Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 196-207.doi: 10.11978/2024120CSTR: 32234.14.2024120
• Marine Environmental Protection • Previous Articles Next Articles
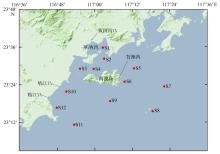
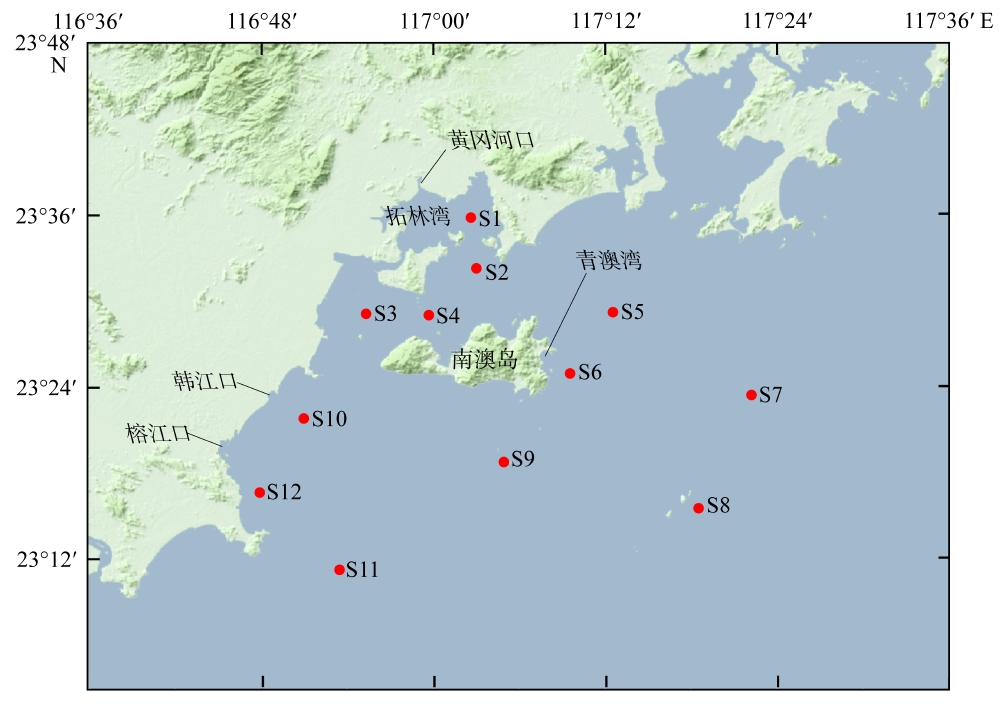
Distribution of nutrients and eutrophication characteristics in the surface water around Nan’ao Island
HUANG Haochen1,2( ), KE Zhixin1,3(
), KE Zhixin1,3( ), ZHOU Zhixi4, ZHOU Weihua1
), ZHOU Zhixi4, ZHOU Weihua1
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Guangdong Provincial Observation and Research Station for Coastal Upwelling Ecosystem, Shantou 515041, China
4. South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou 510642, China
-
Received:2024-06-05Revised:2024-08-19Online:2025-03-10Published:2025-04-11 -
Contact:KE Zhixin -
