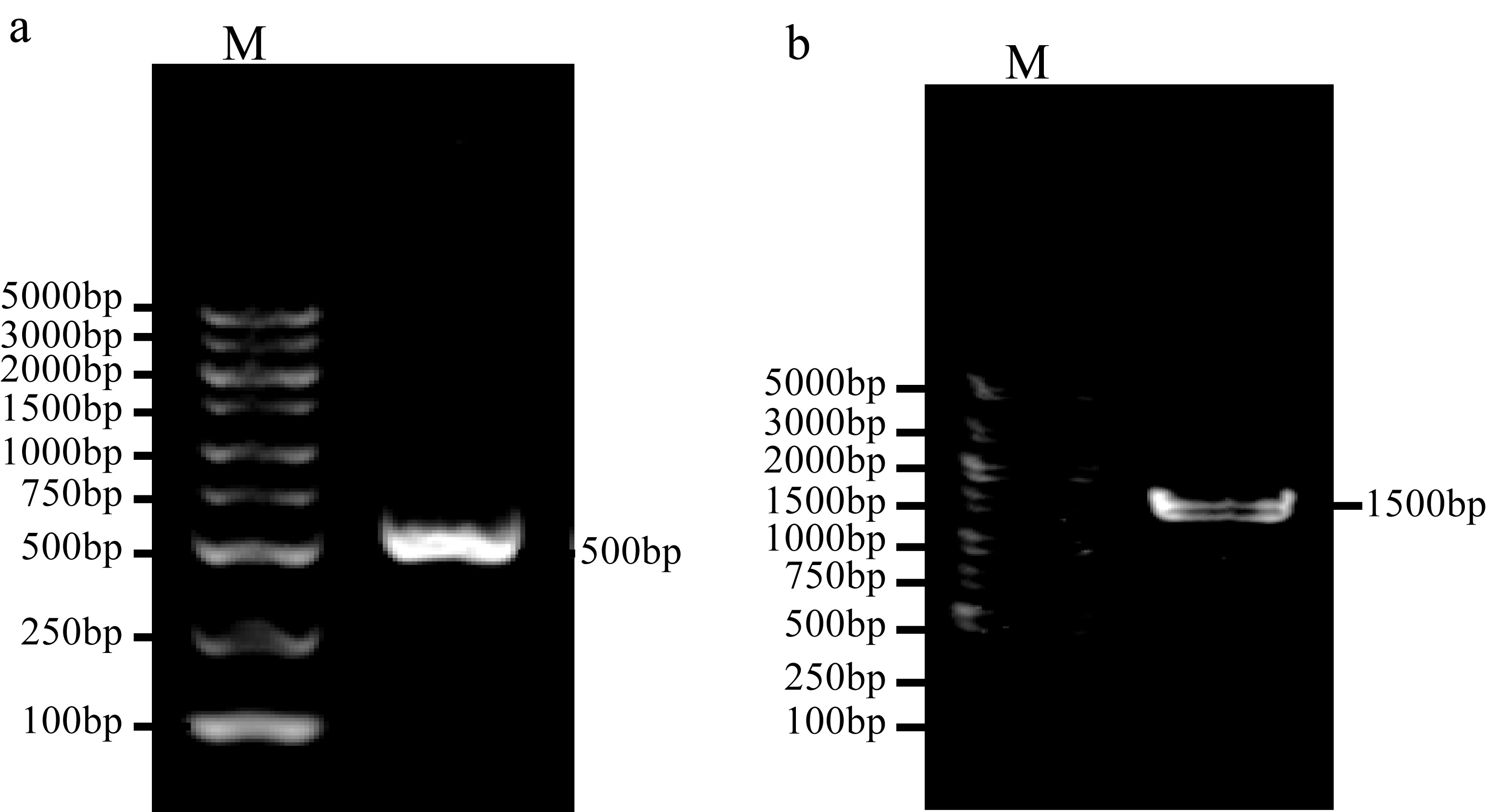
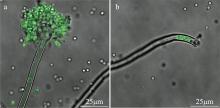
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 56-63.doi: 10.11978/2024104CSTR: 32234.14.2024104
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
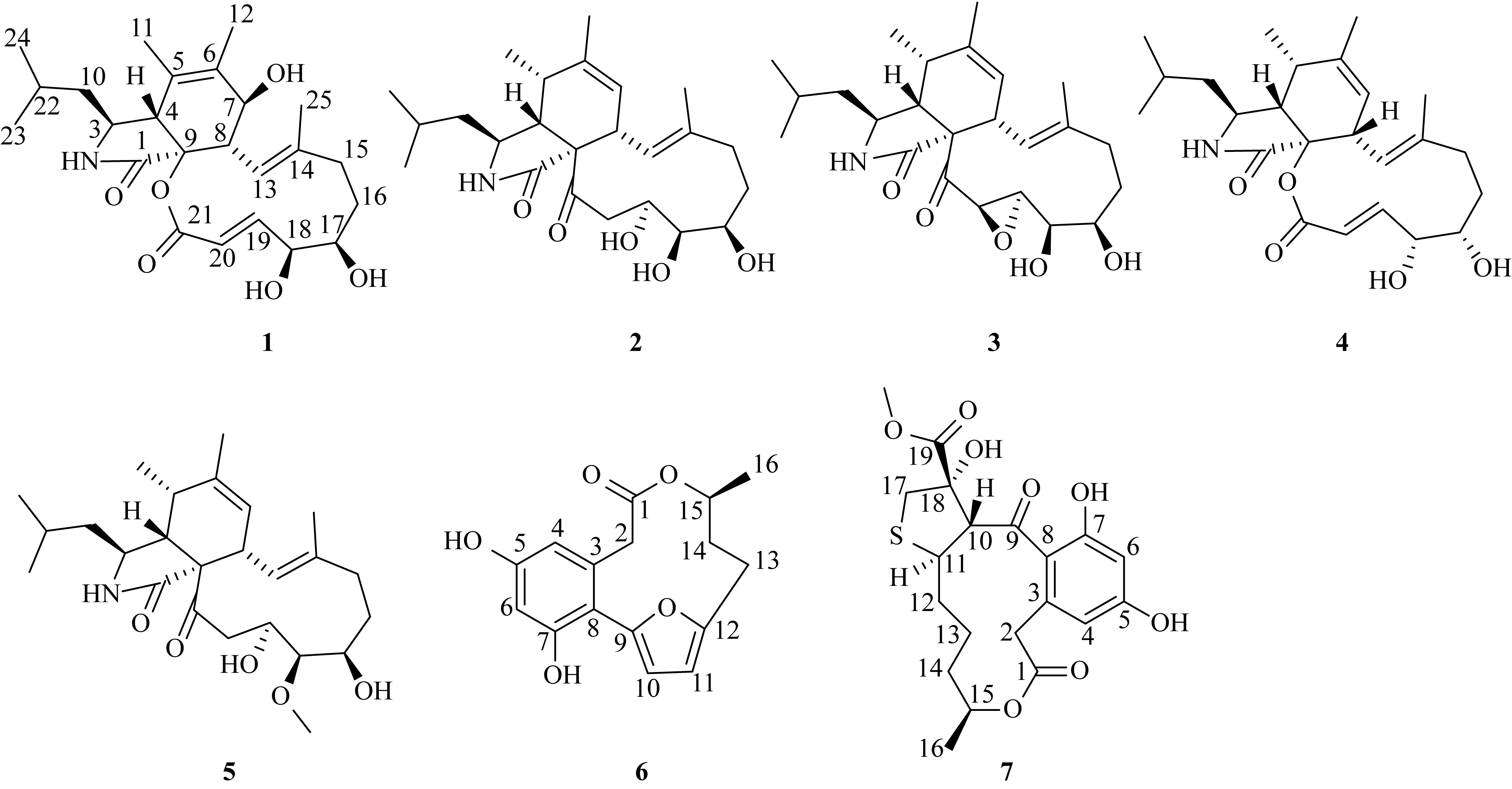
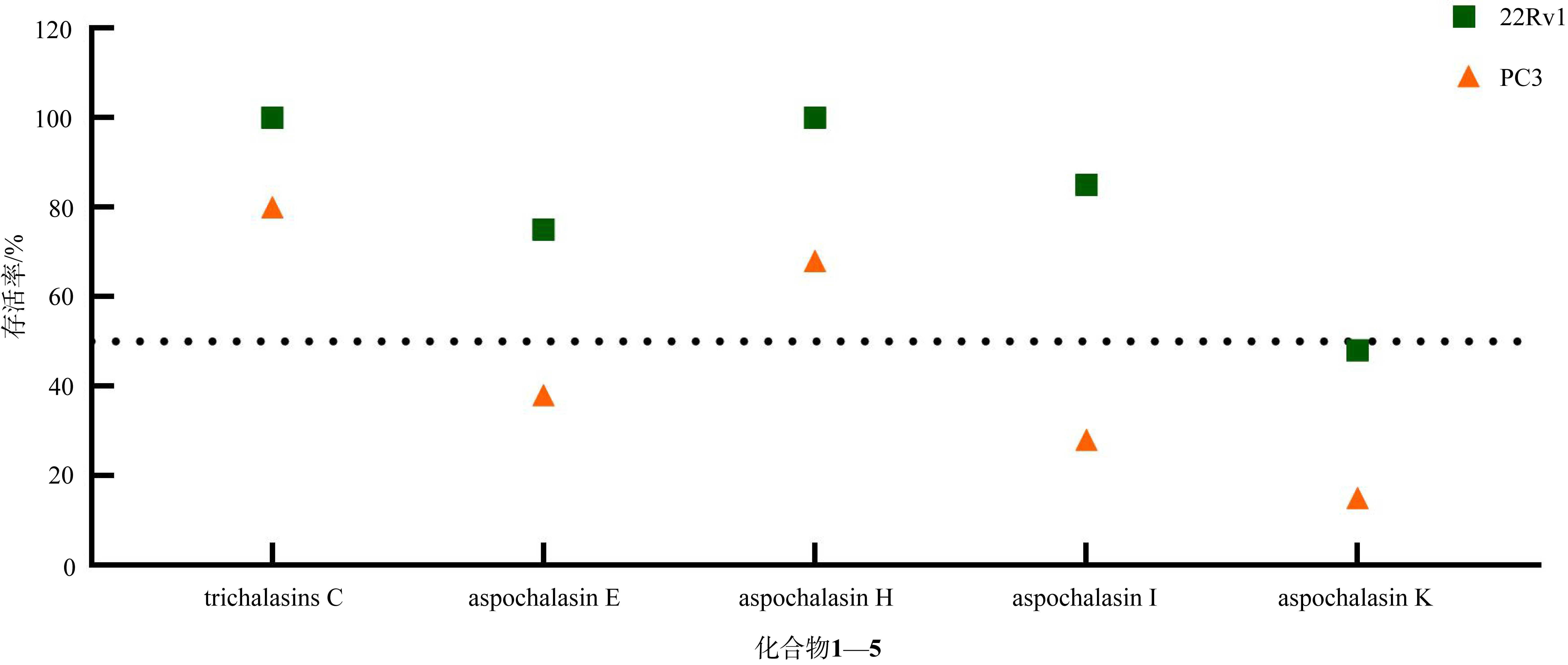
Secondary metabolites from the fungal-bacterial symbiont Aspergillus spelaeus GXIMD 04541 / Sphingomonas echinoides GXIMD 04532 derived from Mauritia arabica
YANG Jie1,2( ), YAO Feihua1,2, LI Xiaoyan1,2, SHI Jieyu2,3, YI Xiangxi2,3, GAO Chenghai1,2(
), YAO Feihua1,2, LI Xiaoyan1,2, SHI Jieyu2,3, YI Xiangxi2,3, GAO Chenghai1,2( )
)
- 1. Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
2. Guangxi Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, Nanning 530200, China
3. Faculty of Pharmacy, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
-
Received:2024-05-17Revised:2024-06-19Online:2025-03-10Published:2025-04-11 -
Contact:GAO Chenghai -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(U20A20101); Guangxi Key Research and Development Programme(AB24010109); Guangxi Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs(2302603); High-level Talent Inheritance, Innovation Team of Guangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine(2022A007)
CLC Number:
- P735.2
Cite this article
YANG Jie, YAO Feihua, LI Xiaoyan, SHI Jieyu, YI Xiangxi, GAO Chenghai. Secondary metabolites from the fungal-bacterial symbiont Aspergillus spelaeus GXIMD 04541 / Sphingomonas echinoides GXIMD 04532 derived from Mauritia arabica[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 56-63.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
高亚欣, 王昊, 戴好富, 等, 2023. 西沙短指软珊瑚Sinularia flexibilis中具有肿瘤细胞毒活性的甾体化合物[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 56-63.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
鞠建华, 邵明伟, 孙长利, 等, [2022-05-06]. 一种海洋真菌-细菌共生体及其代谢产物和在制备抗菌药物中的应用: 中国, CN112694983B[P].
