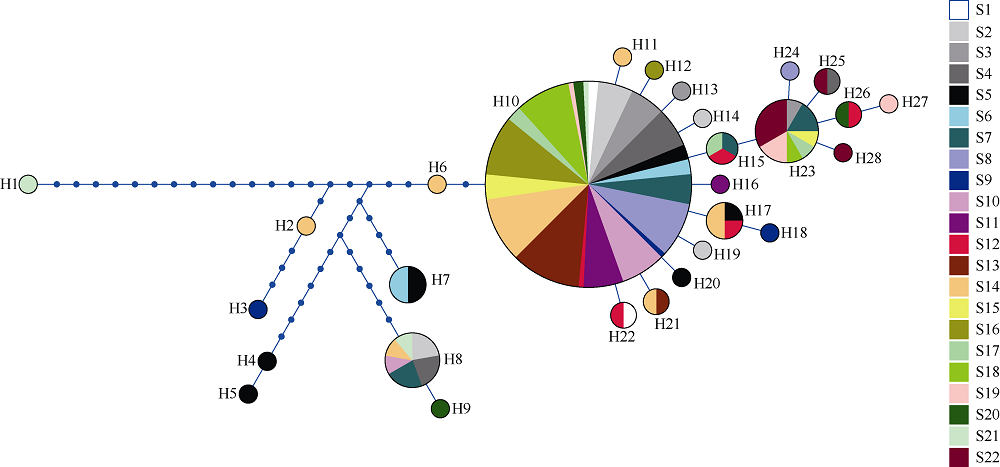
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 89-97.doi: 10.11978/2018112CSTR: 32234.14.2018112
Special Issue: 南海专题
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Genetic structure of Oithona setigera from South China Sea based on 28S rDNA gene
Yingying JI1,2,Lei XU2,Hong LI2,Lianggen WANG2,Feiyan DU2( )
)
- 1. College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai ocean university, Shanghai 201306, China
2. South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fishery Ecology and Environment, Guangzhou 510300, China
-
Received:2018-10-25Revised:2018-12-20Online:2019-05-20Published:2019-06-17 -
Contact:Feiyan DU E-mail:feiyanegg@163.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41406188);South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Scientific Research Funds for Central Non-profit Institutes(2017YB26);South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Scientific Research Funds for Central Non-profit Institutes(2016TS24)
CLC Number:
- Q179.1
Cite this article
Yingying JI,Lei XU,Hong LI,Lianggen WANG,Feiyan DU. Genetic structure of Oithona setigera from South China Sea based on 28S rDNA gene[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 89-97.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
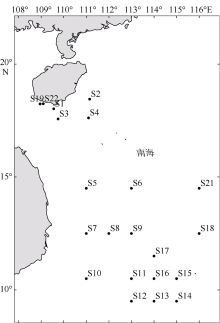
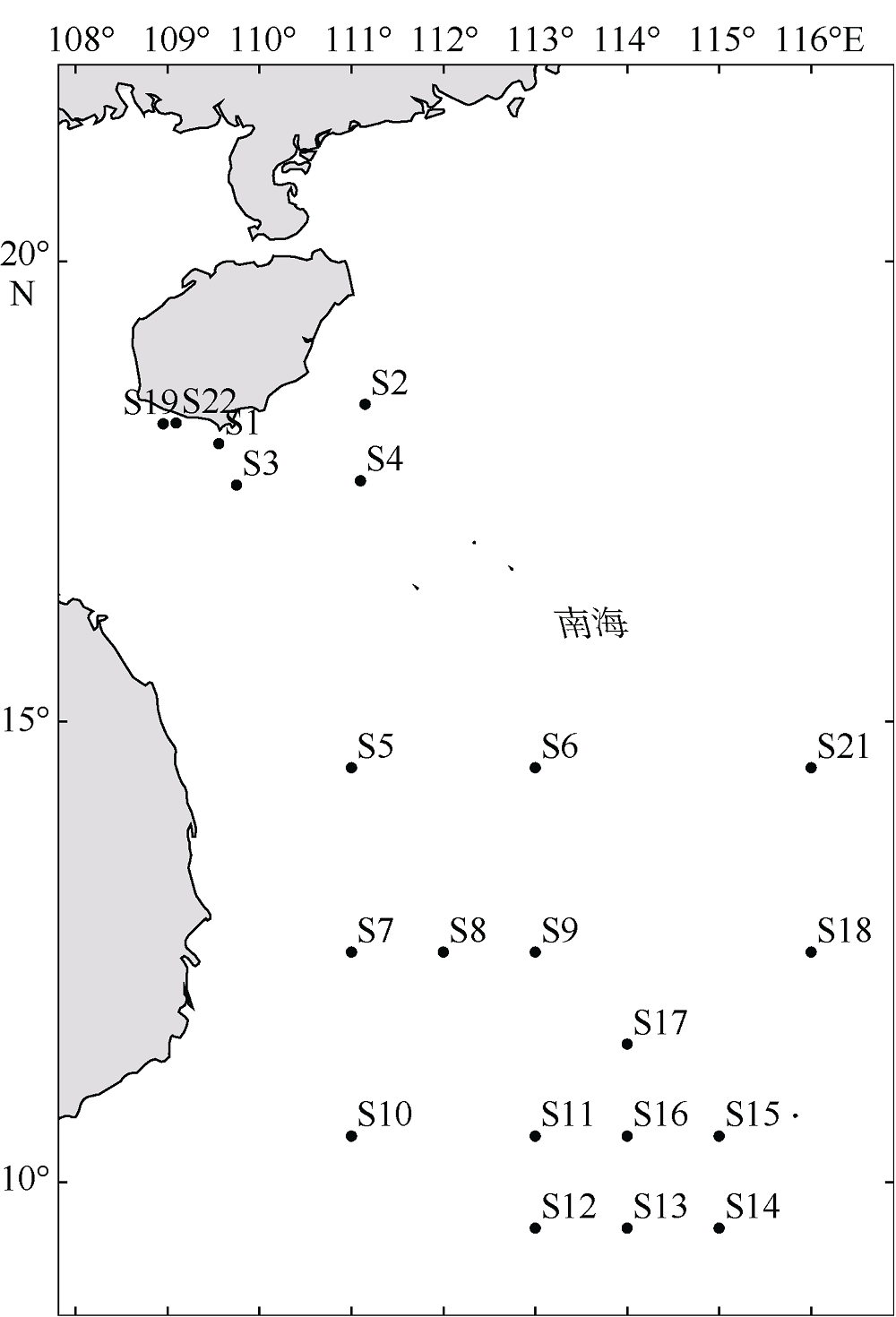
Tab. 1
Information of sample sites of Oithona setigera"
| 站位 | 纬度 | 经度 | 平均水温/℃ | 风速/(m·s-1) | 盐度/‰ | 叶绿素a/(mg·m-3) | 样本 数量 | 单倍型 数量 | 单倍型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 18°15′36″N | 109°33'36"E | 24.49 | 8.19 | NaN | 0.23 | 3 | 2 | H10、H22 |
| S2 | 18°26'59N | 111°9'E | 24.44 | 8.95 | NaN | 0.12 | 11 | 4 | H8、H10、H14、H19 |
| S3 | 17°34'12"N | 109°45'E | 24.60 | 8.71 | NaN | 0.13 | 9 | 3 | H8、H10、H13 |
| S4 | 17°37'12"N | 111°5'59"E | 24.71 | 9.35 | 33.24 | 0.11 | 11 | 2 | H10、H25 |
| S5 | 14°30'N | 111°E | 26.54 | 10.78 | 33.36 | 0.08 | 9 | 5 | H4、H5、H7、H10、H20 |
| S6 | 14°30'N | 113°E | 26.93 | 11.04 | 33.25 | 0.08 | 5 | 2 | H7、H10 |
| S7 | 12°30'N | 111°E | 26.84 | 10.73 | 34.12 | 0.11 | 11 | 4 | H8、H10、H15、H13 |
| S8 | 12°30'N | 112°E | 27.09 | 10.39 | 33.67 | 0.10 | 12 | 1 | H10、H24 |
