Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2018, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 35-44.doi: 10.11978/2017067CSTR: 32234.14.2017067
Special Issue: 南海专题
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
The spectral characteristics of phytoplankton absorption coefficient and assessment of MODIS-Aqua products in typical sea areas of the South China Sea
Wenjing ZHAO1( ), Wenxi CAO2(
), Wenxi CAO2( ), shuibo HU3, Guifen WANG2, Zhenyu LIU4, Min XU1
), shuibo HU3, Guifen WANG2, Zhenyu LIU4, Min XU1
- 1. South China Institute of Environmental Sciences, the Ministry of Environmental Protection of RPC, Guangzhou 510535, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
3. Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Spatial Information Smart Sensing and Services and Key Laboratory for Geo-Environment Monitoring of Coastal Zone of the National Administration of Surveying, Mapping and Geo-Information, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
4. College of Resources and Environmental Science, South-central University for Nationalities, Wuhan 430074, China;
-
Received:2017-06-08Revised:2017-08-15Online:2018-06-10Published:2018-05-03 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (41506202);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2014A030310287);State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography Under Independent Project (LTO1509);Project of Basic Scientific Research Expenses Supported by the Central Public Welfare Research Institute (South China Institute of Environmental Sciences, Ministry of Environmental Protection, PM-zx703-201601-014);Ministry of Environmental Protection department budget Project (The policy research of coastal areas pollution prevention and control technology);Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangxi (AB16380339);Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (BZY15028)
Cite this article
Wenjing ZHAO, Wenxi CAO, shuibo HU, Guifen WANG, Zhenyu LIU, Min XU. The spectral characteristics of phytoplankton absorption coefficient and assessment of MODIS-Aqua products in typical sea areas of the South China Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(3): 35-44.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
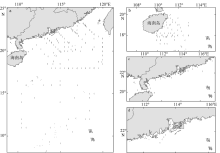
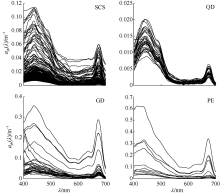
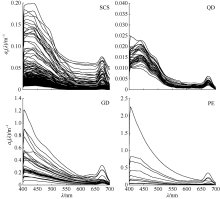
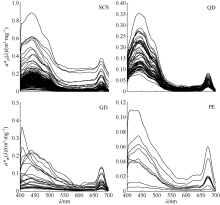
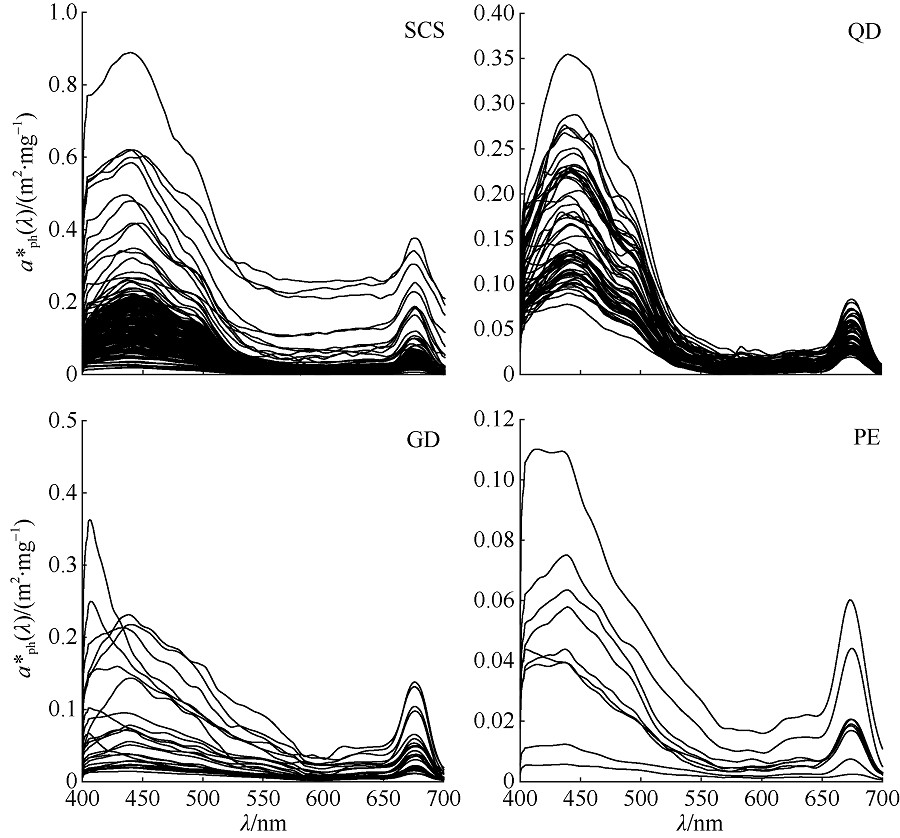
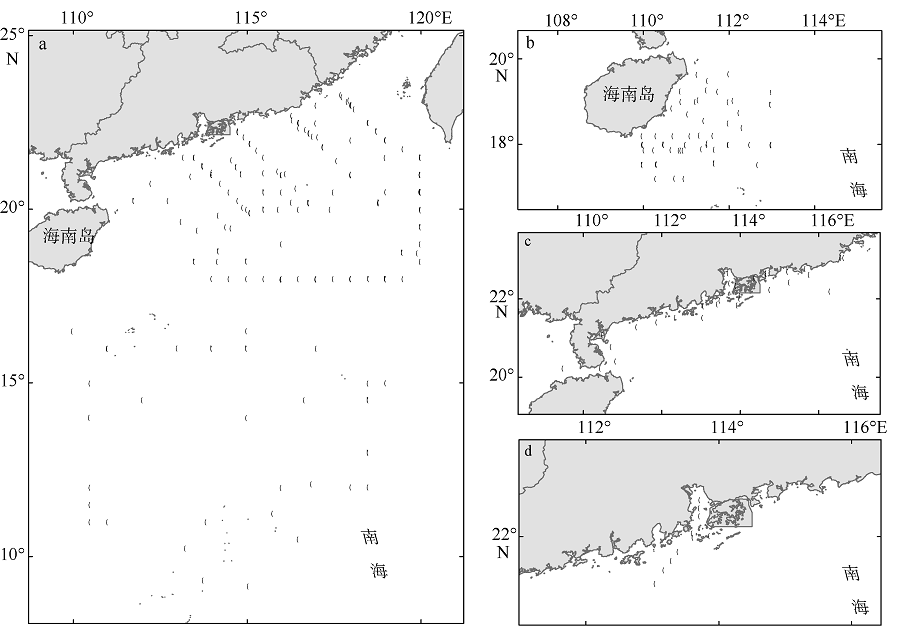
Fig. 1
