热带海洋学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 117-130.doi: 10.11978/2021003CSTR: 32234.14.2021003
中国典型红树林沉积物中多溴联苯醚和替代型溴系阻燃剂污染特征
- 1. 中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2. 中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院, 广东 广州 510301
3. 南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
4. 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
-
收稿日期:2021-01-04修回日期:2021-03-11出版日期:2022-01-10发布日期:2022-01-26 -
通讯作者:徐向荣 -
作者简介:李华薇(1994—), 女, 江西省九江市人, 博士研究生, 从事持久性有机污染物的生物地球化学行为研究。email:soledadlee1227@163.com -
基金资助:国家重点研发项目(2018YFC1406503);中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院自主部署项目(ISEE2019ZR03);中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院自主部署项目(ISEE2018PY03);中国科学院南海生态环境工程创新研究院自主部署项目(ISEE2018ZD02);南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州)人才团队引进重大专项(GML2019ZD0404)
Pollution characteristics of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and alternative brominated flame retardants in sediments from typical mangrove wetlands of China
LI Huawei1,4( ), XU Xiangrong1,2,3(
), XU Xiangrong1,2,3( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
4. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-01-04Revised:2021-03-11Online:2022-01-10Published:2022-01-26 -
Contact:XU Xiangrong -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2018YFC1406503);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2019ZR03);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018PY03);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018ZD02);Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering, Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0404)
摘要:
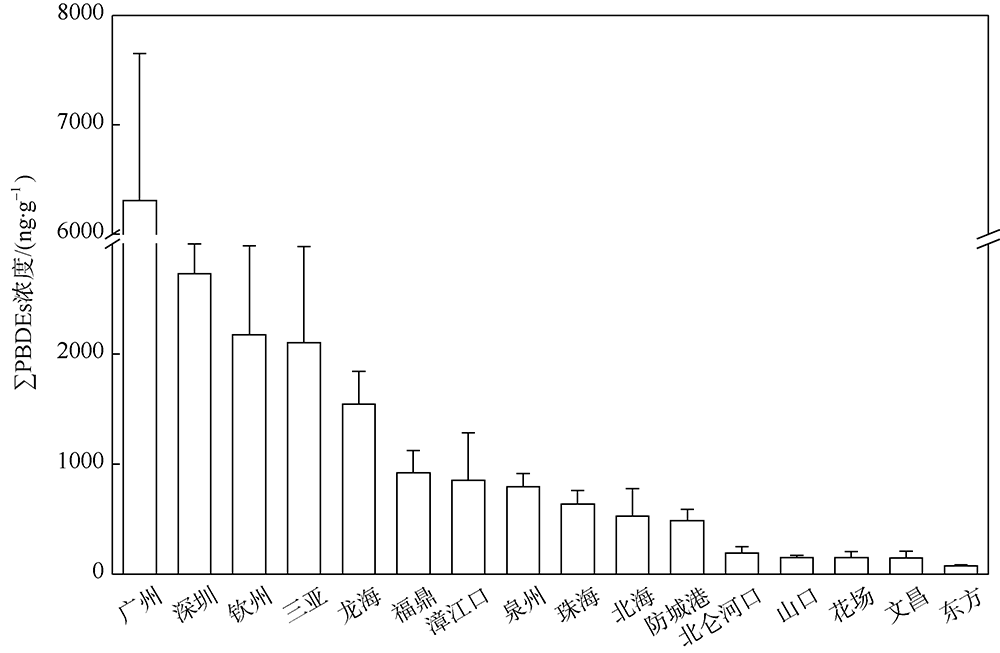
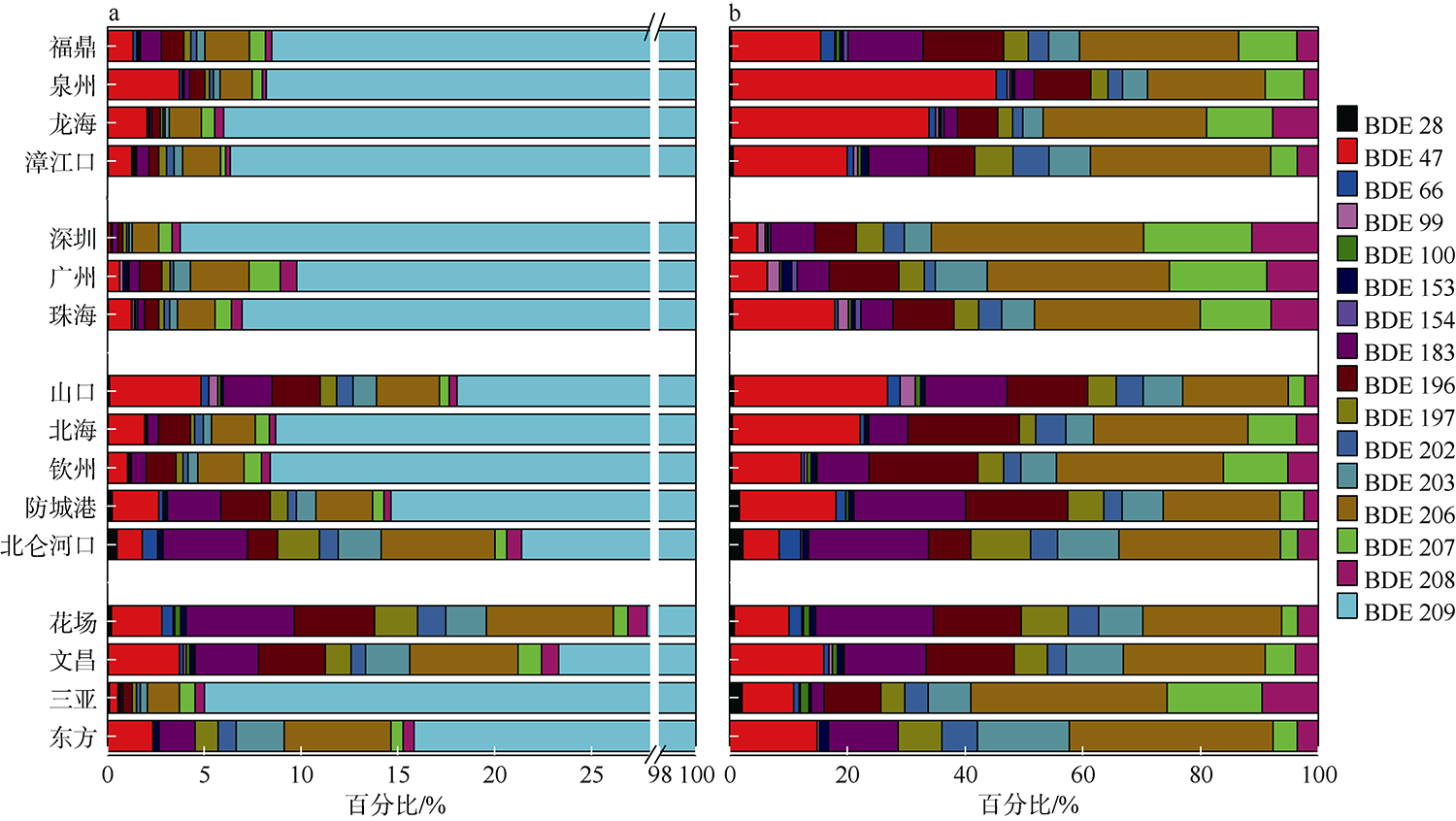
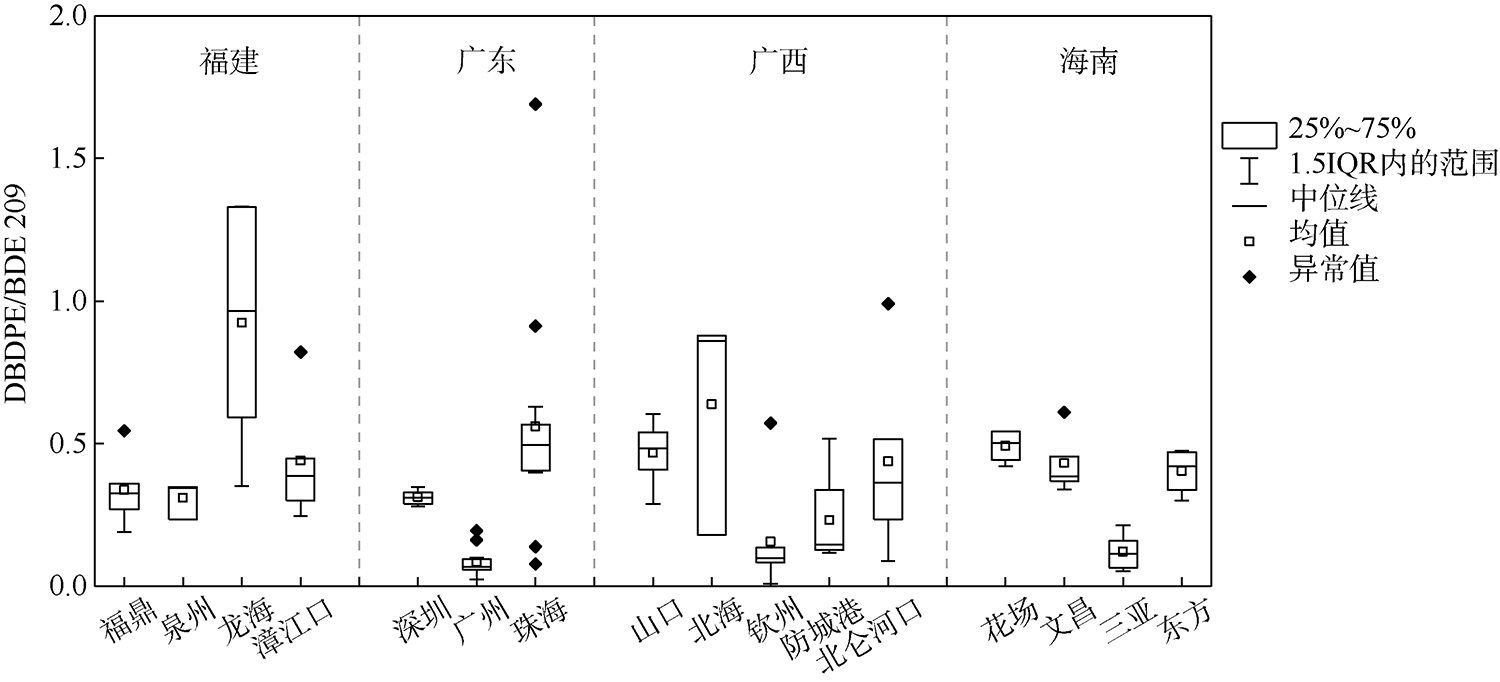
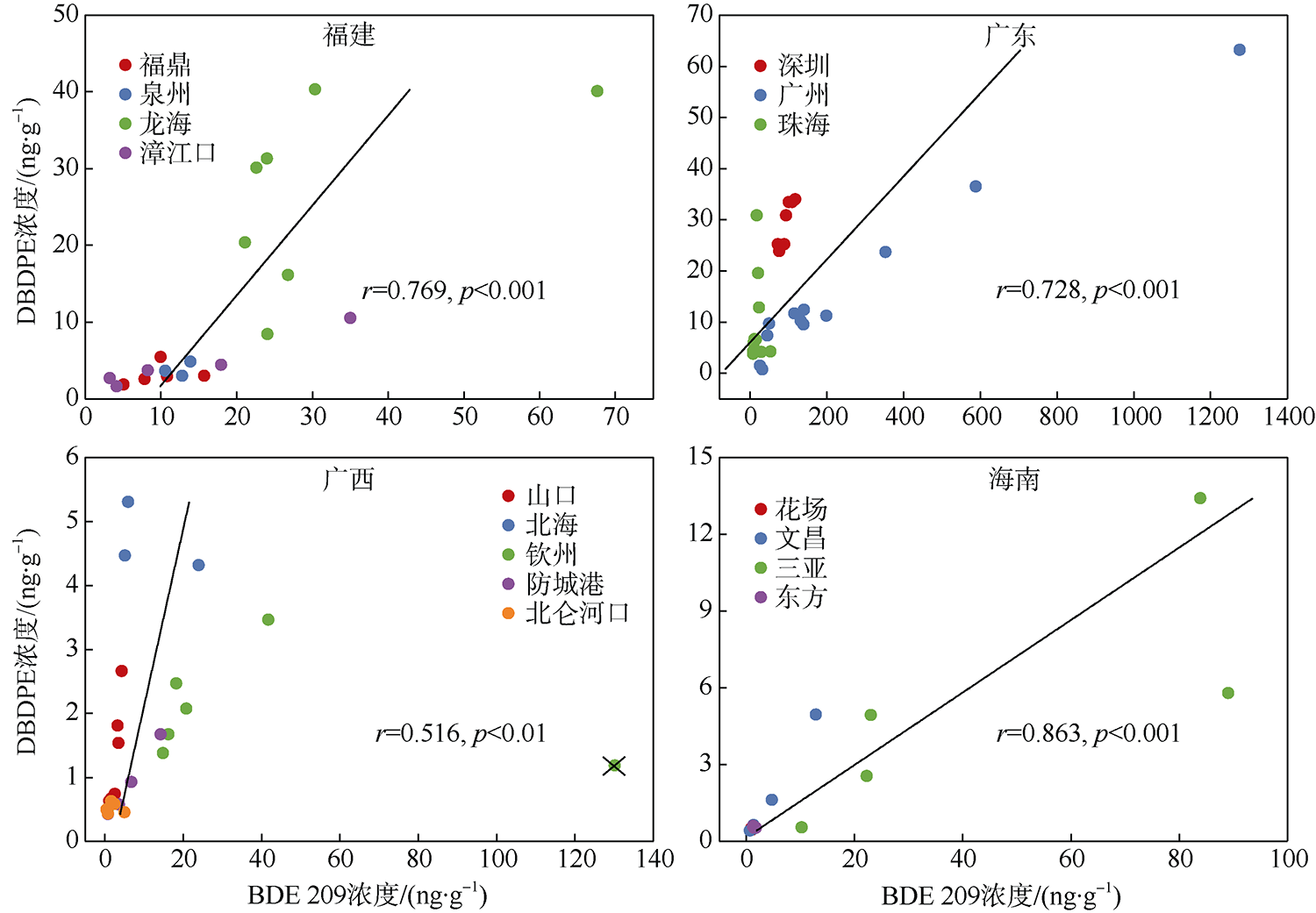
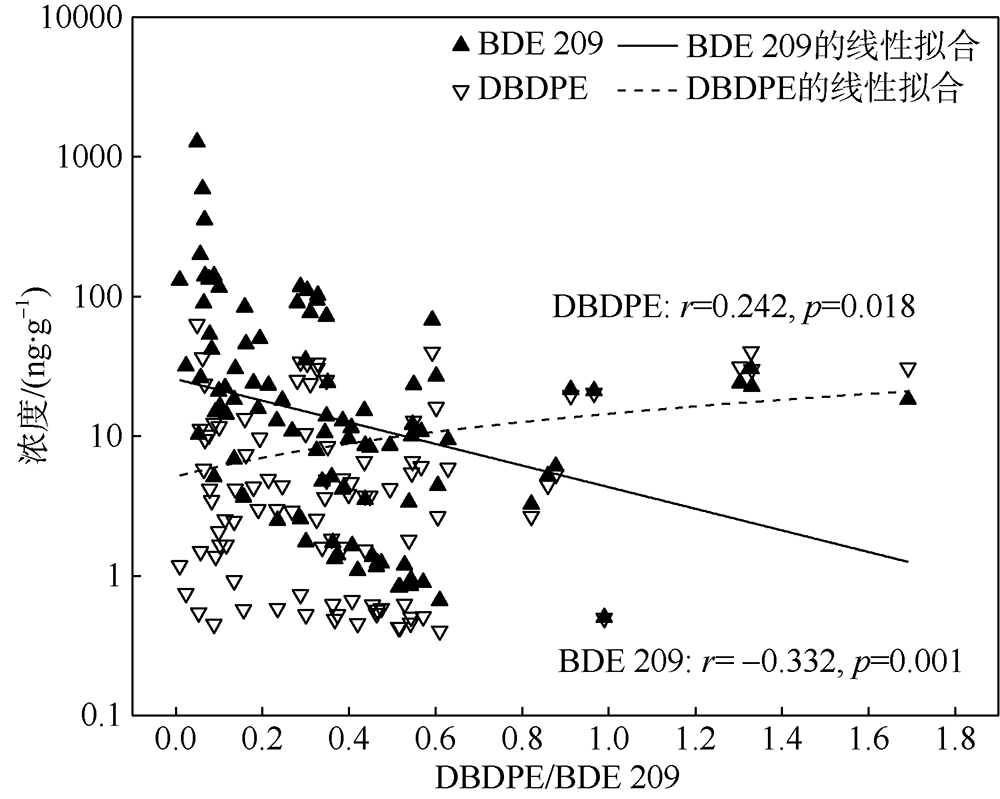
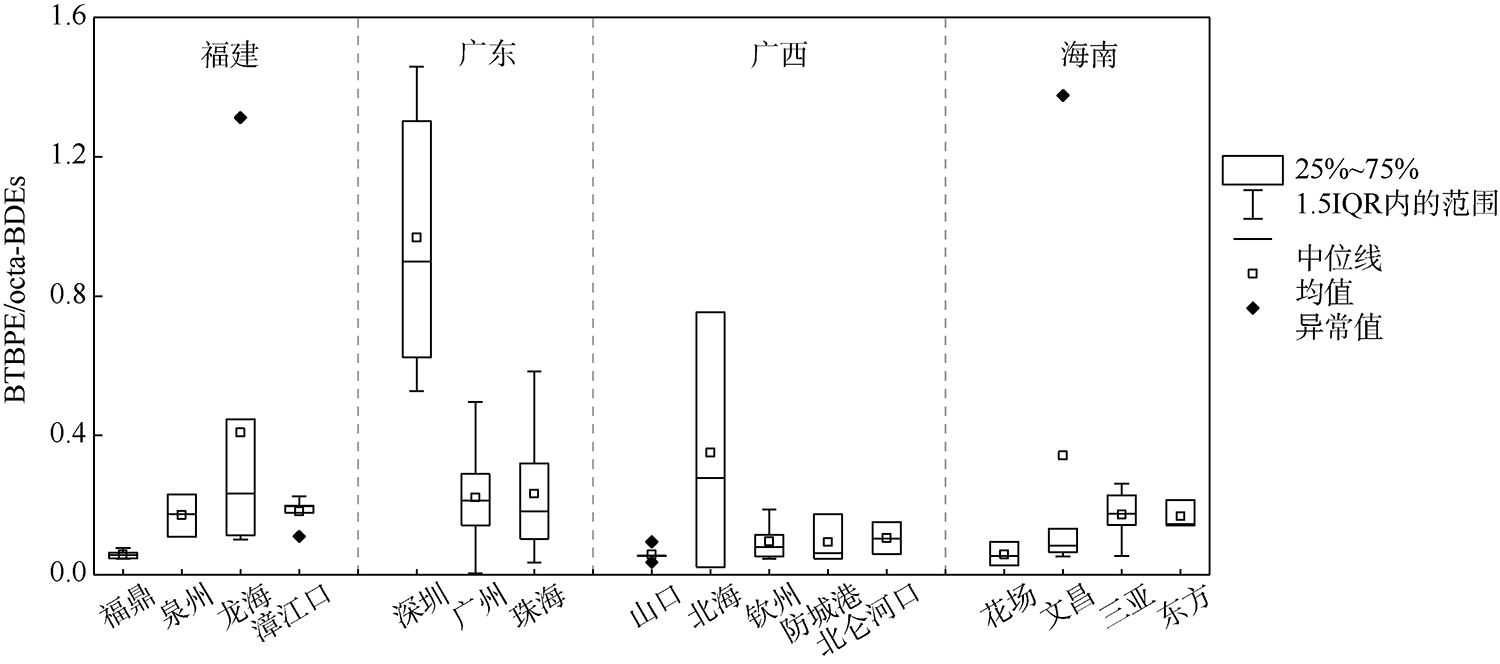
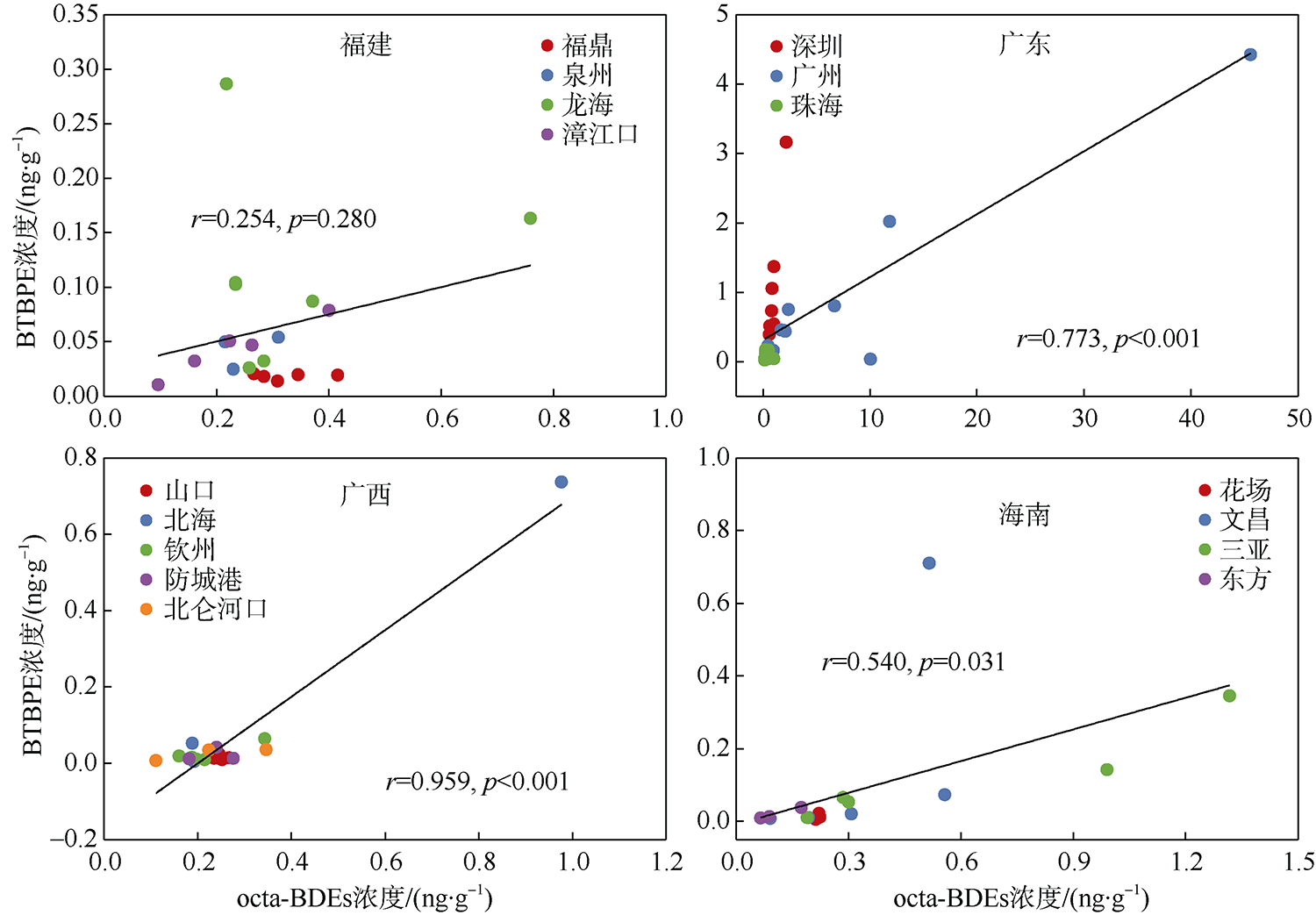
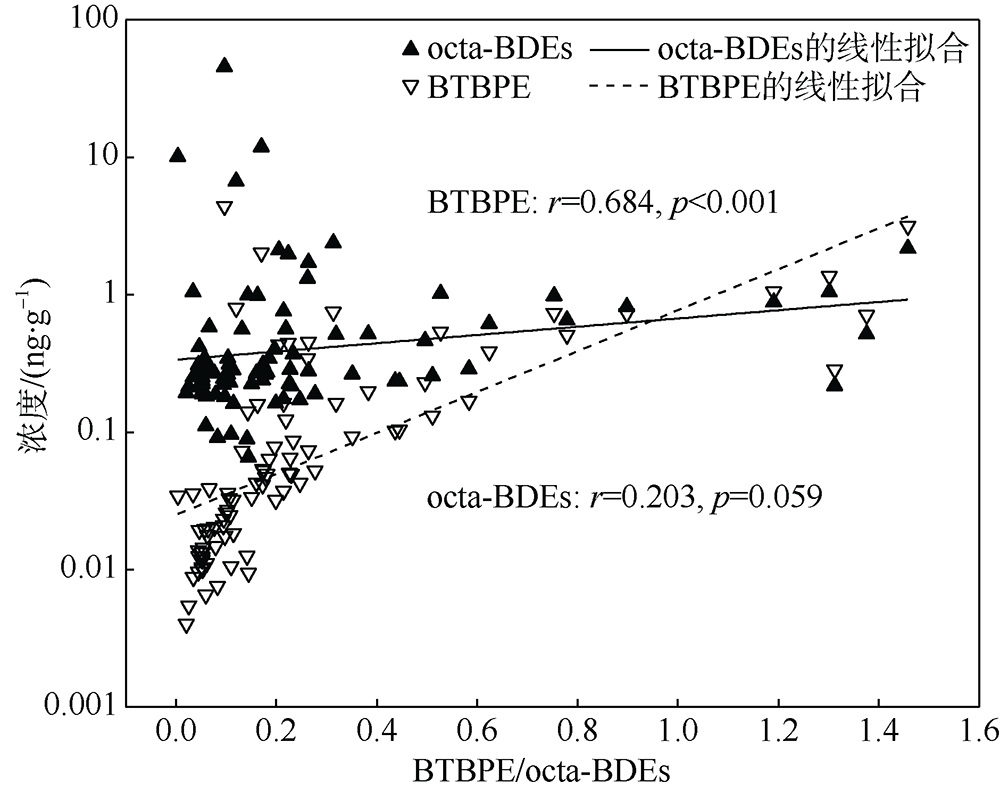
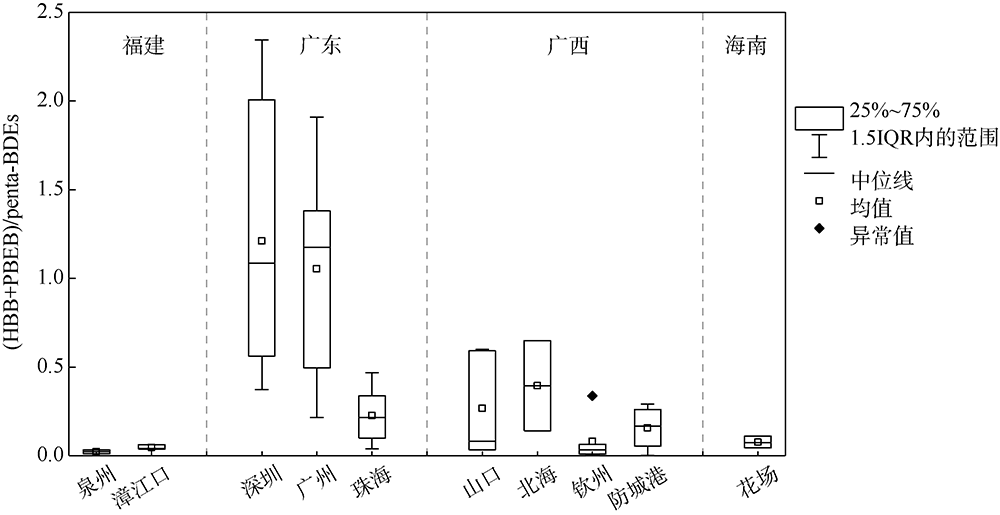
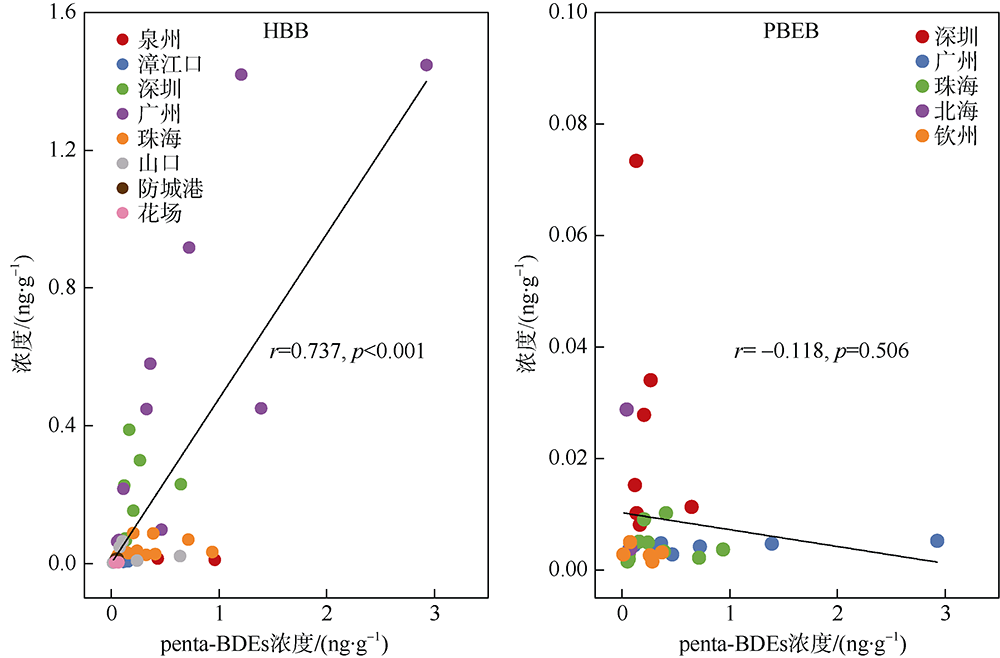
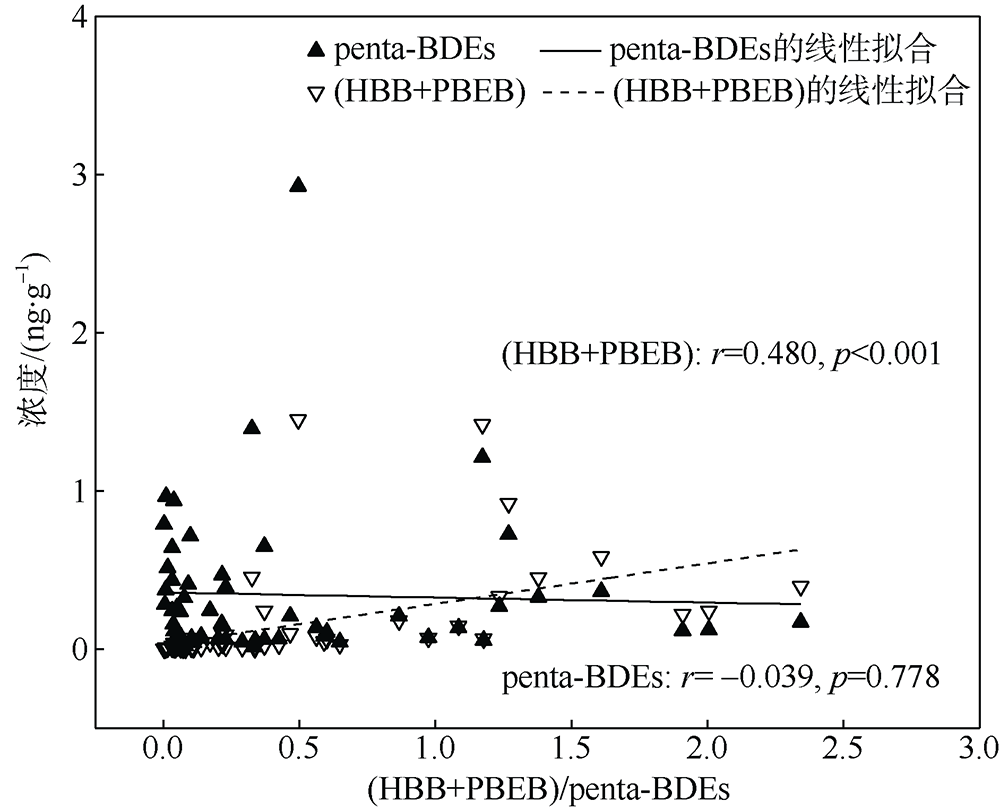