| S9 | 12°30'N | 113°E | 27.23 | 10.13 | 33.50 | 0.08 | 3 | 2 | H10、H18 |
| S10 | 10°30'N | 111°E | 27.20 | 5.05 | 33.14 | 0.08 | 10 | 4 | H8、H10、H23、H27 |
| S11 | 10°30'N | 113°E | 27.36 | 4.35 | 33.53 | 0.10 | 9 | 2 | H10、H16 |
| S12 | 9°30'N | 113°E | 27.39 | 3.43 | 33.57 | 0.09 | 5 | 5 | H10、H22、H17、H15、H26 |
| S13 | 9°30'N | 114°E | 27.92 | 3.57 | 33.21 | 0.09 | 15 | 2 | H10、H21 |
| S14 | 9°30'N | 115°E | 28.13 | 5.88 | 33.36 | 0.11 | 20 | 6 | H2、H6、H8、H10、H11、H17、H21 |
| S15 | 10°30'N | 115°E | 27.97 | 7.62 | 33.32 | 0.10 | 6 | 2 | H10、H23 |
| S16 | 10°30'N | 114°E | 27.77 | 6.48 | 33.06 | 0.09 | 12 | 2 | H10、H12 |
| S17 | 11°30'N | 114°E | 27.57 | 9.17 | 33.25 | 0.11 | 6 | 4 | H1、H10、H15、H23 |
| S18 | 12°30'N | 116°E | 27.83 | 10.00 | 33.46 | 0.08 | 12 | 2 | H10、H23 |
| S19 | 18°14'23"N | 108°57'E | 25.06 | 7.77 | NaN | 0.98 | 4 | 1 | H10 |
| S20 | 14°30'N | 117°E | 27.50 | 10.60 | 33.42 | 0.10 | 4 | 2 | H9、H10、H26 |
| S21 | 14°30'N | 116°E | 27.55 | 10.90 | 33.36 | 0.09 | 2 | 2 | H8、H10 |
| S22 | 18°15'N | 109°5'59"E | 24.76 | 7.89 | NaN | 0.59 | 7 | 3 | H23、H25、H28 |
Tab. 2
Genetic distance (%) of Oithona setigera between two sampling sites"
| S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 | S17 | S18 | S19 | S20 | S21 | S22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S9 | 0.89 | ||||||||||||||
| S10 | 0.18 | 0.99 | |||||||||||||
| S11 | 0.02 | 0.87 | 0.16 | ||||||||||||
| S12 | 0.16 | 1.02 | 0.30 | 0.16 | |||||||||||
| S13 | 0.45 | 1.12 | 0.58 | 0.43 | 0.58 | ||||||||||
| S14 | 0.45 | 1.12 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.70 | |||||||||
| S15 | 0.06 | 0.91 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.47 | 0.47 | ||||||||
| S16 | 0.26 | 1.04 | 0.40 | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.55 | 0.59 | 0.28 | |||||||
| S17 | 0.09 | 0.95 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.09 | 0.32 | ||||||
| S18 | 0.04 | 0.89 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.09 | |||||
| S19 | 0.25 | 1.13 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.24 | 0.50 | 0.22 | 0.25 | ||||
| S20 | 0.53 | 1.30 | 0.60 | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.53 | 0.76 | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.62 | |||
