Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 79-88.doi: 10.11978/2018084CSTR: 32234.14.2018084
Previous Articles Next Articles
[RETRACTED] Species composition of coralline algae and its spatial characteristics related to environmental factors in Sanya coral reefs, China
Xinming LEI1,2,Hui HUANG1,2,3( ),Jiansheng LIAN1,2,Yuyang ZHANG1,2,Jianhui YANG1
),Jiansheng LIAN1,2,Yuyang ZHANG1,2,Jianhui YANG1
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, Guangzhou 510301
3. CAS Tropical Marine Biological Research Station in Hainan, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Sanya 572000, China
-
Received:2018-08-16Revised:2018-09-27Online:2019-05-20Published:2019-06-17 -
Contact:Hui HUANG E-mail:huanghui@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41306144);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41676150);National Key Research and Development Plan(2017YFC0506301);Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA13020402);Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China(2017B0303014052)
CLC Number:
- Q948.8
Cite this article
Xinming LEI, Hui HUANG, Jiansheng LIAN, Yuyang ZHANG, Jianhui YANG. [RETRACTED] Species composition of coralline algae and its spatial characteristics related to environmental factors in Sanya coral reefs, China[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 79-88.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
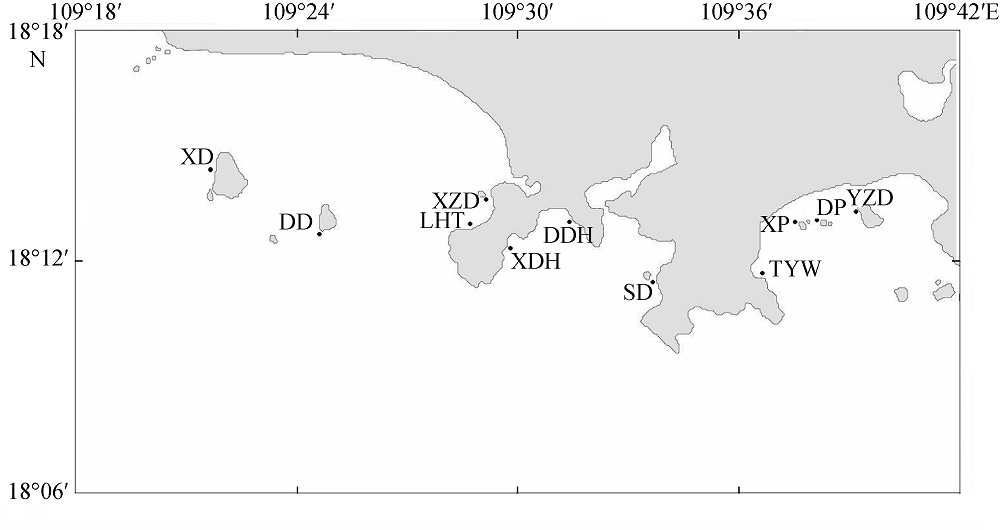
Species list and distribution in the study area"
| 珊瑚藻种类 | 站位 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西岛 | 东岛 | 小洲岛 | 鹿回头 | 小东海 | 大东海 | 野猪岛 | 东排 | 西排 | 太阳湾 | 神岛 | |
| 叉节藻Amphiroa ephedraea | + | + | + | - | + | + | |||||
| 宽扁叉节藻A. anceps | + | + | |||||||||
| 美丽叉节藻 A. beauvoisii | + | ||||||||||
| 矮型石叶藻Lithophyllum pygmaeum | + | + | |||||||||
| *微凹石叶藻L. kotschyanum | + | + | |||||||||
| 三叉新角石藻Neogoniolithon trichotomum | + | ||||||||||