本文研究了中国四省区(福建、广东、广西和海南)共16处红树林湿地表层沉积物中多溴联苯醚(polybrominated diphenyl ethers, PBDEs)和5种替代型溴系阻燃剂(alternative brominated flame retardants, ABFRs)的污染特征, 包括十溴二苯乙烷(decabromodiphenyl ethane, DBDPE)、1, 2-双(2, 4, 6-三溴苯氧基)乙烷[1, 2-bis (2, 4, 6-tribromophenoxy) ethane, BTBPE]、六溴苯(hexabromobenzene, HBB)、五溴甲苯(pentabromotoluene, PBT)和五溴乙苯(pentabromoethylbenzene, PBEB)。结果表明, PBDEs、DBDPE和BTBPE在我国红树林湿地沉积物中广泛存在, 而HBB、PBT和PBEB仅在部分红树林湿地检出。PBDEs总含量的均值范围为1.39~293ng·g-1(干重), 其污染程度具有明显的空间差异性(p=0.016), 并且与当地人口和经济水平显著正相关(p<0.01)。在红树林沉积物样品中, BDE 209是最主要的同系物, 占PBDEs总含量的72%~96%; DBDPE和BTBPE是最主要的ABFRs, 浓度的均值范围分别为0.489~29.4ng·g-1(干重)和0.0127~1.11ng·g-1(干重)。BDE 209与其替代品DBDPE的含量显著正相关(p<0.01), 反映出二者在红树林湿地沉积物中空间分布的相似性, 这说明BDE 209和DBDPE可能具有相似的污染源和/或环境行为。DBDPE与BDE 209的浓度比值范围为0.0839~0.925, 表明我国红树林湿地沉积物中DBDPE的污染水平还未超过BDE 209, 但ABFRs逐渐替代使用而带来的环境问题不容忽视。
中图分类号:
- P734.5
引用本文
李华薇, 徐向荣. 中国典型红树林沉积物中多溴联苯醚和替代型溴系阻燃剂污染特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 117-130.
LI Huawei, XU Xiangrong. Pollution characteristics of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and alternative brominated flame retardants in sediments from typical mangrove wetlands of China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 117-130.
表1
红树林沉积物样品采集信息表"
| 采样点 | 样品数 | 经度范围 | 纬度范围 | 所属红树林或保护区 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 福建 | 福鼎 | 5 | 120°11′43″—120°22′32″E | 27°13′23″—27°16′47″N | 姚家屿红树林自然保护区 |
| 泉州 | 3 | 118°41′2″—118°41′53″E | 24°54′41″—24°57′27″N | 泉州湾红树林省级自然保护区 | |
| 龙海 | 7 | 117°53′27″—117°56′44″E | 24°23′38″—24°28′11″N | 九龙江口红树林省级自然保护区 | |
| 漳江口 | 5 | 117°23′7″—117°27′37″E | 21°54′41″—23°56′15″N | 漳江口红树林国家级自然保护区 | |
| 广东 | 深圳 | 7 | 114°0′19″—114°0′51″E | 22°31′24″—22°31′40″N | 内伶仃岛-福田国家级自然保护区 |
| 广州 | 12 | 113°34′38″—113°34′44″E | 22°48′46″—22°48′50″N | 南沙区坦头红树林 | |
| 珠海 | 13 | 113°37′37″—113°38′00″E | 22°25′36″—22°25′59″N | 淇澳-担杆岛省级自然保护区 | |
| 广西 | 山口 | 6 | 109°40′13″—109°45′32″E | 21°30′12″—21°36′4″N | 山口红树林国家级自然保护区 |
| 北海 | 3 | 109°6′15″—109°9′18″E | 21°33′33″—21°53′13″N | 廉州湾南流江入海口处红树林 | |
| 钦州 | 7 | 108°29′41″—108°37′17″E | 21°44′34″—21°53′13″N | 茅尾海红树林省级自然保护区 | |
| 防城港 | 4 | 108°19′41″—108°25′2″E | 21°36′47″—21°40′58″N | 港口区渔洲坪红树林 | |
| 北仑河口 | 5 | 108°9′25″—108°16′1″E | 21°32′56″—21°36′56″N | 北仑河口国家级自然保护区 | |
| 海南 | 花场 | 4 | 109°59′30″—109°59′52″E | 19°54′43″—19°55′7″N | 花场湾红树林自然保护区 |
| 文昌 | 5 | 110°47′15″—110°50′27″E | 19°33′27″—19°37′32″N | 清澜港红树林省级自然保护区 | |
| 三亚 | 5 | 109°30′27″—109°37′18″E | 18°13′42″—18°16′18″N | 青梅港和三亚河红树林自然保护区 | |