| S21 | 1.78 | 2.17 | 1.79 | 1.76 | 1.90 | 1.94 | 1.94 | 1.81 | 1.90 | 1.84 | 1.78 | 2.03 | 1.98 | ||
| S22 | 0.26 | 1.15 | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.27 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.24 | 0.52 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.15 | 0.60 | 2.04 |
Tab. 3
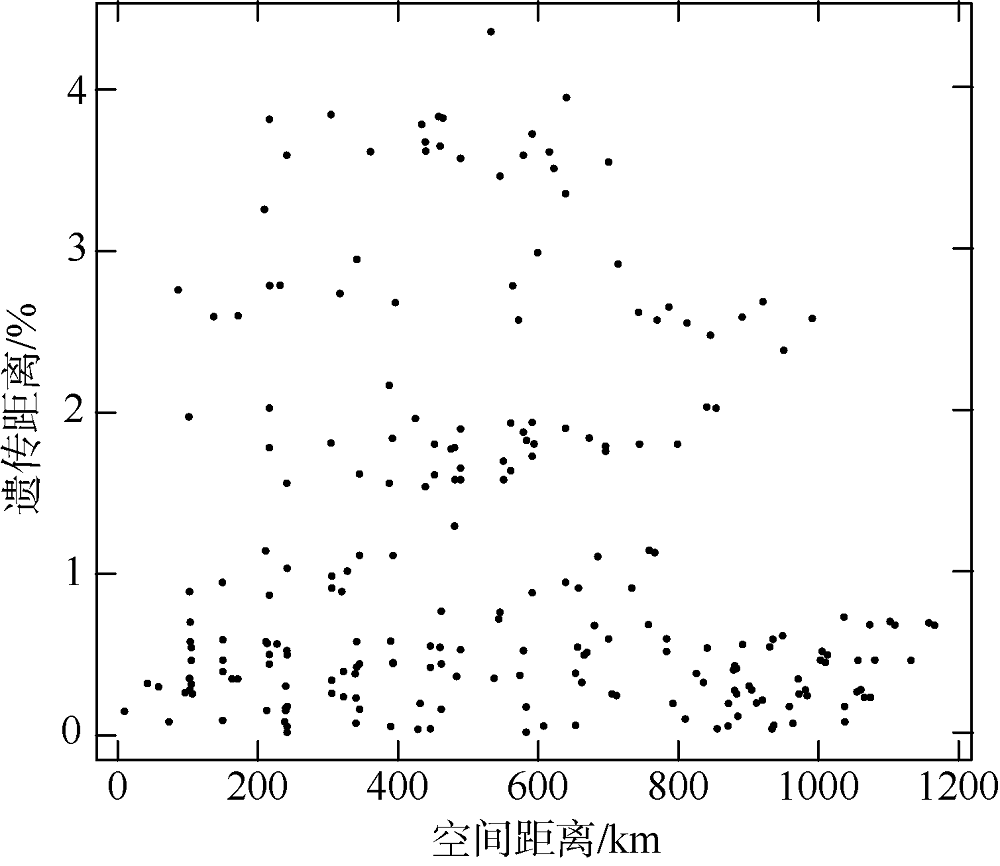
Spatial distance (km) of Oithona setigera between two sampling sites"
| S8 | S9 | S10 | S11 | S12 | S13 | S14 | S15 | S16 | S17 | S18 | S19 | S20 | S21 | S22 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 660 | 740 | 878 | 940 | 1043 | 1087 | 1138 | 1044 | 987 | 891 | 943 | 65 | 898 | 805 | 49 |
| S2 | 669 | 691 | 885 | 907 | 1016 | 1043 | 1079 | 977 | 937 | 832 | 842 | 234 | 764 | 679 | 218 |
| S3 | 614 | 664 | 799 | 862 | 965 | 1009 | 1063 | 970 | 911 | 816 | 877 | 113 | 847 | 751 | 102 |
| S4 | 578 | 605 | 793 | 819 | 927 | 957 | 997 | 897 | 852 | 749 | 776 | 238 | 720 | 629 | 223 |
| S5 | 248 | 311 | 445 | 495 | 598 | 645 | 707 | 622 | 552 | 466 | 585 | 470 | 647 | 539 | 464 |
| S6 | 248 | 223 | 495 | 445 | 557 | 567 | 598 | 495 | 458 | 351 | 394 | 600 | 431 | 323 | 590 |
| S7 | 109 | 217 | 223 | 312 | 399 | 468 | 550 | 490 | 396 | 345 | 543 | 676 | 687 | 585 | 672 |
| S8 | 109 | 248 | 248 | 351 | 399 | 468 | 396 | 312 | 245 | 435 | 718 | 585 | 487 | 712 | |
| S9 | 312 | 223 | 334 | 351 | 399 | 312 | 248 | 156 | 326 | 773 | 487 | 394 | 765 | ||
| S10 | 219 | 246 | 347 | 452 | 438 | 328 | 346 | 589 | 889 | 789 | 702 | 887 | |||
| S11 | 246 | 347 | 452 | 452 | 328 | 346 | 589 | 889 | 789 | 702 | 887 | ||||
| S12 | 110 | 220 | 246 | 156 | 248 | 468 | 1067 | 707 | 645 | 1061 | |||||
| S13 | 110 | 156 | 111 | 223 | 399 | 1115 | 645 | 598 | 1108 | ||||||
| S14 | 111 | 156 | 248 | 351 | 1172 | 598 | 567 | 1164 | |||||||
| S15 | 109 | 156 | 248 | 1080 | 495 | 458 | 1072 | ||||||||
| S16 | 111 | 312 | 1019 | 552 | 495 | 1011 | |||||||||
| S17 | 245 | 926 | 466 | 398 | 918 | ||||||||||
| S18 | 990 | 248 | 223 | 979 | |||||||||||
| S19 | 955 | 860 | 16 | ||||||||||||
| S20 | 108 | 941 | |||||||||||||
| S21 | 847 |
Tab. 4
The redundancy analysis results of spatial variables and environmental variables"
