Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 65-76.doi: 10.11978/2019051CSTR: 32234.14.2019051
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
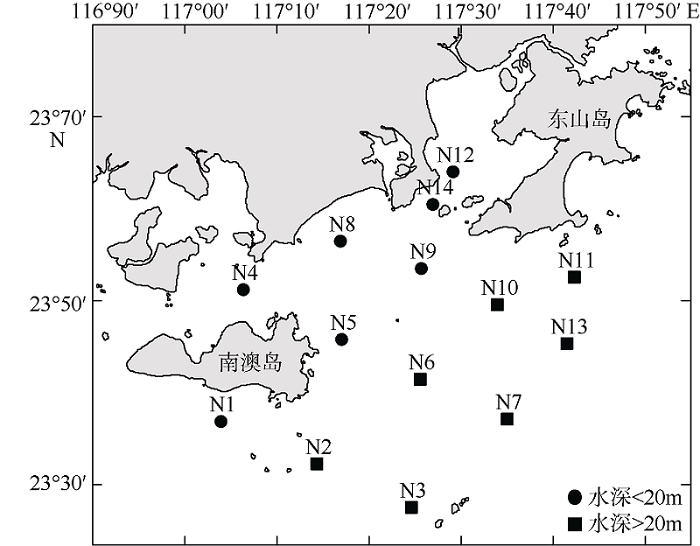
Community structure of zooplankton and its influencing factors in the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island, Guangdong
Yuzheng REN1,2( ), Zhixin KE1,3, Yehui TAN1,2,3, Kaizhi LI1,3(
), Zhixin KE1,3, Yehui TAN1,2,3, Kaizhi LI1,3( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2019-05-20Revised:2019-07-07Online:2020-03-10Published:2020-03-10 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31670458);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41576125);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41976112);Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province of China(2018B030320005);Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest(201403008)
CLC Number:
- P735.532
Cite this article
Yuzheng REN, Zhixin KE, Yehui TAN, Kaizhi LI. Community structure of zooplankton and its influencing factors in the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island, Guangdong[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 65-76.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
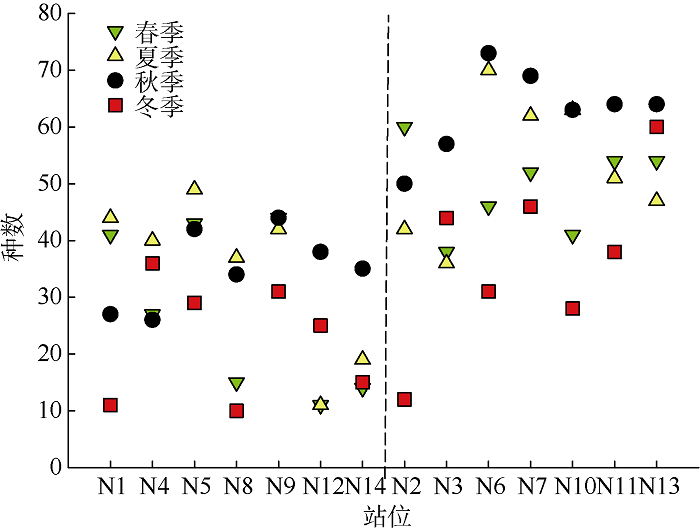
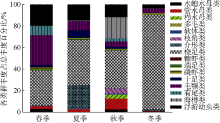
Tab. 1
Species composition of zooplankton in the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island from 2014 to 2016"
| 类群 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | 合计 | 百分比/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水螅水母类 Hydrozoa | 11 | 2 | 18 | 4 | 23 | 11.17 |
| 管水母类 Siphonophorae | 6 | 5 | 8 | 5 | 11 | 5.34 |
| 栉水母类 Ctenophores | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.97 |
| 浮游多毛类 Polychaeta | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 5 | 2.43 |
| 浮游软体类 Mollusca | 0 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1.94 |
| 枝角类 Cladocera | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.97 |
| 介形类 Ostracoda | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 8 | 3.88 |
| 桡足类Copepoda | 63 | 57 | 55 | 54 | 94 | 45.63 |
| 糠虾类 Mysids | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 0.97 |
| 端足类 Amphipods | 7 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 5.34 |
| 磷虾类 Euphaussids | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 6 | 2.91 |
| 十足类 Decapoda | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.97 |
| 毛颚类 Chaetognatha | 13 | 14 | 10 | 11 | 16 | 7.77 |
| 有尾类 Appendicularia | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1.94 |
| 海樽类 Salps | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0.97 |
| 浮游幼虫 Planktonic larvae | 11 | 11 | 13 | 9 | 14 | 6.80 |
| 合计 | 127 | 113 | 135 | 105 | 206 | 100 |
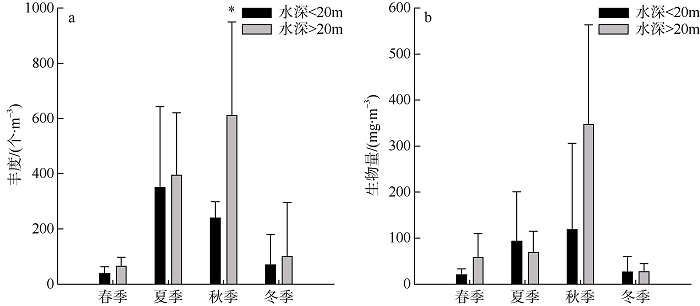
Tab. 2
Variations in the abundance of zooplankton groups in the eastern waters of Nan'ao Island"
| 类群 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水螅水母类 Hydrozoa | 1.60±2.18 | 0.60±1.16 | 10.76±5.67 | 0.43±0.61 |
| 管水母类 Siphonophorae | 1.21±1.57 | 9.24±1 0.60 | 42.53±55.16 | 0.37± 0.63 |
| 栉水母类 Ctenophores | / | 0.36±0.80 | 16.42±39.80 | 0.01±0.05 |
