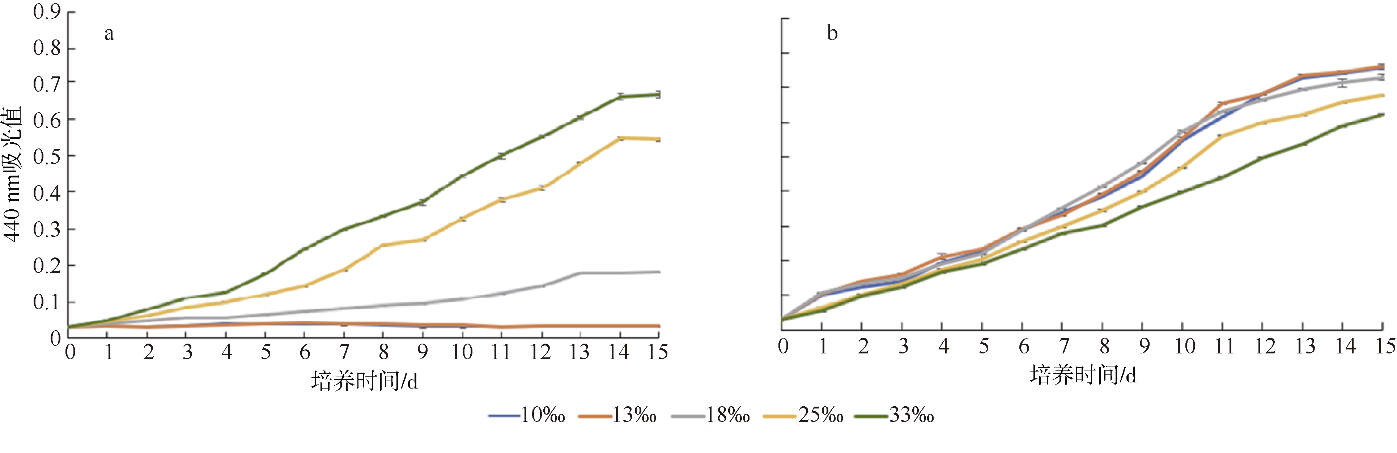
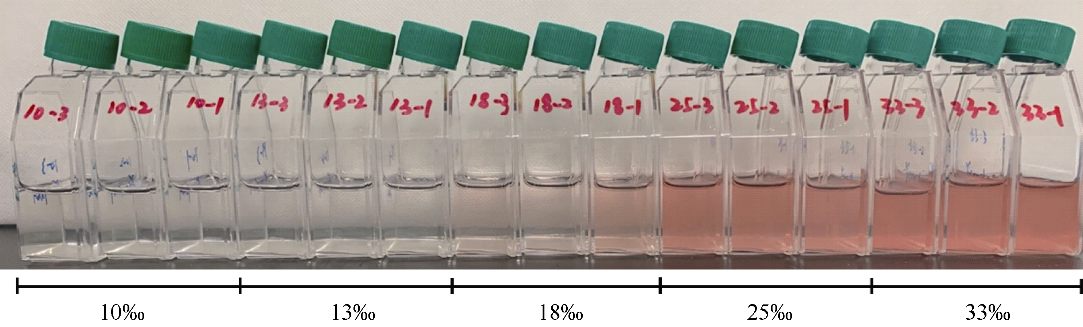
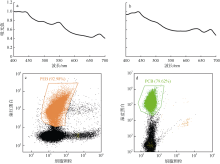
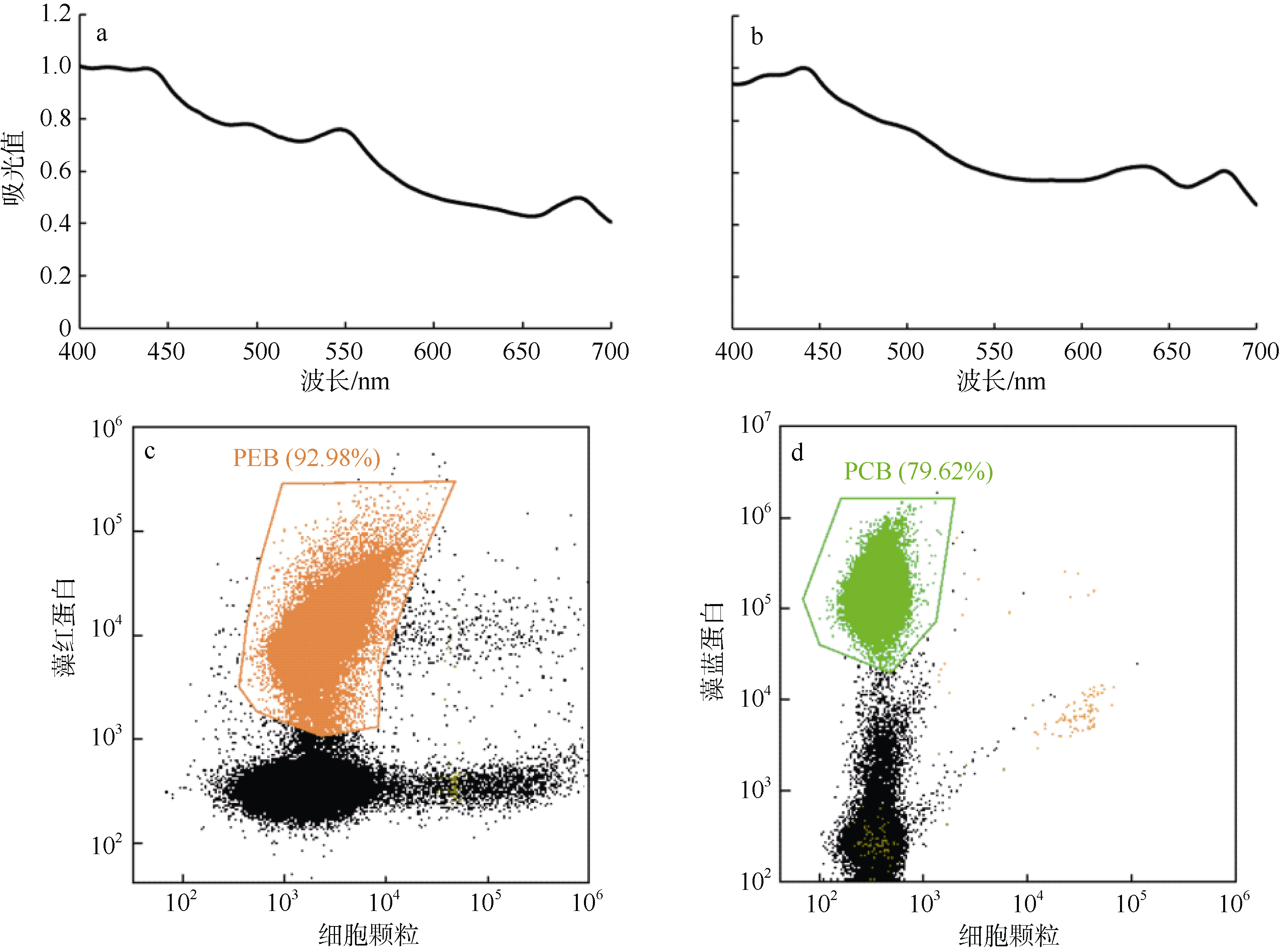
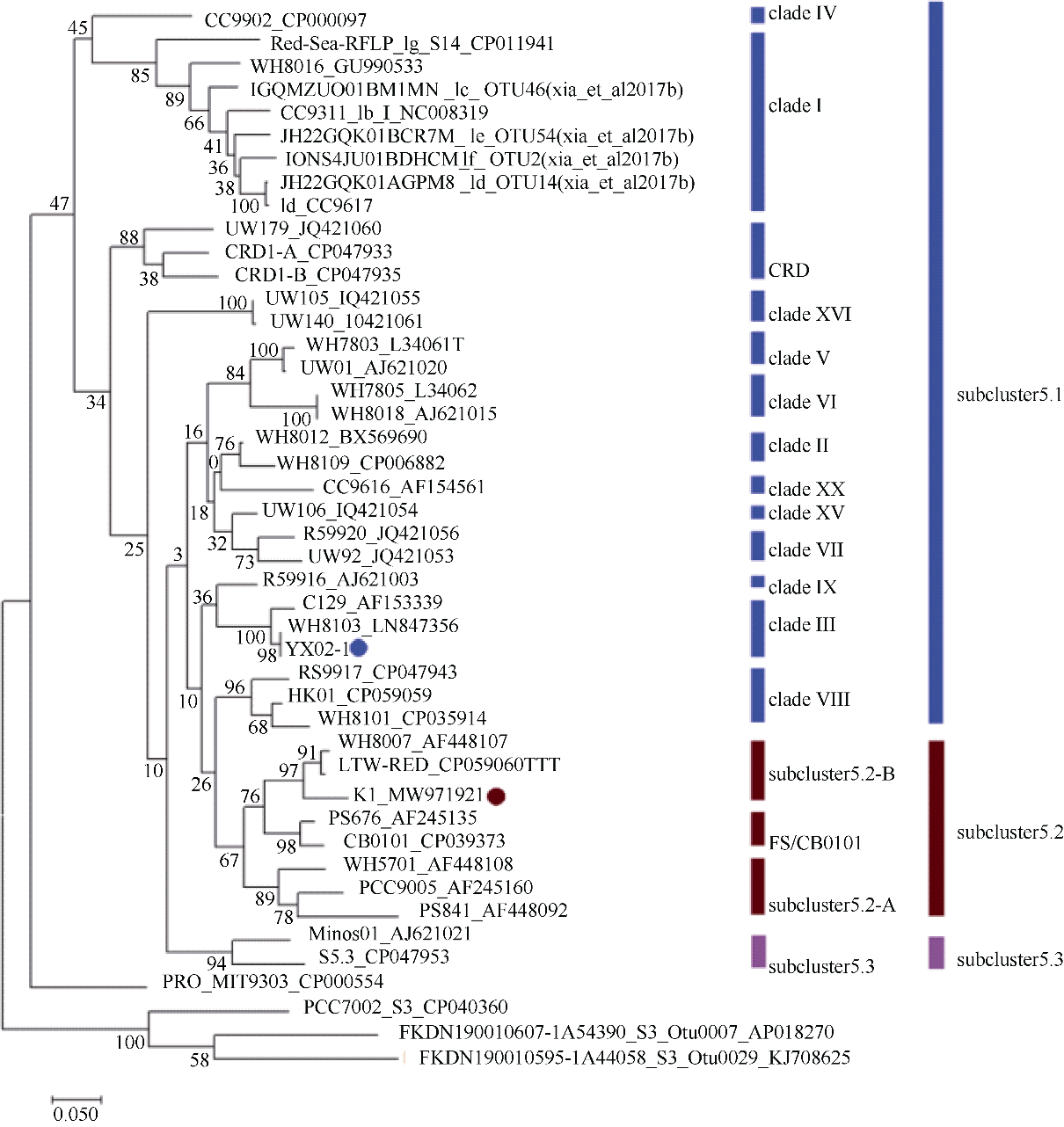
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 159-169.doi: 10.11978/2021040CSTR: 32234.14.2021040
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of salinity on the growth and transcriptome of euryhaline Synechococcus sp. K1*
LIAO Ying1,2( ), XIA Xiaomin1,2(
), XIA Xiaomin1,2( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-04-06Revised:2021-05-01Online:2022-03-10Published:2021-05-03 -
Contact:XIA Xiaomin E-mail:liaoying18@mails.ucas.ac.cn;xiaxiaomin@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:Nature Science Foundation