Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 82-92.doi: 10.11978/2024036CSTR: 32234.14.2024036
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Distribution characteristics and mechanism of the Northwest Pacific marine heatwaves in the summer of 2022*
ZHOU Xiangrun1( ), WANG Ying1(
), WANG Ying1( ), ZHI Hai2
), ZHI Hai2
- 1. School of Marine Sciences, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
2. School of Atmospheric Sciences, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2024-02-05Revised:2024-03-06Online:2025-01-10Published:2025-02-10 -
Contact:WANG Ying -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41905089); Science and Technology Innovation Project of Laoshan Laboratory(LSKJ202202403)
CLC Number:
- P732.6
Cite this article
ZHOU Xiangrun, WANG Ying, ZHI Hai. Distribution characteristics and mechanism of the Northwest Pacific marine heatwaves in the summer of 2022*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 82-92.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Definition of marine heatwave characteristic index"
| 指标 | 英文名称 | 定义 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 阈值 | threshold | 气候基准期内第90百分位数的海温(记为T90) | ℃ |
| 起始时间 | start time | Td≥T90d且Td-1<T90d的这一天, 即热浪开始的日期, 记为ts | |
| 结束时间 | finish time | Td<T90d且Td-1≥T90d的这一天, 即热浪结束的日期, 记为te | |
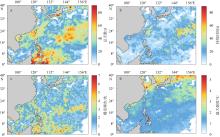
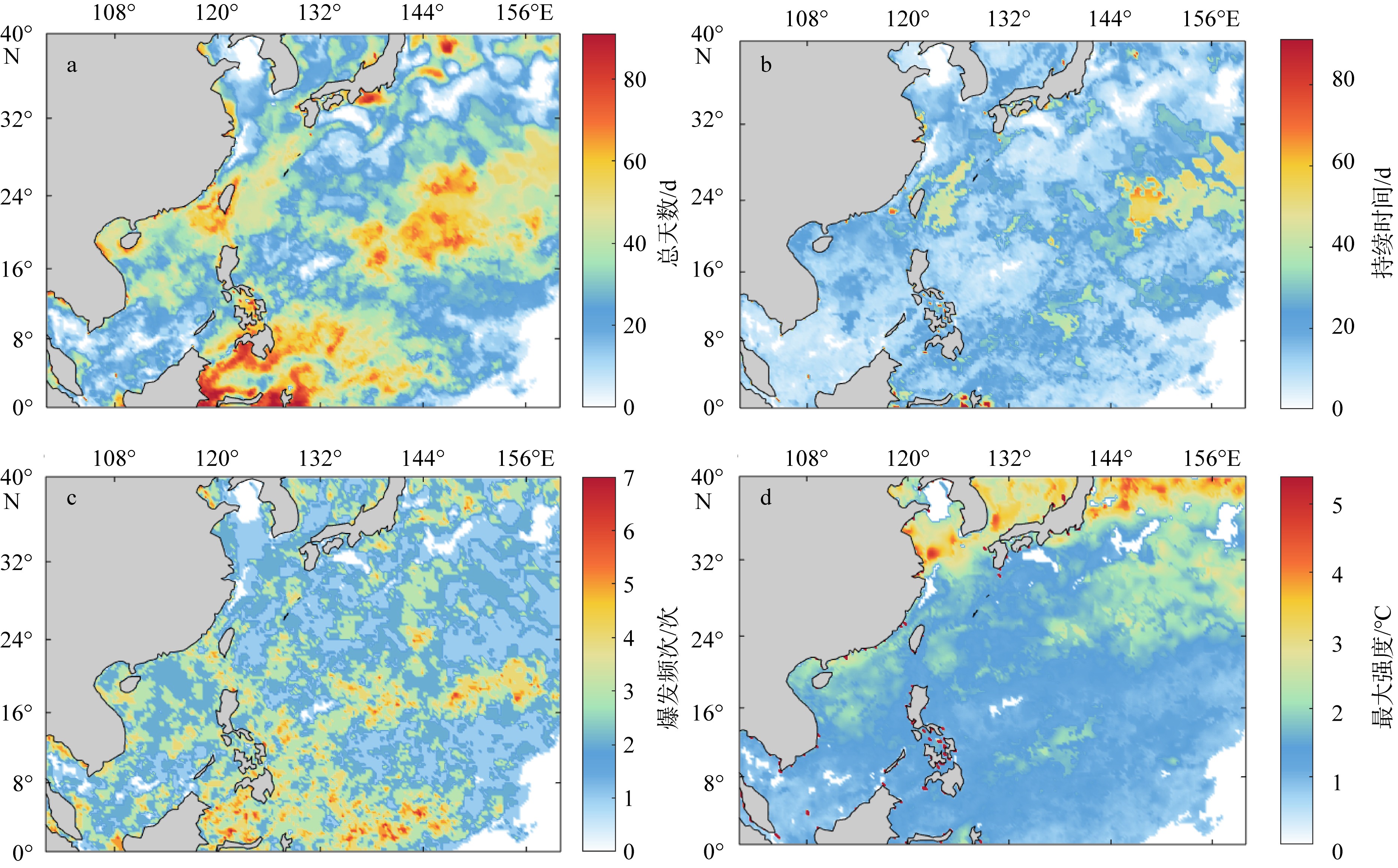
