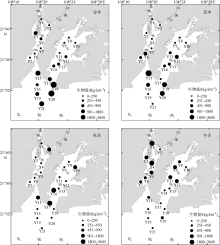
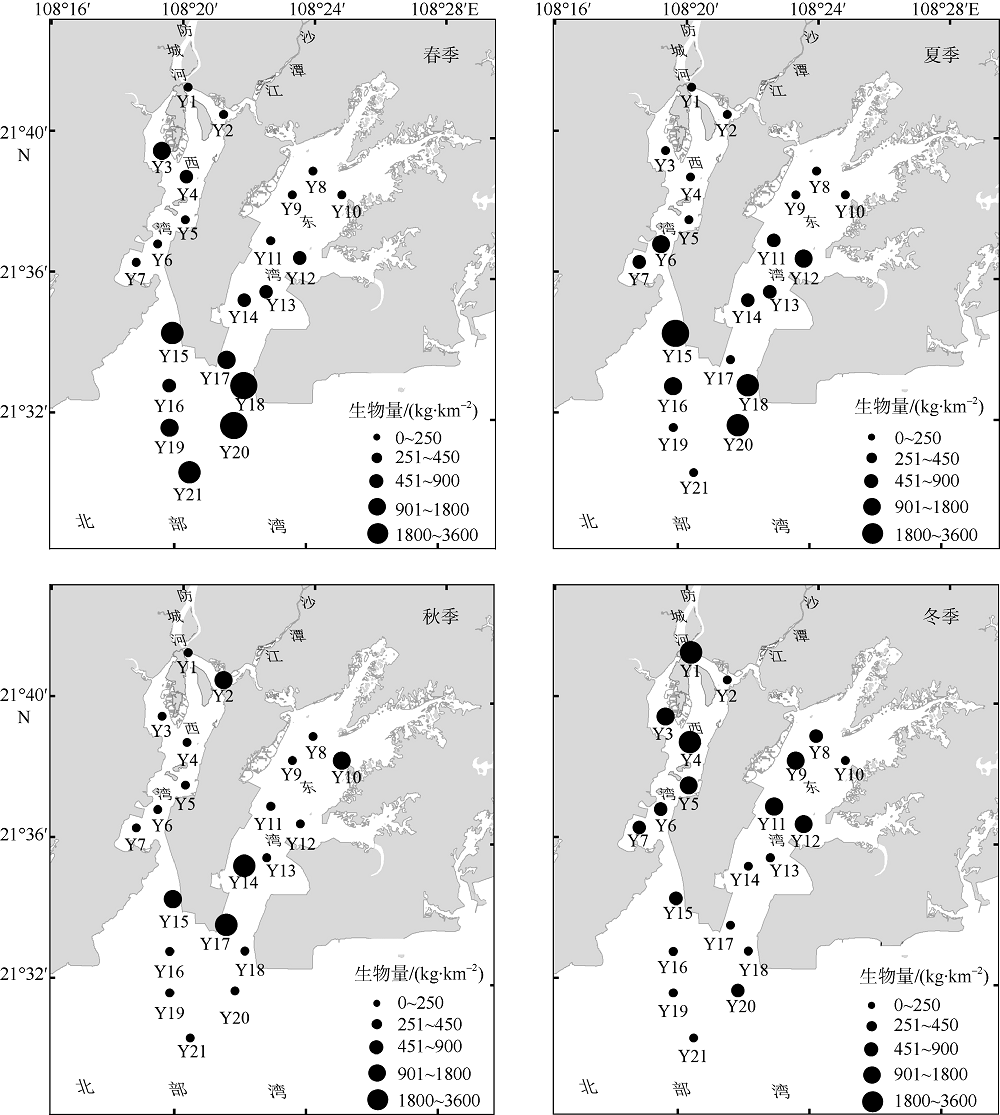
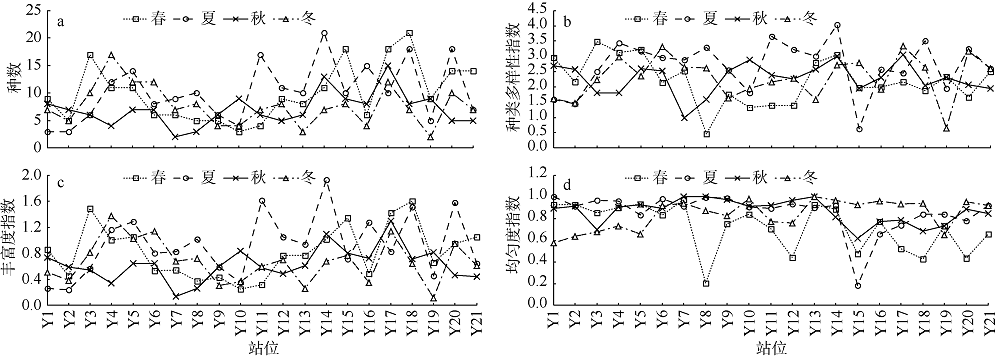
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 86-97.doi: 10.11978/2019001CSTR: 32234.14.2019001
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles
Study on fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China
- 1. College of Life and Environmental Sciences, Minzu University of China, Beijing 100081, China
2. Guangxi Academy of Oceanography, Nanning 530022, China
-
Received:2019-01-01Revised:2019-04-28Online:2019-09-20Published:2019-10-09 -
Contact:Binyuan HE E-mail:hebinyuan2008@126.com -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017YFC0506100);Science and Technology Project of State Oceanic Administration(YLFCJ20164006-F);Science and Technology Project of Guangxi Oceanic Administration(GXHYJ100);Guangxi Science and Technology Project(AA17129002)
CLC Number:
- P735.542
Cite this article
Sixuan HE,Binyuan HE. Study on fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 86-97.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Dominant species and IRI values (units: %) of fish communities in Fangchenghe Estuary"