| RDA | R2 | R2adj | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S (空间变量) | Global model(全模型) | 0.759 | 0.638 | 0.003 |
| dbMEM2 | 0.281 | 0.015 | ||
| dbMEM4 | 0.190 | 0.010 | ||
| dbMEM6 | 0.120 | 0.025 | ||
| dbMEM7 | 0.099 | 0.019 | ||
| E(环境变量) | Global model(全模型) | 0.304 | 0.141 | 0.05 |
| FS(前向选择) | 0.181 | 0.094 | 0.03 | |
| Wind speed(风速) | 0.170 | 0.048 | ||
| S+E(环境与空间变量) | 0.722 | 0.611 | 0.002 | |
| S|E(单纯空间变量) | 0.557 | 0.533 | 0.003 | |
| E|S(单纯环境变量) | 0.165 | 0.077 | NS | |
| Shard(环境与空间变量共享) | 0.084 | |||
| Residuals(残差) | 0.389 |
| [1] | 杜飞雁, 王亮根, 王雪辉 , 等, 2016. 南沙群岛海域长腹剑水蚤(Oithona spp.)的种类组成、数量分布及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(6):1176-1184. |
| DU FEIYAN, WANG LIANGGEN, WANG XUEHUI , et al, 2016. Assemblage and abundance of Oithona and environmental factors in Nansha Islands Waters, South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 47(6):1176-1184 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] |
范启, 何舜平 , 2014. 长江流域䱗种群遗传多样性和遗传结构分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 38(4):627-635.
doi: 10.7541/2014.89 |
|
FAN QI, HE SHUNPING , 2014. The pattern of upper and Middle Yangtze drainages shapes the genetic structure and diversity of Hemiculter leucisculus revealed by mitochondrial DNA locus[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 38(4):627-635 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.7541/2014.89 |
|
| [3] | 黄琦, 徐少林, 徐磊 , 等, 2017. 广东流溪河水库盔型溞(Daphnia galeata)休眠种群与现生种群的单倍型多样性和遗传分化[J]. 湖泊科学, 29(5):1209-1216. |
| HUANG QI, XU SHAOLIN, XU LEI , et al, 2017. Haplotype diversity and genetic differentiation of dormant and active populations of Daphnia galeata in Liuxihe reservoir of Guangdong Province, southern China[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 29(5):1209-1216 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 李纯厚, 贾晓平, 蔡文贵 , 2004. 南海北部浮游动物多样性研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 11(2):139-146. |
| LI CHUNHOU, JIA XIAOPING, CAI WENGUI , 2004. Diversity of marine zooplankton in the north of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 11(2):139-146 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 林元烧 , 2005. 中华哲水蚤种群遗传学研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学. |
