Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 1-12.doi: 10.11978/2018067CSTR: 32234.14.2018067
• Marine Hydrography • Next Articles
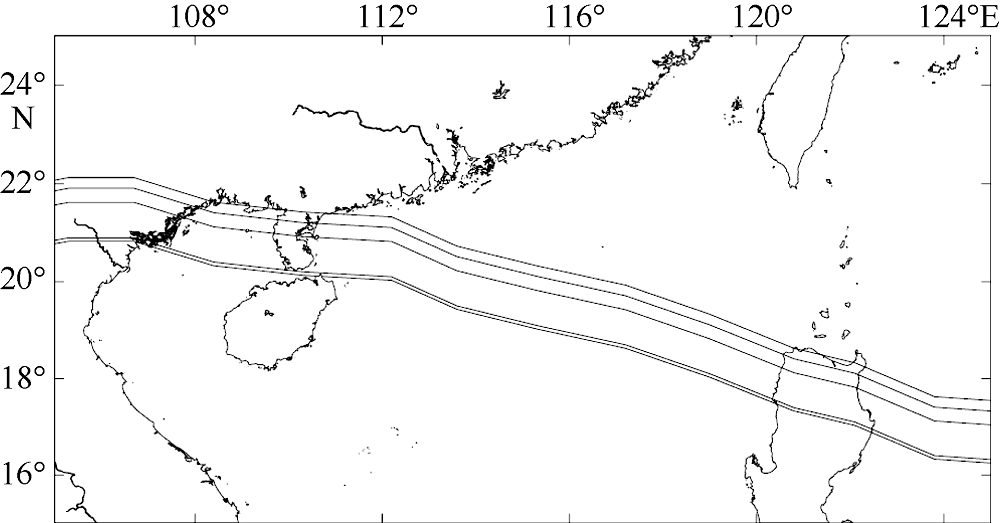
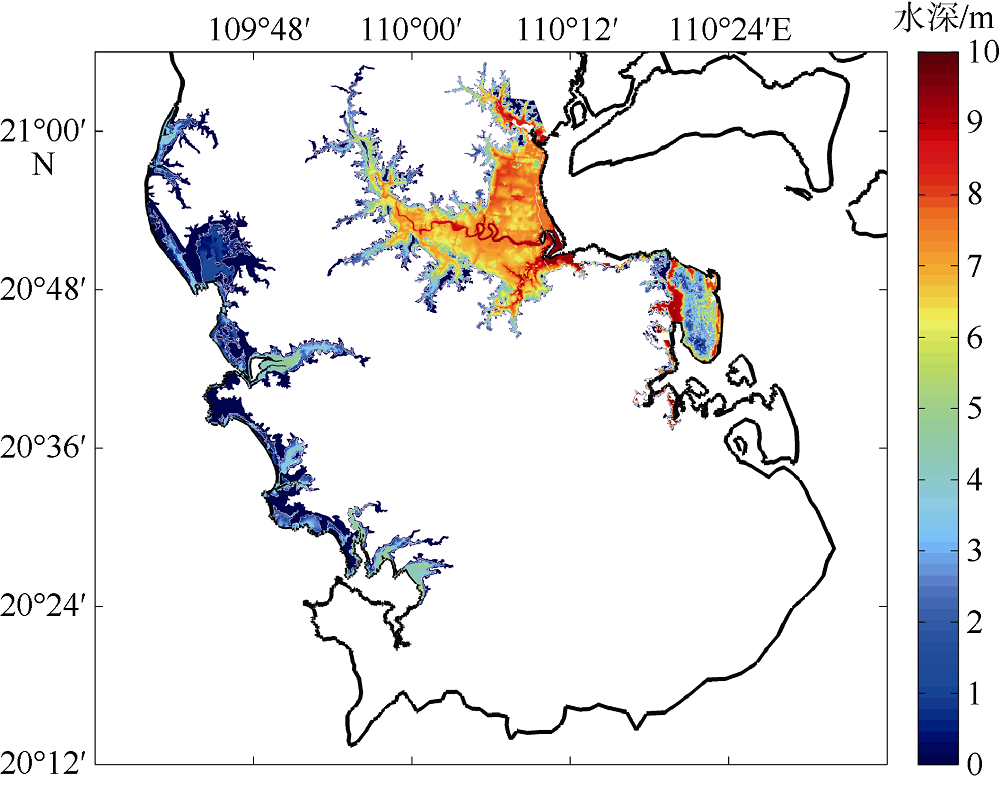
Inundation risk assessment of storm surge along Lei Zhou coastal areas*
Min ZHANG( ), Jun LUO, Jinlei HU, Xuezhi ZENG
), Jun LUO, Jinlei HU, Xuezhi ZENG
- South China Sea Prediction Center, State Oceanic Administration, Guangzhou 510310, China
-
Received:2018-06-25Revised:2018-10-30Online:2019-03-20Published:2019-04-15 -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC1401503);Water Resource Science and Technology Innovation Program of Guangdong Province (2016-02)
CLC Number:
- P732.25
Cite this article
Min ZHANG, Jun LUO, Jinlei HU, Xuezhi ZENG. Inundation risk assessment of storm surge along Lei Zhou coastal areas*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 1-12.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
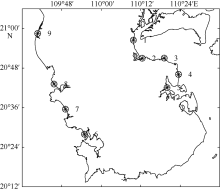
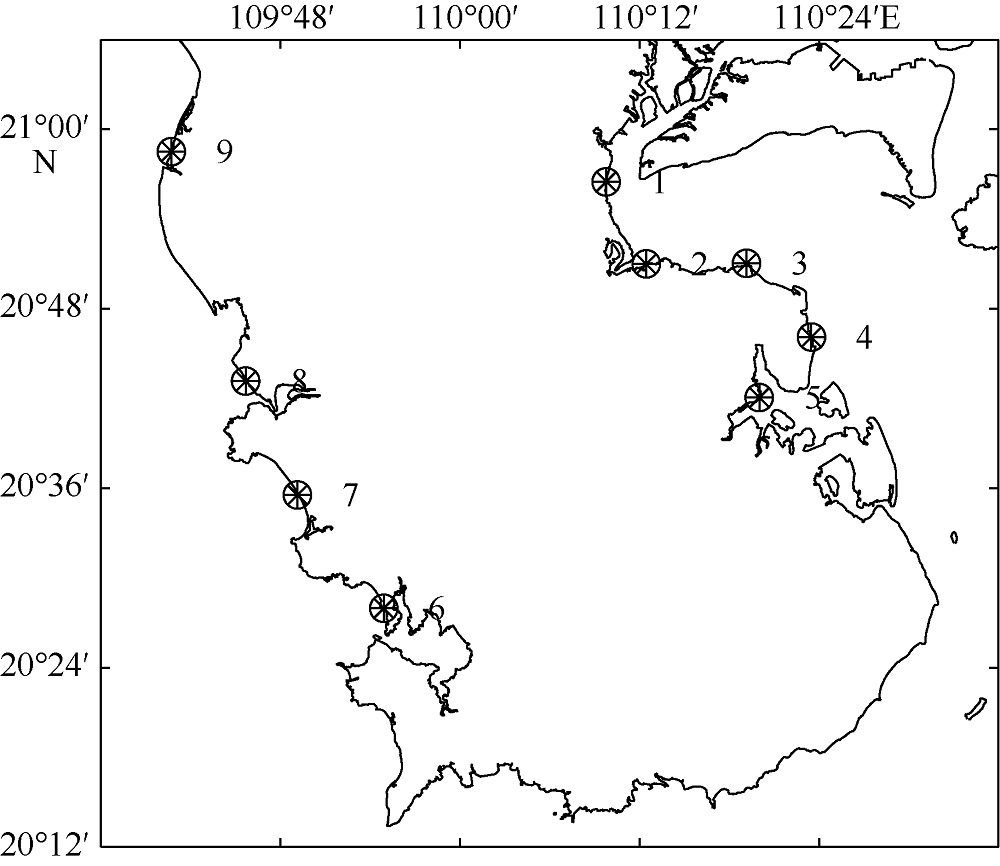
The maximal storm surge (units: m) of every representative point during No. 8007 typhoon cases"
| 路径 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t0 | 4.291 | 4.142 | 3.648 | 3.413 | 3.707 | 0.453 | 0.465 | 0.445 | 0.407 |
| t1 | 4.383 | 4.219 | 3.718 | 3.469 | 3.785 | 0.447 | 0.462 | 0.454 | 0.397 |
| t2 | 4.469 | 4.300 | 3.790 | 3.541 | 3.853 | 0.450 | 0.464 | 0.451 | 0.399 |
| t3 | 4.557 | 4.391 | 3.872 | 3.604 | 3.933 | 0.451 | 0.460 | 0.447 | 0.393 |
| t4 | 4.654 | 4.472 | 3.945 | 3.677 | 4.010 | 0.445 | 0.458 | 0.440 | 0.390 |
| t5 | 4.745 | 4.567 | 4.020 | 3.745 | 4.114 | 0.439 | 0.452 | 0.442 | 0.378 |
