热带海洋学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 90-104.doi: 10.11978/2022013CSTR: 32234.14.2022013
三亚湾珊瑚来源虫黄藻不同株系微环境中微生物群落结构的差异比较分析
黄思军1,2( ), 邱晨1,3, 龙超1,2, 龙丽娟1,2,4
), 邱晨1,3, 龙超1,2, 龙丽娟1,2,4
- 1.中国科学院热带海洋生物资源与生态重点实验室, 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州 510301
2.南方海洋科学与工程广东省实验室(广州), 广东 广州 511458
3.中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
4.三亚海洋生态环境工程研究院, 海南 三亚 572000
-
收稿日期:2022-01-23修回日期:2022-03-29出版日期:2022-11-10发布日期:2022-04-12 -
通讯作者:黄思军 -
作者简介:黄思军(1982—), 男, 福建省光泽县人, 项目研究员, 从事海洋微生物生态学研究。email: huangsijun@scsio.ac.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41576126);国家自然科学基金项目(42176116);广东省自然科学基金(2017A030306020);中国科学院南海海洋研究所“南海新星”项目(NHXX2019ST0101);中国科学院青年创新促进会会员(2018377)
Phycosphere microbial communities of zooxanthellae cultures isolated from corals in Sanya Bay, South China Sea
HUANG Sijun1,2( ), QIU Chen1,3, LONG Chao1,2, LONG Lijuan1,2,4
), QIU Chen1,3, LONG Chao1,2, LONG Lijuan1,2,4
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. Sanya Institute of Ocean Eco-Environmental Engineering, Yazhou Scientific Bay, Sanya 572000, China
-
Received:2022-01-23Revised:2022-03-29Online:2022-11-10Published:2022-04-12 -
Contact:HUANG Sijun -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41576126);National Natural Science Foundation of China(42176116);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2017A030306020);Rising Star Foundation of the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology(NHXX2019ST0101);Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS(2018377)
摘要:
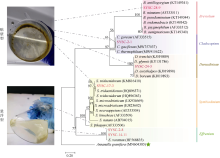
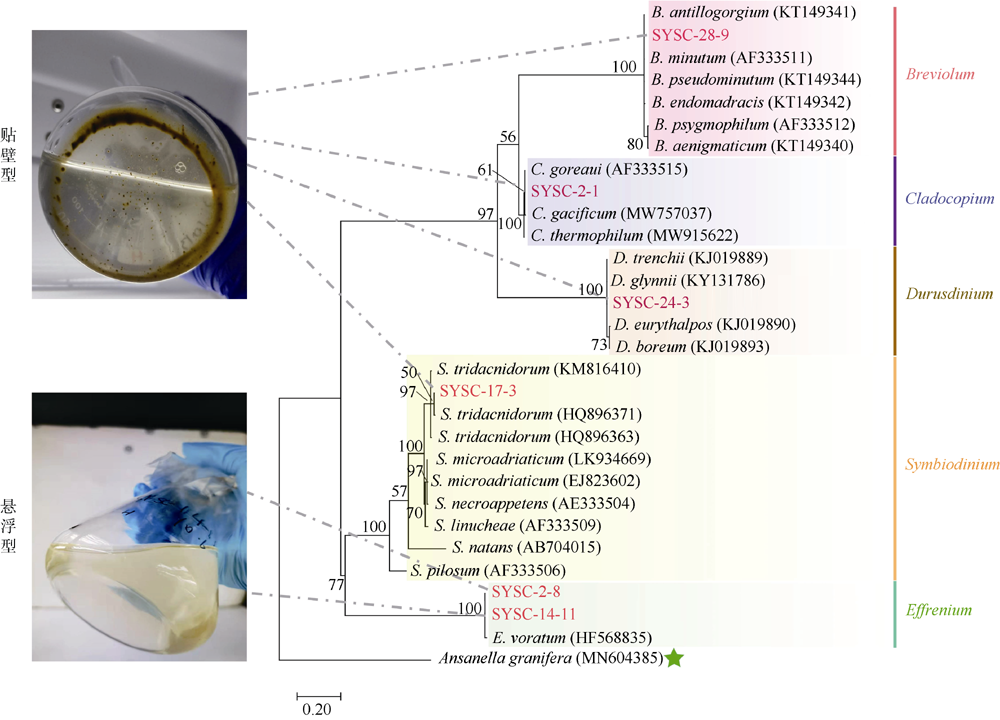
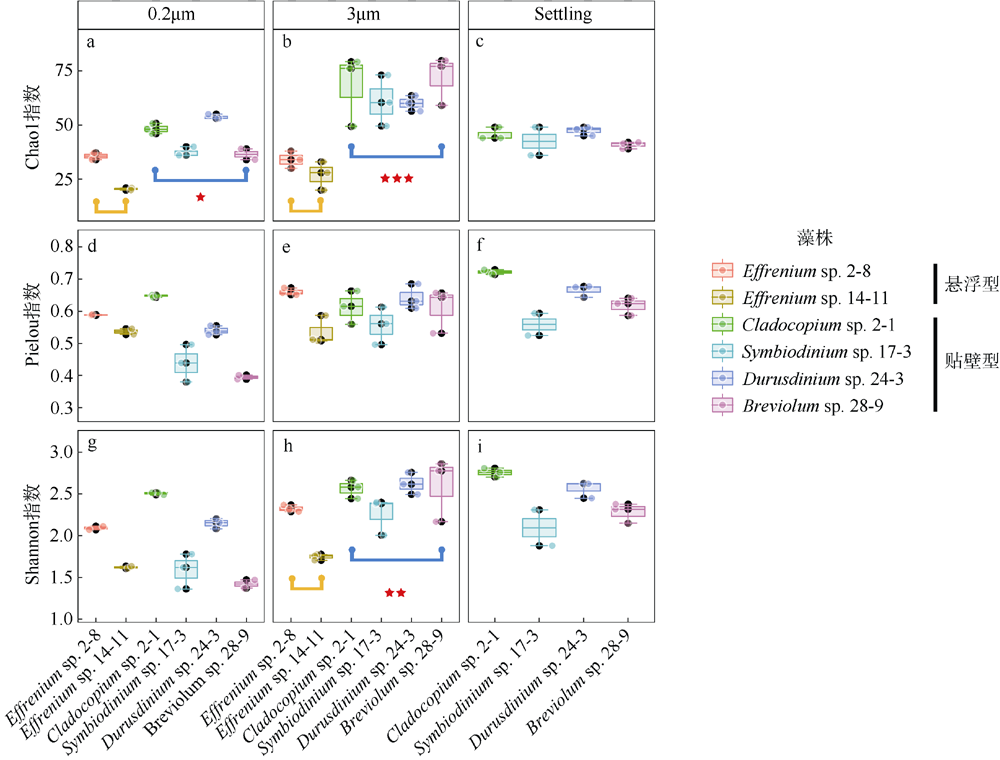
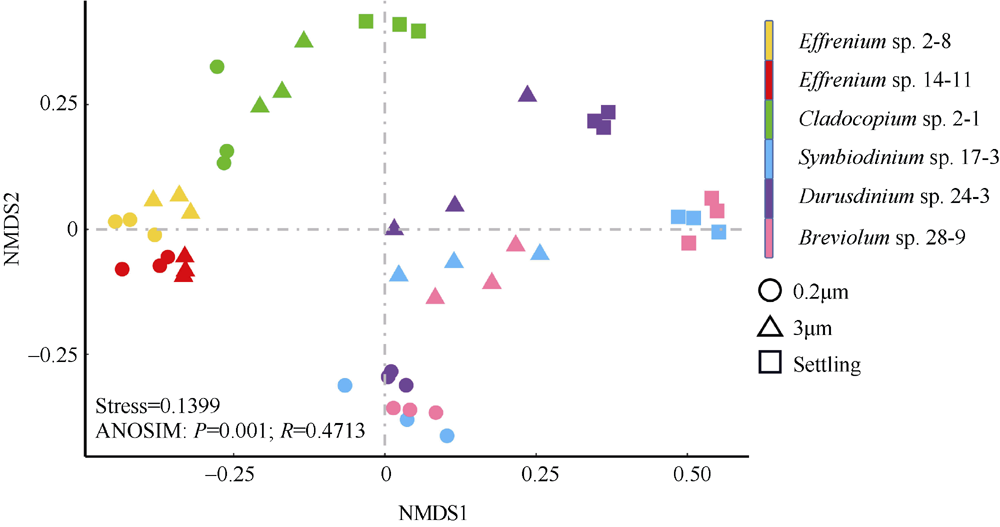
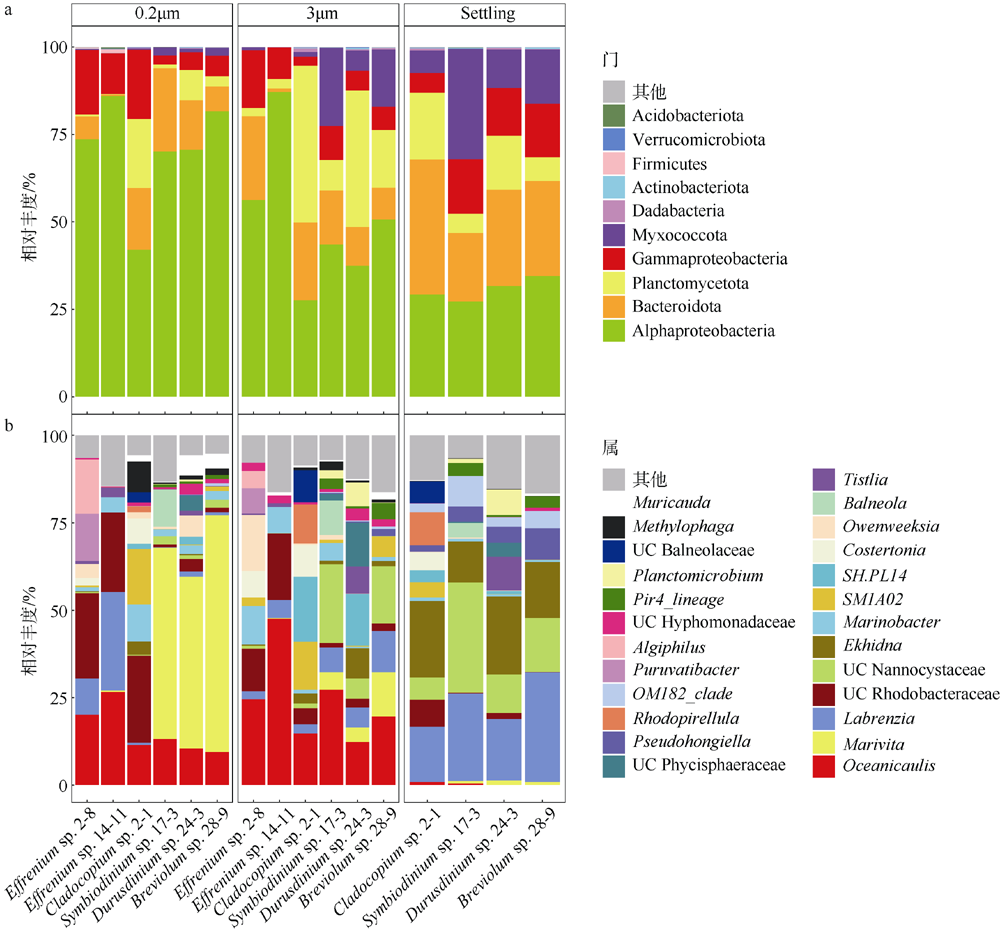
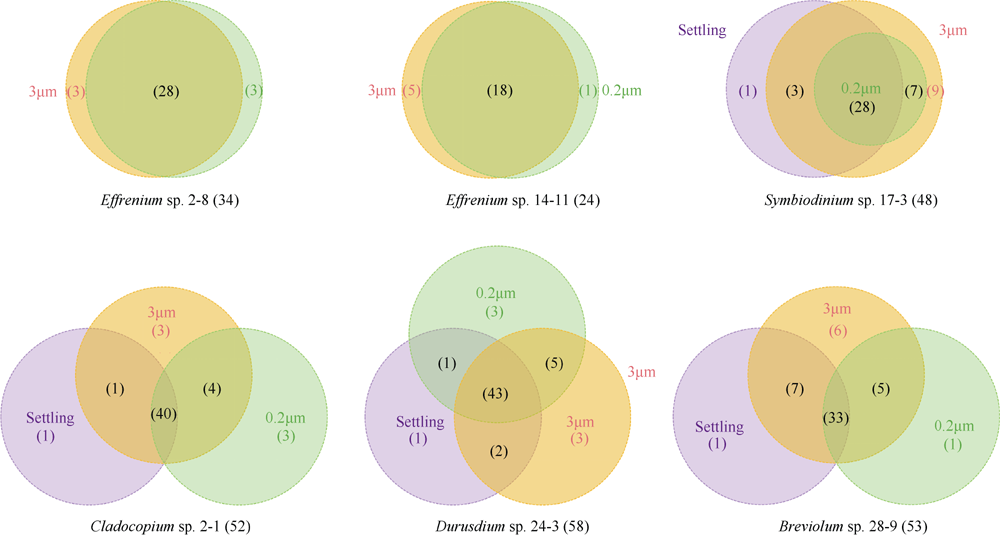
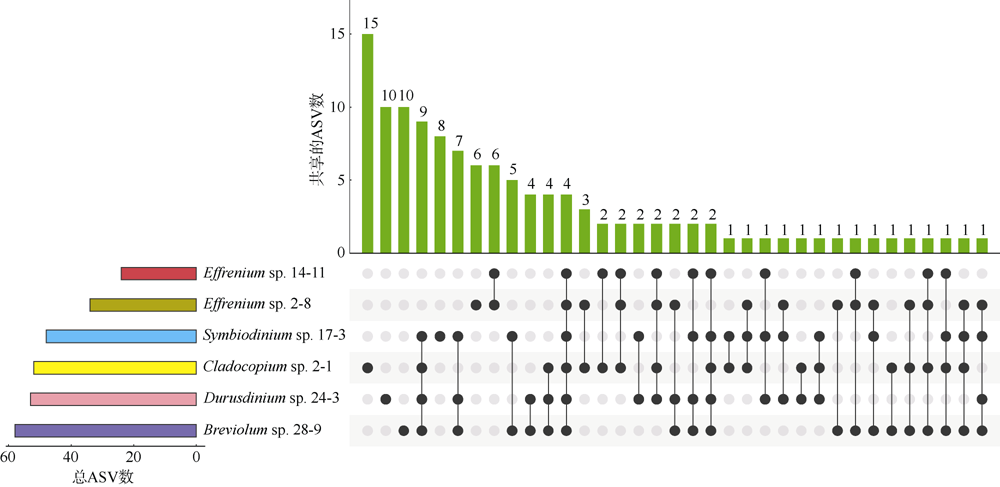
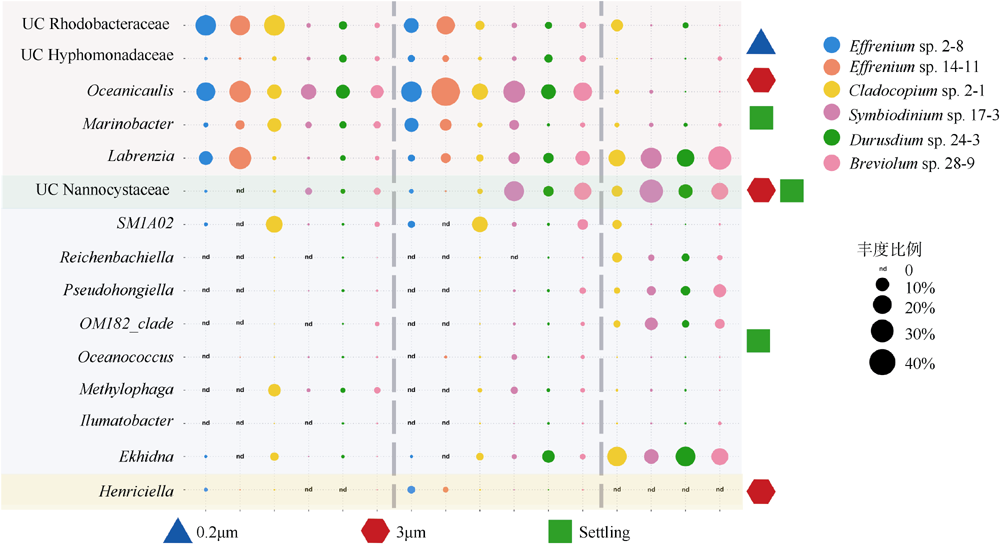
虫黄藻、细菌和造礁石珊瑚有着密切的共生关系, 但虫黄藻藻际细菌群落尚未得到广泛研究。本研究对5个属的6株虫黄藻进行了离体培养, 其中2株为悬浮型虫黄藻(E型), 4株为贴壁型虫黄藻(A—D型)。通过采集藻株培养物3种粒径的样本开展细菌群落分析, 分别为0.2~3μm(自由生活)、>3μm(附着于藻体或颗粒物)与Settling(沉底贴壁藻体上)。结果发现, 2种生活方式的藻株藻际细菌群落具有显著差别, 贴壁型藻株细菌群落的物种丰富度显著高于悬浮型藻株。发现7个属的细菌广泛存在于所有的藻株中, 它们代表了A—E型虫黄藻藻际细菌的核心类群。对3种粒径样本的核心细菌群落比较发现, 自由生和颗粒附着生的核心细菌群落十分相似, 但均与沉底贴壁样本差异明显。
中图分类号:
- Q938
引用本文
黄思军, 邱晨, 龙超, 龙丽娟. 三亚湾珊瑚来源虫黄藻不同株系微环境中微生物群落结构的差异比较分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 90-104.