| 东方 | 4 | 108°37′55″—108°38′15″E | 19°12′55″—19°13′1″N | 东方市四必湾湿地 | |
表2
红树林沉积物中PBDEs的浓度/(ng·g-1 干重)"
| 采样点 | BDE 28 | BDE 47 | BDE 66 | BDE 99 | BDE 100 | BDE 153 | BDE 154 | BDE 183 | BDE 196 | BDE 197 | BDE 202 | BDE 203 | BDE 206 | BDE 207 | BDE 208 | BDE 209 | ∑PBDEsa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 福建省 | |||||||||||||||||
| 福鼎 | 0.00207 ± 0.000288b | 0.123 ± 0.0202 | 0.0172 ± 0.00283 | ndc | nd | 0.00466 ± 0.000544 | 0.00879 ± 0.00139 | 0.0978 ± 0.0157 | 0.117 ± 0.0145 | 0.0361 ± 0.00453 | 0.0271 ± 0.00419 | 0.0466 ± 0.00890 | 0.230 ± 0.0176 | 0.0829 ± 0.0108 | 0.0315 ± 0.00571 | 9.90 ± 1.76 | 10.7 ± 1.79 |
| 泉州 | 0.00363 ± 0.000477 | 0.526 ± 0.205 | 0.0211 ± 0.00366 | nd | nd | 0.00695 ± 0.000207 | nd | 0.0373 ± 0.00613 | 0.108 ± 0.00891 | 0.0329 ± 0.00659 | 0.0278 ± 0.00736 | 0.0462 ± 0.00161 | 0.221 ± 0.0112 | 0.0735 ± 0.0103 | 0.0267 ± 0.00139 | 12.4 ± 0.987 | 13.6 ± 1.22 |
| 龙海 | 0.00381 ± 0.000260 | 0.579 ± 0.176 | 0.0176 ± 0.00360 | 0.0134 ± 0.00407 | 0.00360 ± 0.000552 | 0.00558 ± 0.000366 | 0.00706 ± 0.00113 | 0.0498 ± 0.00666 | 0.138 ± 0.0309 | 0.0495 ± 0.00848 | 0.0334 ± 0.00593 | 0.0737 ± 0.0223 | 0.603 ± 0.198 | 0.258 ± 0.101 | 0.170 ± 0.0590 | 30.9 ± 6.22 | 32.9 ± 6.64 |
| 漳江口 | 0.00286 ± 0.000338 | 0.118 ± 0.0342 | 0.00759 ± 0.00213 | nd | 0.00531 ± 0.000586 | 0.00489 ± 0.000311 | nd | 0.0527 ± 0.00738 | 0.0932 ± 0.00971 | 0.0443 ± 0.0115 | 0.0381 ± 0.00779 | 0.0382 ± 0.00579 | 0.221 ± 0.0705 | 0.0491 ± 0.0283 | 0.0260 ± 0.00983 | 13.7 ± 5.93 | 14.4 ± 6.08 |
| 广东省 | |||||||||||||||||
| 深圳 | 0.0140 ± 0.00463 | 0.145 ± 0.0608 | 0.0126 ± 0.00411 | 0.0459 ± 0.00661 | 0.0135 ± 0.00128 | 0.00823 ± 0.00281 | nd | 0.289 ± 0.104 | 0.262 ± 0.0351 | 0.176 ± 0.0499 | 0.128 ± 0.00531 | 0.174 ± 0.0243 | 1.34 ± 0.132 | 0.682 ± 0.0810 | 0.419 ± 0.0425 | 94.7 ± 6.33 | 98.4 ± 6.62 |
| 广州 | 0.0102 ± 0.000931 | 4.26 ± 2.64 | 0.00710 ± 0.000681 | 0.555 ± 0.273 | 0.0900 ± 0.0424 | 0.292 ± 0.122 | 0.242 ± 0.110 | 0.734 ± 0.263 | 2.93 ± 1.65 | 0.999 ± 0.514 | 0.367 ± 0.154 | 2.04 ± 1.12 | 12.0 ± 6.81 | 6.31 ± 3.53 | 3.82 ± 2.32 | 258 ± 104 | 293 ± 122 |
| 珠海 | 0.00494 ± 0.000676 | 0.235 ± 0.0725 | 0.00575 ± 0.000519 | 0.0204 ± 0.00303 | 0.00591 ± 0.000885 | 0.00564 ± 0.000332 | 0.0158 ± 0.00269 | 0.0676 ± 0.00535 | 0.129 ± 0.0262 | 0.0507 ± 0.00846 | 0.0497 ± 0.0148 | 0.0746 ± 0.0198 | 0.412 ± 0.135 | 0.179 ± 0.0611 | 0.126 ± 0.0501 | 17.9 ± 3.50 | 19.2 ± 3.81 |