| 种 类 | 春 | 夏 | 秋 | 冬 | 周年 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 褐菖鲉Sebastiscus marmoratus | 6184.83 | 90.72 | 64.01 | 65.29 | 1592.22 |
| 长鳍篮子鱼Siganus canaliculatus | 66.70 | 1501.39 | 847.94 | 108.15 | 628.84 |
| 黄鳍棘鲷Acanthopagrus latus | 134.21 | 891.46 | 645.73 | 685.55 | 474.57 |
| 条马鲾Equulites rivulatus | 122.54 | 124.17 | 355.10 | 2140.66 | 375.19 |
| 真赤鲷 Pagrus major | 1625.70 | 161.38 | 3.46 | / | 323.73 |
| 李氏? Callionymus richardsoni | 772.46 | 66.03 | 68.24 | 79.14 | 321.84 |
| 多鳞鱚Sillago sihama | 392.25 | 62.43 | 125.24 | 985.59 | 306.39 |
| 日本银鲈Gerres japonicus | 50.97 | 12.16 | 12.00 | 1352.86 | 173.41 |
| 鲬Platycephalus indicus | 74.28 | 138.30 | 317.88 | 144.40 | 138.94 |
| 二长棘犁齿鲷 Evynnis cardinalis | 539.79 | 7.90 | / | 23.51 | 119.65 |
| 斑头舌鳎Cynoglossus puncticeps | 76.97 | 448.16 | 19.39 | 80.75 | 117.18 |
| 高体斑鲆Pseudorhombus elevatus | 275.72 | 7.73 | 138.95 | 22.60 | 102.12 |
| 皮氏叫姑鱼Johnius belengerii | 37.59 | 172.12 | 573.08 | / | 92.67 |
| 粗高鳍鲉Vespicula trachinoides | 54.92 | 222.20 | 59.10 | 73.96 | 80.99 |
| 黑棘鲷Acanthopagrus schlegelii | 2.50 | 257.20 | 134.66 | 51.30 | 76.44 |
| 卵鳎Solea ovata | 1.94 | 137.25 | 426.65 | 78.47 | 71.42 |