HUANG Sijun, QIU Chen, LONG Chao, LONG Lijuan. Phycosphere microbial communities of zooxanthellae cultures isolated from corals in Sanya Bay, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 90-104.
表1
虫黄藻藻株来源及分类信息"
| 藻株 | 宿主拉丁文名(中文名) | ITS2基因型 | 藻株分类(属级) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SYSC-2-1 | Acropora tenuis (柔枝鹿角珊瑚) | C1 | Cladocopium (C型) |
| SYSC-2-8 | Acropora tenuis (柔枝鹿角珊瑚) | E101 | Effrenium (E型) |
| SYSC-14-11 | Galaxea fascicularis (丛生盔形珊瑚) | E101 | Effrenium (E型) |
| SYSC-17-3 | Galaxea fascicularis (丛生盔形珊瑚) | A6 | Symbiodinium (A型) |
| SYSC-24-3 | Platygyra verwyi (小叶扁脑珊瑚) | D1 | Durusdinium (D型) |
| SYSC-28-9 | Pavona decussate (十字牡丹珊瑚) | B1 | Breviolum (B型) |
表2
不同虫黄藻株两两之间共享ASVs比例"
| 藻株1 | 藻株2 | 两藻株共有ASVs数(取交集)/两藻株总ASVs数(取并集) | 所占比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24-3 | 28-9 | 35/76 | 46.05 |
| 17-3 | 24-3 | 33/73 | 45.21 |
| 17-3 | 28-9 | 30/71 | 42.25 |
| 2-8 | 14-11 | 16/42 | 38.10 |
| 2-1 | 28-9 | 23/82 | 28.05 |
| 2-1 | 24-3 | 24/86 | 27.91 |
| 17-3 | 2-1 | 20/80 | 25.00 |
| 14-11 | 2-1 | 14/62 | 22.58 |
| 2-8 | 24-3 | 15/71 | 21.13 |
| 14-11 | 28-9 | 11/66 | 16.67 |
| 2-8 | 24-3 | 13/79 | 16.46 |
| 14-11 | 17-3 | 10/62 | 16.13 |
| 14-11 | 24-3 | 11/71 | 15.49 |
| 2-8 | 28-9 | 10/77 | 12.99 |
| 2-8 | 17-3 | 9/73 | 12.33 |
| [1] | 李淑, 余克服, 陈天然, 等, 2011. 珊瑚共生虫黄藻密度的季节变化及其与珊瑚白化的关系——以大亚湾石珊瑚为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(2): 39-45. |
|
LI SHU, YU KEFU, CHEN TIANRAN, et al, 2011. Seasonal patterns of densities of symbiotic zooxanthellae in scleractinian corals from Daya Bay, northern South China Sea, and relation to coral bleaching[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30(2): 39-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.02.039 |
|
| [2] | 吴家法, 李洁, 张偲, 2015. 鹿回头岸礁区4种造礁珊瑚中可培养细菌的多样性[J]. 广东农业科学, 42(2): 146-151. |
| WU JIAFA, LI JIE, ZHANG SI, 2015. Diversity of culturable bacteria associated with four scleractinian corals located in Luhuitou fringing reef[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 42(2): 146-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 张增虎, 唐丽丽, 张永雨, 2018. 海洋中藻菌相互关系及其生态功能[J]. 微生物学通报, 45(9): 2043-2053. |
| ZHANG ZENGHU, TANG LILI, ZHANG YONGYU, 2018. Algae-bacteria interactions and their ecological functions in the ocean[J]. Microbiology China, 45(9): 2043-2053. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] |
AINSWORTH T D, KRAUSE L, BRIDGE T, et al, 2015. The coral core microbiome identifies rare bacterial taxa as ubiquitous endosymbionts[J]. The ISME Journal, 9(10): 2261-2274.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.39 |
| [5] |
ALTSCHUL S F, GISH W, MILLER W, et al, 1990. Basic local alignment search tool[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 215(3): 403-410.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2 pmid: 2231712 |
| [6] |
AMIN S A, GREEN D H, HART M C, et al, 2009. Photolysis of iron-siderophore chelates promotes bacterial-algal mutualism[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(40): 17071-17076.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905512106 pmid: 19805106 |
| [7] |
BANASZAK A T, LAJEUNESSE T C, TRENCH R K, 2000. The synthesis of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) by cultured, symbiotic dinoflagellates[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 249(2): 219-233.