Typical area of the South China Sea (SCS), and spatial distribution of in situ aph(l) data (open circles).The dots represent the spatial distribution of relaxed (cross) match-ups for MODIS-Aqua Rrs(l) and aph(l). (a) The open sea of the SCS; (b) the coastal area of Qingdong (QD); (c) the coastal area of Guangdong (GD); and (d) the Pearl River Estuary (PE)"
Tab. 1
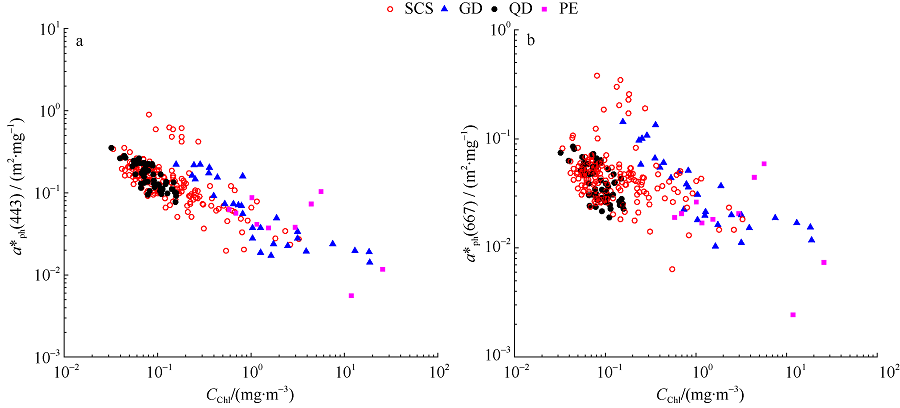
The ranges of aph*(443), aph*(667) and aph*(443)/ aph*(667) in each typical area of the SCS"
| 海区 | aph*(443) | aph*(667) | aph*(443)/aph*(667) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 南海 | 0.02~0.90 (0.16) | 0.006~0.32 (0.05) | 1.33~7.13 (3.85) |
| 琼东 | 0.08~0.35 (0.17) | 0.02~0.07 (0.04) | 3.13~7.61 (4.81) |
| 广东 | 0.01~0.22 (0.08) | 0.008~0.11 (0.04) | 1.15~4.52 (2.26) |
| 珠江口 | 0.006~0.1 (0.05) | 0.002~0.05 (0.02) | 1.79~3.82 (2.58) |
Tab. 2
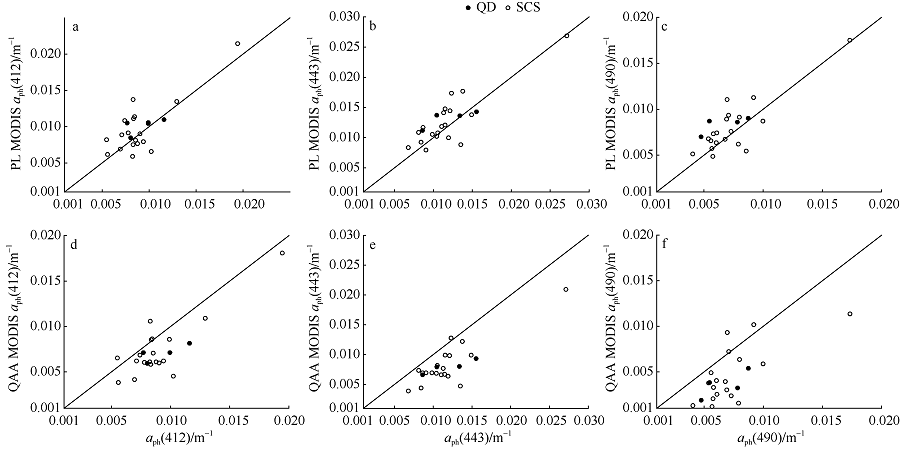
Statistics comparing in situ aph(λ) (λ=412, 443, 490) with MODIS-Aqua products basing on QAA and PL algorithms in the SCS and QD sea waters when relaxed match-ups are included"
| QAA aph(412) | QAA aph(443) | QAA aph(490) | PL aph(412) | PL aph(443) | PL aph(490) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APD/% | 22.49 | 29.68 | 46.89 | 20.15 | 17.94 | 21.65 |
| RPD/% | -18.11 | -29.33 | -42.84 | 10.42 | 10.82 | 14.14 |
| RMS | 0.0023 | 0.0040 | 0.0039 | 0.0022 | 0.0024 | 0.0018 |
| Ratio | 0.7800 | 0.7099 | 0.5778 | 1.0543 | 1.0744 | 1.1448 |
| SIQR | 0.1139 | 0.0981 | 0.1706 | 0.1804 | 0.1507 | 0.1311 |
| R2 | 0.6938 | 0.7231 | 0.3642 | 0.6178 | 0.7160 | 0.6682 |
| Slope | 0.8622 | 0.7434 | 0.6959 | 0.9210 | 0.8504 | 0.8312 |
| Interception | -0.0004 | -0.0004 | -0.0008 | 0.0015 | 0.0028 | 0.0020 |
Tab. 3
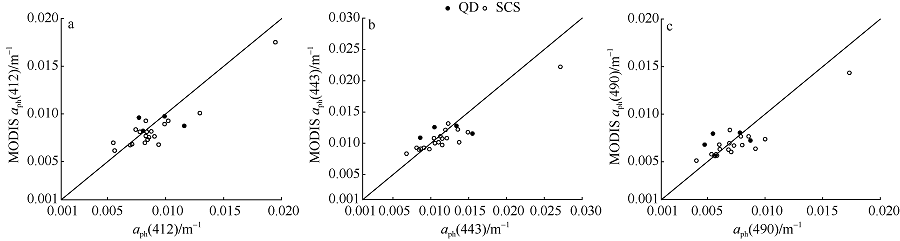
Statistics comparing in situ aph(412), aph(443) and aph(490) with MODIS-Aqua products using the PL algorithm, which is based on Chl-a products derived from the regional algorithm NOCI in the SCS and QD sea waters"
| NOCI aph(412) | NOCI aph(443) | NOCI aph(490) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| APD/% | 12.14 | 11.87 | 13.89 |
| RPD/% | -4.02 | -2.07 | 0.31 |
| RMS | 0.0014 | 0.0019 | 0.0014 |
| Ratio | 0.9331 | 0.9551 | 0.9842 |
| SIQR | 0.0859 | 0.0869 | 0.1024 |
| R2 | 0.8012 | 0.8297 | 0.7538 |
| Slope | 0.7129 | 0.6250 | 0.6007 |
| Interception | 0.0020 | 0.0038 | 0.0026 |
| [1] | 曹文熙, 杨跃忠, 许晓强, 等, 2003. 珠江口悬浮颗粒物的吸收光谱及其区域模式[J]. 科学通报, 48(17): 1876-1882. |
| CAO WENXI, YANG YUEZHONG, XU XIAOQIANG, et al, 2003. Regional patterns of particulate spectral absorption in the Pearl River estuary[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(11): 2344-2351(in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 崔廷伟, 2006. 渤海生物光学特性与水色遥感反演[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学. |