| 广西壮族自治区 | |||||||||||||||||
| 山口 | 0.00382 ± 0.000680 | 0.174 ± 0.0857 | 0.0127 ± 0.00566 | nd | nd | 0.00368 ± 0.0000972 | nd | 0.0822 ± 0.0179 | 0.0811 ± 0.00534 | 0.0247 ± 0.00179 | 0.0266 ± 0.00317 | 0.0362 ± 0.00258 | 0.0980 ± 0.00658 | 0.0170 ± 0.00497 | 0.0147 ± 0.00181 | 2.77 ± 0.495 | 3.32 ± 0.500 |
| 北海 | 0.00309 ± 0.000464 | 0.131 ± 0.0807 | 0.00488 ± 0.000675 | nd | nd | 0.00388 ± 0.000383 | nd | 0.0751 ± 0.0393 | 0.237 ± 0.150 | 0.0227 ± 0.00566 | 0.0838 ± 0.0696 | 0.0420 ± 0.0121 | 0.285 ± 0.142 | 0.115 ± 0.0814 | 0.0534 ± 0.0387 | 11.8 ± 6.15 | 12.8 ± 6.62 |
| 钦州 | 0.00296 ± 0.000417 | 0.265 ± 0.0745 | 0.00456 ± 0.00107 | nd | 0.00451 ± 0.00119 | 0.00488 ± 0.000732 | 0.0154 ± 0.00499 | 0.0734 ± 0.0334 | 0.288 ± 0.192 | 0.101 ± 0.0695 | 0.0371 ± 0.0158 | 0.218 ± 0.161 | 1.47 ± 1.22 | 0.892 ± 0.802 | 0.475 ± 0.428 | 34.7 ± 16.5 | 38.5 ± 19.4 |
| 防城港 | 0.00608 ± 0.00152 | 0.218 ± 0.180 | 0.00587 ± 0.00130 | nd | nd | 0.00397 ± 0.000495 | nd | 0.0636 ± 0.0216 | 0.0830 ± 0.00471 | 0.0313 ± 0.00424 | 0.0227 ± 0.00521 | 0.0380 ± 0.00486 | 0.145 ± 0.0410 | 0.0462 ± 0.0225 | 0.0290 ± 0.00865 | 6.40 ± 2.91 | 7.10 ± 3.14 |
| 北仑河口 | 0.0105 ± 0.00484 | 0.0273 ± 0.00748 | 0.0151 ± 0.00518 | nd | nd | 0.00383 ± 0.000192 | nd | 0.0832 ± 0.0196 | 0.0790 ± 0.00291 | 0.0425 ± 0.00956 | 0.0151 ± 0.00317 | 0.0372 ± 0.00542 | 0.101 ± 0.00877 | 0.0114 ± 0.00136 | 0.0160 ± 0.00498 | 2.13 ± 0.820 | 2.54 ± 0.868 |
| 海南省 | |||||||||||||||||
| 花场 | 0.00402 ± 0.00104 | 0.0362 ± 0.00734 | 0.00833 ± 0.00262 | nd | nd | 0.00387 ± 0.000114 | nd | 0.0778 ± 0.00741 | 0.0737 ± 0.00194 | 0.0301 ± 0.00445 | 0.0204 ± 0.00483 | 0.0290 ± 0.00215 | 0.0908 ± 0.00409 | 0.0104 ± 0.00113 | 0.0170 ± 0.00171 | 1.00 ± 0.0704 | 1.39 ± 0.0719 |
| 文昌 | 0.00670 ± 0.00180 | 0.0911 ± 0.0318 | 0.00742 ± 0.00332 | nd | nd | 0.00717 ± 0.00185 | nd | 0.0628 ± 0.0208 | 0.117 ± 0.0115 | 0.0571 ± 0.0245 | 0.0503 ± 0.0228 | 0.0793 ± 0.0241 | 0.196 ± 0.0587 | 0.0853 ± 0.0506 | 0.0714 ± 0.0328 | 4.18 ± 2.28 | 4.98 ± 2.49 |