pmid: 10841936 |
| [8] |
BAYER T, NEAVE M J, ALSHEIKH-HUSSAIN A, et al, 2013. The microbiome of the red sea coral Stylophora pistillata is dominated by tissue-associated Endozoicomonas bacteria[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(15): 4759-4762.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00695-13 |
| [9] |
BEHRINGER G, OCHSENKÜHN M A, FEI CONG, et al, 2018. Bacterial communities of diatoms display strong conservation across strains and time[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9: 659.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00659 pmid: 29681892 |
| [10] |
BLACKALL L L, WILSON B, VAN OPPEN M J H, 2015. Coral—the world's most diverse symbiotic ecosystem[J]. Molecular Ecology, 24(21): 5330-5347.
doi: 10.1111/mec.13400 |
| [11] |
BLANK R J, HUSS V A R, 1989. DNA divergency and speciation in Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae)[J]. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 163(3): 153-163.
doi: 10.1007/BF00936511 |
| [12] |
BLANK R J, TRENCH R K, 1985. Speciation and symbiotic dinoflagellates[J]. Science, 229(4714): 656-658.
pmid: 17739379 |
| [13] |
BOLYEN E, RIDEOUT J R, DILLON M R, et al, 2019. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 37(8): 852-857.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9 pmid: 31341288 |
| [14] |
BONGAERTS P, RIGINOS C, RIDGWAY T, et al, 2010. Genetic divergence across habitats in the widespread coral Seriatopora hystrix and its associated Symbiodinium[J]. PLoS One, 5(5): e10871.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010871 |
| [15] |
BOSCH T C G, 2013. Cnidarian-microbe interactions and the origin of innate immunity in metazoans[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 67: 499-518.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155626 pmid: 23808329 |
| [16] |
BOURNE D, IIDA Y, UTHICKE S, et al, 2008. Changes in coral-associated microbial communities during a bleaching event[J]. The ISME Journal, 2(4): 350-363.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2007.112 |
| [17] |
BOURNE D G, MORROW K M, WEBSTER N S, 2016. Insights into the coral microbiome: underpinning the health and resilience of reef ecosystems[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 70: 317-340.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095440 pmid: 27482741 |
| [18] |
CAMP E F, KAHLKE T, NITSCHKE M R, et al, 2020. Revealing changes in the microbiome of Symbiodiniaceae under thermal stress[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 22(4): 1294-1309.
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14935 pmid: 31997503 |
| [19] |
CURSON A R J, LIU JI, MARTÍNEZ A B, et al, 2017. Dimethylsulfoniopropionate biosynthesis in marine bacteria and identification of the key gene in this process[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2(5): 17009.
doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.9 pmid: 28191900 |
| [20] |
EIGEMANN F, HILT S, SALKA I, et al, 2013. Bacterial community composition associated with freshwater algae: species specificity vs. dependency on environmental conditions and source community[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 83(3): 650-663.
doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12022 pmid: 23030046 |
| [21] |
FREUDENTHAL H D, 1962. Symbiodinium gen. nov. and Symbiodinium microadriaticum sp. nov., a zooxanthella: taxonomy, life cycle, and morphology[J]. The Journal of Protozoology, 9(1): 45-52.
doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1962.tb02579.x |
| [22] | FROMMLET J C, SOUSA M L, ALVES A, et al, 2015. Coral symbiotic algae calcify ex hospite in partnership with bacteria[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(19): 6158-6163. |
| [23] |
GARDNER S G, RAINA J B, NITSCHKE M R, et al, 2017. A multi-trait systems approach reveals a response cascade to bleaching in corals[J]. BMC Biology, 15(1): 117.
doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0459-2 pmid: 29216891 |
| [24] |
GARREN M, WALSH S M, CACCONE A, et al, 2006. Patterns of association between Symbiodinium and members of the Montastraea annularis species complex on spatial scales ranging from within colonies to between geographic regions[J]. Coral Reefs, 25(4): 503-512.
doi: 10.1007/s00338-006-0146-1 |
| [25] |
GORDON B R, LEGGAT W, 2010. Symbiodinium-invertebrate symbioses and the role of metabolomics[J]. Marine Drugs, 8(10): 2546-2568.
doi: 10.3390/md8102546 pmid: 21116405 |
| [26] |
GROSSART H P, LEVOLD F, ALLGAIER M, et al, 2005. Marine diatom species harbour distinct bacterial communities[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 7(6): 860-873.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00759.x |
| [27] |
GROTTOLI A G, MARTINS P D, WILKINS M J, et al, 2018. Coral physiology and microbiome dynamics under combined warming and ocean acidification[J]. PLoS One, 13(1): e0191156.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191156 |
| [28] |
GUIDI F, PEZZOLESI L, VANUCCI S, 2018. Microbial dynamics during harmful dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata growth: bacterial succession and viral abundance pattern[J]. MicrobiologyOpen, 7(4): e00584.
doi: 10.1002/mbo3.584 |
| [29] |
HERNANDEZ-AGREDA A, GATES R D, AINSWORTH T D, 2017. Defining the core microbiome in corals' microbial soup[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 25(2): 125-140.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.11.003 |
| [30] |
HIROSE M, REIMER J D, HIDAKA M, et al, 2008. Phylogenetic analyses of potentially free-living Symbiodinium spp. isolated from coral reef sand in Okinawa, Japan[J]. Marine Biology, 155(1): 105-112.
doi: 10.1007/s00227-008-1011-2 |
| [31] |
ISHIKURA M, HAGIWARA K, TAKISHITA K, et al, 2004. Isolation of new Symbiodinium strains from tridacnid giant clam (Tridacna crocea) and sea slug (Pteraeolidia ianthina) using culture medium containing giant clam tissue homogenate[J]. Marine Biotechnology, 6(4): 378-385.