| 总天数 | total days | 某时段热浪日的累加和即为总天数 | d |
| 爆发频次 | frequency | 从ts开始到te结束且te−ts≥5, 记为一次热浪, 某时段发生的热浪次数之和即为爆发频次 | |
| 持续时间 | duration | te−ts即为持续时间 | d |
| 最大强度 | max intensity | imax = max(Td−Tmd) | ℃ |
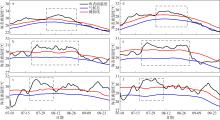
Fig. 3
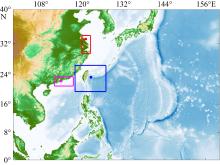
From July 1 to September 30, 2022, the marine heatwaves occurred at (a) station in the offshore area of Jiangsu (Fig. 2 red dot point station); (b) station in the Kuroshio basin near Taiwan (Fig. 2 blue dot point station); (c) station in the offshore area of Guangdong ( Fig. 2 pink dot point station); (d) the offshore area of Jiangsu (Fig. 2 red box); (e) the Kuroshio basin near Taiwan (Fig. 2 blue box); (f) the offshore area of Guangdong (Fig. 2 pink box). The dotted line frame represents the marine heatwave analyzed in this paper"

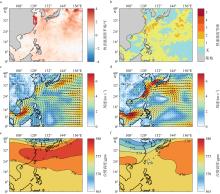
Fig. 4
(a) Sea surface temperature anomaly field and (b) intensity level of the peak time of the marine heatwave (August 15, 2022); (c) 10 m average wind speed and wind direction field and (e) 500 hPa average geopotential height during the marine heatwave period (August 4 to August 31); (d) 10 m average wind speed and wind direction field and (f) 500 hPa average geopotential height during the non-marine heatwave period (September 1 to September 30) in the offshore area of Jiangsu (red box area)"

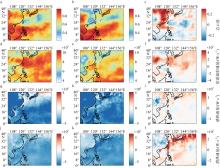