| CUI TINGWEI, 2006. Bio-optical properties and ocean color inversion of the Bohai Sea[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China (in Chinese). | |
| [3] | 郝艳玲, 曹文熙, 崔廷伟, 等, 2011. 基于半分析算法的赤潮水体固有光学性质反演[J]. 海洋学报, 33(1): 52-65. |
| HAO YANLING, CAO WENXI, CUI TINGWEI, et al, 2011. The retrieval of oceanic inherent optical properties based on semianalytical algorithm during the red ride[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 33(1): 52-65 (in Chinese). | |
| [4] | 王桂芬, 2008. 南海北部水体光学特性及水色反演模式[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. |
| WANG GUIFEN, 2008. Optical properties of seawater and ocean color models in Northern South China Sea[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese). | |
| [5] | 汪文琦, 董强, 商少凌, 等, 2009. 基于两种半分析算法的水体吸收系数反演[J]. 热带海洋学报, 28(5): 35-42. |
| WANG WENQI, DONG QIANG, SHANG SHAOLING, et al, 2009. An evaluation of two semi-analytical ocean color algorithms for waters of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 28(5): 35-42 (in Chinese). | |
| [6] | 赵冬至, 罗虎, 傅云娜, 等, 2004. 海洋水色组分吸收系数的测定方法研究[J]. 海洋通报, 23(3): 81-86. |
| ZHAO DONGZHI, LUO HU, FU YUNNA, et al, 2004. Determination of spectral absorption coefficients of particles, dissolved material and phytoplankton for ocean discrete water samples[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 23(3): 81-86 (in Chinese). | |
| [7] | 赵文静, 2014. 南海水色遥感产品精度检验及算法修正[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学. |
| ZHAO WENJING, 2014. Assessment of ocean color products and modification of operational algorithms in the South China Sea[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese). | |
| [8] | 赵文静, 曹文熙, 王桂芬, 等, 2014. 南海海域MODIS-Aqua叶绿素浓度产品的精度对比和区域性算法修正[J]. 光学精密工程, 22(11): 3081-3090. |
| ZHAO WENJING, CAO WENXI, WANG GUIFEN, et al, 2014. Comparison of chlorophyll products derived from MODIS-Aqua and modification of operational algorithms in the South China Sea[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 22(11): 3081-3090 (in Chinese). | |
| [9] | AIKEN J, FISHWICK J R, LAVENDER S, et al, 2007. Validation of MERIS reflectance and chlorophyll during the BENCAL cruise October 2002: preliminary validation of new demonstration products for phytoplankton functional types and photosynthetic parameters[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 28(3-4): 497-516. |