doi: 10.1007/s10126-004-1800-7 |
| [32] |
JEONG H J, YOO Y D, KANG N S, et al, 2012. Heterotrophic feeding as a newly identified survival strategy of the dinoflagellate Symbiodinium[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(31): 12604-12609.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204302109 |
| [33] |
KIMBREL J A, SAMO T J, WARD C, et al, 2019. Host selection and stochastic effects influence bacterial community assembly on the microalgal phycosphere[J]. Algal Research, 40: 101489.
doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2019.101489 |
| [34] |
KROHN-MOLT I, ALAWI M, FÖRSTNER K U, et al, 2017. Insights into microalga and bacteria interactions of selected phycosphere biofilms using metagenomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic approaches[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 1941.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01941 |
| [35] |
KUMAR S, STECHER G, LI M, et al, 2018. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35(6): 1547-1549.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096 pmid: 29722887 |
| [36] |
LAJEUNESSE T C, BHAGOOLI R, HIDAKA M, et al, 2004. Closely related Symbiodinium spp. differ in relative dominance in coral reef host communities across environmental, latitudinal and biogeographic gradients[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 284: 147-161.
doi: 10.3354/meps284147 |
| [37] |
LAJEUNESSE T C, PARKINSON J E, GABRIELSON P W, et al, 2018. Systematic revision of Symbiodiniaceae highlights the antiquity and diversity of coral endosymbionts[J]. Current Biology, 28(16): 2570-2580.e6.
doi: S0960-9822(18)30907-2 pmid: 30100341 |
| [38] |
LAWSON C A, RAINA J B, KAHLKE T, et al, 2018. Defining the core microbiome of the symbiotic dinoflagellate, Symbiodinium[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 10(1): 7-11.
doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12599 |
| [39] |
LI JIE, CHEN QI, LONG LIJUAN, et al, 2014. Bacterial dynamics within the mucus, tissue and skeleton of the coral Porites lutea during different seasons[J]. Scientific Reports, 4: 7320.
doi: 10.1038/srep07320 |
| [40] |
LIU MIN, LIU LEMIAN, CHEN HUIHUANG, et al, 2019. Community dynamics of free-living and particle-attached bacteria following a reservoir Microcystis bloom[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 660: 501-511.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.414 |
| [41] |
MAIRE J, GIRVAN S K, BARKLA S E, et al, 2021. Intracellular bacteria are common and taxonomically diverse in cultured and in hospite algal endosymbionts of coral reefs[J]. The ISME Journal, 15(7): 2028-2042.
doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-00902-4 |
| [42] |
MATTHEWS J L, RAINA J B, KAHLKE T, et al, 2020. Symbiodiniaceae-bacteria interactions: rethinking metabolite exchange in reef-building corals as multi-partner metabolic networks[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 22(5): 1675-1687.
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14918 pmid: 31943674 |
| [43] |
MIZUYAMA M, IGUCHI A, IIJIMA M, et al, 2020. Comparison of Symbiodiniaceae diversities in different members of a Palythoa species complex (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Zoantharia)—implications for ecological adaptations to different microhabitats[J]. PeerJ, 8: e8449.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.8449 |
| [44] |
MÖNNICH J, TEBBEN J, BERGEMANN J, et al, 2020. Niche-based assembly of bacterial consortia on the diatom Thalassiosira rotula is stable and reproducible[J]. The ISME Journal, 14(6): 1614-1625.
doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-0631-5 |
| [45] |
MOORE R B, FERGUSON K M, LOH W K W, et al, 2003. Highly organized structure in the non-coding region of the psbA minicircle from clade C Symbiodinium[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53(Pt 6): 1725-1734.
doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02594-0 |
| [46] |
MORROW K M, MOSS A G, CHADWICK N E, et al, 2012. Bacterial associates of two Caribbean coral species reveal species-specific distribution and geographic variability[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(18): 6438-6449.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.01162-12 pmid: 22773636 |
| [47] | MOTONE K, TAKAGI T, ABURAYA S, et al, 2020. A zeaxanthin-producing bacterium isolated from the algal phycosphere protects coral endosymbionts from environmental stress[J]. mBio, 11(1): e01019-19. |
| [48] |
MUSCATINE L, PORTER J W, 1977. Reef corals: mutualistic symbioses adapted to nutrient-poor environments[J]. BioScience, 27(7): 454-460.
doi: 10.2307/1297526 |
| [49] | MUSCATINE L, 1990. The role of symbiotic algae in carbon and energy flux in reef corals[J]. Ecosystems of the World, 25: 75-87. |
| [50] |
NEAVE M J, RACHMAWATI R, XUN LIPING, et al, 2017. Differential specificity between closely related corals and abundant Endozoicomonas endosymbionts across global scales[J]. The ISME Journal, 11(1): 186-200.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.95 |
| [51] |
NG T Y, ANG P, 2016. Low symbiont diversity as a potential adaptive strategy in a marginal non-reefal environment: a case study of corals in Hong Kong[J]. Coral Reefs, 35(3): 941-957.
doi: 10.1007/s00338-016-1458-4 |
| [52] |
NISSIMOV J, ROSENBERG E, MUNN C B, 2009. Antimicrobial properties of resident coral mucus bacteria of Oculina patagonica[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 292(2): 210-215.
