Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 50-64.doi: 10.11978/2024240CSTR: 32234.14.2024240
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
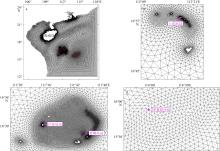
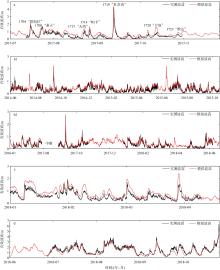
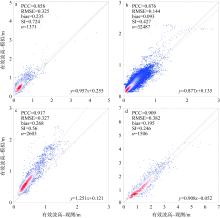
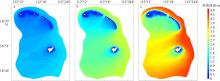
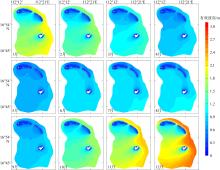
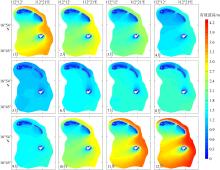
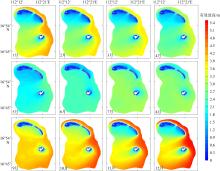
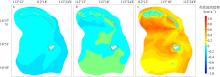
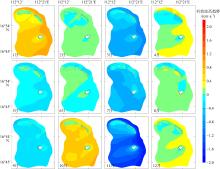
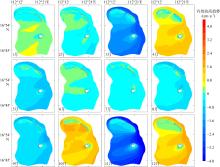
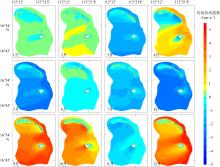
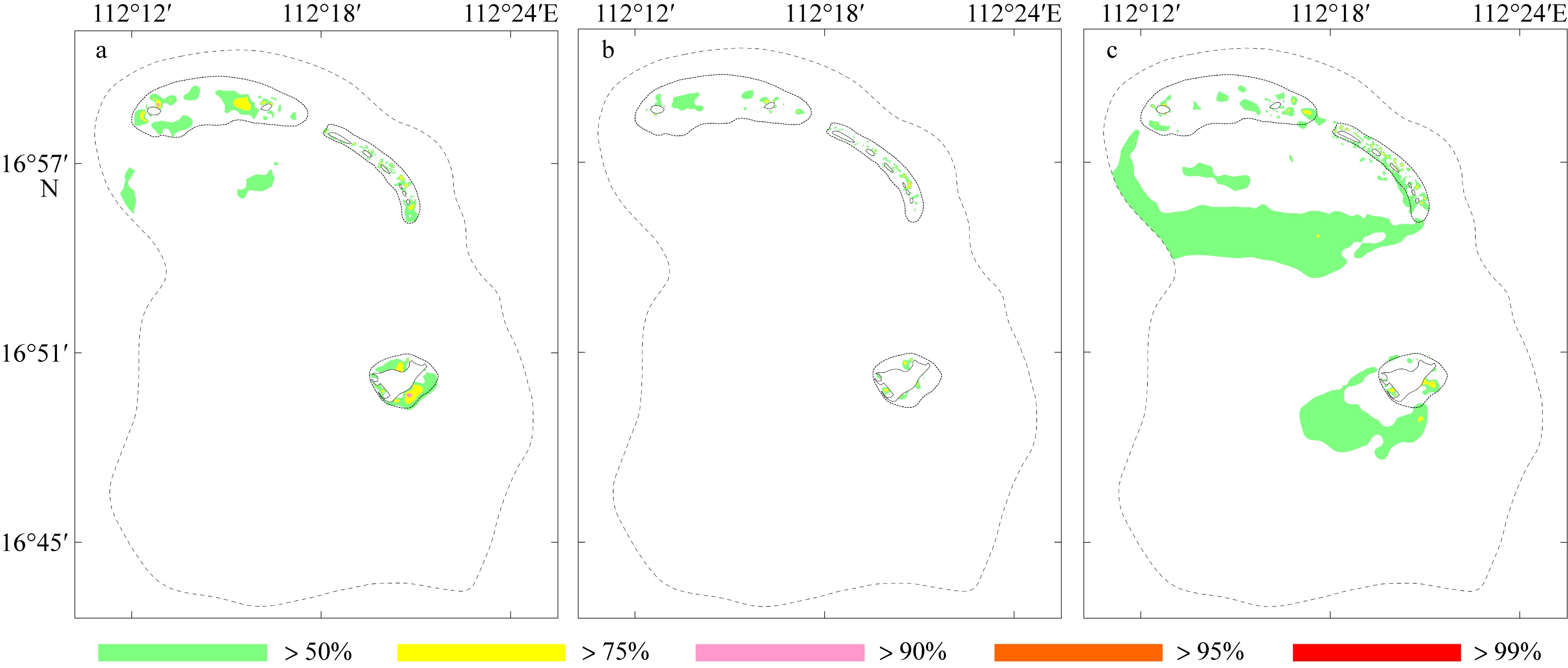
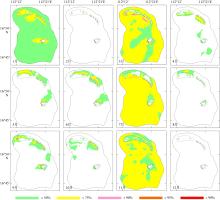
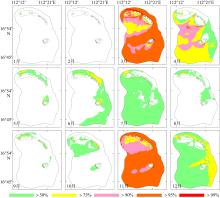
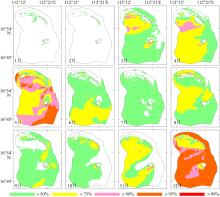
Wave distribution characteristics of Xuande Atoll, Xisha Islands*
QIU Liguo( ), LIANG Xiaoli, CHEN Bin, WANG Shengjian, WANG Fayun(
), LIANG Xiaoli, CHEN Bin, WANG Shengjian, WANG Fayun( )
)
- Hainan Academy of Ocean and Fisheries Sciences, Haikou 571126, China
-
Received:2024-12-25Revised:2025-03-10Online:2025-09-10Published:2025-10-14 -
Contact:WANG Fayun -
Supported by:Research project surplus funds of Hainan Academy of Marine and Fishery Sciences(JYJF20231226)
CLC Number:
- P731.22
Cite this article
QIU Liguo, LIANG Xiaoli, CHEN Bin, WANG Shengjian, WANG Fayun. Wave distribution characteristics of Xuande Atoll, Xisha Islands*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 50-64.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] |
白珍胜, 宗智, 孙泽, 等, 2020. 基于WAVEWATCH Ⅲ的近岛礁波浪演化研究[J]. 船舶力学, 24(10): 1261-1269.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
董进, 2019. 南海近岛礁波浪演化数值模拟研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
何其江, 刘刚, 王雪木, 等, 2021. 西沙群岛宣德环礁的精细水下地貌组合特征及其成因机制[J]. 海洋学报, 43(8): 81-92.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1126/science.1197219 pmid: 21436400 |
| [1] | CHEN Yuchen, FU Dongyang, TAO Bangyi, LI Jizhe, ZHU Yixian, LIU Bei, LIN Ye, CHAI Xia. Study on remote sensing monitoring and time series change of shallow sea topography of typical islands and reefs in the South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(5): 140-153. |
| [2] | LI Wei, QU Ke, WANG Chao, YU Renshi, ZHANG Ze. Experimental study on the influence of submerged breakwater on the wave characteristics of infragravity waves on coral reefs [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(4): 177-186. |
| [3] | XIONG Xin, FENG Yingci, YANG Renhui, SUN Jie, LI Jian, ZHAN Wenhuan, LYU Kaiyun. Study on the characteristics of internal solitary waves in the Dongsha area of the northern South China Sea based on acoustic backscatter data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(3): 14-23. |