| 太平洋新角石藻N. pacificum | + | + | |||||||||
| 串胞新角石藻N. fosliei | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||
| 变胞新角石藻N. variabile | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 锥窝新角石藻N. conicum | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 巨大新角石藻N. megalocystum | + | ||||||||||
| 撒切尔新角石藻 N. setchellii | + | + | |||||||||
| *小石孔藻Lithoporella melobesioides | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| *太平洋小石孔藻L. pacifica | + | + | + | ||||||||
| *孔石藻Porolithon onkodes | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| *水石藻Hydrolithon reinboldii | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| 布氏水石藻H. boergesenii | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||
| 圆锥呼叶藻Pneophyllum conicum | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 太平洋石枝藻Lithothamnion pacificum | + | + | + | + | |||||||
| 中间石枝藻L. intermedium | + | + | |||||||||
| 尖顶石枝藻L. aculeiferum | + | ||||||||||
| 石枝藻 Lithothamnion sp. | + | ||||||||||
| *中叶藻Mesophyllum mesomorphum | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |||
| *拟中叶藻M. simulans | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | ||||
| *孢石藻Sporolithon erythraeum | + | + | + | + | |||||||
Tab. 2
Contribution of each taxa group (percentage of the total) collected from each study site"
| 站位 | 珊瑚藻所占比例/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 珊瑚藻科 | 混石藻科 | 孢石藻科 | |
| 西岛 | 70.59 | 11.76 | 17.65 |
| 东岛 | 50 | 50 | 0 |
| 小洲岛 | 80.95 | 19.05 | 0 |
| 鹿回头 | 15 | 75 | 10 |
| 小东海 | 67.65 | 32.35 | 0 |
| 大东海 | 95.24 | 0 | 4.76 |
| 神岛 | 72.22 | 27.78 | 0 |
| 太阳湾 | 77.27 | 18.18 | 4.55 |
| 西排 | 77.27 | 18.18 | 4.55 |
| 东排 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 野猪岛 | 95.83 | 4.17 | 0 |
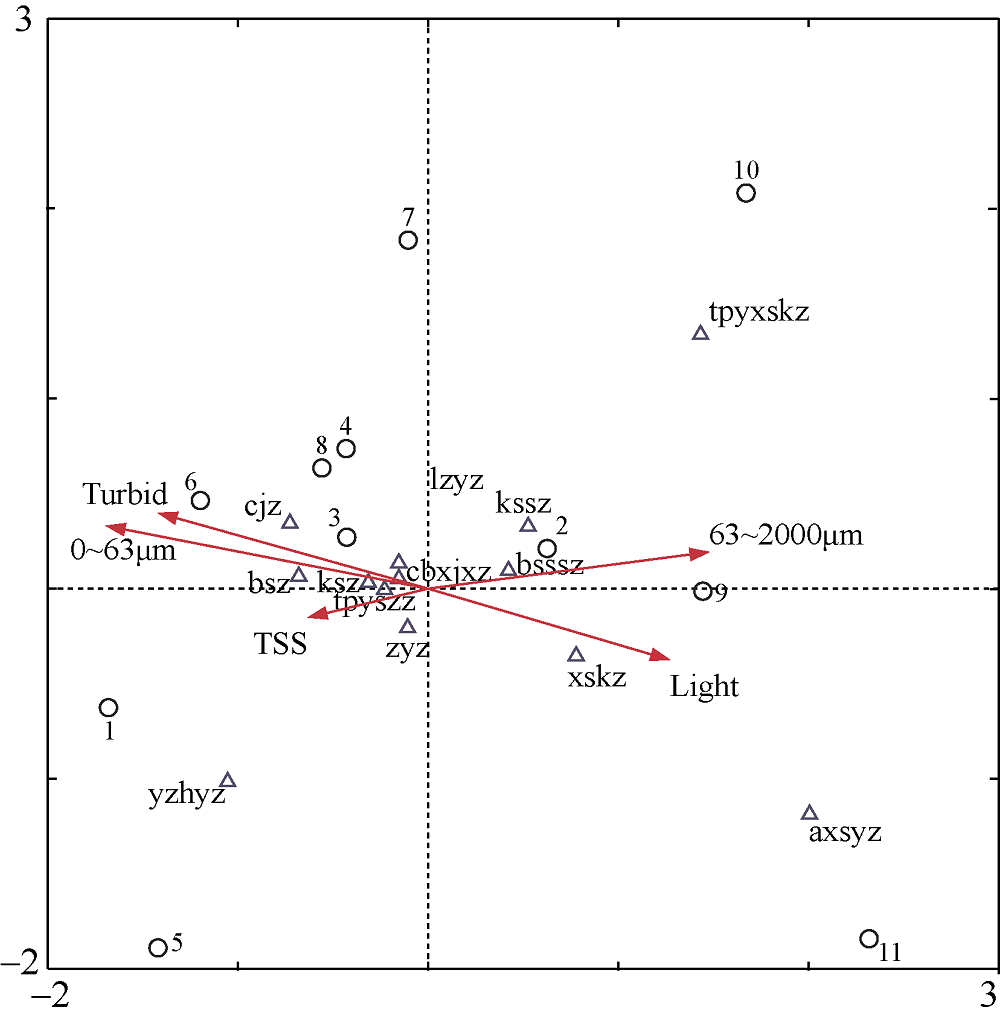
Fig. 4