| LIN YUANSHAO , 2005. Population genetics of a marine copepod, Calanus sinicus Brodsky[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 刘光兴, 林坚 , 2007. 遗传标记技术在海洋桡足类生物多样性和系统发生研究中的应用[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 37(1):33-37. |
| LIU GUANGXING, LIN JIAN , 2007. Application of genetic marker technique to the study of systematics, biodiversity and phylogenetics for marine copepods[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 37(1):33-37 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 曲若竹, 侯林, 吕红丽 , 等, 2004. 群体遗传结构中的基因流[J]. 遗传, 26(3):377-382. |
| QUN RUOZHU, HOU LIN, LV HONGLI , et al, 2004. The gene flow of population genetic structure[J]. Hereditas, 26(3):377-382 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] |
孙柔鑫, 王彦国, 连光山 , 等, 2014. 海南岛西北沿岸海域浮游桡足类的分布及群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 22(3):320-328.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13137 |
|
SUN ROUXIN, WANG YANGUO, LIAN GUANGSHAN , et al, 2014. Distribution and community characteristics of planktonic copepods in the northwest coastal waters off Hainan Island[J]. Biodiversity Science, 22(3):320-328 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13137 |
|
| [9] | 田志富 , 2012. 基于RDA的白洋淀浮游植物群落结构动态特征分析[D]. 保定: 河北大学. |
| TIAN ZHIFU , 2012. Structure and dynamics of phytoplankton community based on the redundancy analysis (RDA)[D]. Baoding: Hebei University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 王敏晓 , 2010. 分子标记在中国近海浮游桡足类研究中的应用 [D]. 青岛:中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所). |
| WANG MINXIAO , 2010. Application of molecular markers to the researches on pelagic copepods in the Chinese coastal regions[D]. Qingdao:The Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 王兴霞, 徐磊, 王亮根 , 等, 2018. 基于COI基因序列的长腹剑水蚤系统进化关系[J]. 海洋学报, 40(6):92-103. |
| WANG XINGXIA, XU LEI, WANG LIANGGEN , et al, 2018. Molecular phylogenetic of Oithona based on COI sequence[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 40(6):92-103 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 徐兆礼 , 2006. 中国海洋浮游动物研究的新进展[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 45(S2):16-23. |