Fig. 5
The average total cloud cover, shortwave radiation flux, sensible heat flux and latent heat flux during marine heatwave period (left column) (August 4 to August 31) and non-marine heatwave period (middle column) (September 1 to September 30), and the difference of four meteorological data between two periods (right column ) in the offshore area of Jiangsu. Vertical fluxes are all positive"
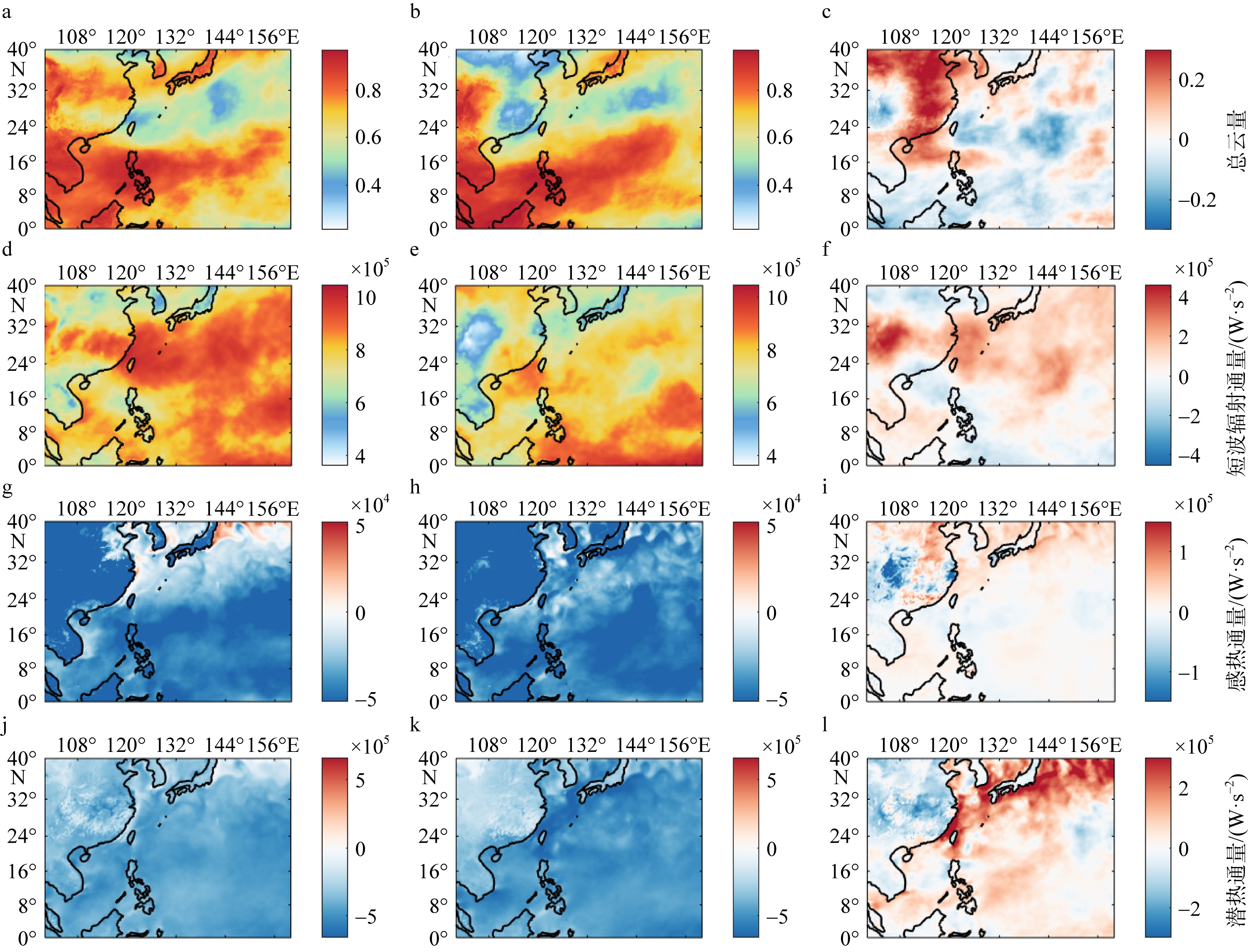
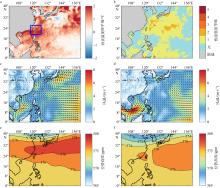
Fig. 6
(a) Sea surface temperature anomaly field and (b) intensity level of the peak time of the marine heatwave (July 26, 2022); (c) 10 m average wind speed and wind direction field and (e) 500 hPa average geopotential height during the marine heatwave period (July 21 to September 1); (d) 10 m average wind speed and wind direction field and (f) 500 hPa average geopotential height during the non-marine heatwave period (July 1 to July 20, September 2 to September 30) in the Kuroshio basin near Taiwan (blue box area)"

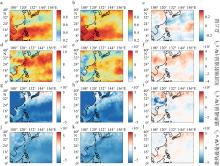
Fig. 7
The average total cloud cover, shortwave radiation flux, sensible heat flux and latent heat flux during marine heatwave period (left column) (July 21 to September 1) and non-marine heatwave period (middle column) (July 1 to July 20, September 2 to September 30), respectively; the difference of four meteorological data between two periods (right column) in the Kuroshio basin near Taiwan. Vertical fluxes are all positive"