| 浮游多毛类 Polychaeta | / | 0.52±1.13 | 0.34±0.77 | / |
| 浮游软体类 Mollusca | 0.01±0.05 | 2.43±3.32 | 3.68±4.39 | 0.02±0.06 |
| 枝角类 Cladocera | 0.04±0.10 | 1.25±2.45 | 19.44±19.78 | 0.10±0.38 |
| 介形类 Ostracoda | 0.32±0.93 | 79.32±109.19 | 1.37±2.51 | 1.39±1.58 |
| 桡足类 Copepod | 16.78±9.51 | 156.65±96.11 | 150.19±137.25 | 74.58±146.28 |
| 糠虾类 Mysids | 0.03±0.11 | / | 0.19±0.70 | / |
| 端足类 Amphipods | 0.52±0.82 | 3.75±3.53 | 2.55±4.99 | 0.38±0.62 |
| 磷虾类 Euphaussids | 0.86±0.83 | 2.44±1.93 | 2.49±2.16 | 0.92±0.93 |
| 十足类 Decapoda | 1.20±1.93 | 26.48±34.15 | 8.52±7.24 | 0.10±0.22 |
| 毛颚类 Chaetognatha | 14.29±12.07 | 31.21±24.30 | 20.82±18.47 | 3.37±2.59 |
| 有尾类 Appendicularians | 4.32±9.06 | 0.71±1.10 | 12.61±11.59 | 0.02±0.06 |
| 海樽类 Salps | 0.11±0.28 | 1.61±2.14 | 83.30±106.38 | 0.19±0.53 |
| 浮游幼虫 Planktonic larvae | 10.24±3.97 | 55.38±54.21 | 50.17±28.42 | 3.15±4.23 |
Tab. 3
Composition, abundance, and dominance of dominant species of zooplankton in the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island"
| 种类 | 春季 | 夏季 | 秋季 | 冬季 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 丰度/(个·m-3) | 优势度 | 丰度/(个·m-3) | 优势度 | 丰度/(个·m-3) | 优势度 | 丰度/(个·m-3) | 优势度 | |
| 球型侧腕水母 Pleurobrachia globosa | - | - | - | - | 16.2±39.9 | 0.03 | - | - |
| 双生水母 Diphyes chamissonis | - | - | - | - | 20.1±33.5 | 0.04 | - | - |
| 细浅室水母 Lensia subtilis | - | - | - | - | 9.3±16.4 | 0.02 | - | - |
| 鸟喙尖头溞 Penilia avirostris | - | - | - | - | 19.0±19.1 | 0.04 | - | - |
| 针刺真浮萤 Euconchoecia aculeata | - | - | 33.1±50.5 | 0.07 | - | - | - | - |
| 后圆真浮萤 Euconchoecia maimai | - | - | 45.5±58.3 | 0.10 | - | - | - | - |
| 锥形宽水蚤 Temora turbinata | - | - | 16.2±24.6 | 0.04 | 32.7±58.3 | 0.08 | - | - |
| 小拟哲水蚤 Paracalanus parvus | 1.3±1.0 | 0.02 | 11.7±13.3 | 0.03 | - | - | 5.8±11.5 | 0.06 |
| 精致真刺水蚤 Euchaeta concinna | 2.5±2.8 | 0.03 | - | - | - | - | 6.6±4.7 | 0.07 |
| 瘦拟哲水蚤 Paracalanus gracilis | - | - | 11.4±17.0 | 0.02 | - | - | 4.9±12.0 | 0.03 |
| 微刺哲水蚤 Canthocalanus pauper | - | - | - | - | 47.8±81.9 | 0.12 | 3.2±5.1 | 0.02 |
| 中华哲水蚤 Calanus sinicus | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.8±2.8 | 0.02 |
| 奥氏胸刺水蚤 Centropages orsinii | 1.5±1.9 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 异尾宽水蚤 Temora discaudata | 1.6±2.0 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 红纺锤水蚤 Acartia erythraea | - | - | 47.9±50.4 | 0.12 | - | - | - | - |
| 钳形歪水蚤 Tortanus forcipatus | - | - | 11.0±10.8 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - |
| 中型莹虾 Lucifer intermedius | - | - | 26.5±38.5 | 0.06 | - | - | - | - |
| 肥胖软箭虫 Flaccisagitta enflata | - | - | 17.9±18.6 | 0.04 | 13.1±15.9 | 0.02 | - | - |
| 百陶带箭虫 Zonosagitta bedoti | 6.4±10.0 | 0.09 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 红住囊虫 Oikopleura rufescens | 1.4±3.1 | 0.02 | - | - | 7.7±6.3 | 0.02 | - | - |
| 长尾住囊虫 Oikopleura longicauda | 1.7±2.7 | 0.03 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 小齿海樽 Doliolum denticulatum | - | - | - | - | 78.5±105.4 | 0.17 | - | - |
| 长尾类幼虫 Macrura larvae | 4.3±2.2 | 0.08 | 17.4±16.2 | 0.05 | 21.7±17.5 | 0.05 | 1.5±1.9 | 0.02 |
Tab. 5
Comparisons of zooplankton between the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island and other coastal embayments"