| 中国花鲈Lateolabrax maculatus | 78.96 | 88.09 | 67.05 | 21.58 | 67.74 |
| 短吻鲾Leiognathus brevirostris | / | / | 8.72 | 505.31 | 34.13 |
| 鹿斑仰口鲾Secutor ruconius | / | 278.94 | 52.68 | 2.30 | 28.30 |
| 铅点多纪鲀Takifugu alboplumbeus | 15.44 | 37.45 | 30.74 | 38.14 | 26.64 |
| 条纹叫姑鱼Johnius fasciatus | / | 228.55 | 43.58 | / | 25.45 |
| 及达副叶鲹Alepes djedaba | 16.42 | 130.99 | 8.77 | / | 21.10 |
| 红尾银鲈Gerres erythrourus | 9.79 | / | 6.01 | 153.31 | 20.39 |
| 横带棘线鲬Grammoplites scaber | 21.95 | 63.98 | 2.68 | 1.80 | 16.72 |
| 斑纹舌鰕虎鱼Glossogobius olivaceus | 3.43 | / | 6.91 | 101.56 | 15.94 |
| 东方宽箬鳎 Brachirus orientalis | 32.67 | 21.60 | 1.50 | 9.34 | 15.94 |
| 日本钩嘴鳎 Heteromycteris japonicus | 21.88 | / | 2.10 | 68.47 | 12.67 |
| 长棘银鲈 Gerres filamentosus | 8.29 | / | 64.84 | 8.01 | 12.00 |
| 十刺银鲈Gerres decacanthus | / | / | 313.84 | / | 11.62 |
| 大头银姑鱼 Pennahia macrocephalus | 0.48 | 59.19 | 48.76 | / | 11.28 |
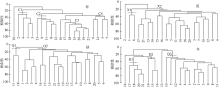
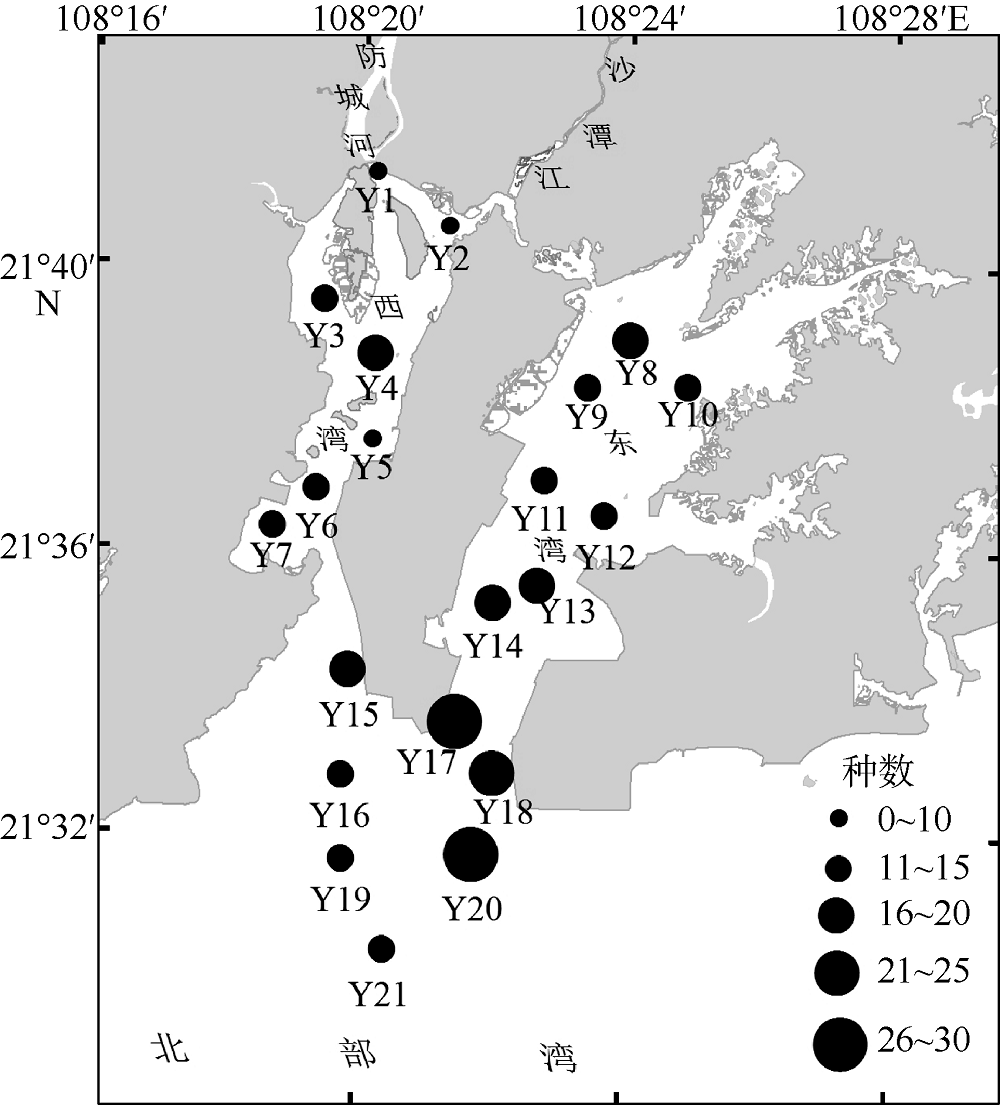
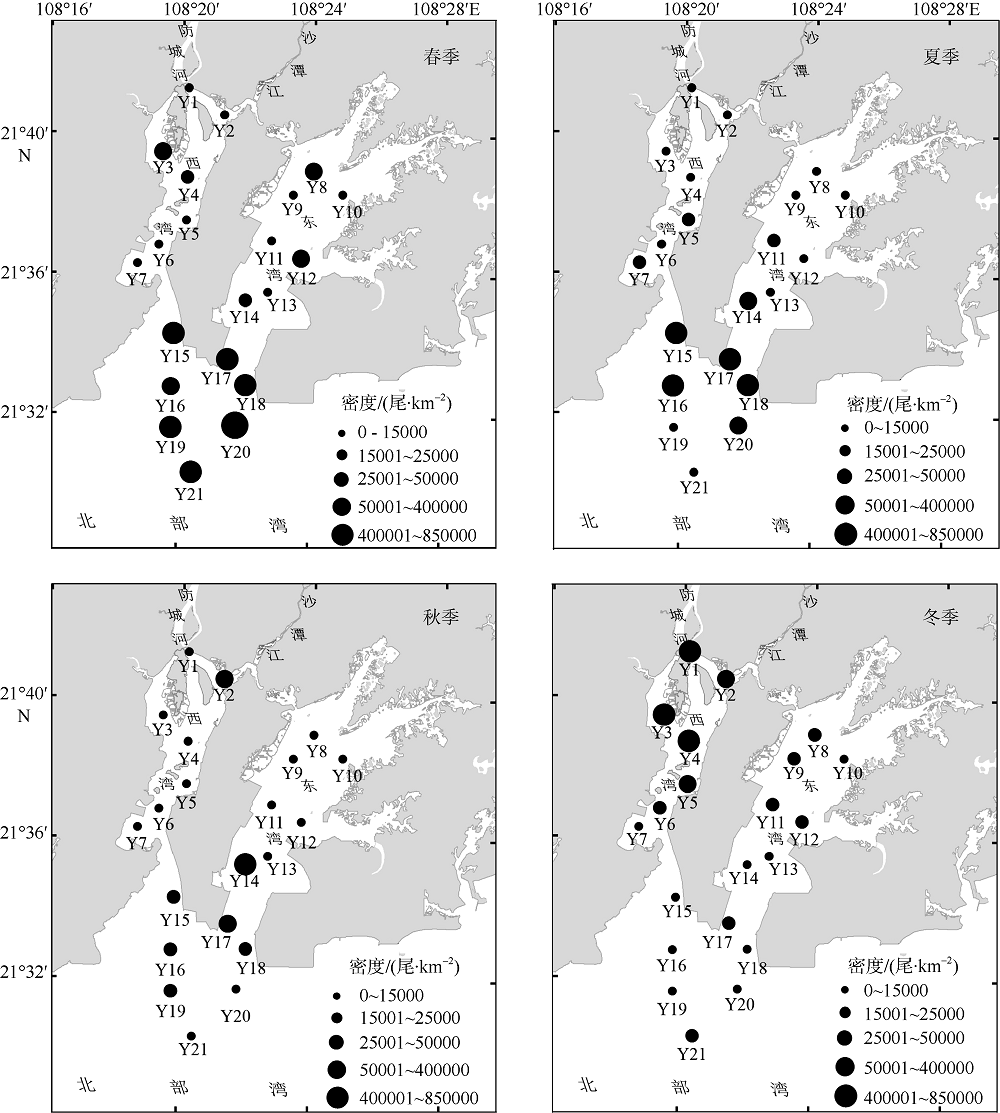
Fig. 5