| 三亚 | 0.160 ± 0.121 | 0.262 ± 0.155 | 0.0359 ± 0.0307 | nd | nd | 0.00765 ± 0.00174 | nd | 0.0774 ± 0.0546 | 0.181 ± 0.0467 | 0.107 ± 0.0532 | 0.113 ± 0.0493 | 0.169 ± 0.0584 | 0.729 ± 0.253 | 0.409 ± 0.163 | 0.275 ± 0.120 | 45.7 ± 16.8 | 48.1 ± 17.8 |
| 东方 | nd | 0.0392 ± 0.00942 | nd | nd | nd | 0.00386 ± 0.000329 | nd | 0.0412 ± 0.0152 | nd | 0.0225 ± 0.00461 | 0.0151 ± 0.00254 | 0.0405 ± 0.00520 | 0.0903 ± 0.00167 | 0.0105 ± 0.000243 | 0.00938 ± 0.000560 | 1.40 ± 0.123 | 1.66 ± 0.122 |
| 总检出率 | 85% | 98% | 86% | 51% | 60% | 91% | 45% | 92% | 88% | 98% | 99% | 99% | 100% | 100% | 95% | 100% | 100% |
表3
红树林沉积物中ABFRs的浓度[单位: ng·g-1 (干重)]"
| 采样点 | DBDPE | BTBPE | HBB | PBT | PBEB | ∑ABFRs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 福建 | 福鼎 | 3.15±0.612 | 0.0182±0.00118 | nd | nd | nd | 3.18±0.610 |
| 泉州 | 3.83±0.543 | 0.0428±0.00907 | 0.0123±0.00144 | nd | nd | 3.88±0.550 | |
| 龙海 | 26.7±4.58 | 0.114±0.0336 | nd | nd | nd | 26.8±4.60 | |
| 漳江口 | 4.58±1.56 | 0.0438±0.0112 | 0.00838±0.00245 | nd | nd | 4.63±1.57 | |
| 广东 | 深圳 | 29.4±1.71 | 1.11±0.366 | 0.205±0.0444 | 0.0243±0.00116 | 0.0257±0.00874 | 30.8±1.93 |
| 广州 | 16.5±5.07 | 0.839±0.360 | 0.571±0.152 | 0.0242±0.00194 | 0.00409±0.000235 | 17.8±5.38 | |
| 珠海 | 8.71±2.23 | 0.0706±0.0145 | 0.0385±0.00710 | nd | 0.00427±0.000800 | 8.83±2.23 | |
| 广西 | 山口 | 1.34±0.332 | 0.0144±0.00242 | 0.0284±0.0108 | nd | nd | 1.37±0.332 |
| 北海 | 4.69±0.309 | 0.264±0.236 | nd | nd | 0.0163±0.0102 | 4.97±0.260 | |
| 钦州 | 1.82±0.363 | 0.0234±0.0103 | nd | nd | 0.00302±0.000476 | 1.84±0.370 | |
| 防城港 | 0.899±0.277 | 0.0217±0.00989 | 0.0113±0.00188 | nd | nd | 0.933±0.279 | |
| 北仑河口 | 0.516±0.0382 | 0.0255±0.00946 | nd | nd | nd | 0.532±0.0455 | |
| 海南 | 花场 | 0.489±0.0198 | 0.0127±0.00449 | 0.00344±0.000448 | nd | nd | 0.501±0.0167 |
| 文昌 | 1.61±0.860 | 0.164±0.137 | nd | 0.00978±0.00114 | nd | 1.79±0.882 | |
| 三亚 | 5.44±2.19 | 0.123±0.0595 | nd | 0.0303±0.0159 | nd | 5.59±2.25 | |
| 东方 | 0.552±0.0146 | 0.0198±0.00883 | nd | 0.0101±0.00104 | nd | 0.578±0.0214 | |
| 总检出率 | 100% | 92% | 59% | 33% | 42% | 100% | |
| [1] |
林鹏, 2003. 中国红树林湿地与生态工程的几个问题[J]. 中国工程科学, 5(6): 33-38.
doi: 10.11648/j.es.20200503.12 |
|
LIN PENG, 2003. The characteristics of mangrove wetlands and some ecological engineering questions in China[J]. Engineering Science, 5(6): 33-38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11648/j.es.20200503.12 |
|