| 海域 | 调查时间/(年.月) | 网目孔径/μm | 桡足类种数 | 总丰度 /(个·m-3) | 总生物量 /(mg·m-3) | 多样性指数 | 均匀度 | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mediterranean Coast | 1984.01—1985.12 | 200 | 30 | 1.5×103 | - | 3.25 | 0.56 | |
| Little Bay | 1995.10—1996.07 | 90 | - | 2.4×104 | - | 1.47 | 0.44 | |
| La Garonne Bay | 1995.10—1996.07 | 90 | - | 3.3×103 | - | 2.19 | 0.65 | |
| Niel Bay | 1995.10—1996.07 | 90 | - | 2.5×103 | - | 2.13 | 0.69 | |
| 柘林湾 | 2000.07—2001.07 | 200 | 57 | 6.8×103 | 115.7 | 2.43 | 0.72 | |
| 柘林湾 | 2001.04—2002.04 | 169 | 60 | 1.5×104 | 227.8 | 2.49 | 0.69 | |
| 东山湾 | 2007.03—2007.11 | 505 | 37 | 982.30 | 163.2 | 3.01 | 0.70 | |
| 南澳岛北部海域 | 2011.04—2012.02 | 505 | 52 | 144.67 | 98.67 | 2.80 | 0.75 | |
| 诏安湾及毗邻海域 | 2015.08—2015.10 | 505 | 54 | 421.00 | 144.5 | 2.80 | - | |
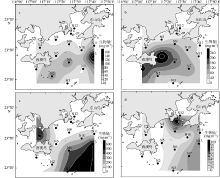
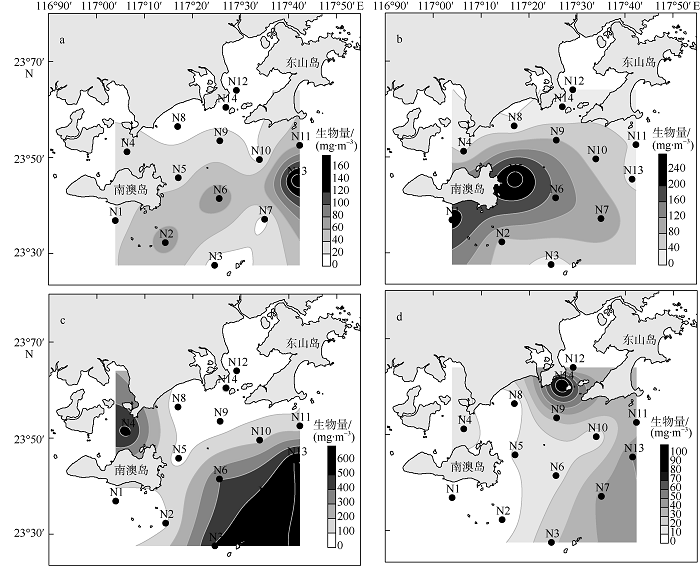
| 南澳岛东部海域 | 2014.09—2016.07 | 505 | 94 | 233.48 | 94.8 | 3.51 | 0.67 | 本文 |
| 1 | 蔡尚湛, 吴日升, 许金电 , 2011. 2006年夏季粤东至闽南近岸海域上升流的特征[J]. 台湾海峡, 30(4):489-497. |
| CAI SHANGZHAN, WU RISHENG, XU JINDIAN, 2011. Characteristics of upwelling in eastern Guangdong and southern Fujian coastal waters during 2006 summer[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 30(4):489-497 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 2 | 戴红, 董炜峰, 陈瑶 , 等, 2018. 诏安湾及毗邻海域浮游动物的群落结构[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 37(1):135-140. |
| DAI HONG, DONG WEIFENG, CHEN YAO, et al, 2018. Community characters of zooplankton in and near Zhao’an Bay[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 37(1):135-140 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 3 | 黄长江, 陈善文, 何歆 , 等, 2003. 2001—2002年粤东柘林湾浮游动物的生态学研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 34(2):117-130. |
| HUANG CHANGJIANG, CHEN SHANWEN, HE XIN, et al, 2003. Ecological study of zooplankton in Zhelin Bay of eastern Guangdong: 2001-2002[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 34(2):117-130 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 4 | 黄小平, 张景平, 江志坚 , 2015. 人类活动引起的营养物质输入对海湾生态环境的影响机理与调控原理[J]. 地球科学进展, 30(9):961-969. |
| HUANG XIAOPING, ZHANG JINGPING, JIANG ZHIJIAN, 2015. Eco-environmental effects of nutrients input caused by human activities on the semi-enclosed bay and its management strategy[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 30(9):961-969 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 5 | 姜胜, 黄长江, 陈善文 , 等, 2002. 2000—2001年柘林湾浮游动物的群落结构及时空分布[J]. 生态学报, 22(6):828-840. |
| JIANG SHENG, HUANG CHANGJIANG, CHEN SHANWEN, et al, 2002. Community structure and temporal and spatial distribution of zooplankton in Zhelin Bay, China (2000-2001)[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 22(6):828-840 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 6 | 柯志新, 陈丹婷, 谭烨辉 , 等, 2019. 汕头南澳—东山海域初级生产力的时空特征[J]. 中国水产科学, 26(1):44-52. |
| KE ZHIXIN, CHEN DANTING, TAN YEHUI, et al, 2019. Temporal and spatial variations in primary production in the coastal region of Dongshan-Nan’ao[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 26(1):44-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 7 | 刘陈, 魏南, 王庆 , 等, 2019. 广东汕头南澳岛近岸海域浮游植物群落结构与环境特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 25(5):1091-1098. |