of China(41906131);Key Deployment Program of Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences(COMS2020Q09);Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2019A1515011340)
CLC Number:
- P735.121
Cite this article
LIAO Ying, XIA Xiaomin. Effects of salinity on the growth and transcriptome of euryhaline Synechococcus sp. K1*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 159-169.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
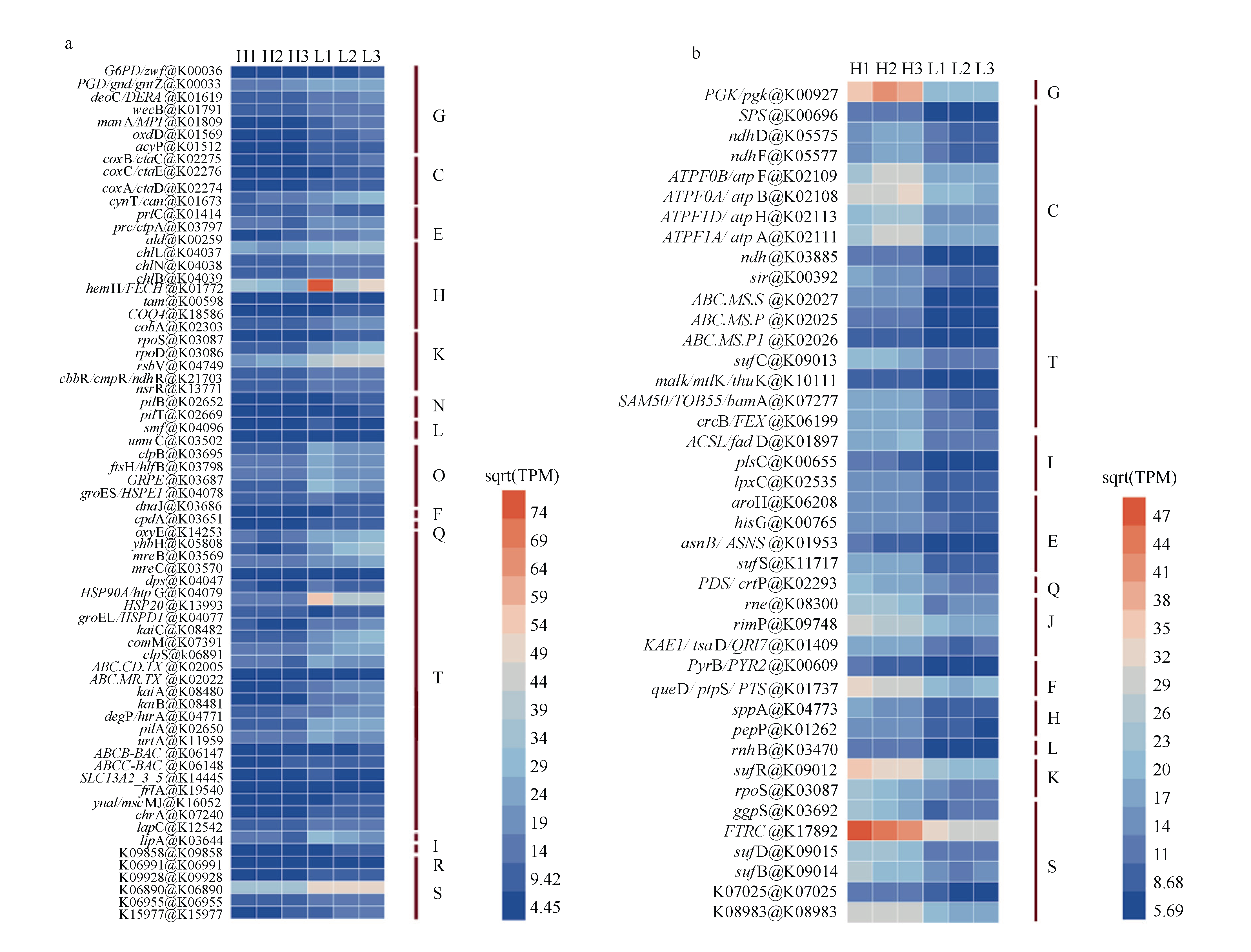
Tab. 1
The medium formula of f/2 without silicon"
| 成分 | 质量浓度/(g·L-1) | |
|---|---|---|
| 常量元素 | NaNO3 | 7.5×10 -2 |
| NaH2PO4H2O | 5.0×10 -3 | |
| 微量金属 | FeCl3·6H2O Na2EDTA2·H2O CuSO4·5H2O Na2MoO4·2H2O ZnSO4·7H2O CoCl2·6H2O MnCl4·4H2O | 3.15×10 -3 4.36×10 -3 9.8×10 -3 6.3×10 -3 2.2×10 -2 1.0×10 -2 1.8×10 -1 |
