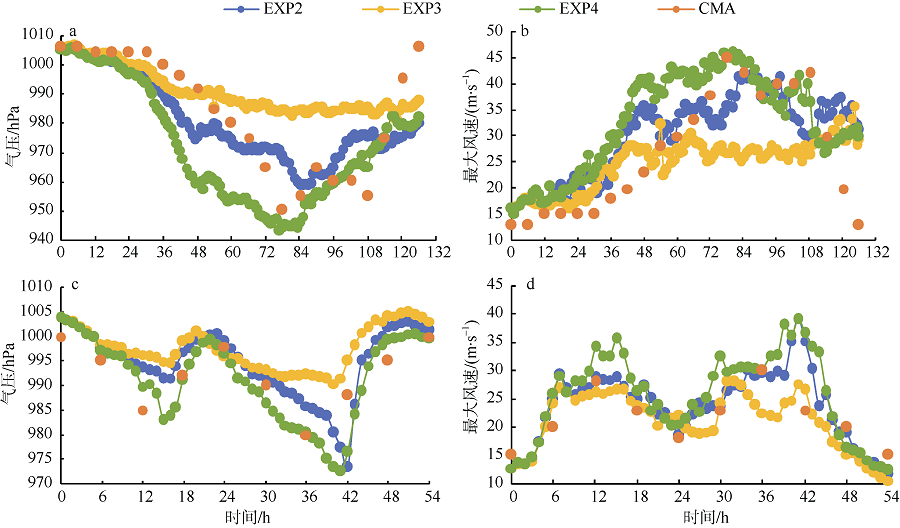
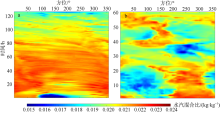
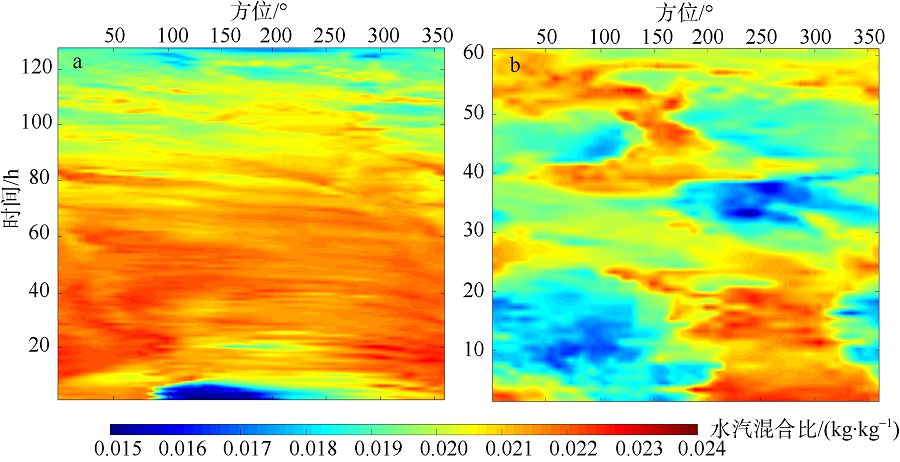
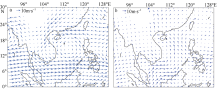
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2018, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 26-34.doi: 10.11978/2017073CSTR: 32234.14.2017073
Special Issue: 南海专题
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of environmental factors on the intensity of Typhoons Wutip and Mirinae in the South China Sea
- 1. Marine Ecosystem and Environmental Laboratory, College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
2. National Oceanic Fisheries Engineering Research Center, Shanghai 201306, China
-
Received:2017-06-27Revised:2017-09-26Online:2018-06-10Published:2018-05-03 -
Supported by:Haiyan Project of Shanghai Ocean University (A2-0203-00-100520);Research Business Expenses of College of Marine Sciences in Shanghai Ocean University (D-8002-15-8003);Basic Research Business Expenses of Guangxi Academy of Sciences (13YJ22HY07)
Cite this article
Haoliang WU, Song HU. Effect of environmental factors on the intensity of Typhoons Wutip and Mirinae in the South China Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 26-34.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] | 陈国民, 沈新勇, 刘佳, 2010. 垂直风切变对热带气旋强度及结构的影响[J]. 气象研究与应用, 31(1): 1-4, 10. |
| CHEN GUOMIN, SHEN XINYONG, LIU JIA, 2010. Role of vertical wind shear on tropical cyclone intensity and structure[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research and Application, 31(1): 1-4, 10 (in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 崔琳琳, 胡松, 2012. 2008年东海海面WRF风场和QuikSCAT风场差异分析[J]. 海洋预报, 29(5): 39-47. |
| CUI LINLIN, HU SONG, 2012. Analysis on difference of sea surface wind field between WRF and QuikSCAT over the East China Sea of 2008[J]. Marine Forecasts, 29(5): 39-47 (in Chinese). | |
| [3] | 方宗义, 1982. 台风发生发展过程中的云型特征与高空环境流场的关系[J]. 大气科学, 6(3): 274-282. |
| FANG ZONGYI, 1982. The relationship between the cloud pattern and the environmental flow pattern of the upper troposphere during the genesis and development of typhoon[J]. Scientia Atmospherica Sinica, 6(3): 274-282 (in Chinese). | |
| [4] | 胡春梅, 端义宏, 余晖, 等, 2005. 华南地区热带气旋登陆前强度突变的大尺度环境诊断分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 21(4): 377-382. |
| HU CHUNMEI, DUAN YIHONG, YU HUI, et al, 2005. The diagnostic analysis of the rapid change in tropical cyclones intensity before landfall in South China[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 21(4): 377-382 (in Chinese). | |
| [5] | 李崇银, 1983. 环境流场对台风发生发展的影响[J]. 气象学报, 41(3): 275-284. |