The hierarchical cluster dendrogram of fish communities in Fangchenghe Estuary. C1~C4 represent the four significantly different station groups in spring. X1 and X2 represent the two significantly different station groups in summer. Q1 and Q2 represent the two significantly different station groups in autumn. D1~D3 represent the three significantly different station groups in winter. The dotted line in the figure represents the range of stations included in each group"
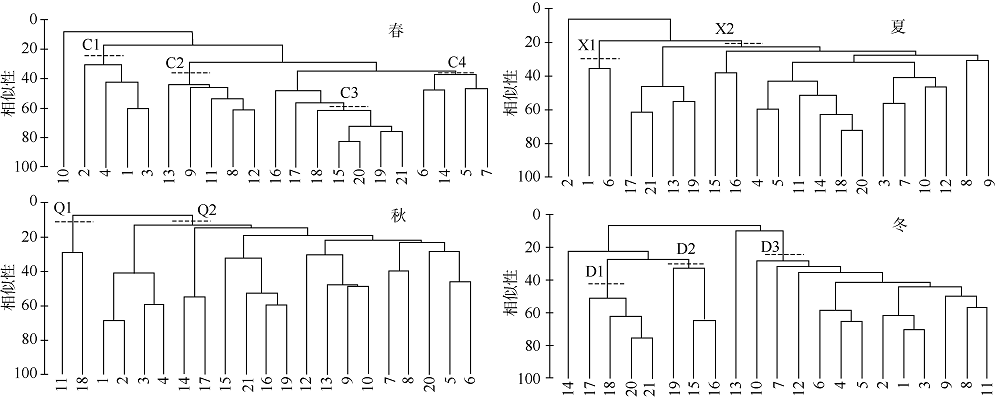
Tab. 2
Correlations between numerical indexes of fish community and their environmental factors in Fangchenghe Estuary"
| 季节 | 数量指标 | 显著正相关因子 | 显著负相关因子 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 春季 | J | 水温、溶解氧饱和度、无机磷 | 水深、盐度 |
| d | / | 悬浮物、COD、亚硝酸、盐硝酸盐、无机氮、总氮、硅酸盐 | |
| H′ | 溶解氧饱和度 | 悬浮物、COD、硝酸盐、氨氮、无机氮 | |
| S | / | COD、硝酸盐、无机氮、总氮 | |
| 生物量 | 盐度 | 水温、硝酸盐 | |
| 密度 | 盐度 | 水温、硝酸盐 | |
| 夏季 | J | 水温 | pH、溶解氧饱和度、BOD |
| d | 盐度 | / | |
| H′ | 水温、盐度 | COD | |
| S | 盐度 | 亚硝酸盐、硝酸盐、无机氮、总氮、无机磷、硅酸盐 | |
| 生物量 | pH、溶解氧饱和度、BOD | 水温 | |
| 密度 | pH、溶解氧饱和度、BOD | 水温 | |
| 秋季 | J | 水色、无机磷、总氮、总磷 | 透明度、硅酸盐 |
| d | 水深 | / | |
| H′ | / | / | |
| S | 透明度 | 水色、无机磷 | |
| 生物量 | / | / | |
| 密度 | / | / | |
| 冬季 | J | 盐度、悬浮物、pH、总磷 | 透明度 |
| d | / | BOD | |
| H′ | / | BOD、叶绿素a | |
| S | / | BOD | |
| 生物量 | / | 盐度、水温、pH | |