| LIU CHEN, WEI NAN, WANG QING, et al, 2019. Phytoplankton community and environmental characteristics in the coastal waters of Nan’ao Island, Shantou, Guangdong[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 25(5):1091-1098 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 8 | 彭璇, 马胜伟, 陈海刚 , 等, 2014. 夏季柘林湾—南澳岛海洋牧场营养盐的空间分布及其评价[J]. 南方水产科学, 10(6):27-35. |
| PENG XUAN, MA SHENGWEI, CHEN HAIGANG, et al, 2014. Spatial distribution and assessment of nutrients in marine ranching in Zhelin Bay-Nanao Island in summer[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 10(6):27-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 9 | 舒业强, 王强, 俎婷婷 , 2018. 南海北部陆架陆坡流系研究进展[J]. 中国科学 D辑: 地球科学, 61(5):560-571. |
| SHU YEQIANG, WANG QIANG, ZU TINGTING, 2018. Progress on shelf and slope circulation in the northern South China Sea[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 61(5):560-571 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 10 | 孙鲁峰, 柯昶, 徐兆礼 , 等, 2013. 上升流和水团对浙江中部近海浮游动物生态类群分布的影响[J]. 生态学报, 33(6):1811-1821. |
| SUN LUFENG, KE CHANG, XU ZHAOLI, et al, 2013. The influence of upwelling and water mass on the ecological group distribution of zooplankton in Zhejiang coastal waters[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(6):1811-1821 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 11 | 孙鲁峰, 李秀启, 徐兆礼 , 2017. 东山湾浮游动物数量特征与养殖活动及水团关系分析[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 32(4):465-472. |
| SUN LUFENG, LI XIUQI, XU ZHAOLI, 2017. Relationship between quantity characteristics of zooplankton and aquaculture activity and water masses in Dongshan bay[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 32(4):465-472 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 12 | 孙松, 李超伦, 张光涛 , 等, 2011. 胶州湾浮游动物群落长期变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 42(5):625-631. |
| SUN SONG, LI CHAOLUN, ZHANG GUANGTAO, et al, 2011. Long-term changes in the zooplankton community in the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 42(5):625-631 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 13 | 王翠, 郭晓峰, 方婧 , 等, 2018. 闽浙沿岸流扩展范围的季节特征及其对典型海湾的影响[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 37(1):1-8. |
| WANG CUI, GUO XIAOFENG, FANG JING, et al, 2018. Characteristics of seasonal spatial expansion of Fujian and Zhejiang Coastal Current and their bay effects[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 37(1):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 14 | 王亮根, 杜飞雁, 陈丕茂 , 等, 2016. 南澳岛北部海域浮游动物生态学特征及水团影响[J]. 南方水产科学, 12(5):23-33. |
| WANG LIANGGEN, DU FEIYAN, CHEN PIMAO, et al, 2016. Ecological characteristics of zooplankton and impact of water masses in the northern waters of Nan’ao Islands[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 12(5):23-33 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 15 | 许金电, 黄奖, 邱云 , 等, 2015. 浙闽沿岸水的空间结构特征及生消过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(1):1-7. |