| XU ZHAOLI , 2006. Advance and future of our study on marine zooplankton[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 45(S2):16-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 薛亚东, 李丽, 吴巩胜 , 等, 2011. 景观遗传学: 概念与方法[J]. 生态学报, 31(6):1756-1762. |
| XUE YADONG, LI LI, WU GONGSHENG , et al, 2011. Concepts and techniques of landscape genetics[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(6):1756-1762 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 杨海军, 刘秦玉 , 1998. 南海海洋环流研究综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 13(4):364-368. |
| YANG HAIJUN, LIU QINYU , 1998. A summary on ocean circulation study of the South China Sea[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 13(4):364-368 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 张才学, 龚玉艳, 王学锋 , 等, 2011. 湛江港湾浮游桡足类群落结构的季节变化和影响因素[J]. 生态学报, 31(23):7086-7096. |
| ZHANG CAIXUE, GONG YUYAN, WANG XUEFENG , et al, 2011. The effects of season and environmental factors on community structure of planktonic copepods in Zhanjiang Bay, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(23):7086-7096 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] | 张武昌, 赵楠, 陶振铖 , 等, 2010. 中国海浮游桡足类图谱[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 800. |
| ZHANG WUCHANG, ZHAO NAN, TAO ZHENCHENG , et al, 2010. An illustrated guide to marine planktonic copepods in China seas[M]. Beijing: Science Press: 800 (in Chinese). | |
| [17] | 赵静, 孙洋, 谭永安 , 等, 2014. 基于COI及28S rDNA序列分析的扶桑绵粉蚧地理科群的遗传分化研究[J]. 棉花学报, 26(2):130-137. |
| ZHAO JING, SUN YANG, TAN YONG’AN , et al, 2014. Genetic differentiation among different geographic populations of Phenacoccus solenopsis based on sequences of COI and 28S rDNA[J]. Cotton Science, 26(2):130-137 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [18] | 朱伟军, 孙照渤, 齐卫宁 , 1997. 南海季风爆发及其环流特征[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 20(4):440-446. |
| ZHU WEIJUN, SUN ZHAOBO, QI WEINING , 1997. South-China-Sea monsoon onset with its circulation structure[J]. Journal of Nanjing Institute of Meteorology, 20(4):440-446 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [19] |
AJIBOYE O O, YAKUBU A F, ADAMS T E , et al, 2011. A review of the use of copepods in marine fish larviculture[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 21(2):225-246.