Supported by:Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province(2021B1212050023); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province(2023B1212060047); National Natural Science Foundation of China(32171548); Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2022A1515010656)
CLC Number:
- P761.4
Cite this article
HUANG Haochen, KE Zhixin, ZHOU Zhixi, ZHOU Weihua. Distribution of nutrients and eutrophication characteristics in the surface water around Nan’ao Island[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 196-207.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
The environmental factors and eutrophication index in the surface water around Nan’ao Island in different seasons (mean ± SD)"
| 因子或指数 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度/℃ | 23.38 ± 0.46c | 27.07 ± 1.99a | 25.85 ± 0.28b | 17.00 ± 0.21d |
| 盐度/‰ | 31.71 ± 0.46a | 31.42 ± 2.63a | 32.67 ± 1.77a | 30.78 ± 2.40a |
| DIN/(mg·L-1) | 0.10 ± 0.09b | 0.08 ± 0.06b | 0.17 ± 0.10b | 0.49 ± 0.26a |
| DIP/(mg·L-1) | 0.014 ± 0.016bc | 0.011 ± 0.009c | 0.030 ± 0.013b | 0.050 ± 0.020a |
| DSi/(mg·L-1) | 0.44 ± 0.28b | 0.77 ± 0.52ab | 0.88 ± 0.36ab | 1.06 ± 0.47a |
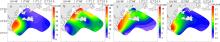
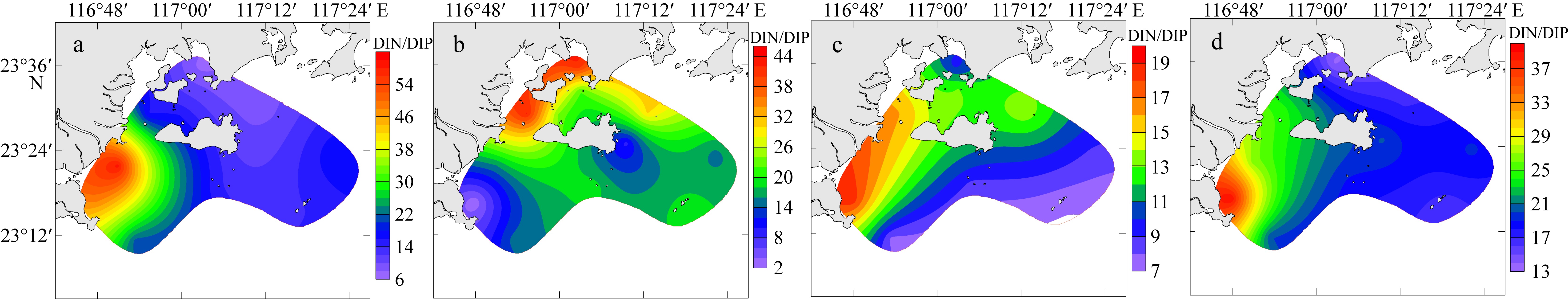
| DIN/DIP | 20.42 ± 15.97a | 21.41 ± 11.80a | 12.08 ± 3.77a | 21.22 ± 6.58a |
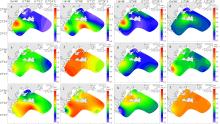
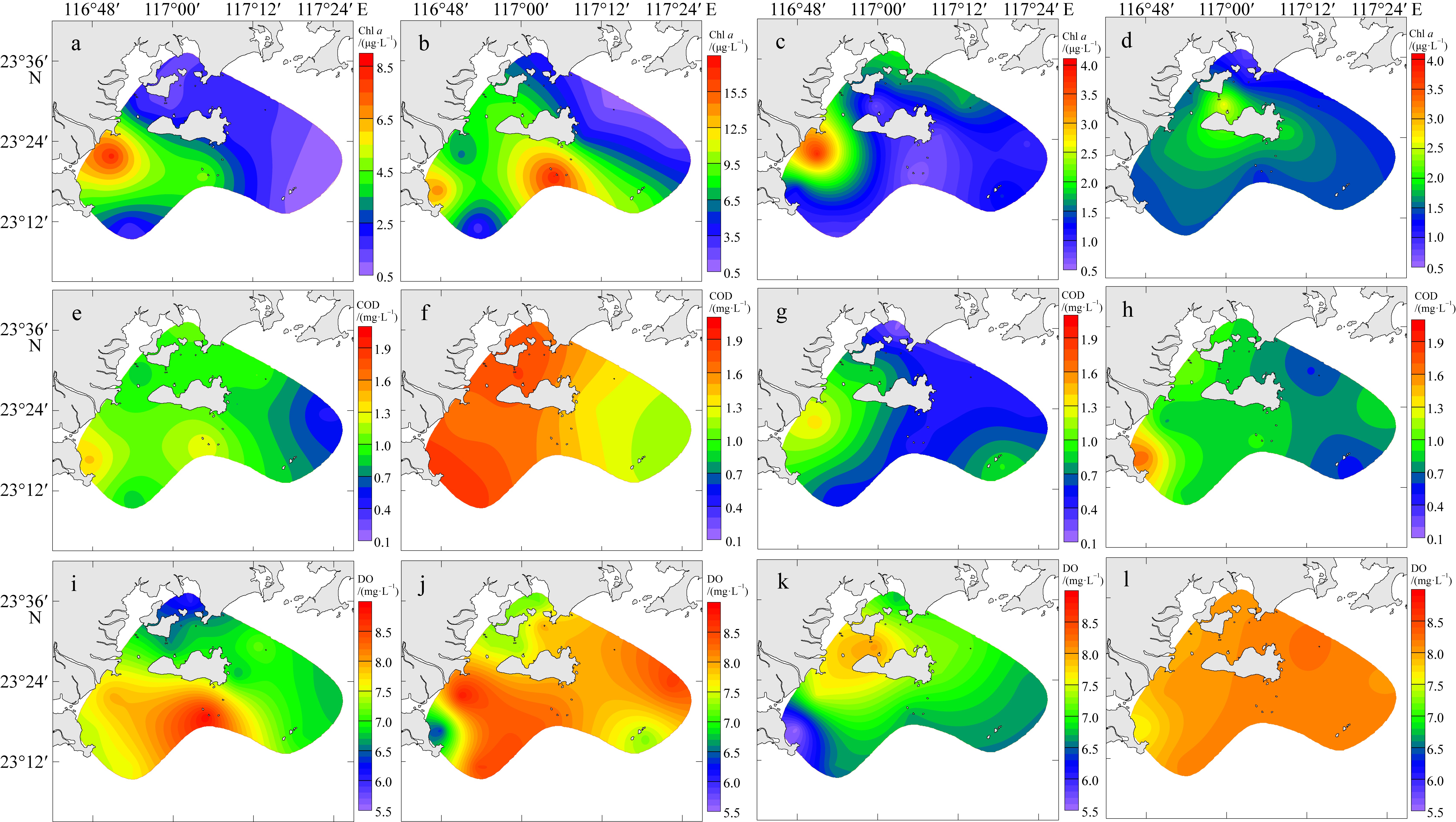
| Chl a/(μg·L-1) | 2.55 ± 2.24b | 7.05 ± 4.94a | 1.44 ± 0.84b | 1.53 ± 0.43b |
| COD/(mg·L-1) | 0.96 ± 0.25b | 1.57 ± 0.26a | 0.68 ± 0.33b | 0.89 ± 0.28b |
| DO/(mg·L-1) | 7.15 ± 0.74bc | 7.79 ± 0.71ab | 7.00 ± 0.67c | 8.07 ± 0.16a |
| EI指数 | 0.51 ± 0.76b | 0.37 ± 0.48b | 0.98 ± 1.06b | 6.34 ± 7.32a |
| NQI指数 | 1.65 ± 0.90b | 2.57 ± 1.00b | 2.10 ± 0.81b | 3.88 ± 1.47a |
| TRIX指数 | 4.43 ± 0.89a | 5.08 ± 0.33a | 4.91 ± 0.70a | 4.87 ± 0.47a |
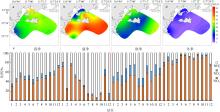
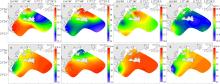