| XU JINDIAN, HUANG JIANG, QIU YUN, et al, 2015. Spatial structure characteristics of Zhejiang and Fujian coastal water and their evolution[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 34(1):1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 16 | 徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿 , 1989. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 8(4):13-15, 19. |
| XU ZHAOLI, CHEN YAQU, 1989. Aggregated intensity of dominant species of zooplankton in autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 8(4):13-15, 19 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 17 | 尹健强, 黄良民, 李开枝 , 等, 2013. 南海西北部陆架区沿岸流和上升流对中华哲水蚤分布的影响[J]. 海洋学报, 35(2):143-153. |
| YIN JIANQIANG, HUANG LIANGMIN, LI KAIZHI, et al, 2013. Effects of coastal current and upwelling on the distributions of Calanus sinicus on the northwest continental shelf of the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(2):143-153 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 18 | 郑惠东 , 2009. 福建东山湾浮游动物的种类组成与数量分布特点[J]. 福建水产, (2):11-17. |
| ZHENG HUIDONG, 2009. Species composition and distribution of zooplankton in Dongshan Bay[J]. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, (2):11-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 19 | 郑重, 李少菁, 许振祖 , 1984. 海洋浮游生物学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-653(in Chinese). |
| 20 | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2008. GB/T 12763.6-2007 海洋调查规范第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| GENERAL ADMINISTRATION OF QUALITY SUPERVISION, INSPECTION AND QUARANTINE OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF CHINA, STANDARDIZATION ADMINISTRATION OF CHINA, 2008. GB/T 12763.6-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese). | |
| 21 | 庄伟, 王东晓, 吴日升 , 等, 2005. 2000年夏季福建、广东沿海上升流的遥感与船舶观测分析[J]. 大气科学, 29(3):438-444. |
| ZHUANG WEI, WANG DONGXIAO, WU RISHENG, et al, 2005. Coastal upwelling off eastern Fujian-Guangdong detected by remote sensing[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 29(3):438-444 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 22 | BEAUGRAND G, REID P C, IBAÑEZ F , et al, 2002. Reorganization of North Atlantic marine copepod biodiversity and climate[J]. Science, 296(5573):1692-1694. |
| 23 | JAMET J L, BOGÉ G, RICHARD S , et al, 2001. The zooplankton community in bays of Toulon area (northwest Mediterranean Sea, France)[J]. Hydrobiologia, 457(1-3):155-165. |
| 24 | LI KAI ZHI, YIN JIANQIANG, HUANG LIANGMIN , et al, 2012. Comparison of siphonophore distributions during the southwest and northeast monsoons on the northwest continental shelf of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 34(7):636-641. |
| 25 | Li KAIZHI, YIN JIANQIANG, HUANG LIANGMIN , et al, 2013 Spatio-temporal variations in the siphonophore community of the northern South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 31(2):312-326. |
| 26 | LI KAIZHI, YIN JIANQIANG, TAN YEHUI , et al, 2014. Short-term variation in zooplankton community from Daya Bay with outbreaks of Penilia avirostris[J]. Oceanologia, 56(3):583-602. |
| 27 | SHANNON C E , 1948. A mathematical theory of communication[J]. The Bell System Technical Journal, 27(3):379-423. |