| [10] | AIKEN J, HARDMAN-MOUNTFORD N J, BARLOW R, et al, 2008. Functional links between bioenergetics and bio-optical traits of phytoplankton taxonomic groups: an overarching hypothesis with applications for ocean colour remote sensing[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 30(2): 165-181. |
| [11] | BAILEY S W, WERDELL P J, 2006. A multi-sensor approach for the on-orbit validation of ocean color satellite data products[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 102(1-2): 12-23. |
| [12] | BRICAUD A, MOREL A, BABIN M, et al, 1998. Variations of light absorption by suspended particles with chlorophyll a concentration in oceanic (case 1) waters: analysis and implications for bio‐optical models[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 103(C13): 31033-31044. |
| [13] | CARDER K L, HAWES S, BAKER K A, et al, 1991. Reflectance model for quantifying chlorophyll a in the presence of productivity degradation products[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 96(C11): 20599-20611. |
| [14] | CARDER K L, CHEN F R, LEE Z P, et al, 1999. Semianalytic moderate-resolution imaging spectrometer algorithms for chlorophyll a and absorption with bio-optical domains based on nitrate-depletion temperatures[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 104(C3): 5403-5421. |
| [15] | CARDER K L, CHEN F R, CANNIZZARO J P, et al, 2004. Performance of the MODIS semi-analytical ocean color algorithm for chlorophyll-a[J]. Advances in Space Research, 33(7): 1152-1159. |
| [16] | CUI TINGWEI, ZHANG JIE, GROOM S, et al, 2010. Validation of MERIS ocean-color products in the Bohai Sea: a case study for turbid coastal waters[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114(10): 2326-2336. |
| [17] | GORDON H R, BROWN O B, EVANS R H, et al, 1988. A semianalytic radiance model of ocean color[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 93(D9): 10909-10924. |
| [18] | GORDON H R, WANG MENGHUA, 1994. Retrieval of water-leaving radiance and aerosol optical thickness over the oceans with SeaWiFS: a preliminary algorithm[J]. Applied Optics, 33(3): 443-452. |
| [19] | HU CHUANMIN, LEE Z, FRANZ B, 2012. Chlorophyll a algorithms for oligotrophic oceans: a novel approach based on three‐band reflectance difference[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C1): C01011. |
| [20] | LEE Z, WEIDEMANN A, KINDLE J, et al, 2007. Euphotic zone depth: its derivation and implication to ocean-color remote sensing[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 112(C3): C03009. |
| [21] | LEE Z P, CARDER K L, MARRA J, et al, 1996. Estimating primary production at depth from remote sensing[J]. Applied Optics, 35(3): 463-74. |