| 密度 | 亚硝酸盐、硝酸盐、无机氮、氨氮、总氮、无机磷、硅酸盐 | 水温、悬浮物、pH、盐度 |
| [1] | 崔磊, 吕颂辉, 董悦镭 , 等, 2017. 围填海工程对淇澳岛附近水域环境因子与生物群落的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(2):96-105. |
| CUI LEI, LÜ SONGHUI, DONG YUELEI , et al, 2017. Influence on the biological community and environmental factors around Qi’ao Island caused by reclamation project[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(2):96-105 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 单秀娟, 陈云龙, 戴芳群 , 等, 2014. 黄海中南部不同断面鱼类群落结构及其多样性[J]. 生态学报, 34(2):377-389. |
| SHAN XIUJUAN, CHEN YUNLONG, DAI FANGQUN , et al, 2014. Variations in fish community structure and diversity in the sections of the central and southern Yellow Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(2):377-389 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 傅昕龙, 徐兆礼, 阙江龙 , 等, 2019. 北部湾西北部近海鱼类资源的时空分布特征研究[J]. 水产科学, 38(1):10-18. |
| FU XINLONG, XU ZHAOLI, QUE JIANGLONG , et al, 2019. Temporal-spatial distribution characteristics of fish stocks in north-west coastal waters of Beibu Gulf[J]. Fisheries Science, 38(1):10-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] |
管伟, 徐兆礼, 陈佳杰 , 2017. 福建南日岛南部水域鱼类群落结构及多样性[J]. 生态学报, 37(9):3172-3181.