| 维生素 | Thiamine HCl (vit. B1) Biotin (vit. H) Cyanocobalamin (vit. B12) | 2.0×10 -4 1.0×10 -3 1.0×10 -3 |
| [1] | 路荣昭, 王淑芝, 关志英, 等, 1991. 聚球藻(Synechococcus leopoliensis 625)藻胆体-类囊体膜光谱特性和光能传递的研究[J]. 水生生物学报, 15(4): 368-371. |
| LU RONGZHAO, WANG SHUZHI, GUAN ZHIYING, et al, 1991. Studies on the spectroscopic properties and energy transfer of phycobilisome-thylakoid of Synechococcus leopoliensis 625[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 15(4): 368-371. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 马英, 焦念志, 2004. 聚球藻(Synechococcus)分子生态学研究进展[J]. 自然科学进展, 14(9): 967-972. |
| MA YING, JIAO NIANZHI, 2004. Progress in molecular ecology of Synechococcus[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 14(9): 967-972. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] |
AHLGREN N A, ROCAP G, 2006. Culture isolation and culture-independent clone libraries reveal new marine Synechococcus ecotypes with distinctive light and N physiologies[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(11): 7193-7204.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00358-06 |
| [4] | CALLIERI C, STOCKNER J G, 2002. Freshwater autotrophic picoplankton: a review[J]. Journal of Limnology, 61(1): 1-14. |
| [5] |
CELEPLI N, SUNDH J, EKMAN M, et al, 2017. Meta-omic analyses of Baltic Sea cyanobacteria: diversity, community structure and salt acclimation[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 19(2): 673-686.