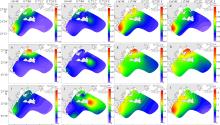
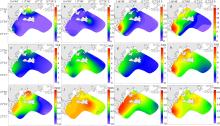
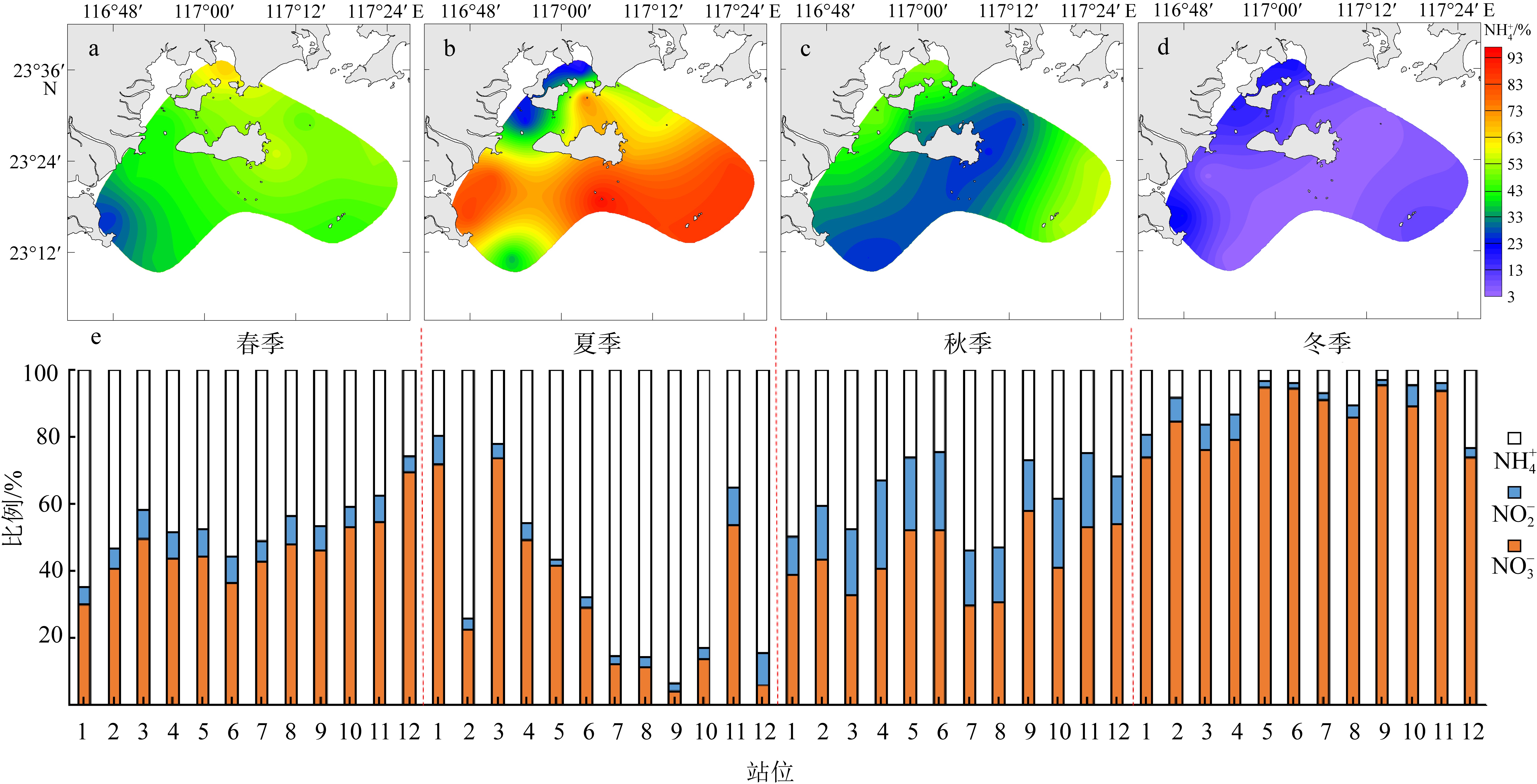
Fig. 4
Seasonal variations of the percentages of nitrate ( N O 3 −), nitrite ( N O 2 −) and ammonia ( N H 4 +) in the surface water around Nan’ao Island a. Spring ammonia nitrogen ratio; b. Summer ammonia nitrogen ratio; c. Autumn ammonia nitrogen ratio; d. Winter ammonia nitrogen ratio; e. DIN composition at different stations in different seasons"
| [1] |
陈丹婷, 柯志新, 谭烨辉, 等, 2020. 汕头南澳—东山海域营养盐季节分布特征及其对浮游植物生长的潜在性限制[J]. 生态科学, 39(4): 41-50.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
郭康丽, 龙超, 党二莎, 等, 2022. 珠海市近岸海域水质状况与富营养化评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 41(2): 222-229.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
国家环境保护局, 1997. 海水水质标准: GB 3097-1997[S/OL]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/shjzlbz/199807/t19980701_66499.shtml, [2024-12-20].