doi: 10.5846/stxb201601240167 |
|
GUAN WEI, XU ZHAOLI, CHEN JIAJIE , 2017. Structure and diversity of fish communities in the waters south of Nanri Island[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 37(9):3172-3181 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.5846/stxb201601240167 |
|
| [5] | 广西海洋开发保护管理委员会, 1996. 广西海岛资源综合调查报告[M]. 南宁: 广西科学技术出版社. |
| Guangxi Oceanic Development and Protection Administration, 1996. Investigation report on the Guangxi sea island resources[M]. Nanning: Guangxi Science and Technology Press (in Chinese). | |
| [6] | 何斌源 , 1999. 广西两港湾红树林鱼类生态的比较研究[J]. 海洋通报, 18(1):28-35. |
| HE BINYUAN , 1999. Comparative study on the ecology of mangrove fishes between two bays of Guangxi[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 18(1):28-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 何斌源, 范航清, 莫竹承 , 2001. 广西英罗港红树林区鱼类多样性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 20(4):74-79. |
| HE BINYUAN, FAN HANGQING, MO ZHUCHENG , 2001. Study on species diversity of fishes in mangrove area of Yingluo Bay, Guangxi province[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 20(4):74-79 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 何秀玲, 叶宁, 宣立强 , 2003. 雷州半岛红树林海区的鱼类种类调查[J]. 湛江海洋大学学报, 23(3):3-10. |
| HE XIULING, YE NING, XUAN LIQIANG , 2003. Investigation of fishes in mangrove areas of Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Journal of Zhanjiang Ocean University, 23(3):3-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 胡聪 , 2014. 围填海开发活动对海洋资源影响评价方法研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学. |
| HU CONG , 2014. Evaluation methods of reclamation impact on marine resources[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 黄德练, 吴志强, 黄亮亮 , 等, 2013. 钦州港红树林鱼类群落时间变化格局及其与潮差等环境因子关系[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 33(3):454-460. |
| HUANG DELIAN, WU ZHIQIANG, HUANG LIANGLIANG , et al, 2013. Temporal variation of fish community and correlation with environmental variables in Qinzhou harbor mangroves[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 33(3):454-460 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 赖廷和, 何斌源 , 2016. 广西北部湾海洋硬骨鱼类图鉴[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| LAI TINGHE, HE BINYUAN , 2016. Marine osteichthyes fishes in Guangxi Beibu Gulf of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese). | |
| [12] | 黎清华, 万世明, 何军 , 等, 2014. 近两百年来人类活动对北部湾潮间带环境的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(1):57-64. |
| LI QINGHUA, WAN SHIMING, HE JUN , et al, 2014. Human impact on the intertidal environment in Beibu Gulf over the last 200 years[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 34(1):57-64 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 李显森, 梁志辉, 蒋明星 , 1987. 北部湾北部我国沿岸海区鱼类区系的初步调查[J]. 广西科学院学报, 3(2):95-116. |
| LI XIANSEN, LIANG ZHIHUI, JIANG MINGXING , 1987. A preliminary study on the fish fauna in the northern Beibu Gulf along our coastal area[J]. Journal of Guangxi Academy, 3(2):95-116 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 李显森, 于振海, 孙珊 , 等, 2013. 长江口及其毗邻海域鱼类群落优势种的生态位宽度与重叠[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(8):2353-2359. |
| LI XIANSEN, YU ZHENHAI, SUN SHAN , et al, 2013. Ecological niche breadth and niche overlap of dominant species of fish assemblage in Yangtze River estuary and its adjacent waters[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(8):2353-2359 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 李渊, 张静, 张然 , 等, 2016. 南沙群岛西南部海域和北部湾口海域底层游泳动物多样性[J]. 中国水产科学, 23(1):177-187. |
| LI YUAN, ZHANG JING, ZHANG RAN , et al, 2016. Diversity of demersal nekton in the southwestern sea of the Nansha Islands and the mouth of Beibu Bay[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 23(1):177-187 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 陆健健 , 2003. 河口生态学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. |
| LU JIANJIAN , 2003. Estuary ecology[M]. Beijing: Chinese Ocean Press (in Chinese). | |
| [17] | 罗春业, 李英, 朱瑜 , 等, 1999. 广西北部湾鱼类区系的再研究[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 17(2):85-89. |
| LUO CHUNYE, LI YING, ZHU YU , et al, 1999. A further faunistic study of fishes from the Beibu Bay[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University, 17(2):85-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] |
求锦津, 王咏雪, 李铁军 , 等, 2018. 舟山长白海域主要游泳动物生态位及其分化研究[J]. 生态学报, 38(18):6759-6767.