| t6 | 4.852 | 4.657 | 4.111 | 3.835 | 4.218 | 0.442 | 0.445 | 0.435 | 0.374 |
| t7 | 4.967 | 4.777 | 4.206 | 3.937 | 4.361 | 0.435 | 0.442 | 0.434 | 0.394 |
| t8 | 5.103 | 4.896 | 4.318 | 4.056 | 4.508 | 0.436 | 0.441 | 0.423 | 0.442 |
| t9 | 5.251 | 5.044 | 4.434 | 4.189 | 4.675 | 0.439 | 0.448 | 0.432 | 0.452 |
| t10 | 5.424 | 5.192 | 4.563 | 4.325 | 4.849 | 0.442 | 0.450 | 0.431 | 0.451 |
| t11 | 5.593 | 5.352 | 4.682 | 4.456 | 5.028 | 0.456 | 0.453 | 0.449 | 0.492 |
| t12 | 5.768 | 5.504 | 4.806 | 4.577 | 5.180 | 0.465 | 0.475 | 0.440 | 0.465 |
| t13 | 5.922 | 5.632 | 4.911 | 4.663 | 5.294 | 0.495 | 0.480 | 0.467 | 0.499 |
| t14 | 6.033 | 5.723 | 4.980 | 4.697 | 5.324 | 0.509 | 0.487 | 0.485 | 0.507 |
| t15 | 6.064 | 5.706 | 4.953 | 4.587 | 5.028 | 0.699 | 0.512 | 0.473 | 0.493 |
| t16 | 5.966 | 5.565 | 4.832 | 4.346 | 4.649 | 0.829 | 0.505 | 0.489 | 0.501 |
| t17 | 5.718 | 5.266 | 4.567 | 4.075 | 4.436 | 0.892 | 0.623 | 0.489 | 0.519 |
| t18 | 5.433 | 4.942 | 4.240 | 3.818 | 4.117 | 0.916 | 0.727 | 0.480 | 0.484 |
| t19 | 5.151 | 4.649 | 3.979 | 3.560 | 3.750 | 0.929 | 0.791 | 0.481 | 0.527 |
| t20 | 4.763 | 4.265 | 3.681 | 3.297 | 3.400 | 1.018 | 0.866 | 0.477 | 0.503 |
| t21 | 4.346 | 3.850 | 3.377 | 3.038 | 3.065 | 1.099 | 0.948 | 0.478 | 0.545 |
| t22 | 3.918 | 3.436 | 3.078 | 2.773 | 2.736 | 1.174 | 1.049 | 0.516 | 0.571 |
| t23 | 3.587 | 3.121 | 2.809 | 2.508 | 2.399 | 1.205 | 1.184 | 0.631 | 0.534 |
| t24 | 3.332 | 2.867 | 2.550 | 2.233 | 2.045 | 1.221 | 1.225 | 0.731 | 0.538 |
| t25 | 3.062 | 2.607 | 2.294 | 1.944 | 1.742 | 1.233 | 1.230 | 0.821 | 0.554 |
| t26 | 2.777 | 2.342 | 2.083 | 1.743 | 1.643 | 1.169 | 1.186 | 0.931 | 0.575 |