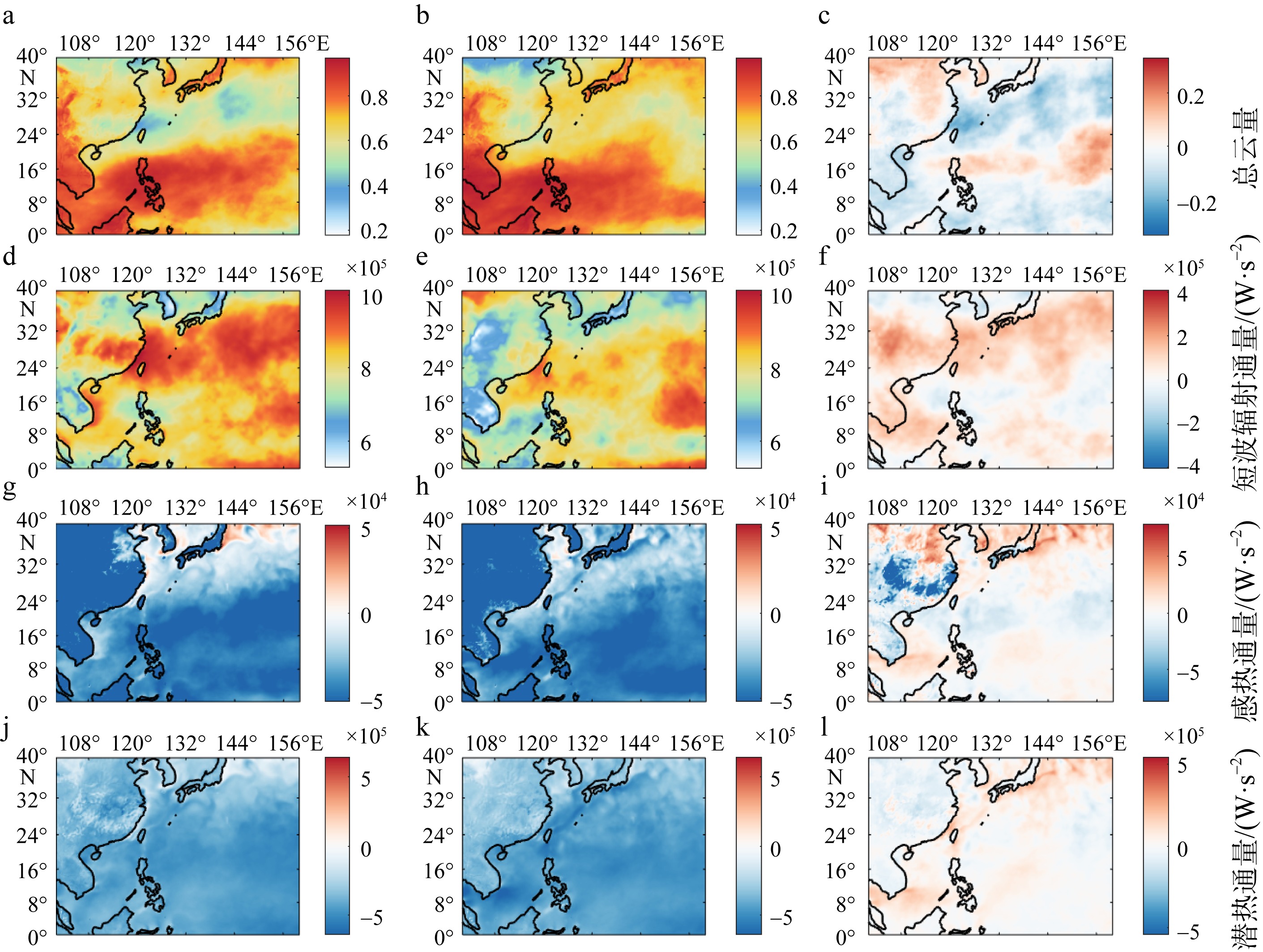
Fig. 8
(a) Sea surface temperature anomaly field and (b) intensity level of the peak time of the marine heatwave (July 25, 2022); (c) 10 m average wind speed and wind direction field and (e) 500 hPa average geopotential height during the marine heatwave period (July 19 to August 9); (d) 10 m average wind speed and wind direction field and (f) 500 hPa average geopotential height during the non-marine heatwave period (July 1 to July 18) in the offshore area of Guangdong (pink box area)"
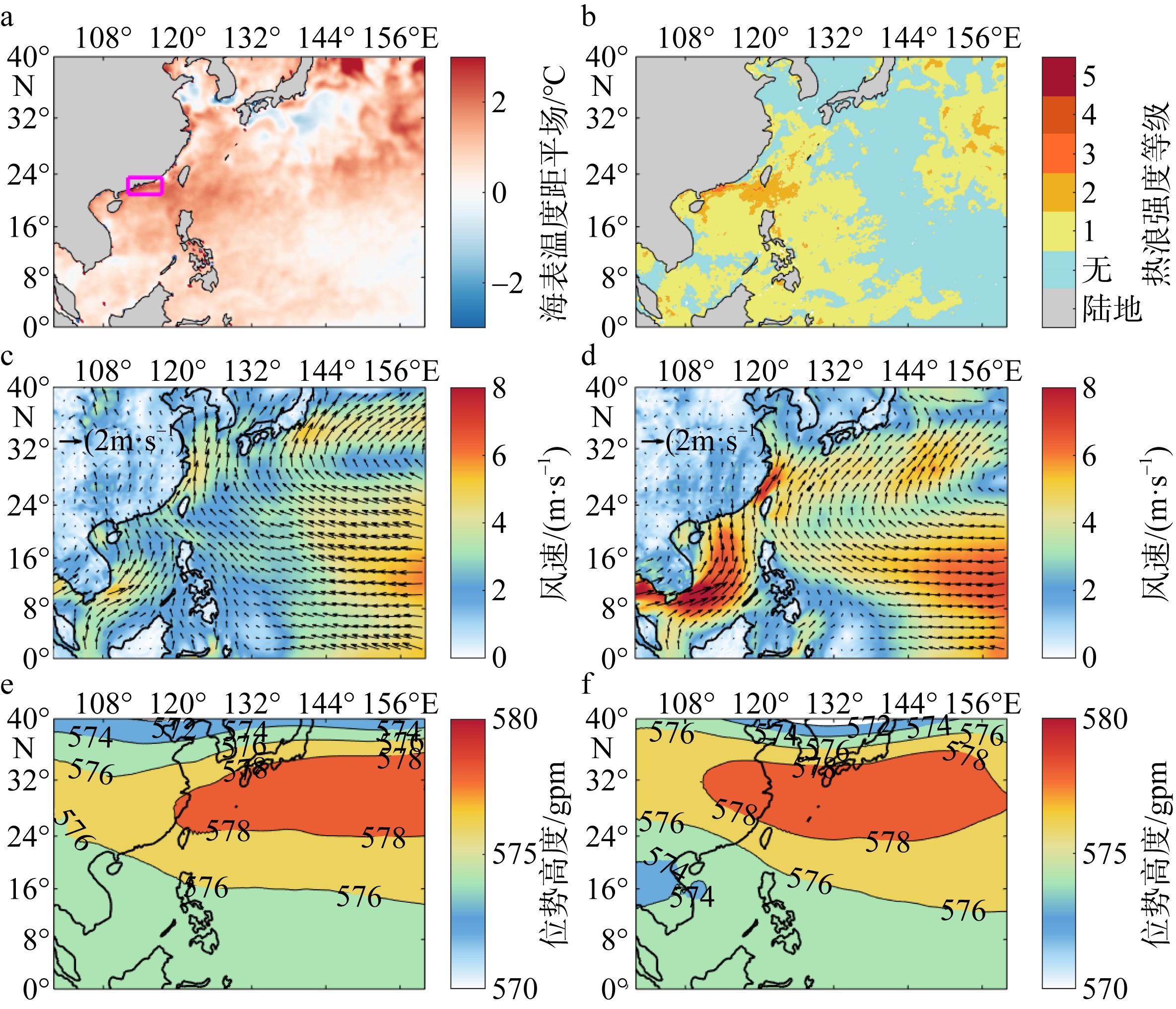
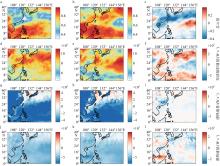
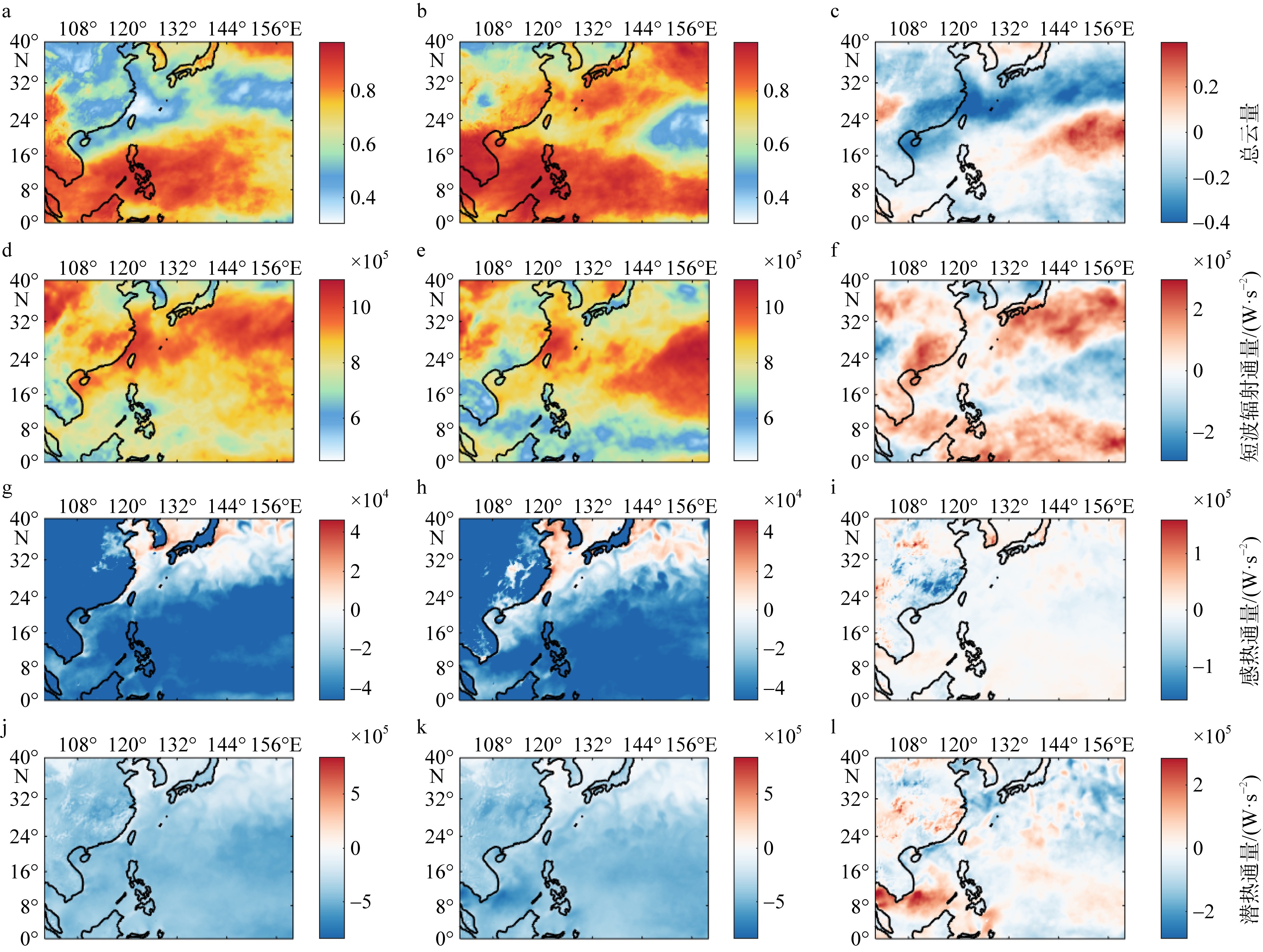
Fig. 9
The average total cloud cover, shortwave radiation flux, sensible heat flux and latent heat flux during marine heatwave period (left column) (July 19 to August 9) and non-marine heatwave period (middle column) (July 1 to July 18), and the difference of four meteorological data between two periods (right column) in the offshore area of Guangdong. Vertical fluxes are all positive"
| [1] |
高川, 陈茂楠, 周路, 等, 2022. 2020-2021年热带太平洋持续性双拉尼娜事件的演变[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 52(12): 2353-2372.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
胡石建, 李诗翰, 2022. 海洋热浪研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 37(1): 51-64.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