| [22] | LEE Z P, CARDER K L, STEWARD R G, et al, 1998. An empirical algorithm for light absorption by ocean water based on color[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 103(C12): 27967-27978. |
| [23] | LOISEL H, STRAMSKI D, 2000. Estimation of the inherent optical properties of natural waters from the irradiance attenuation coefficient and reflectance in the presence of Raman scattering[J]. Applied Optics, 39(18): 3001-3011. |
| [24] | LOISEL H, STRAMSKI D, MITCHELL B G, et al, 2001. Comparison of the ocean inherent optical properties obtained from measurements and inverse modeling[J]. Applied Optics, 40(15): 2384-2397. |
| [25] | O’REILLY J E, MARITORENA S, SIEGEL D A, et al, 2000. Ocean color chlorophyll a algorithms for SeaWiFS, OC2, and OC4: version 4[M]//HOOKER S B, FIRESTONE E R. SeaWiFS Postlaunch Calibration and Validation Analyses, Part 3. Greenbelt, Maryland: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, 11: 9-23. |
| [26] | PARSONS T R, MAITA Y, LALLI C M, 1984. A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press: 173. |
| [27] | POPE R M, FRY E S, 1997. Absorption spectrum (380-700 nm) of pure water. II. Integrating cavity measurements[J]. Applied Optics, 36(33): 8710-8723. |
| [28] | PRIEUR L, SATHYENDRANATH S, 1981. An optical classification of coastal and oceanic waters based on the specific spectral absorption curves of phytoplankton pigments, dissolved organic matter, and other particulate materials[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 26(4): 671-689. |
| [29] | QING SONG, ZHANG JIE, CUI TINGWEI, et al, 2012. Remote sensing retrieval of total absorption coefficient in the Bohai Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 30(5): 806-813. |
| [30] | ROESLER C S, PERRY M J, CARDER K L, 1989. Modeling in situ phytoplankton absorption from total absorption spectra in productive inland marine waters[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 34(8): 1510-1523. |
| [31] | WANG MENGHUA, 2005. A refinement for the Rayleigh radiance computation with variation of the atmospheric pressure[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26(24): 5651-5663. |
| [32] | ZHAO W J, WANG G Q, CAO W X, et al, 2014. Assessment of SeaWiFS, MODIS, and MERIS ocean colour products in the South China Sea[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(11-12): 4252-4274. |