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01490.x |
| [53] |
POCHON X, PAWLOWSKI J, ZANINETTI L, et al, 2001. High genetic diversity and relative specificity among Symbiodinium-like endosymbiotic dinoflagellates in soritid foraminiferans[J]. Marine Biology, 139(6): 1069-1078.
doi: 10.1007/s002270100674 |
| [54] |
POCHON X, GATES R D, 2010. A new Symbiodinium clade (Dinophyceae) from soritid foraminifera in Hawai’i[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56(1): 492-497.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.03.040 |
| [55] |
POOTAKHAM W, MHUANTONG W, YOOCHA T, et al, 2021. Taxonomic profiling of Symbiodiniaceae and bacterial communities associated with Indo-Pacific corals in the Gulf of Thailand using PacBio sequencing of full-length ITS and 16S rRNA genes[J]. Genomics, 113(4): 2717-2729.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.06.001 pmid: 34089786 |
| [56] |
QIN ZHENJUN, YU KEFU, CHEN BIAO, et al, 2019. Diversity of Symbiodiniaceae in 15 coral species from the southern South China sea: potential relationship with coral thermal adaptability[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10: 2343.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02343 pmid: 31681208 |
| [57] |
QUAST C, PRUESSE E, YILMAZ P, et al, 2013. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1): D590-D596.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1219 |
| [58] |
RÄDECKER N, POGOREUTZ C, VOOLSTRA C R, et al, 2015. Nitrogen cycling in corals: the key to understanding holobiont functioning?[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 23(8): 490-497.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.03.008 pmid: 25868684 |
| [59] |
RAINA J B, DINSDALE E A, WILLIS B L, et al, 2010. Do the organic sulfur compounds DMSP and DMS drive coral microbial associations?[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 18(3): 101-108.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.12.002 |
| [60] |
REICHMAN J R, VIZE P D, 2014. Separate introns gained within short and long soluble peridinin-chlorophyll a-protein genes during radiation of Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae) clade A and B lineages[J]. PLoS One, 9(10): e110608.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110608 |
| [61] |
RODRIGUEZ-LANETTY M, KRUPP D A, WEIS V M, 2004. Distinct ITS types of Symbiodinium in Clade C correlate with cnidarian/dinoflagellate specificity during onset of symbiosis[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 275: 97-102.
doi: 10.3354/meps275097 |
| [62] |
ROHWER F, BREITBART M, JARA J, et al, 2001. Diversity of bacteria associated with the Caribbean coral Montastraea franksi[J]. Coral Reefs, 20(1): 85-91.
doi: 10.1007/s003380100138 |
| [63] |
ROHWER F, SEGURITAN V, AZAM F, et al, 2002. Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 243: 1-10.
doi: 10.3354/meps243001 |
| [64] |
ROWAN R, POWERS D A, 1991. Molecular genetic identification of symbiotic dinoflagellates (zooxanthellae)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress, 71(1): 65-73.
doi: 10.3354/meps071065 |
| [65] |
SAKAMOTO T, BRYANT D A, 1997. Growth at low temperature causes nitrogen limitation in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 169(1): 10-19.
doi: 10.1007/s002030050535 |
| [66] | SCHOENBERG D A, TRENCH R K, 1980. Genetic variation in Symbiodinium (= Gymnodinium) microadriaticum Freudenthal, and specificity in its symbiosis with marine invertebrates. Ⅲ. Specificity and inlfectivity of Symbiodinium microadriaticum[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 207(1169): 445-460. |
| [67] |
SEYMOUR J R, AMIN S A, RAINA J B, et al, 2017. Zooming in on the phycosphere: the ecological interface for phytoplankton-bacteria relationships[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2(7): 17065.
doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.65 pmid: 28555622 |
| [68] |
SHADE A, HANDELSMAN J, 2012. Beyond the Venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 14(1): 4-12.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02585.x pmid: 22004523 |
| [69] |
SHARP K H, DISTEL D, PAUL V J, 2012. Diversity and dynamics of bacterial communities in early life stages of the Caribbean coral Porites astreoides[J]. The ISME Journal, 6(4): 790-801.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.144 |
| [70] | SHARPE G C, GIFFORD S M, SEPTER A N, 2020. A model Roseobacter, Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3, employs a diffusible killing mechanism to eliminate competitors[J]. mSystems, 5(4): e00443-20. |
| [71] |
SHI TUO, NIU GAOFENG, KVITT H, et al, 2021. Untangling ITS2 genotypes of algal symbionts in zooxanthellate corals[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21(1): 137-152.
doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13250 |
| [72] | SPALDING M D, RAVILIOUS C, GREEN E P, 2001. World atlas of coral reefs[M]. Berkeley: University of California Press. |
| [73] |
SUBRAMANIAN B, GAO SHENGHAN, LERCHER M J, et al, 2019. Evolview v3: a webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 47(W1): W270-W275.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz357 |
| [74] |
SUNDA W, KIEBER D J, KIENE R P, et al, 2002. An antioxidant function for DMSP and DMS in marine algae[J]. Nature, 418(6895): 317-320.
doi: 10.1038/nature00851 |
| [75] |
TAKABAYASHI M, SANTOS S R, COOK C B, 2004. Mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of the symbiotic dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium, Dinophyta)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 40(1): 160-164.
doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3646.2003.03-097.x |
| [76] |
TRENCH R K, THINH L V, 1995. Gymnodinium linucheae sp. nov.: the dinoflagellate symbiont of the jellyfish Linuche unguiculata[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 30(2): 149-154.
doi: 10.1080/09670269500650911 |
| [77] |
TURNBAUGH P J, LEY R E, HAMADY M, et al, 2007. The human microbiome project[J]. Nature, 449(7164): 804-810.