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
凌娟, 梁童茵, 岳维忠, 等, 2023. 热带海草泰来草沉积物真菌的群落结构、功能与分子生态网络研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 42(5): 64-75.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
马丽丽, 田新朋, 李桂菊, 等, 2021. 海洋微生物来源天然产物研究现状与态势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(5): 134-146.
doi: 10.11978/2020104 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020104 |
|
| [5] |
张涵, 谭雁鸿, 杨斌, 等, 2021. 中国南海软珊瑚附生真菌Acremonium sp. SCSIO41216的次级代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(6): 135-139.
doi: 10.11978/2020103 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020103 |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.02272-07 pmid: 18296538 |
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.02928-09 pmid: 20435775 |
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01239-y pmid: 32968175 |
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [1] | LIANG Xuecheng, CHANG Wenjun, DAI Haofu, ZHOU Lihua, ZENG Yanbo. Secondary metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Penicillium sp. G5A-11 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 73-83. |
| [2] | KONG Weiqi, JIN Xin, LIU Yonghong, GAO Chenghai, CHEN Xianqiang. Studies on secondary metabolites of Sargassum fusiforme derived fungus Aspergillus sp. GXIMD 02045 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 154-161. |
| [3] | YUAN Yuan, ZHANG Yuanyuan, XU Fuquan, LIU Qingchao, WANG Junfeng. Secondary metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41018 and their free radical scavenging activity [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 196-200. |
| [4] | XIAO Yang, YAN Jing, YANG Shuyu, ZHANG Tangjie, WENG Jie, LI Qilin, LIU Hongcun, MENG Juan, YANG Lifang. Study on the secondary metabolites and hypoglycemic and lipid lowering activities of actinomyces Streptomyces olivaceuss 10127 from the Guangxi mangrove sediments [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 181-189. |
| [5] | AN Fan, JIANG Yue, WANG Yu, CAO Guangping, GAO Chenghai, LIU Yonghong, YI Xiangxi, BAI Meng. Studies on secondary metabolites of endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus GXIMD 03158 isolated from mangroves Acanthus ilicifolius L. [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 41-48. |
| [6] | LIN Yingting, SUN Ying, HU Jiangnan, DONG Shuai. Study on secondary metabolites of the endophytic fungus Talaromyces sp. XXH006 Isolated from Conus literatus [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 181-188. |
| [7] | WANG Jiaxi, LU Humu, QI Xin, GAO Chenghai, LIU Yonghong, LUO Xiaowei. Study on the secondary metabolites from the Weizhou Island coral Acropora austera associated fungus Arachniotus ruber GXIMD 02510 and their antibacterial activity [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 174-180. |
| [8] | QUAN Miaomiao, MA Qingyun, YANG Li, XIE Qingyi, DAI Haofu, HAO Yu’e, ZHAO Youxing. Study on the secondary metabolites of marine fungus Phaeospheriopsis sp. ZYX-Z-811 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 121-127. |
| [9] | LIU Ying, XIAO Yang, ZHU Zhenxin, LIU Hongcun, JIANG Mingguo, ZHU Yuzhang, LIN Kun, WU Jincheng, LU Xiaomei, HUANG Xiaoning, LIANG Haina, LU Wensen, YANG Lifang. Study on the Secondary Metabolites of Marine Streptomyces Sporoverrucosus 33510 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 128-134. |
| [10] | FENG Guangfu, HE Jeyi, BAI Meng, YI Xiangxi, LIU Xinming, LUO Lianxiang, GAO Chenghai. Secondary Metabolites from Hydaranth of Coral Goniopora columna in the Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 135-139. |
| [11] | GAO Yaxin, WANG Hao, DAI Haofu, XIA Zhihui, ZENG Yanbo. Cytotoxic steroids from the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis collected off the Xisha [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 56-63. |
| [12] | XING Nannan, REN Runxin, TANG Zhenzhou, LUO Zhihong, XIA Chenxi, LIU Yonghong, PENG Liang, CHEN Xianqiang. Study on the secondary metabolites of fungus Aspergillus sp. GXIMD02003 derived from marine sediment in the Weizhou island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 154-160. |
| [13] | LIANG Hanqiao, CHEN Wenfeng, FAN Yikai, ZHU Zidong, MA Guoxu, CHEN Deli, TIAN Jing. Research progress on the secondary metabolites and activities of endophytic fungi of genus Aspergillus and Trichoderma from mangroves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 12-24. |
| [14] | LIAO Shengrong, XU Huayan, LI Xiaolin, LIU Yonghong. Design, synthesis and cytotoxicity of novel glycosyl-2, 5-diketopiperazine derivatives [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 174-185. |
| [15] | YE Yuxiu, LUO Xiaowei, YANG Bin, LIN Xiuping, LIU Yonghong, ZHOU Xuefeng. Study on the secondary metabolites of reef habitat algae-derived fungus Pestalotiopsis neglecta SCSIO41403 from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 186-190. |
|
||