|
|
NATIONAL ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY, 1997. Sea water quality standard: GB 3097-1997[S/OL]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/shjzlbz/199807/t19980701_66499.Shtml, [2024-12-20](in Chinese).
|
|
| [4] |
洪启明, 李立, 1991. 粤东陆架区夏季的上升流[J]. 台湾海峡, 10(3): 271-277.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
柯志新, 陈丹婷, 谭烨辉, 等, 2019. 汕头南澳-东山海域初级生产力的时空特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 26(1): 44-52.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
李妙聪, 刘文胜, 江锦花, 2021. 乐清湾海水养殖环境水质质量时空变化及富营养化状况评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 40(5): 724-731.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
李赛赛, 裴绍峰, 赵俐红, 等, 2024. 杭州湾及其邻近海域夏季营养盐污染与富营养化评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 40(6): 39-52.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
林荣根, 1996. 海水富营养化水平评价方法浅析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 15(2): 28-31.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
林温迪, 2023. 南澳岛旅游经济发展问题与对策研究[J]. 中国集体经济, (2): 133-136 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
林晓娟, 高姗, 仉天宇, 等, 2018. 海水富营养化评价方法的研究进展与应用现状[J]. 地球科学进展, 33(4): 373-384.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.04.0373 |
|
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.04.0373 |
|
| [11] |
林小涛, 晏荣军, 黄长江, 2006. 粤东大规模养殖区柘林湾细菌的分布与环境因素关系[J]. 海洋学报, 28(3): 167-172.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
刘陈, 魏南, 王庆, 等, 2019. 广东汕头南澳岛近岸海域浮游植物群落结构与环境特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(5): 1091-1098.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
柳原, 柯志新, 李开枝, 等, 2024. 人类活动和沿岸流影响下的粤东近海浮游动物群落特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 43(4): 98-111.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
南澳县人民政府, 2022. 汕头南澳: 北回归线上“蚝”丰收[EB/OL]. 南澳县人民政府门户网站, http://www.nanao.gov.cn/na/hddt/content/post_2126097.Html, [2024-5-7]
|
| [15] |
彭璇, 马胜伟, 陈海刚, 等, 2014. 夏季柘林湾-南澳岛海洋牧场营养盐的空间分布及其评价[J]. 南方水产科学, 10(6): 27-35.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
舒业强, 王强, 俎婷婷, 2018. 南海北部陆架陆坡流系研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 48(3): 276-287.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
王翠, 郭晓峰, 方婧, 等, 2018. 闽浙沿岸流扩展范围的季节特征及其对典型海湾的影响[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 37(1): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
王焕松, 雷坤, 李子成, 等, 2010. 辽东湾海域水体富营养化的模糊综合评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 23(4): 413-419.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
吴鹏, 刘永, 肖雅元, 等, 2022. 春季珠江口万山群岛毗邻海域渔业生态环境状况评价[J]. 南方水产科学, 18(5): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
许金电, 蔡尚湛, 宣莉莉, 等, 2014. 粤东至闽南沿岸海域夏季上升流的调查研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(2): 1-9.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2014.02.001 |
|
|
|
| [21] |
杨红生, 茹小尚, 张立斌, 等, 2019. 海洋牧场与海上风电融合发展: 理念与展望[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 34(6): 700-707.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
杨宇峰, 罗洪添, 王庆, 等, 2021. 大型海藻规模栽培是增加海洋碳汇和解决近海环境问题的有效途径[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 36(3): 259-269.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
张彩云, 商少凌, 陈德文, 等, 2005. 冬季浙闽沿岸水分布的短期变动与风的关系初探[J]. 遥感学报, 9(4): 452-458.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
中华人民共和国环境保护部, 2008. 近岸海域环境监测规范: HJ 442-2008[S/OL]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/200811/t20081111_131115.htm, [2024-12-20].