李泓, 李丽平, 王盘兴, 2001. 太平洋地区海气系统年代际变率研究的若干进展[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 24(4): 591-598.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
缪予晴, 徐海明, 刘佳伟, 2021. 西北太平洋夏季海洋热浪的变化特征及海气关系[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(1): 31-43.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
王庆元, 李清泉, 李琰, 等, 2021. 1982—2019年渤、黄海海洋热浪时空变化特征分析[J]. 海洋学报, 43(12): 38-49.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
王越奇, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等, 2019. 近千年来台湾以东黑潮主流区沉积物来源及其对气候波动的响应[J]. 海洋科学进展, 37(2): 231-244.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
张荣华, 高川, 王宏娜, 等, 2021. 中间型海洋-大气耦合模式及其ENSO模拟和预测[M]. 北京: 科学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [8] |
张荣华, 2024. 用于厄尔尼诺-南方涛动(ENSO)研究的海气耦合模式综述: 中间型和混合型模式[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 55(1): 1-23.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [1] | SUN Zeming, HAN Shuzong, WANG Mingjie, SU Hanxiang. Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 17-31. |
| [2] | YUAN Yu, XU Haiming, MA Jing, ZHANG Tong. Impact of Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on interannual relationship between ENSO and early summer marine heatwaves in the Western Pacific* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 1-16. |