| t27 | 2.469 | 2.062 | 1.859 | 1.570 | 1.507 | 1.088 | 1.107 | 0.983 | 0.572 |
| t28 | 2.167 | 1.778 | 1.642 | 1.408 | 1.347 | 1.027 | 1.012 | 0.955 | 0.601 |
| t29 | 1.958 | 1.584 | 1.415 | 1.221 | 1.161 | 0.957 | 0.932 | 1.015 | 0.663 |
| t30 | 1.694 | 1.341 | 1.186 | 1.040 | 0.908 | 0.886 | 0.864 | 0.982 | 0.717 |
| t31 | 1.387 | 1.060 | 0.981 | 0.900 | 0.722 | 0.826 | 0.803 | 0.900 | 0.747 |
| t32 | 1.227 | 0.899 | 0.814 | 0.793 | 0.627 | 0.751 | 0.725 | 0.811 | 0.863 |
| t33 | 1.107 | 0.791 | 0.709 | 0.696 | 0.569 | 0.690 | 0.651 | 0.727 | 0.819 |
| t34 | 1.017 | 0.713 | 0.652 | 0.628 | 0.507 | 0.622 | 0.580 | 0.642 | 0.746 |
| t35 | 0.950 | 0.659 | 0.609 | 0.568 | 0.476 | 0.572 | 0.530 | 0.554 | 0.758 |
Tab. 3
The maximum storm surge and water level of Zhanjiang, Naozhou, and Nandu stations during the typoon of each strength grade (under 85 elevation datum)"
| 级别 | 最低气压/hPa | 湛江站 | 南渡站 | 硇洲站 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最大增水/m | 最高潮位/m | 最大增水/m | 最高潮位/m | 最大增水/m | 最高潮位/m | ||
| Ⅰ | 900 | 5.993 | 7.694 | 6.898 | 9.691 | 4.892 | 5.222 |
| Ⅱ | 910 | 5.586 | 7.335 | 6.455 | 9.333 | 4.522 | 4.852 |
| Ⅲ | 920 | 5.202 | 7.053 | 6.093 | 8.949 | 4.261 | 4.591 |
| Ⅳ | 930 | 4.759 | 6.737 | 5.637 | 8.348 | 3.969 | 4.299 |
| Ⅴ | 940 | 4.373 | 6.443 | 5.162 | 7.721 | 3.674 | 4.004 |
| Ⅵ | 950 | 3.532 | 5.772 | 4.369 | 6.728 | 3.108 | 3.438 |
| Ⅶ | 960 | 3.066 | 5.368 | 3.798 | 6.049 | 2.653 | 2.983 |
Tab. 4
Area statistics of submerge depth in eastern and western coastal areas of Leizhou during the typoon of each strength grade"