| LI CHONGYIN, 1983. The effect of ambient flow on generation ane development of typhoon[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 41(3): 21-30 (in Chinese). | |
| [6] | 李瑞, 李本亮, 胡鹏, 等, 2014. 环境垂直风切变对0509号台风“麦莎”的影响分析[J]. 海洋学研究, 32(2): 14-22. |
| LI RUI, LI BENLIANG, HU PENG, et al, 2014. Effects of environmental vertical wind shear on typhoon Matsa (0509)[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 32(2): 14-22 (in Chinese). | |
| [7] | 林秀斌, 2007. 西北太平洋热带气旋强度变化及其影响因子的研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学. |
| LIN XIUBING, 2007. Studys on the maximum intensity changes of tropical cyclone and their influencing factors on Northwest Pacific[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology (in Chinese). | |
| [8] | 刘翔, 蒋国荣, 卓海峰, 2009. SST对台风“珍珠”影响的数值试验[J]. 海洋预报, 26(3): 1-11. |
| LIU XIANG, JIANG GUORONG, ZHUO HAIFENG, 2009. Numerical experiment for the impact of SST to typhoon “Chanchu”[J]. Marine Forecasts, 26(3): 1-11 (in Chinese). | |
| [9] | 沈桐立, 2010. 数值天气预报[M]. 北京: 气象出版社. |
| [10] | 吴迪生, 赵雪, 冯伟忠, 等, 2005. 南海灾害性土台风统计分析[J]. 热带气象学报, 21(3): 309-314. |
| WU DISHENG, ZHAO XUE, FENG WEIZHONG, et al, 2005. The statistical analyse to the local harmful typhoon of South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 21(3): 309-314 (in Chinese). | |
| [11] | 徐桂妹, 李丽平, 2014. 1013号台风“鲶鱼”的台风环流分离方法比较[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 6(2): 152-157. |
| XU GUIMEI, LI LIPING, 2014. Comparisons of different approaches in separating Typhoon Megi (1013) circulation from its environment[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 6(2): 152-157 (in Chinese). | |
| [12] | 阎俊岳, 1996. 近海热带气旋迅速加强的气候特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 7(1): 28-35. |
| YAN JUNYUE, 1996. Climatological characteristics of rapidly intensifying tropical cyclones over the offshore of China[J]. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 7(1): 28-35 (in Chinese). | |
| [13] | 于玉斌, 2012. 冷空气影响热带气旋发生发展的研究进展[J]. 海洋学报,34(3): 173-178 |
| YU YUBIN, 2012. Research advances of cold air impacts on the tropical cyclone genesis and development[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 34(3): 173-178 (in Chinese). | |
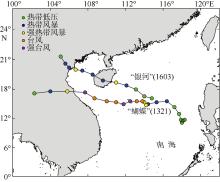
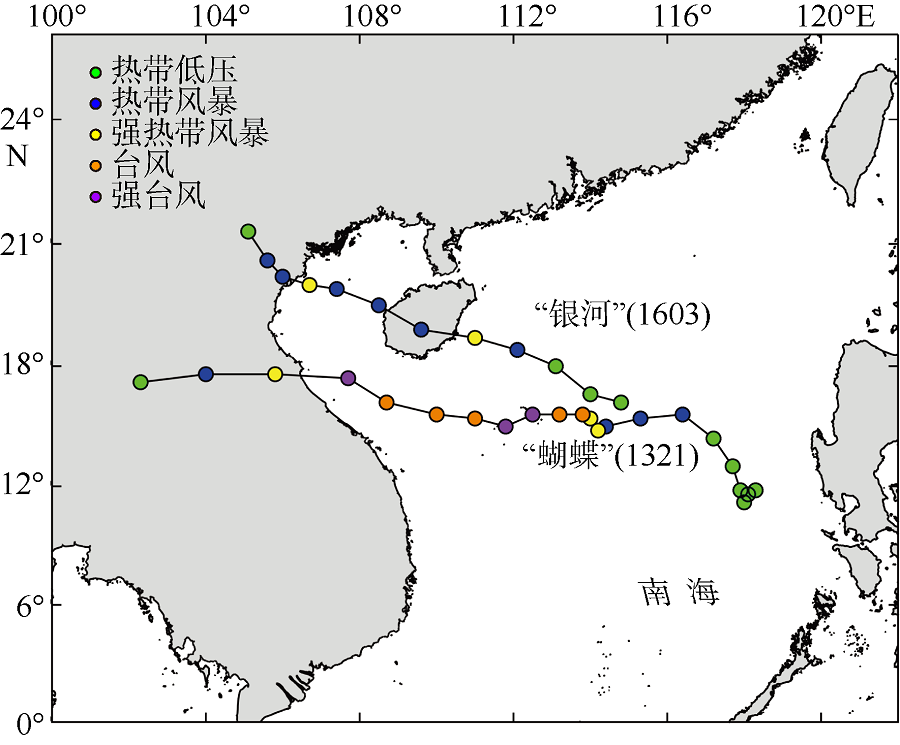
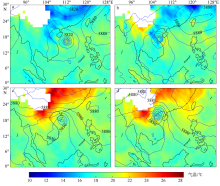
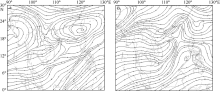
| [14] | 赵小平, 朱晶晶, 吴慧, 等, 2014. 1321号台风“蝴蝶”强度变化特征和影响因素分析[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 33(3): 404-411. |
| ZHAO XIAOPING, ZHU JINGJING, WU HUI, et al, 2014. Intensity evolution characteristics and influencing factors of the typhoon “Wutip” (1321)[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 33(3): 404-411 (in Chinese). | |