| [2] | 卢晓霞, 张姝, 陈超琪, 等, 2012. 天津滨海地区表层沉积物中持久性有机污染物的含量特征与生态风险[J]. 环境科学, 33(10): 3426-3433. |
| LU XIAOXIA, ZHANG SHU, CHEN CHAOQI, et al, 2012. Concentration characteristics and ecological risk of persistent organic pollutants in the surface sediments of Tianjin coastal area[J]. Environmental Science, 33(10): 3426-3433. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] |
邱孟德, 邓代永, 余乐洹, 等, 2012. 典型电器工业区河涌沉积物中的多溴联苯醚空间和垂直分布[J]. 环境科学, 33(2): 580-586.
doi: 10.1021/es9803207 |
|
QIU MENGDE, DENG DAIYONG, YU LEHUAN, et al, 2012. Horizontal and vertical distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in river sediment from a typical electrical equipment industrial area[J]. Environmental Science, 33(2): 580-586. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.1021/es9803207 |
|
| [4] | 孙娟, 郑文教, 陈文田, 2005. 红树林湿地多环芳烃污染研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 24(10): 1211-1214. |
| SUN JUAN, ZHENG WENJIAO, CHEN WENTIAN, 2005. Research advance in ecological effects of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in mangrove wetland[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 24(10): 1211-1214. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 王森, 张兆祥, 2020. 环境介质中十溴二苯乙烷和1, 2-双(2, 4, 6-三溴苯氧基)乙烷分布特征的研究进展[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 48(3): 407-417, 455. |
| WANG SEN, ZHANG ZHAOXIANG,2020. Research progress on distribution characteristics of DBDPE and BTBPE in environment[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 48(3): 407-417, 455. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] |
王亚韡, 蔡亚岐, 江桂斌, 2010. 斯德哥尔摩公约新增持久性有机污染物的一些研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 化学, 40(2): 99-123.
doi: 10.1360/zb2010-40-2-99 |
|
WANG YAWEI, CAI YAQI, JIANG GUIBIN, 2010. Research processes of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) newly listed and candidate POPs in Stockholm Convention[J]. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 40(2): 99-123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.1360/zb2010-40-2-99 |
|
| [7] | 吴辉, 金军, 王英, 等, 2014. 典型地区大气中多溴联苯醚和新型溴代阻燃剂的水平及组成分布[J]. 环境科学, 35(4): 1230-1237. |
