.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
闫玉科, 魏紫珊, 林志豪, 2021. 海南省深水网箱养殖业发展研究——以临高县为例[J]. 渔业信息与战略, 36(1): 9-15.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
杨振雄, 张敬怀, 吕向立, 等, 2021. 涠洲岛造礁石珊瑚群落变化特征及其环境影响因子[J]. 生态学报, 41(18): 7168-7179.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
周红英, 姚雪梅, 黎李, 等, 2017. 海南岛周边海域造礁石珊瑚的群落结构及其分布[J]. 生物多样性, 25(10): 1123-1130.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2017079 |
|
doi: 10.17520/biods.2017079 |
|
| [21] |
周洁, 施祺, 余克服, 2014. 三亚造礁石珊瑚虫黄藻光合作用效率的日周期及其调控因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(1): 81-89.
|
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2014.01.011 |
|
| [22] |
邹仁林, 2001. 中国动物志: 腔肠动物门. 珊瑚虫纲. 石珊瑚目: 造礁石珊瑚[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-242 (in Chinese).
|
| [23] |
doi: S0141-1136(19)30090-X pmid: 31029435 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1126/science.199.4335.1302 pmid: 17840770 |
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
doi: 10.1111/gcb.12658 pmid: 25044878 |
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
doi: 10.1038/srep29616 pmid: 27432782 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30234-6 pmid: 35504876 |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
doi: 10.1111/gcb.16083 pmid: 35106864 |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
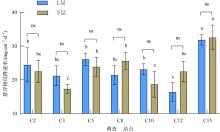
| [3] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [4] | GENG Wanlu, XING Yongze, ZHANG Qiufeng, GUAN Weibing. Structural characteristics of macrobenthic communities at intertidal zone for mangrove in Beihai, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [5] | ZHANG Lanlan, CHENG Xiawen, XIANG Rong, QIU Zhuoya, CHANG Hu. Changes of radiolarian community structure with depth in the central Bay of Bengal in spring 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [6] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [7] | CHEN Jingfu, ZHONG Yu, WANG Lei, GUO Yupei, QIU Dajun. Noctiluca scintillans effects on eukaryotic plankton community structure using Environmental DNA analysis in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [8] | MA Wengang, XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang, LI Xiubao, WANG Aimin. Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [9] | LIU Yue, LI Li, ZHAI Xiaohui, ZHOU Juan, YE Penghao, HUANG Shengdong. Analysis of the bloom caused by colonial Phaeocystis globosa in Mirs Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 164-171. |
| [10] | ZHU Wentao, XIA Jingquan, LIU Xiangbo, YIN Hongyang, ZHU Ming, REN Yuxiao, XIE Minrui, HUANG Jianzhong, LI Xiubao. Analysis of photosynthetic physiology and symbiotic fungi community in Galaxea fascicularis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 132-141. |
| [11] | ZHANG Liming, TAN Yehui, LI Jiajun, HUANG Xiaoping, LIU Jiaxing. Characteristics of the phytoplankton community and its response to Dan’ao River input in Daya Bay in summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [12] | Yuzheng REN, Zhixin KE, Yehui TAN, Kaizhi LI. Community structure of zooplankton and its influencing factors in the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island, Guangdong [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 65-76. |
| [13] | Tongchen LIAO, Jianqiang YIN, Kaizhi LI, Yehui TAN. Distribution of planktonic ostracods and its influencing factors during summer and winter in the northwestern coastal waters of South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 77-87. |
| [14] | Sixuan HE,Binyuan HE. Study on fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 86-97. |
| [15] | Xinming LEI, Hui HUANG, Jiansheng LIAN, Yuyang ZHANG, Jianhui YANG. [RETRACTED] Species composition of coralline algae and its spatial characteristics related to environmental factors in Sanya coral reefs, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 79-88. |
|
||