| 东岸淹没面积/km2 | 西岸淹没面积/km2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 危险性等级 | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | 合计 | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | 合计 |
| 淹没水深/m | [3,+∞) | [1.2~3.0) | [0.5~1.2) | [0.15~0.5) | [3,+∞) | [1.2~3.0) | [0.5~1.2) | [0.15~0.5) | ||
| 一级, 900hPa | 176.5 | 162.4 | 23.5 | 5.4 | 367.8 | 0.3 | 59.6 | 23.9 | 11.6 | 95.4 |
| 二级, 910 hPa | 131.9 | 161.7 | 38.1 | 6.1 | 337.8 | 0 | 45.8 | 27.2 | 11.1 | 84.1 |
| 三级, 920 hPa | 67.4 | 96.3 | 79.8 | 27.9 | 271.4 | 0 | 44.3 | 22.9 | 10.1 | 77.3 |
| 四级, 930 hPa | 57.3 | 23.7 | 36.0 | 15.1 | 132.1 | 0 | 42.3 | 23.5 | 9.4 | 75.2 |
| 五级, 940 hPa | 50.7 | 17.9 | 32.6 | 12.3 | 113.5 | 0 | 35.4 | 23.2 | 9.7 | 68.3 |
| 六级, 950 hPa | 32.3 | 19.4 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 55.9 | 0 | 14.2 | 32.6 | 11.5 | 58.3 |
| 七级, 960 hPa | 27.7 | 17.7 | 4.0 | 0.2 | 49.6 | 0 | 9.3 | 35.0 | 11.9 | 56.2 |
Tab. 5
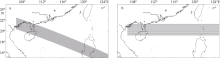
The maximal storm surge (units: m) of every representative point during the typhoon in four directions"
| 角度 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 67°30′ | 8.410 | 7.989 | 6.998 | 6.968 | 8.146 | 3.075 | 2.734 | 1.776 | 0.488 |
| 75°00′ | 9.057 | 8.442 | 7.651 | 6.843 | 7.603 | 2.788 | 2.341 | 1.541 | 0.330 |
| 82°30′ | 9.321 | 8.641 | 7.536 | 6.696 | 6.743 | 2.631 | 2.164 | 1.254 | 0.476 |
| 90°00′ | 9.347 | 9.007 | 7.733 | 6.950 | 6.910 | 2.450 | 1.893 | 0.608 | 0.468 |
Tab. 7
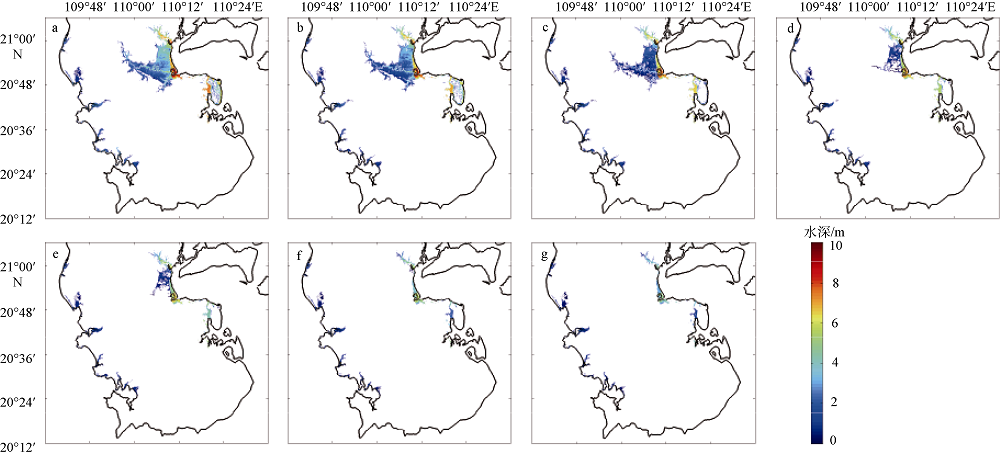
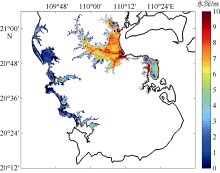
Area statistics of submerge depth in eastern and western coastal areas of Leizhou during possible maximum typoon"