doi: 10.1038/nature06244 |
| [78] |
VAN OPPEN M J H, PALSTRA F P, PIQUET A M T, et al, 2001. Patterns of coral-dinoflagellate associations in Acropora: significance of local availability and physiology of Symbiodinium strains and host-symbiont selectivity[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 268(1478): 1759-1767.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2001.1733 |
| [79] |
WAGNER-DÖBLER I, BIEBL H, 2006. Environmental biology of the marine Roseobacter lineage[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 60: 255-280.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.60.080805.142115 |
| [80] | WALTERS W, HYDE E R, BERG-LYONS D, et al, 2015. Improved bacterial 16S rRNA gene (V4 and V4-5) and fungal internal transcribed spacer marker gene primers for microbial community surveys[J]. mSystems, 1(1): e00009-15. |
| [81] |
WEGLEY L, EDWARDS R, RODRIGUEZ-BRITO B, et al, 2007. Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community associated with the coral Porites astreoides[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 9(11): 2707-2719.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01383.x |
| [82] |
XIANG TINGTING, HAMBLETON E A, DENOFRIO J C, et al, 2013. Isolation of clonal axenic strains of the symbiotic dinoflagellate Symbiodinium and their growth and host specificity[J]. Journal of Phycology, 49(3): 447-458.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.12055 |
| [83] |
YANG FANGFANG, LONG CHAO, WEI ZHANGLIANG, et al, 2020. Optimization of medium using response surface methodology to enhance the growth of Effrenium voratum (Symbiodiniaceae, Dinophyceae)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 56(5): 1208-1215.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.13007 |
| [84] |
YANG QINGSONG, ZHANG YING, AHMAD M, et al, 2021. Microbial community structure shifts and potential Symbiodinium partner bacterial groups of bleaching coral Pocillopora verrucosa in South China Sea[J]. Ecotoxicology, 30(5): 966-974.
doi: 10.1007/s10646-021-02380-y |
| [85] |
ZHAO MEIXIA, YU KEFU, ZHANG QIAOMIN, et al, 2012. Long-term decline of a fringing coral reef in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 28(5): 1088-1099.
doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-10-00172.1 |
| [86] |
ZHOU GUOWEI, HUANG HUI, 2011. Low genetic diversity of symbiotic dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium) in scleractinian corals from tropical reefs in southern Hainan Island, China[J]. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 49(6): 598-605.
doi: 10.1111/j.1759-6831.2011.00161.x |
| [87] |
ZHOU GUOWEI, HUANG HUI, LIAN JIANSHENG, et al, 2012. Habitat correlation of Symbiodinium diversity in two reef-building coral species in an upwelling region, eastern Hainan Island, China[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 92(6): 1309-1316.
doi: 10.1017/S0025315411001548 |
| [88] |
ZHOU GUOWEI, CAI LIN, LI YUANCHAO, et al, 2017. Temperature-driven local acclimatization of Symbiodnium hosted by the coral Galaxea fascicularis at Hainan Island, China[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 2487.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02487 |
| [1] | 王佳熹, 卢护木, 齐鑫, 高程海, 刘永宏, 罗小卫. 涠洲岛鹿角珊瑚共附生真菌Arachniotus ruber GXIMD 02510的次级代谢产物及抑菌活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 174-180. |
| [2] | 孙曼曼, 曾艳波, 许含, 姚励功, 郭跃伟, 苏明智. 中国南海豆荚软珊瑚Lobophytum sp. 的化学成分及其抗菌活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 189-197. |
| [3] | 莫丹杨, 宁志铭, 杨斌, 夏荣林, 刘志金. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁区沉积物硝酸盐异化还原过程对温度变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [4] | 李子若, 罗晏杰, 曹政, CHIN Yaoxian, 王沛政. 短指软珊瑚(Sinularia acuta)热休克蛋白HSP70家族特征及进化分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 123-136. |
| [5] | 周伟华, 李颖心, 郭亚娟, 霍嘉欣, 宋严, 朱晴, 袁翔城, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海水酸化和升温对两种造礁石珊瑚生长和钙化的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 49-57. |
| [6] | 袁翔城, 梁宇娴, 宋严, 俞晓磊, 黄晖, 周伟华. CO2升高对风信子鹿角珊瑚(Acropora hyacinthus)钙化速率和基因表达的影响*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 40-48. |
| [7] | 霍嘉欣, 李颖心, 宋严, 朱晴, 周伟华, 袁翔城, 黄晖, 刘胜. 木珊瑚科Cladopsammia gracilis和Rhizopsammia wettsteini 线粒体全基因组比较与系统进化分析*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 22-30. |
| [8] | 江绿苗, 陈天然, 赵宽, 张婷, 许莉佳. 南海北部涠洲岛边缘珊瑚礁的生物侵蚀实验研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [9] | 贾男, 周天成, 胡思敏, 张琛, 黄晖, 刘胜. 南沙群岛海域珊瑚礁区三种寄居蟹的摄食差异比较[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 109-121. |
| [10] | 彭尔曼, 姚宇, 李壮志, 许从昊. 波流共同作用下珊瑚礁海岸水动力特性数值模拟研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 187-194. |
| [11] | 赵贺, 张峻菱, 王浩, 柯景召, 朱铭, 王爱民, 李秀保. 两种造礁石珊瑚固碳能力初步研究*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 146-154. |
| [12] | 罗勇, 黄林韬, 杨剑辉, 练健生, 刘骋跃, 江雷, 梁宇娴, 陈伦举, 雷新明, 刘胜, 黄晖. 海南临高红牌—马袅沿岸海域造礁石珊瑚群落结构及其环境影响因子[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [13] | 黄晖, 袁翔城, 宋严, 李颖心, 周伟华, 龙爱民. 珊瑚礁生态系统固碳过程及储碳机制研究进展*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 13-21. |
| [14] | 王永智, 许莉佳, 黄柏强, 杨天件, 綦世斌, 陈辉, 杨静. 西沙永乐环礁造礁石珊瑚共生体对低光环境的生理响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 31-39. |
| [15] | 黄晖, 俞晓磊, 黄林韬, 江雷. 珊瑚礁生态学研究现状和展望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 3-12. |
|
||