CCA analysis between the main species of coralline algae composition and environmental variables (Turbid: turbidity; 0~63μm and 63~2000μm represent different deposition rates; TSS: total suspended solids; Light: light attenuation coefficient. Numbers from 1 to 11 represent stations: Xidao, Dongdao, Xiaozhoudao, Luhuitou, Xiaodonghai, Dadonghai, Shendao, Taiyangwan, Xipai, Dongpai, Yezhudao. Species abbreviation are as follows. cjz: Amphiroa ephedraea; lzyz: Mesophyllum simulans; cbxjxz: Neogoniolithon fosliei; zyz: Mesophyllum mesomorphum; yzhyz: Pneophyllum conicum; axsyz: Lithophyllum pygmaeum; ksz: Porolithon onkodes; tpyxskz: Lithoporella pacifica; xskz: Lithoporella melobesioides; bsssz: Hydrolithon boergesenii; kssz: Hydrolithon onkodes; tpyszz: Lithothamnion pacificum; bsz: Sporolithon erythraeum"
Tab. 4
Summary of CCA analysis between the main species of coralline algae composition and environmental variables"
| 轴1 | 轴2 | 总变异 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 环境因子与排序轴的相关系数 | 浊度 | -0.699 | 0.158 | |
| 光照 | 0.625 | -0.149 | ||
| 总悬浮物含量 | -0.308 | -0.060 | ||
| 沉积速率(0~63μm) | -0.835 | 0.131 | ||
| 沉积速率(63~2000μm) | 0.728 | 0.077 | ||
| 排序轴的 统计结果 | 特征根 | 0.353 | 0.205 | |
| 物种-环境相关性 | 0.935 | 0.835 | ||
| 累计变异百分数 | ||||
| 物种数据 | 20.7 | 32.8 | ||
| 物种-环境数据 | 41.4 | 65.5 | ||
| 特征根之和 | 1.705 | |||
| 典型特征根之和 | 0.853 |
| [1] | 李秀保 , 2011. 三亚造礁石珊瑚群落组成、时空分布及主要影响因子识别研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院: 1-115. |
| LI XIUBAO . 2011. Identification of major factors influencing the composition, spatial and temporal variation of scleractinian coral community in Sanya China[D]. Beijing: Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1-115 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 练健生, 黄晖, 黄良民 , 等, 2010. 三亚珊瑚礁及其生物多样性[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-106. |
| LIAN JIANSHENG, HUANG HUI, HUANG LIANGMIN , et al, 2010. Coral reef and its biodiversity of Sanya[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press: 1-106(in Chinese). | |
| [3] |
邢帅, 谭烨辉, 周林滨 , 等, 2012. 水体浑浊度对不同造礁石珊瑚种类共生虫黄藻的影响[J]. 科学通报, 57(5):348-354.