doi: 10.5846/stxb201803300680 |
|
QIU JINJIN, WANG YONGXUE, LI TIEJUN , et al, 2018. Study on the niche and differentiation of major nekton species in the Zhoushan Changbai Sea area[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(18):6759-6767 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.5846/stxb201803300680 |
|
| [19] | 邱永松 , 1988. 南海北部大陆架鱼类群落的区域性变化[J]. 水产学报, 12(4):303-313. |
| QIU YONGSONG , 1988. The regional changes of fish community on the northern continental shelf of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 12(4):303-313 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [20] | 孙典荣 , 2008. 北部湾渔业资源与渔业可持续发展研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学. |
| SUN DIANRONG , 2008. A study on fishery resources and sustainable fishery development in the Beibu Bay[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China (in Chinese). | |
| [21] |
孙鹏飞, 单秀娟, 吴强 , 等, 2014. 莱州湾及黄河口水域鱼类群落结构的季节变化[J]. 生态学报, 34(2):367-376.
doi: 10.5846/stxb201303060354 |
|
SUN PENGFEI, SHAN XIUJUAN, WU QIANG , et al, 2014. Variations in fish community structure in the Laizhou Bay and the Yellow River Estuary[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(2):367-376 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.5846/stxb201303060354 |
|
| [22] | 王倩, 杨光, 吴孝兵 , 等, 2006. 广西合浦儒艮国家级自然保护区及邻近水域鱼类种数及保护对策[J]. 应用生态学报, 17(9):1715-1720. |
| WANG QIAN, YANG GUANG, WU XIAOBING , et al, 2006. Fish resources and their conservation strategies in Hepu Dugong State Nature Reserve and its adjacent waters[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 17(9):1715-1720 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [23] | 王小林, 徐宾铎, 纪毓鹏 , 等, 2013. 海州湾及邻近海域冬季鱼类群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 24(6):1707-1714. |
| WANG XIAOLIN, XU BINDUO, JI YUPENG , et al, 2013. Fish community structure and its relationships with environmental factors in Haizhou Bay and adjacent waters of East China in winter[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 24(6):1707-1714 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [24] |
王雪辉, 邱永松, 杜飞雁 , 等, 2010. 北部湾鱼类群落格局及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 水产学报, 34(10):1579-1586.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2010.06827 |
|
WANG XUEHUI, QIU YONGSONG, DU FEIYAN , et al, 2010. Fish community pattern and its relation to environmental factors in the Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 34(10):1579-1586 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1231.2010.06827 |
|
| [25] | 王雪辉, 邱永松, 杜飞雁 , 等, 2011. 北部湾鱼类多样性及优势种的时空变化[J]. 中国水产科学, 18(2):427-436. |
| WANG XUEHUI, QIU YONGSONG, DU FEIYAN , et al, 2011. Spatio-temporal variability of fish diversity and dominant species in the Beibu Gulf[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 18(2):427-436 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [26] |
王雪辉, 林昭进, 杜飞雁 , 等, 2013. 南海西北部陆架区鱼类的种类组成与群落格局[J]. 生态学报, 33(7):2225-2235.
doi: 10.5846/stxb201112261975 |
|
WANG XUEHUI, LIN ZHAOJIN, DU FEIYAN , et al, 2013. Fish species composition and community pattern in the continental shelf of northwestern South China Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(7):2225-2235 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.5846/stxb201112261975 |
|
| [27] | 徐兆礼 , 2008. 瓯江口海域夏秋季鱼类多样性[J]. 生态学报, 28(12):5948-5956. |
| XU ZHAOLI , 2008. Analysis of fish diversity in the waters off the Oujiang estuary in summer and autumn[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(12):5948-5956 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [28] | 叶孙忠, 罗冬莲, 蔡建堤 , 等, 2018. 东山湾渔业生物群落结构及生物量分布特征[J]. 渔业研究, 40(5):358-365. |
| YE SUNZHONG, LUO DONGLIAN, CAI JIANDI , et al, 2018. Characteristics of community structure and biomass distribution of fishery resources in Dongshan Bay[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 40(5):358-365 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [29] | 翟璐, 徐宾铎, 纪毓鹏 , 等, 2015. 黄河口及其邻近水域夏季鱼类群落空间格局及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 应用生态学报, 26(9):2852-2858. |
| ZHAI LU, XU BINDUO, JI YUPENG , et al, 2015. Spatial pattern of fish assemblage and the relationship with environmental factors in Yellow River Estuary and its adjacent waters in summer[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 26(9):2852-2858 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [30] | 张静, 陈永俊, 宋普庆 , 等, 2013. 福建东山湾游泳动物群落物种组成及其多样性[J]. 海洋渔业, 35(1):15-23. |
| ZHANG JING, CHEN YONGJUN, SONG PUQING , et al, 2013. Nekton composition and diversity of Dongshan Bay, Fujian[J]. Marine Fisheries, 35(1):15-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [31] | 张文超, 叶振江, 田永军 , 等, 2017. 北部湾洋浦海域鱼类群落结构[J]. 生态学杂志, 36(7):1894-1904. |