| [15] | CHAN J C L, DUAN YIHONG, SHAY L K, 2001. Tropical cyclone intensity change from a simple ocean-atmosphere coupled model[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 58(2): 154-172. |
| [16] | EMANUEL K A, 1988. The maximum intensity of hurricanes[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 45(7): 1143-1155. |
| [17] | FRANK W M, RITCHIE E A, 2001. Effects of vertical wind shear on the intensity and structure of numerically simulated hurricanes[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 129(9): 2249-2269. |
| [18] | GRAY W M, 1998. The formation of tropical cyclones[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 67(1-4): 37-69. |
| [19] | KAPLAN J, DEMARIA M, 2003. Large-scale characteristics of rapidly intensifying tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic basin[J]. Weather and Forecasting, 18(6): 1093-1108. |
| [20] | MOLINARI J, VOLLARO D, 2010. Rapid intensification of a sheared tropical storm[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 138(138): 3869-3885. |
| [21] | NGUYEN L T, MOLINARI J, 2012. Rapid intensification of a sheared, fast-moving hurricane over the gulf stream[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 140(10): 3361-3378. |
| [22] | TULEYA R E, KURIHARA Y, 1981. A numerical study on the effects of environmental flow on tropical storm genesis[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 109(12): 2487-2506. |
| [23] | WANG HUI, WANG YUQING, 2014. A numerical study of typhoon Megi (2010). Part I: Rapid intensification[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 142(1): 29-48. |
| [24] | YING MING, ZHANG WEI, YU HUI, et al, 2014. An overview of the China meteorological administration tropical cyclone database[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 31(2): 287-301. |
| [25] | ZEHR R M, 1992. Tropical cyclogenesis in the Western North Pacific[D]. Colorado: Colorado State University. |
| [1] | LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [2] | LIU Yue, LI Li, ZHAI Xiaohui, ZHOU Juan, YE Penghao, HUANG Shengdong. Analysis of the bloom caused by colonial Phaeocystis globosa in Mirs Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 164-171. |
| [3] | MA Wengang, XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang, LI Xiubao, WANG Aimin. Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [4] | Sixuan HE,Binyuan HE. Study on fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 86-97. |