|
|
MINISTRY OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA, 2008. Specification for offshore environmental monitoring:[S/OL]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/200811/t20081111_131115.htm, [2024-12-20](in Chinese).
|
|
| [25] |
周凯, 黄长江, 姜胜, 等, 2002. 2000-2001年柘林湾浮游植物群落结构及数量变动的周年调查[J]. 生态学报, 22(5): 688-698.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
邹景忠, 董丽萍, 秦保平, 1983. 渤海湾富营养化和赤潮问题的初步探讨[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2(2): 41-54 (in Chinese).
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.07.005 pmid: 18715596 |
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: S0043-1354(19)30331-8 pmid: 31075499 |
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
pmid: 14972584 |
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [1] | ZHOU Zhixi, TANG Huijuan, KE Zhixin, LIU Jiaxing, ZHOU Weihua. Phytoplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in the spring coastal region of Nan’ao based on morphology and high-throughput sequencing [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 53-65. |
| [2] | INYANG Aniefiok Ini, ZHOU Yueyue, WANG Youshao. Characteristics of water quality and their eutrophication assessment on the mangrove ecosystems along the Guangdong coast [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 1-11. |
| [3] | ZHANG Liming, TAN Yehui, LI Jiajun, HUANG Xiaoping, LIU Jiaxing. Characteristics of the phytoplankton community and its response to Dan’ao River input in Daya Bay in summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [4] | Yuzheng REN, Zhixin KE, Yehui TAN, Kaizhi LI. Community structure of zooplankton and its influencing factors in the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island, Guangdong [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 65-76. |
| [5] | Fuwu XIE, Xingyu SONG, Yehui TAN, Meiting TAN, Yadong HUANG, Huaxue LIU. Impact of simulated warming and nutrients input on plankton community metabolism in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 48-57. |
| [6] | Guofeng XU, Yongping CUI, Lian LIU. Assessment of eutrophication status by using the Pressure-Status-Response Model in Xiangshan Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(4): 52-60. |
| [7] | Fuwu XIE, Huaxue LIU, Honghui HUANG, Xingyu SONG. Effects of thermal discharge and nutrients input on size structure of phytoplankton in Daya Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 55-64. |
| [8] | CHEN Jin, LU Ping, CHEN Zhong-ying, YAN Hui-hua, LI Lai-sheng. Atmospheric deposition of nitrogen and phosphorus at Daya Bay in Huizhou during spring and summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(2): 109-114. |
| [9] | ZHOU Yi-chun, PENG Peng-fei, HU Chao-qun, ZHONG Ming, CHEN Yan-feng, ZHAO Zhe, XIA Jian-jun. Analysis of nutritional value and observation of biological characteristics in microalga Amphora sp. as food for sea cucumber Stichopus horrens [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(3): 59-64. |
| [10] | HUANG Xiao-ping,TIAN Lei,PENG Bo,ZHANG Da-wen. Environmental pollution in the Pearl River Estuary: a review [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(1): 1-7. |
|
||