| [3] | WENG Shaojia, CAI Jinhai, PANG Yunxi, LUO Rongzhen. Application of convolutional neural network to sea surface temperature prediction in the coastal waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 40-47. |
| [4] | TANG Ling, NIE Yuhua, WANG Ping, TANG Chaolian. Trend analysis of marine heatwaves variability in the outer Pearl River estuary from 1974 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 143-150. |
| [5] | MIAO Yuqing, XU Haiming, LIU Jiawei. Variation of summer marine heatwaves in the Northwest Pacific and associated air-sea interaction [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 31-43. |
| [6] | LIU Lei, XU Lanfang, GUAN Hongxiang, SUN Zhilei, WANG Libo, MAO Shengyi, LIU Lihua, WU Nengyou. The source of glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraethers and temperature reconstruction since 8.2 ka in the central Okinawa Trough [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 77-92. |
| [7] | Yequ LIU, Shilin TANG. Study on the characteristics of high-frequency variation of Qiongdong upwelling in summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 1-12. |
| [8] | CHEN Wuyang, LI Junmin, HE Qingyou, TANG Shilin, SHI Ping. Spatial-temporal variation of sea surface chlorophyll around islands and reefs in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(6): 21-28. |
| [9] | Ke FANG,Jinhua YU. Influence of sea surface temperature gradients in the tropical Pacific and Indian oceans of the Northern Hemisphere on the frequency of tropical cyclone generation in the western North Pacific in summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 42-51. |
| [10] | Haoliang WU, Song HU. Effect of environmental factors on the intensity of Typhoons Wutip and Mirinae in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 26-34. |
| [11] | Yanping SHI, Yan DU, Zesheng CHEN. Impacts of Northwest Pacific anomalous anticyclone on sea surface height and circulation [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(4): 10-17. |
| [12] | Zilong LIU, Jian SHI, Guorong JIANG, Lin XIAO. Response of tropical SST to non-breaking surface wave-induced vertical mixing in a climate model [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(4): 77-86. |
| [13] | Tiantian GUO, Shengbo CHEN, Tianqi LU. The inversion of multiple-phase SSTs based on the MODIS data: a case study on the southwest coastal waters of Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(1): 9-14. |
| [14] | LI Xue, FU Dongyang, ZHANG Ying, LIU Dazhao, DING Youzhuan, WANG Wenfang, LUAN Hong, JIANG Chengfei. The impacts of super typhoon Rammasun on the environment of the northwestern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(6): 19-28. |
| [15] | WANG Minyang, LUO Yiyong, DU Yan. The variation of tropical instability waves in the Pacific Ocean and its relationship to ENSO* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(3): 41-47. |
|
||