doi: 10.1007/s11160-010-9169-3 |
| [20] |
BAUS E, DARROCK D J, BRUFORD M W , 2005. Gene-flow pattern in Atlantic and Mediterranean populations of the Lusitanian sea star Asterina gibbosa[J]. Molecular Ecology, 14(11):3373-3382.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02681.x pmid: 16156809 |
| [21] |
BARATTI M, GOTI E, MESSANA G G , 2005. High level of genetic differentiation in the marine isopod Sphaeroma terebrans (Crustacea Isopoda Sphaeromatidae) as inferred by mitochondrial DNA analysis[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 315(2):225-234.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2004.09.020 |
| [22] | CHEN GANG , 2006. Cryptic biodiversity and speciation in marine populations: The holoplankton paradox[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 45(S2):68-76. |
| [23] |
CASTELIN M, FEUTRY P, HAUTECOEUR M , et al, 2013. New insight on population genetic connectivity of widespread amphidromous prawn Macrobrachium lar (fabricius, 1798) (Crustacea: Decapoda: Palaemonidae)[J]. Marine Biology, 160(6):1395-1406.
doi: 10.1007/s00227-013-2191-y |
| [24] |
CORNILS A, WEND-HECKMANN B, HELD C , 2017. Global phylogeography of Oithona similis s.l. (Crustacea, Copepoda, Oithonidae) - A cosmopolitan plankton species or a complex of cryptic lineages?[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 107:473-485.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2016.12.019 |
| [25] |
COSTA F O, DEWAARD J R, BOUTILLIER J , et al, 2007. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes: the case of the Crustacea[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 64(2):272-295.
doi: 10.1139/f07-008 |
| [26] |
ELLIS C D, HODGSON D J, DANIELS C L , et al, 2017. Population genetic structure in European lobsters: implications for connectivity, diversity and hatchery stocking[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 563:123-137.
doi: 10.3354/meps11957 |
| [27] |
GOETZE E , 2003. Cryptic speciation on the high seas; global phylogenetics of the copepod family Eucalanidae[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 270(1531):2321-2331.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2003.2505 |
| [28] |
GILG M R, HOWARD R, TURNER R , et al, 2014. Estimating the dispersal capacity of the introduced green mussel, Perna viridis (Linnaeus, 1758), from field collections and oceanographic modeling[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 461:233-242.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2014.08.004 |
| [29] | HALL T A , 1999. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT[J]. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41:95-98. |
| [30] |
HILBISH T J, KOEHN R K , 1985. The Physiological Basis of Natural Selection at the Lap Locus[J]. Evolution, 39(6):1302-1317.
doi: 10.2307/2408787 pmid: 28564261 |
| [31] |
HAYE P A, SEGOVIA N I, MUNOZHERRERA N C , et al, 2014. Phylogeographic structure in benthic marine invertebrates of the southeast pacific coast of Chile with differing dispersal potential[J]. Plos One, 9(2):e88613
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088613 |
| [32] |
HORNE J B, VAN HERWERDEN L, CHOAT J H , et al, 2008. High population connectivity across the Indo-Pacific: congruent lack of phylogeographic structure in three reef fish congeners[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 49(2):629-638.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2008.08.023 |
| [33] | IZZARD R, DRAY L, KARAKAS A , et al, 2006. Population nucleosynjournal in single and binary stars I. Model[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 460(2):565-572. |
| [34] |
KUMAR S, NEI M, DUDLEY J , et al, 2008. MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 9(4):299-306.
doi: 10.1093/bib/bbn017 |
| [35] |
KENCHINGTON E L, PATWARY M U, ZOUROS E , et al, 2006. Genetic differentiation in relation to marine landscape in a broadcast spawning bivalve mollusc (Placopecten magellanicus)[J]. Molecular Ecology, 15(7):1781-1796.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02915.x |
| [36] |
LUTTIKHUIZEN P C, DRENT J, BAKER A J , 2003. Disjunct distribution of highly diverged mitochondrial lineage clade and population subdivision in a marine bivalve with pelagic larval dispersal[J]. Molecular Ecology, 12(8):2215-2229.
doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.01872.x |
| [37] | NIELSEN E E, KENCHINGTON E . 2001. Prioritising marine fish and shellfish populations for conservation: A useful concept?[J]. Fish Fisher, 7:328-343. |
| [38] |
NAKAMURA Y, TURNER J T , 1997. Predation and respiration by the small cyclopoid copepod Oithona similisr: How important is feeding on ciliates and heterotrophic flagellates?[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 19(9):1275-1288.