| ZHANG WENCHAO, YE ZHENJIANG, TIAN YONGJUN , et al, 2017. Fish community structure in Yangpu waters of Beibu Gulf[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(7):1894-1904 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [32] | 中国海湾志编纂委员会, 1993. 中国海湾志第十二分册(广西海湾)[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. |
| China Gulf Chronicle Compilation Committee, 1993. Editorial board of China bay survey (Vol. 12) Guangxi Bay[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press (in Chinese). | |
| [33] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2008. GB 17378. 4-2007 海洋监测规范第4部分: 海水分析[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China, 2008. GB 17378.4-2007 The specification for marine monitoring— Part 4: seawater analysis[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China (in Chinese). | |
| [34] | 中华人民共和国农业部, 2013. SC/T 9403-2012 海洋渔业资源调查规范[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社. |
| Ministry of Agriculture of the PRC, 2013. SC/T 9403-2012 Technical specification for marine fishery resources survey[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press (in Chinese). | |
| [35] | ASCHAN M, FOSSHEIM M, GREENACRE M , et al, 2013. Change in fish community structure in the Barents Sea[J]. PLoS One, 8(4):e62748. |
| [36] | CLARKE K R , 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure[J]. Australian Journal of Ecology, 18(1):117-143. |
| [37] | CLARKE K R, WARWICK R M , 2001. Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation[M]. Plymouth: Plymouth Marine Laboratory. |
| [38] | COLVOCORESSES J A, MUSICK J A , 1984. Species associations and community composition of middle Atlantic Bight continental shelf demersal fishes[J]. Fishery Bulletin, 82(2):295-313. |
| [39] | GREENWOOD M F D, MATHESON R E JR, MCMICHAEL R H JR , et al, 2007. Community structure of shoreline nekton in the estuarine portion of the Alafia River, Florida: differences along a salinity gradient and inflow-related changes[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 74(1-2):223-238. |
| [40] | LECHÊNE A, BOËT P, LAFFAILLE P , et al, 2018. Nekton communities of tidally restored marshes: a whole- estuary approach[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 207:368-382. |
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [3] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [4] | LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [5] | LIN Xianzhi, ZHOU Yanyan, LIN Haoye, HU Simin, HUANG Hui, ZHANG Li, LIU Sheng. Diet analysis of the parrotfish (Scarus globiceps) in coral reefs of the Nansha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 100-108. |
| [6] | LEI Mingfeng, YU Kefu, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Biao, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Xiaoyan. The rapid ecological degradation and its impact on fish of the Yinyu Island in the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [7] | LAN Zhenqiang, ZHENG Jitao, CHEN Yun, CHEN Nan, WANG Shuhong. Copulation, embryonic and post-embryonic development of Sphaeramia nematoptera [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 116-125. |
| [8] | GENG Wanlu, XING Yongze, ZHANG Qiufeng, GUAN Weibing. Structural characteristics of macrobenthic communities at intertidal zone for mangrove in Beihai, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [9] | YANG Bin, SALENDRA Limbadri, LIU Juan, LIU Yonghong. Alkaloids from the Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus SCSIO41214 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 195-201. |
| [10] | ZHANG Lanlan, CHENG Xiawen, XIANG Rong, QIU Zhuoya, CHANG Hu. Changes of radiolarian community structure with depth in the central Bay of Bengal in spring 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [11] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [12] | WANG Zihan, ZENG Cong, JIANG Ziyu, CAO Ling. Conservation gap analysis of threatened fish in the East China Sea and adjacent sea areas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 66-86. |
| [13] | CHEN Jingfu, ZHONG Yu, WANG Lei, GUO Yupei, QIU Dajun. Noctiluca scintillans effects on eukaryotic plankton community structure using Environmental DNA analysis in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [14] | MA Wengang, XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang, LI Xiubao, WANG Aimin. Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [15] | ZHANG Wanru, LIU Qingxia, HUANG Honghui, QIN Xiaoqing, LI Jiajun, CHEN Jianhua. Study on stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen of main fishery organisms in the southwestern waters of Daya Bay, South China Sea in winter 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
|
||