doi: 10.1360/972011-1184 |
|
XING SHUAI, TAN YEHUI, ZHOU LINBIN , et al, 2012. Effects of water turbidity on the symbiotic zooxanthella of hermatypic corals[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(5):348-354 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.1360/972011-1184 |
|
| [4] | 徐兆礼, 陈亚瞿 , 1989. 东黄海秋季浮游动物优势种聚集强度与鲐鲹渔场的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 8(4):13-15. |
| Xu ZHAOLI, CHEN YAQU , 1989. Aggregated intensity of dominant species of Zooplankton in Autumn in the East China Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Ecology, 8(4):13-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 张德瑞, 周锦华 , 1978. 西沙群岛珊瑚藻科的研究Ⅰ[J]. 海洋科学集刊, 12:17-23. |
| ZHANG DERUI, ZHOU JINHUA , 1978. Studies on the Corallinaceae of the Xisha islands, Guangdong Province, China. Ⅰ[J]. Studia Marina Sinica, 12:17-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | ADEY W H, TOWNSEND R A, BOYKINS W T , 1982. The crustose coralline algae (Rhodophyta: Corallinaceae) of the Hawaiian Islands[M]. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press: 1-74. |
| [7] |
ANTHONY K R N, KLINE D I, DIAZ-PULIDO G , et al, 2008. Ocean acidification causes bleaching and productivity loss in coral reef builders[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(45):17442-17446.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804478105 |
| [8] | BARNES D J, CHALKER B E , 1990. Calcification and photosynbook in reef-building corals and algae[M] // DUBINSKY Z. Ecosystems of the world. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Elsevier. |
| [9] | BRAGA J C, BOSENCE D W J, STENECK R S , 1993. New anatomical characters in fossil coralline algae and their taxonomic implications[J]. Palaeontology, 36:535-547. |
| [10] | BRODIE J, ZUCCARELLO G C , 2007. Systematics of the species-rich algae: Red algal classification, phylogeny and speciation[M] //HODKINSON R T, PARNELL J, WALDREN S. The taxonomy and systematics of large and species-rich taxa: building and using the tree of life. Boca Raton: CRC Press: 323-336. |
| [11] |
CARAGNANO A, COLOMBO F, RODONDI G , et al, 2009. 3-D distribution of nongeniculate corallinales: a case study from a reef crest of South Sinai (Red Sea, Egypt)[J]. Coral Reefs, 28(4):881-891.
doi: 10.1007/s00338-009-0524-6 |
| [12] | CLARKE K R, GORLEY R N , 2006a. Primer V6: user manual/tutorial[M]. Plymouth: Primer-E :1-126. |
| [13] | CLARKE K R, WARWICK R M , 2006b. Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation[M]. Plymouth: PRIMER-E. |
| [14] |
FABRICIUS K, DE’ATH G , 2001. Environmental factors associated with the spatial distribution of crustose coralline algae on the Great Barrier Reef[J]. Coral Reefs, 19(4):303-309.
doi: 10.1007/s003380000120 |
| [15] | FARR T, BROOM J, HART D , et al, 2009. Common coralline algae of northern New Zealand: an identification guide[M]. Wellington: NIWA:1-125. |
| [16] |
GARBARY D J, JOHANSEN H W , 1982. Scanning electron microscopy of Corallina and Haliptilon (Corallinaceae, Rhodophyta): surface features and their taxonomic implications[J]. Journal of Phycology, 18(2):211-219.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.1982.18.issue-2 |
| [17] |
HARVEY A S, WOELKERLING W J , 2007. A guide to nongeniculate coralline red algal (Corallinales, Rhodophyta) rhodolith identification[J]. Ciencias Marinas, 33(4):411-426.
doi: 10.7773/cm |
| [18] |
HEYWARD A J, NEGRI A P , 1999. Natural inducers for coral larval metamorphosis[J]. Coral Reefs, 18(3):273-279.