doi: 10.1093/plankt/19.9.1275 |
| [39] |
PALUMBI S R , 1994. Genetic divergence, reproductive isolation, and marine speciation[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 25:547-572.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.25.110194.002555 |
| [40] |
ROZAS J, SÁNCHEZ-DELBARRIO J C, MESSEGUER X , et al, 2003. DnaSP, DNA polymorphism analyses by the coalescent and other methods[J]. Bioinformatics, 19(18):2496-2497.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg359 |
| [41] |
SALZBURGER W, EWING G B, VON HAESELER A , 2011. The performance of phylogenetic algorithms in estimating haplotype genealogies with migration[J]. Molecular Ecology, 20(9):1952-1963.
doi: 10.1111/mec.2011.20.issue-9 |
| [42] |
TAYLOR M S, HELLBERG M E , 2006. Comparative phylogeography in a genus of coral reef fishes: biogeographic and genetic concordance in the Caribbean[J]. Molecular Ecology, 15(3):695-707.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02820.x |
| [43] |
WANG LIANGGEN, DU FEIYAN, WANG XUEHUI , et al, 2017. Distribution and role of the genus Oithona (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) in the South China Sea[J]. Oceanologia, 59(3):300-310.
doi: 10.1016/j.oceano.2017.03.009 |
| [44] |
WAPLES R S , 1998. Separating the wheat from the chaff: Patterns of genetic differentiation in high gene flow species[J]. Journal of Heredity, 89(5):438-450.
doi: 10.1093/jhered/89.5.438 |
| [45] |
Ward R D, WOODWARK M, SKIBINSK D O F , 1994. A comparison of genetic diversity levels in marine, fresh-water, and anadromous fishes[J]. Journal Fish Biology, 44(2):213-232.
doi: 10.1111/jfb.1994.44.issue-2 |
| [46] |
WEERSING K, TOONEN R J , 2009. Population genetics, larval dispersal, and connectivity in marine systems[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 393:1-12.
doi: 10.3354/meps08287 |
| [47] |
WHITE C, SELKOE K A, WATSON J , et al, 2010. Ocean currents help explain population genetic structure[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 277(1688):1685-1694.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.2214 pmid: 2871860 |
| [1] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 3. data sharing service and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [2] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, HE Yunkai, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 1. data reorganization technology and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [3] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, XU Xiaolu, YUAN Li. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 2. data curation and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [4] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [5] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [6] | JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [7] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [8] | ZHAO Minghui, YUAN Ye, ZHANG Jiazheng, ZHANG Cuimei, GAO Jinwei, WANG Qiang, SUN Zhen, CHENG Jinhui. New developments on the rift-breakup of the continent-ocean transition zone in the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [9] | HUANG Yu, WANG Lin, MAI Zhimao, LI Jie, ZHANG Si. Isolation and characterization of sand fixation ability of bacteria in biological soil crusts of the tropical islands, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [10] | WANG Chenyan, SHI Jingwen, YAN Annan, KANG Yaru, WANG Yuxuan, QIN Suli, HAN Minwei, ZHANG Ruijie, YU Kefu. Bioaccumulation characteristics and source apportionment of organophosphate esters in Acanthaster planci from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
| [11] | LI Niu, DI Pengfei, FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu. The impact of cold seepage on geochemical indices for redox conditions of marine sediments ―Site F active seep site in the northeastern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zhisheng, XIE Lingling, LI Junyi, LI Qiang. Comparative analysis of mesoscale eddy evolution during life cycle in marginal sea and open ocean: South China Sea and Kuroshio Extension [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 63-76. |
| [13] | YANG Lei, WEN Jinhui, WANG Qiang, LUO Xi, HUANG Huaming, HE Yunkai, CHEN Ju. Recent research progress in the influence of tropical cyclones on the Luzon Strait transport* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 40-51. |
| [14] | ZHAO Zhongxian, SUN Zhen, MAO Yunhua, ZHANG Huodai. Heterogeneous extension and pulsed tectonic subsidence in the northern South China Sea margin* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 96-115. |
| [15] | LIU Qinyan, LI Wenlian, SHI Rui, CHEN Ju, LI Chunhui, XIE Qiang. The characteristics of eddy in western boundary current of South China Sea and its relationship with winter circulation [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 52-66. |
|
||