doi: 10.1111/emi.2017.19.issue-2 |
| [6] |
DESHNIUM P, LOS D A, HAYASHI H, et al, 1995. Transformation of Synechococcus with a gene for choline oxidase enhances tolerance to salt stress[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 29(5): 897-907.
doi: 10.1007/BF00014964 |
| [7] |
EVERROAD R C, WOOD A M, 2012. Phycoerythrin evolution and diversification of spectral phenotype in marine Synechococcus and related picocyanobacteria[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 64(3): 381-392.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2012.04.013 |
| [8] |
FULLER N J, MARIE D, PARTENSKY F, et al, 2003. Clade-specific 16S ribosomal DNA oligonucleotides reveal the predominance of a single marine Synechococcus clade throughout a stratified water column in the Red Sea[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69(5): 2430-2443.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.5.2430-2443.2003 |
| [9] |
GUILLARD R R L, RYTHER J H, 1962. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: Ⅰ. Cyclotella nana hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) gran[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 8(2): 229-239.
doi: 10.1139/m62-029 |
| [10] | HERDMAN M, CASTENHOLZ RW, WATERNURY J B, et al, 2001. Form-genus ⅩⅢ. Synechococcus[M]//BOONE D R, CASTENHOLZ R W. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. New York, NY: Springer-Verlag, 508-512. |
| [11] |
KUMAR S, STECHER G, TAMURA K, 2016. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 33(7): 1870-1874.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054 |
| [12] |
LUDWIG M, BRYANT D A, 2012. Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002 transcriptome: acclimation to temperature, salinity, oxidative stress, and mixotrophic growth conditions[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 3: 354, doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012. 00354.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012. 00354 |
| [13] |
MARSAN D, PLACE A, FUCICH D, et al, 2017. Toxin-Antitoxin systems in estuarine Synechococcus strain CB0101 and their transcriptomic responses to environmental stressors[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 1213, doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01213.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01213 |
| [14] |
MOORE L R, POST A F, ROCAP G, et al, 2002. Utilization of different nitrogen sources by the marine cyanobacteria Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 47(4): 989-996.
doi: 10.4319/lo.2002.47.4.0989 |
| [15] |
MÜHLING M, FULLER N J, MILLARD A, et al, 2005. Genetic diversity of marine Synechococcus and co-occurring cyanophage communities: evidence for viral control of phytoplankton[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 7(4): 499-508.
doi: 10.1111/emi.2005.7.issue-4 |
| [16] |
PALENIK B, BRAHAMSHA B, LARIMER F W, et al, 2003. The genome of a motile marine Synechococcus[J]. Nature, 424(6952): 1037-1042.
doi: 10.1038/nature01943 |
| [17] |
ROCAP G, DISTEL D L, WATERBURY J B, et al, 2002. Resolution of Prochlorococcus and Synechococcus ecotypes by using 16S-23S ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 68(3): 1180-1191.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.3.1180-1191.2002 |
| [18] |
SIX C, THOMAS J C, GARCZAREK L, et al, 2007. Diversity and evolution of phycobilisomes in marine Synechococcus spp.: a comparative genomics study[J]. Genome Biology, 8(12): R259.
doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-12-r259 |
| [19] |
WANG KUI, WOMMACK K E, CHEN FENG, 2011. Abundance and distribution of Synechococcus spp. and cyanophages in the Chesapeake Bay[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77(21): 7459-7468.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00267-11 |
| [20] |
XIA XIAOMIN, VIDYARATHNA N K, PALENIK B, et al, 2015. Comparison of the seasonal variations of Synechococcus assemblage structures in estuarine waters and coastal waters of Hong Kong[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 81(21): 7644-7655.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.01895-15 |
| [21] |
XIA XIAOMIN, GUO WANG, TAN SHANGJIN, et al, 2017. Synechococcus assemblages across the salinity gradient in a salt wedge estuary[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 1254, doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01254.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01254 |
| [22] |
XIA XIAOMIN, LIU HONGBIN, CHOI D, et al, 2018. Variation of Synechococcus pigment genetic diversity along two turbidity gradients in the China Seas[J]. Microbial Ecology, 75(1): 10-21.