| 东岸 | 西岸 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 危险性等级 | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | 合计 | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | 合计 |
| 淹没水深/m | [3,+∞) | [1.2~3.0) | [0.5~1.2) | [0.15~0.5) | [3,+∞) | [1.2~3.0) | [0.5~1.2) | [0.15~0.5) | ||
| 面积/km2 | 408.9 | 41.1 | 6.2 | 0.8 | 457.0 | 56.9 | 44.5 | 31.2 | 12.4 | 145.0 |
| [1] | 曹丛华, 白涛, 高松, 等, 2013. 胶州湾高分辨率三维风暴潮漫滩数值模拟[J]. 海洋科学, 37(2): 118-125. |
| CAO CONGHUA, BAI TAO, GAO SONG, et al, 2013. High resolution 3D storm surge and inundation numerical model used in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, 37(2): 118-125 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] |
陈华伟, 葛建忠, 丁平兴, 2010. 波浪对台风风暴潮过程的影响分析[J]. 华东师范大学学报(自然科学版), (4): 16-25.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5641.2010.04.003 |
|
CHEN HUAWEI, GE JIANZHONG, DING PINGXING, 2010. Analysis of storm surge’s process under the influence of waves[J]. Journal of East China Normal University (Natural Science), (4): 16-25 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5641.2010.04.003 |
|
| [3] | 国家能源局, 2011. NB/T25002-2011 核电厂海工构筑物设计规范[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社: 1-197 (in Chinese). |
| [4] | 国家核安全局政策法规处, 1991. HAF0113 核电厂安全导则汇编—核电厂设计基准热带气旋[G]. 北京: 中国法制出版社: 277-295 (in Chinese). |
| [5] | 何佩东, 左军成, 顾云碧, 等, 2015. 普陀沿海风暴潮淹没危险性评估[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, (1): 1-8. |
| HE PEIDONG, ZUO JUNCHENG, GU YUNBI, et al, 2015. Inundation risk assessment of storm surge along Putuo coastal areas[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, (1): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] |
李颖, 方伟华, 林伟, 等, 2014. 可能最大风暴潮风险评估中各等级热带气旋设定方法[J]. 海洋科学, 38(4): 71-80.