doi: 10.1007/s003380050193 |
| [19] |
HUANG LIANGMIN, TAN YEHUI, SONG XINGYU , et al, 2003. The status of the ecological environment and a proposed protection strategy in Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 47(1-6):180-186.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(03)00070-5 |
| [20] | IRYU Y, MATSUDA S, 1988. Depth distribution, abundance and species assemblages of nonarticulated coralline algae in the Ryukyu Islands, southwestern Japan [C]//Proceedings of the 6th international coral reef symposium. Townsville, Sixth International Coral Reef Symposium Executive Committee, 3:101-106. |
| [21] |
KLUMPP D W, MCKINNON A D , 1992. Community structure, biomass and productivity of epilithic algal communities on the great barrier reef: dynamics at different spatial scales[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 86:77-89.
doi: 10.3354/meps086077 |
| [22] | KUFFNER I B, ANDERSSON A J, JOKIEL P L , et al, 2008. Decreased abundance of crustose coralline algae due to ocean acidification[J]. Nature Geoscience, 1(2):114-117. |
| [23] |
LASKER H R, KIM K , 1996. Larval development and settlement behavior of the gorgonian coral Plexaura kuna (Lasker, Kim and Coffroth)[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 207(1-2):161-175.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(96)02625-1 |
| [24] | LITTLER D S, LITTLER M M , 2003. South Pacific reef plants: a divers' guide to the plant life of South Pacific coral reefs[M]. Washington, D.C.: Offshore Graphics: 1-331. |
| [25] | LITTLER M M, LITTLER D S , 1984. Models of tropical reef biogenesis: the contribution of algae[M] //ROUND F E, CHAPMAN D J. Progress in phycological research. Amsterdam: Elsevier Biomedical Press, 3:323-364. |
| [26] | MAUDSLEY B , 1990. Defenders of the reef[J]. New Scientist, 126(1714):52-56. |
| [27] | MINTON D, CONKLIN E, COUCH C S , et al, 2011. Survey of the coral reefs of Pelekane Bay[R]. Honolulu: The Nature Conservancy: 1-69. |
| [28] |
OLIVER R L, MITROVIC S M, REES C , 2010. Influence of salinity on light conditions and phytoplankton growth in a turbid river[J]. River Research and Applications, 26(7):894-903.
doi: 10.1002/rra.v26:7 |
| [29] |
STELLER D L, FOSTER M S . 1995. Environmental factors influencing distribution and morphology of rhodoliths in Bahía Concepción, B.C.S., México[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 194(2):201-212.
doi: 10.1016/0022-0981(95)00086-0 |
| [30] | STENECK R S, TESTA V, 1997. Are calcareous algae important to reefs today or in the past? [C]// Proceedings of 8th International coral reef symposium. Panama: Balboa, 1:685-688. |
| [31] |
SZMANT A M , 2001. Introduction to the special issue of Coral Reefs on “Coral Reef Algal Community Dynamics” - Why are coral reefs world-wide becoming overgrown by algae? ‘Algae, algae everywhere, and nowhere a bite to eat!’[J]. Coral Reefs, 19(4):299-302.
doi: 10.1007/s003380000130 |
| [32] | TSENG C K , 1983. Common seaweeds of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 1-316. |
| [33] |
VAN DER MEIJ S E T, SUHAR SONO, HOEKSEMA B W , 2010. Long-term changes in coral assemblages under natural and anthropogenic stress in Jakarta Bay (1920-2005)[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 60(9):1442-1454.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.05.011 |
| [34] |
VIDAL R, MENESES I, SMITH M , 2003. Molecular genetic identification of crustose representatives of the order Corallinales (Rhodophyta) in Chile[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 28(3):404-419.
doi: 10.1016/S1055-7903(03)00123-4 |
| [35] |
WALKER D I, ORMOND R F G , 1982. Coral Death from Sewage and Phosphate Pollution at Aqaba, Red Sea[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 13(1):21-25.
doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(82)90492-1 |
| [36] |
WILLIAMS E A, CRAIGIE A, YEATES A , et al, 2008. Articulated coralline algae of the genus Amphiroa are highly effective natural inducers of settlement in the tropical abalone Haliotis asinina[J]. Biological Bulletin, 215(1):98-107.
doi: 10.2307/25470687 |
| [37] |
WILSON S, BLAKE C, BERGES J A , et al, 2004. Environmental tolerances of free-living coralline algae (maerl): implications for European marine conservation[J]. Biological Conservation, 120(2):279-289.
doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2004.03.001 |
| [38] | WOELKERLING W J , 1988. The coralline red algae: an analysis of the genera and subfamilies of nongeniculate corallinaceae[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press: 1-127. |
| [39] |
WOELKERLING W J, HARVEY A , 1993. An account of southern Australian species of Mesophyllum (Corallinaceae, Rhodophyta)[J]. Australian Systematic Botany, 6(6):571-673.
doi: 10.1071/sb9930571 |
| [1] | LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [2] | LIU Yue, LI Li, ZHAI Xiaohui, ZHOU Juan, YE Penghao, HUANG Shengdong. Analysis of the bloom caused by colonial Phaeocystis globosa in Mirs Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 164-171. |
| [3] | MA Wengang, XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang, LI Xiubao, WANG Aimin. Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [4] | Sixuan HE,Binyuan HE. Study on fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 86-97. |
| [5] | Xinming LEI,Hui HUANG,Jiansheng LIAN,Laurence J MCCOOK. The diversity and distribution of coralline algae in China: state of knowledge and research [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 30-40. |
| [6] | FENG Bo, LI Zhong-lu, HOU Gang. Fish species and quantity in the South China Sea surveyed by deep longline [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(1): 64-70. |
| [7] | ZHOU Jie, SHI Qi, YU Ke-fu. Exploration of factors that influence photosynthetic efficiency of symbiotic zooxanthellae of scleractinian corals in a Sanya fringing reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(1): 81-89. |
| [8] | XIAO Yu-zhang, WANG Rong, ZHENG Yan-jing, HE Wei. Species composition and abundance distribution of ichthyoplankton in the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(6): 80-87. |
| [9] | ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Jie-xiang, ZHANG Yu-bin, LU Dong-wei, DING Yu-jing, SUN Xing-li. Temporal and spatial distributions of bacterioplankton biomass and the influenced factors in Shenzhen Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(3): 65-71. |
| [10] | KE Zhi-xin,HUANG Liang-min,TAN Ye-hui,YIN Jian-qiang. Species composition and abundance of phytoplankton in the northern South China Sea in summer 2007 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 131-143. |
| [11] | JIANG Fa-jun,HU Zhang-li,HU Chao-qun. Correlation between spatial-temporal distribution of bacterioplankton and environmental factors in the Dapeng Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 96-100. |
| [12] | SUN Da-wei,OU Lin-jian,QI Yu-zao,CHEN Ju-fang. Dynamics of Skeletonema costatum population and its relationship with environ-mental factors at the Daya Bay, Guangdong Province [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(6): 46-50. |
| [13] | JIANG Xiao,REN Chun-hua,HU Chao-qun,LUO Peng,CHEN Chang,FENG Jing-bi. On dynamic change of Vibrio species in the Daya Bay using molecular identification method [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(4): 154-159. |
| [14] | LI Tao,LIU Sheng,WANG Gui-fen,CAO Wen-xi,HUANG Liang-min,LIN Qiu-yan. Species composition of phytoplankton and its distribution in the northern South China Sea in autumn 2004 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2010, 29(2): 65-73. |
| [15] |
ZHU Ai-jia,HUANG Liang-min,LIN Qiu-yan,XU Zhan-zhou,.
Influence of Nitrogen and Phosphorus on Phytoplankton Community Structure in Dapeng’ao Bay, Daya Bay II Species Composition [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2009, 28(6): 103-111. |
|
||