doi: 10.1007/s00248-017-1021-z |
| [23] |
XIA XIAOMIN, CHEUNG S, ENDO H, et al, 2019. Latitudinal and vertical variation of Synechococcus assemblage composition along 170° W transect from the South Pacific to the Arctic Ocean[J]. Microbial Ecology, 77(2): 333-342.
doi: 10.1007/s00248-018-1308-8 |
| [24] | XIA XIAOMIN, LEE P, CHEUNG S, et al, 2020. Discovery of euryhaline phycoerythrobilin-containing Synechococcus and its mechanisms for adaptation to estuarine environments[J]. mSystems, 5(6): e00842-20. |
| [25] |
YAMANAKA G, GLAZER A N, 1981. Dynamic aspects of phycobilisome structure: modulation of phycocyanin content of Synechococcus phycobilisomes[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 130(1): 23-30.
doi: 10.1007/BF00527067 |
| [1] | LIN Guihuan, YAN Youfang, LIU Ying. Ocean stratification in the Indonesian-Australian basin and its influencing factors [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 57-67. |
| [2] | SUN Wenjie, LI Jiamin, WANG Hualong, MI Tiezhu, ZHEN Yu. Transcriptomic analysis of fatty acid metabolism in the Thalassiosira pseudonana under low salinity stress [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 92-103. |
| [3] | TANG Jiaoyu, WANG Weiqiang, XU Kang, ZHANG Zhenqiu. Interannual variability of subsurface high salinity water in eastern equatorial Indian Ocean* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 10-21. |
| [4] | LYU Hongke, GONG Yuanfa, WANG Guihua. A linear Markov model for the forecast of sea surface salinity in the Indian Ocean and its improvement method [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 151-158. |
| [5] | DONG Lanfang, XU Mingzhu, LIU Haijuan, ZENG Mengqing, CHEN Ruifang, LI Shicai. Effects of salinity on growth, molting, Na+-K+-ATP enzyme activities, immune index, and antioxidantion of juvenile Chinese horseshoe crab, Tachypleus tridentatus [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 156-163. |
| [6] | QIU Shuang, YE Haijun, ZHANG Yuhong, TANG Shilin. Multi-linear regression of partial pressure of sea-surface carbon dioxide in the South China Sea and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 106-116. |
| [7] | HE Zikang, WANG Xidong, CHEN Zhiqiang, FAN Kaigui. Reconstructing salinity profile using temperature profile and sea surface salinity [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 41-51. |
| [8] | LU Mengying, SU Maoliang, ZHANG Junbin. Effects of salinity changes on serum and kidney immune status associated with injection of Aeromonas hydrophila in Scatophagus argus [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 114-123. |
| [9] | Xiaolan PAN, Huiru LIU, Meng XU, Hanzhi XU, Hua ZHANG, Maoxian HE. Cloning and expression analysis of aquaporin gene AQP4 cDNA from Pinctada fucata martensii [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(3): 66-75. |
| [10] | Jianwei CHI,Tangdong QU,Ying ZHANY,Ping SHI,Yan DU. Seasonal variability of the Eastern Tropical Pacific Fresh Pool * [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 1-9. |
| [11] | Xiangpeng WANG,Yuhong ZHANG,Aimei WANG,Wei ZHAO,Yan DU. Low-frequency variability of subsurface salinity in the South China Sea and its relationship with the Pacific Decadal Oscillation [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 1-9. |
| [12] | Zhujun FANG, Hai ZHI, Pengfei LIN, Xiang WEI. Distinguishing two types of El Niño in the Tropical Pacific using key region sea surface salinity index [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 32-42. |
| [13] | Yan XU, Xiangquan LIU, Rengang SONG, Xianrong CEN, Shuangxi GUO, Shengqi ZHOU. Numerical simulation of diffusive convection staircase [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(1): 11-18. |
| [14] | Wenhao CAO, Jin YAN, Meiping FENG, Shuaishuai HAN, Mingqing LIN. Effects of salinity on larval development of two common barnacles from the southeast coast of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(6): 85-91. |
| [15] | Yuanyuan FU, Xuhua CHENG, Yuhong ZHANG, Youfang YAN, Yan DU. The freshening trend of surface salinity in the South China Sea in recent two decades and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(4): 18-24. |
|
||