doi: 10.11759/hykx20120829002 |
|
LI YING, FANG WEIHUA, LIN WEI, et al, 2014. Parameterization of synthetic tropical cyclones at various scales for probable maximum storm surge risk modeling[J]. Marine Sciences, 38(4): 71-80 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11759/hykx20120829002 |
|
| [7] | 刘秋兴, 于福江, 王培涛, 等, 2011. 辐射应力对台风风暴潮预报的影响和数值研究[J]. 海洋学报, 33(5): 47-53. |
| LIU QIUXING, YU FUJIANG, WANG PEITAO, et al, 2011. Numerical study on storm surge forecasting considering wave-induced radiation stress[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 33(5): 47-53 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] |
莎日娜, 尹宝树, 杨德周, 等, 2007. 天津近岸台风暴潮漫滩数值模式研究[J]. 海洋科学, 31(7): 63-67.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.07.012 |
|
SHA RINA, YIN BAOSHU, YANG DEZHOU, et al, 2007. A numerical study on storm surge and inundation induced by hurricanes in the nearshore of Tianjin[J]. Marine Sciences, 31(7): 63-67 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3096.2007.07.012 |
|
| [9] | 王喜年, 1989. 开阔海风暴潮的数值计算[J]. 海洋通报, 8(3): 11-20 (in Chinese). |
| [10] | 王喜年, 尹庆江, 张保明, 1991. 中国海台风风暴潮预报模式的研究与应用[J]. 水科学进展, 2(1): 1-10. |
| WANG XINIAN, YIN QINGJIANG, ZHANG BAOMING, 1991. Research and applications of a forecasting model of typhoon surges in china seas[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2(1): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] |
吴玮, 傅赐福, 于福江, 等, 2012. 温州近岸围堤对风暴潮漫滩影响的数值研究[J]. 海洋学研究, 20(2): 36-42.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2012.02.006 |
|
WU WEI, FU CIFU, YU FUJIANG, et al, 2012. Numerical simulation of the influence of Wenzhou coastal dike on storm surge inundation[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 20(2): 36-42 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2012.02.006 |
|
| [12] |
郑国诞, 谢亚力, 胡金春, 等, 2016. 台州温岭市风暴潮淹没危险性分析[J]. 海洋预报, 33(6): 40-50.
doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2016.06.005 |
|
ZHENG GUODAN, XIE YALI, HU JINCHUN, et al, 2016. Inundation risk assessment of typhoon storm surge along Taizhou Wenling city[J]. Marine forecasts, 33(6): 40-50 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11737/j.issn.1003-0239.2016.06.005 |
|
| [13] |
周水华, 李远芳, 冯伟忠, 等, 2010. “0601”号台风控制下的广东近岸浪特征[J]. 海洋通报, 29(2): 130-134.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2010.02.002 |
|
ZHOU SHUIHUA, LI YUANFANG, FENG WEIZHONG, et al, 2010. Wave characteristics dominated by typhoon named ‘Pearl’[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 29(2): 130-134 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2010.02.002 |
|
| [14] | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2012. GB/T50663-2011 核电厂工程水文技术规范[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社: 1-116 (in Chinese). |
| [15] |
ATKINSON G D, HOLLIDAY C R, 1977. Tropical cyclone minimum sea level pressure/maximum sustained wind relationship for the Western North Pacific[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 105(4): 421-427.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1977)1052.0.CO;2 |
| [16] |
BLAIN C A, MASSEY T, 2004. Application of a coupled discontinuous-continuous galerkin finite element shallow water model to coastal ocean dynamics[J]. Ocean Modelling, 10(3-4): 283-315.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2004.09.002 |
| [17] | FUJITA T, 1952. Pressure distribution in typhoon[J]. Geophysical Magazine, 23: 437-452. |
| [18] | HENDERSON F M, 1966. Open channel flow[M]. New York: Macmillan. |
| [19] |
RIS R C, HOLTHUIJSEN L H, BOOIJ N, 1999. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions 2. Verification[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104(C4): 7667-7681.