| [1] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 3. data sharing service and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [2] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, HE Yunkai, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 1. data reorganization technology and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [3] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, XU Xiaolu, YUAN Li. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 2. data curation and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [4] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [5] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [6] | JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [7] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [8] | ZHAO Minghui, YUAN Ye, ZHANG Jiazheng, ZHANG Cuimei, GAO Jinwei, WANG Qiang, SUN Zhen, CHENG Jinhui. New developments on the rift-breakup of the continent-ocean transition zone in the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [9] | HUANG Yu, WANG Lin, MAI Zhimao, LI Jie, ZHANG Si. Isolation and characterization of sand fixation ability of bacteria in biological soil crusts of the tropical islands, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [10] | WANG Chenyan, SHI Jingwen, YAN Annan, KANG Yaru, WANG Yuxuan, QIN Suli, HAN Minwei, ZHANG Ruijie, YU Kefu. Bioaccumulation characteristics and source apportionment of organophosphate esters in Acanthaster planci from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
| [11] | LI Niu, DI Pengfei, FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu. The impact of cold seepage on geochemical indices for redox conditions of marine sediments ―Site F active seep site in the northeastern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
| [12] | ZHANG Zhisheng, XIE Lingling, LI Junyi, LI Qiang. Comparative analysis of mesoscale eddy evolution during life cycle in marginal sea and open ocean: South China Sea and Kuroshio Extension [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 63-76. |
| [13] | YANG Lei, WEN Jinhui, WANG Qiang, LUO Xi, HUANG Huaming, HE Yunkai, CHEN Ju. Recent research progress in the influence of tropical cyclones on the Luzon Strait transport* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 40-51. |
| [14] | ZHAO Zhongxian, SUN Zhen, MAO Yunhua, ZHANG Huodai. Heterogeneous extension and pulsed tectonic subsidence in the northern South China Sea margin* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 96-115. |
| [15] | LIU Qinyan, LI Wenlian, SHI Rui, CHEN Ju, LI Chunhui, XIE Qiang. The characteristics of eddy in western boundary current of South China Sea and its relationship with winter circulation [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 52-66. |
|
||