| 28 | SIOKOU-FRANGOU I, PAPATHANASSIOU E, LEPRETRE A , et al, 1998. Zooplankton assemblages and influence of environmental parameters on them in a Mediterranean coastal area[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 20(5):847-870. |
| 29 | SKJOLDAL H R, WIEBE P H, POSTEL L , et al, 2013. Intercomparison of zooplankton (net) sampling systems: results from the ICES/GLOBEC sea-going workshop[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 108:1-42. |
| 30 | SUTTON T T , 2013. Vertical ecology of the pelagic ocean: classical patterns and new perspectives[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 83(6):1508-1527. |
| 31 | WHITTAKER R H , 1972. Evolution and measurement of species diversity[J]. Taxon, 21(2-3):213-251. |
| 32 | w |
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [3] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [4] | LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [5] | GENG Wanlu, XING Yongze, ZHANG Qiufeng, GUAN Weibing. Structural characteristics of macrobenthic communities at intertidal zone for mangrove in Beihai, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lanlan, CHENG Xiawen, XIANG Rong, QIU Zhuoya, CHANG Hu. Changes of radiolarian community structure with depth in the central Bay of Bengal in spring 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [7] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [8] | LI Ruofei, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, LIU Jiaxin, TAN Yehui. Vertical distribution of zooplankton in the “Haima” cold seep region based on ZooScan image analysis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 87-96. |
| [9] | CHEN Jingfu, ZHONG Yu, WANG Lei, GUO Yupei, QIU Dajun. Noctiluca scintillans effects on eukaryotic plankton community structure using Environmental DNA analysis in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [10] | MA Wengang, XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang, LI Xiubao, WANG Aimin. Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [11] | YIN Tianqi, WANG Qing, YANG Yufeng, CEN Jingyi. Comparative study on zooplankton community structure in Pearl River Estuary based on morphological and DNA identification [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 172-185. |
| [12] | YIN Jianqiang, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui. Bathyconchoecia nanshaensis sp. nov. (Myodocopa, Halocyprididae), a new species of ostracod from the southern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 193-197. |
| [13] | LI Kaizhi, KE Zhixin, WANG Junxing, TAN Yehui. Preliminary study on the community structure of zooplankton in coral reef waters of Xisha Islands* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [14] | ZHU Wentao, XIA Jingquan, LIU Xiangbo, YIN Hongyang, ZHU Ming, REN Yuxiao, XIE Minrui, HUANG Jianzhong, LI Xiubao. Analysis of photosynthetic physiology and symbiotic fungi community in Galaxea fascicularis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 132-141. |
| [15] | MA Mengzhen, LI Qian, WU Zhengchao, CHEN Yinchao, YU Jiancheng. Underwater glider observation of oxygen minimum zone in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 131-142. |
|
||