doi: 10.1029/1998JC900123 |
| [20] | TAKAHASHI K, 1939. Distribution of pressure and wind in a typhoon[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 17(2): 417-421. |
| [1] | DING Yiting, DONG Dibo. Study on comprehensive risk assessment of storm surges for Fujian Province from the perspective of resilience [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 126-136. |
| [2] | ZHANG Zheran, HU Junyang, ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Penghui, XING Jiuxing, CHEN Shengli. Storm surge simulations of the coastal area of Shenzhen using different types of typhoon meteorological fields—a case study of Typhoon Mangkhut* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
| [3] | TIAN Cheng, LI Xin, DU Yang, LI Ming, XIE Yong, XIA Jilu. Assessment of tropical cyclone disaster risk based on the Bayesian network and GIS [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 17-29. |
| [4] | GAO Na, ZHAO Mingli, MA Yi, XU Wanming, ZHAN Haigang, CAI Shuqun. Effect of typhoon on storm surge in the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 32-42. |
| [5] | XU Jie, GUO Jibing, CHEN Zhiqiang, ZHU Zhihui, WANG Qin, TANG Yanling. Comparative study on the contribution of various influential factors and characteristics analysis of an extra-tropical storm surge caused by cold front in the Yangshan Port and its adjacent area [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 126-135. |
| [6] | DENG Guotong, LIU Mincong, XING Jiuxing, SHENG Jinyu, ZHOU Kai, CHEN Shengli. Analysis on the influencing factors of storm surges near Shenzhen [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 91-100. |
| [7] | SUN Fenglin. Disaster loss assessment of storm surge based on Dempster-Shafer theory of evidence [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 75-81. |
| [8] | SHEN Qianying, JI Xiaomei, ZHANG Wei, XU Yanwen. Impact of estuarine storm surge barriers on spatiotemporal variation of tidal asymmetry in a delta* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 1-9. |
| [9] | WANG Yuanqi, YANG Yang, ZHOU Liang, WANG Yaping, GAO Shu. Interpreting the origin of coastal boulders on a coral reef flat at Xiaodonghai of Hainan Island based on storm wave energy analysis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 110-121. |
| [10] | YIN Chengtuan, ZHANG Jinshan, XIONG Mengjie, XU Junhui. Trend analysis of typhoon and storm surge disaster on the South China Sea coast of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(1): 35-42. |
| [11] | Zeting XU, Shiyu LI, Jiatang HU, Siying WANG, Bin WANG, Mingxian GUO, Bingxu GENG. Summer phytoplankton responses to upwelling and river plume in northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(6): 92-103. |
| [12] | Zhishen CHEN, Weiyong SHI, Jianfei LU. Comparative analysis on four recurrence levels of joint distribution of wave height and period* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 18-23. |
| [13] | XIA Li-hua, WU Hui-ming, LIU Ming, LENG Dian-song, LI Ting-ting. Characteristic analysis of storm surges along Fujian coast associated with tropical cyclones [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(3): 40-45. |
| [14] | LI Xin, HONG Mei, WANG Bo, ZHANG Ren, GE Shan-shan, QIAN Long-xia. Disaster assessment and risk zoning concerning the South China Sea and Indian Ocean safety [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(6): 121-127. |
| [15] | DU Juan,ZHENG Fei,ZHU Jiang. A reconstructed subsurface entrainment temperature data over the tropical Pacific for the past 153y [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(1): 1-9. |
|
||