| [5] | Xinming LEI, Hui HUANG, Jiansheng LIAN, Yuyang ZHANG, Jianhui YANG. [RETRACTED] Species composition of coralline algae and its spatial characteristics related to environmental factors in Sanya coral reefs, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 79-88. |
| [6] | Lei CUI, Songhui LÜ, Yuelei DONG, Xingchen GAO, Li LI, Fenghua LIU, Jingyi CEN. Influence on the biological community and environmental factors around Qi’ao Island caused by reclamation project [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(2): 96-105. |
| [7] | HAN Xue, CAI Yi, CHEN Xing-rong, LI Yan. Analysis of temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of winter SST anomalies in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea and their influencing factors [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(5): 1-12. |
| [8] | ZHOU Jie, SHI Qi, YU Ke-fu. Exploration of factors that influence photosynthetic efficiency of symbiotic zooxanthellae of scleractinian corals in a Sanya fringing reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2014, 33(1): 81-89. |
| [9] | ZHENG Shan-shan, CHEN Chu-qun. A method for SST retrieval from ASTER image without using in-situ data [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(5): 9-14. |
| [10] | LIU Qiao, LONG Li-juan. Effect of environmental factors on the growth of Prorocentrum rhathymum [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(3): 93-100. |
| [11] | ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Jie-xiang, ZHANG Yu-bin, LU Dong-wei, DING Yu-jing, SUN Xing-li. Temporal and spatial distributions of bacterioplankton biomass and the influenced factors in Shenzhen Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2013, 32(3): 65-71. |
| [12] | LI Hai-ping ,YAN Qing-pi ,XU Xiao-jin ,SU Yong-quan ,QIN Ying-xue . Establishment of in vitro biofilm model and characteristics of biofilm formation of Vibrio harveyi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(3): 99-104. |
| [13] |
LIU Wen-guang,LI Qi,GAO Feng-xiang,YU Rui-hai,KONG Ling-feng.
Seasonal variation in reproductive cycle and biochemical composition in relation to environmental factors in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(3): 88-93. |
| [14] | XIAO Xian-jun,HE Na ,ZHANG Zu-qiang,LIU Huai-ming,WANG Dong-xiao . Variation assimilation using satellite data of sea surface temperature and altimeter [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(3): 1-8. |
| [15] | JIANG Fa-jun,HU Zhang-li,HU Chao-qun. Correlation between spatial-temporal distribution of bacterioplankton and environmental factors in the Dapeng Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2011, 30(1): 96-100. |
|
||