| [4] | ZHONG Danni, YAO Yu, ZHOU Ting. Study on wave transformation and run-up around the three-dimensional barrier reef under the action of solitary waves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 39-47. |
| [5] | WANG Chao, QU Ke, WANG Xu, GAO Rongze, WANG Aoyu. Influences of artificial fish reef on wave hydrodynamics of solitary wave on an uneven fringing reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 30-38. |
| [6] | ZHOU Xiangrun, WANG Ying, ZHI Hai. Distribution characteristics and mechanism of the Northwest Pacific marine heatwaves in the summer of 2022* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 82-92. |
| [7] | LIU Jie, YAN Tong, JING Zhiyou. Observations of near-inertial waves generated by three successive typhoons in the northwestern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 66-81. |
| [8] | JIANG Rouyun, JIAN Lili, SHI Songbiao, TIAN Xinpeng. Diversity of culturable bacteria in the sedimentary sands of the Meiji Reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 170-180. |
| [9] | YUAN Yu, XU Haiming, MA Jing, ZHANG Tong. Impact of Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on interannual relationship between ENSO and early summer marine heatwaves in the Western Pacific* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 1-16. |
| [10] | LI Junmin, LI Bo, CHEN Wuyang, LIU Junliang. Observation characteristics of coastal waves in Sanya and their responses to typhoon processes [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 25-35. |
| [11] | CHU Xiaoqing, PENG Qihua. The role of alongshore wind and ocean wave in generating the northward Somali Current [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 1-8. |
| [12] | LI Yanjie, ZHU Yousheng, CHEN Guanjun, WANG Shu, WANG Weiwei. Analysis of shallow surface fine geological characteristics and hazard factors of the seabed in the northern part of Dongsha, South China Sea based on AUV data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 114-123. |
| [13] | TANG Ling, NIE Yuhua, WANG Ping, TANG Chaolian. Trend analysis of marine heatwaves variability in the outer Pearl River estuary from 1974 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 143-150. |
| [14] | XIE Jieshuo, GONG Yankun, NIU Jianwei, HE Yinghui, CHEN Zhiwu, XU Jiexin, CAI Shuqu. Spatial-temporal variations of the dynamic parameters of internal solitary waves in the Sulu-Celebes Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 132-142. |
| [15] | CHEN Mei, XIA Zhen, LIU Wentao, HE Jian, MA Shengzhong. Geohazards characteristics in the southeast of Xuande Atoll, Xisha, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 103-111. |
|
||