| WU HUI, JIN JUN, WANG YING, et al, 2014. Comparative study of the level and distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and new brominated flame retardants in the atmosphere of typical urban[J]. Environmental Science, 35(4): 1230-1237. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 向鑫鑫, 鲁垠涛, 阮起炀, 等, 2020. 中国东北沈抚地区土壤中PBDEs的残留、来源及风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 41(1): 368-376. |
| XIANG XINXIN, LU YINTAO, RUAN QIYANG, et al, 2020. Occurrence, distribution, source, and health risk assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface soil from the Shen-Fu region, northeast China[J]. Environmental Science, 41(1): 368-376. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] |
BAYEN S, WURL O, KARUPPIAH S, et al, 2005. Persistent organic pollutants in mangrove food webs in Singapore[J]. Chemosphere, 61(3): 303-313.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.097 |
| [10] |
BINELLI A, SARKAR S K, CHATTERJEE M, et al, 2007. Concentration of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediment cores of Sundarban mangrove wetland, northeastern part of Bay of Bengal (India)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54(8): 1220-1229.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.03.021 |
| [11] |
BODIN N, KA R N G, LE LOC'H F, et al, 2011. Are exploited mangrove molluscs exposed to persistent organic pollutant contamination in Senegal, West Africa?[J]. Chemosphere, 84(3): 318-327.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.012 |
| [12] |
CHAI MINWEI, DING HUAN, SHEN XIAOXUE, et al, 2019. Contamination and ecological risk of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in surface sediments of mangrove wetlands: a nationwide study in China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 249: 992-1001.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.02.044 |
| [13] |
COVACI A, HARRAD S, ABDALLAH M A E, et al, 2011. Novel brominated flame retardants: a review of their analysis, environmental fate and behaviour[J]. Environment International, 37(2): 532-556.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2010.11.007 |
| [14] |
DE BOER J, WESTER P G, VAN DER HORST A, et al, 2003. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in influents, suspended particulate matter, sediments, sewage treatment plant and effluents and biota from the Netherlands[J]. Environmental Pollution, 122(1): 63-74.
doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00280-4 |
| [15] |
DE WIT C A, 2002. An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment[J]. Chemosphere, 46(5): 583-624.
doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00225-9 |
| [16] |
HE JIANZHONG, ROBROCK K R, ALVAREZ-COHEN L, 2006. Microbial reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 40(14): 4429-4434.
doi: 10.1021/es052508d |
| [17] |
HOH E, ZHU LINGYAN, HITES R A, 2005. Novel flame retardants, 1, 2-bis(2, 4, 6-tribromophenoxy)ethane and 2, 3, 4, 5, 6-pentabromoethylbenzene, in United States' environmental samples[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(8): 2472-2477.
doi: 10.1021/es048508f |
| [18] |
HU YONGXIA, PEI NANCAI, SUN YUXIN, et al, 2019. Halogenated flame retardants in mangrove sediments from the Pearl River Estuary, South China: comparison with historical data and correlation with microbial community[J]. Chemosphere, 227: 315-322.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.04.075 |
| [19] | HUANG HUANGWEN, CHANG B V, LEE C C, 2014. Reductive debromination of decabromodiphenyl ether by anaerobic microbes from river sediment[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 87: 60-65. |
| [20] |
MADDELA N R, VENKATESWARLU K, KAKARLA D, et al, 2020. Inevitable human exposure to emissions of polybrominated diphenyl ethers: a perspective on potential health risks[J]. Environmental Pollution, 266: 115240.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115240 |
| [21] |
MAI BIXIAN, CHEN SHEJUN, LUO XIAOJUN, et al, 2005. Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Pearl River Delta and adjacent South China Sea[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 39(10): 3521-3527.
doi: 10.1021/es048083x |
| [22] |
QIU YAOWEN, QIU HAILIN, ZHANG GAN, et al, 2019. Bioaccumulation and cycling of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and dechlorane plus (DP) in three natural mangrove ecosystems of South China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 651: 1788-1795.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.055 |
| [23] |
REN GUOFA, YAN XIAOLING, CHU XIAODONG, et al, 2019. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and polychlorinated biphenyls in mangrove sediments of Shantou, China: occurrence, profiles, depth-distribution, and risk assessment[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 183: 109564.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109564 |
| [24] |
SHARKEY M, HARRAD S, ABOU-ELWAFA ABDALLAH M, et al, 2020. Phasing-out of legacy brominated flame retardants: The UNEP Stockholm Convention and other legislative action worldwide[J]. Environment International, 144: 106041.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106041 |
| [25] |
TAO LIN, ZHANG YING, WU JIANGPING, et al, 2019. Biomagnification of PBDEs and alternative brominated flame retardants in a predatory fish: Using fatty acid signature as a primer[J]. Environment International, 127: 226-232.
doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.03.036 |
| [26] |
WANG PU, ZHANG QINGHUA, WANG T, et al, 2012. PCBs and PBDEs in environmental samples from King George Island and Ardley Island, Antarctica[J]. RSC Advances, 2(4): 1350-1355.
doi: 10.1039/C1RA00462J |
| [27] |
XIONG PING, YAN XUETING, ZHU QINGQING, et al, 2019. A review of environmental occurrence, fate, and toxicity of novel brominated flame retardants[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(23): 13551-13569.
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.9b03159 |
| [28] |
ZHANG ZAIWANG, SUN YUXIN, SUN KAIFENG, et al, 2015. Brominated flame retardants in mangrove sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, South China: spatial distribution, temporal trend and mass inventory[J]. Chemosphere, 123: 26-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.11.042 |
| [29] |
ZHANG ZAIWANG, PEI NANCAI, SUN YUXIN, et al, 2019. Halogenated organic pollutants in sediments and organisms from mangrove wetlands of the Jiulong River Estuary, South China[J]. Environmental Research, 171: 145-152.
doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2019.01.028 |
| [30] |
ZHU HAOWEN, WANG YING, WANG XIAOWEI, et al, 2014. Distribution and accumulation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Hong Kong mangrove sediments[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 468-469: 130-139.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.021 |
| [31] |
ZUIDERVEEN E A R, SLOOTWEG J C, DE BOER J,2020. Novel brominated flame retardants - a review of their occurrence in indoor air, dust, consumer goods and food[J]. Chemosphere, 255: 126816.
doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126816 |
| [1] | 吴鸿博, 罗锋, 陈治澎, 朱飞, 曾靖伟, 张弛, 李瑞杰. 红树林生态重建效果预测研究新模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 86-97. |
| [2] | 郑法, 黄福林, 陈泽恒, 丁伟品. 基于LUCC和景观格局变化的广西山口红树林湿地动态研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 165-173. |
| [3] | 莫丹杨, 宁志铭, 杨斌, 夏荣林, 刘志金. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁区沉积物硝酸盐异化还原过程对温度变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [4] | 高洁, 余克服, 许慎栋, 黄学勇, 陈飚, 王永刚. 西沙群岛永乐环礁礁外坡沉积物中有机碳的含量与来源分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [5] | 周治刚, 岳文, 李辉权, 林阳阳. 树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥红树林碳储量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 108-120. |
| [6] | 申键, 简焯锴, 欧阳雪敏, 艾彬. 结合潮位校正的雷州半岛红树林湿地动态变迁遥感监测[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 137-153. |
| [7] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [8] | 邢楠楠, 任润馨, 唐振洲, 罗志宏, 夏辰曦, 刘永宏, 彭亮, 陈显强. 涠洲岛海洋沉积物来源真菌Aspergillus sp. GXIMD02003的代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 154-160. |
| [9] | 孙翠慈, 岳维忠, 赵文杰, 王友绍. 大亚湾表层沉积物碳水化合物活性酶基因分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [10] | 董俊德, 黄小芳, 龙爱民, 王友绍, 凌娟, 杨清松. 红树林固氮微生物及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 1-11. |
| [11] | 梁寒峭, 陈文凤, 范益铠, 朱子冬, 马国需, 陈德力, 田婧. 红树林来源曲霉属和木霉属内生真菌次生代谢产物及活性研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 12-24. |
| [12] | 张程飞, 任广波, 吴培强, 胡亚斌, 马毅, 阎宇, 张菁锐. 基于高分光学与全极化SAR的海南八门湾红树林种间分类方法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 153-168. |
| [13] | 周月月, 王友绍. 广东沿海红树林区水质变化特征与富营养状态评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 1-11. |
| [14] | 吴伟志, 赵志霞, 杨升, 梁立成, 陈秋夏, 卢翔, 刘星, 张小伟. 浙江省红树林分布和造林成效分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 67-74. |
| [15] | 郝露露, 柯明思, 朱奕秀, 许燕敏, 张颖, 郑春芳. 低温胁迫下红榄李(Lumnitzera littorea)DEAD-box RNA解旋酶基因的表达分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 44-55. |
|
||