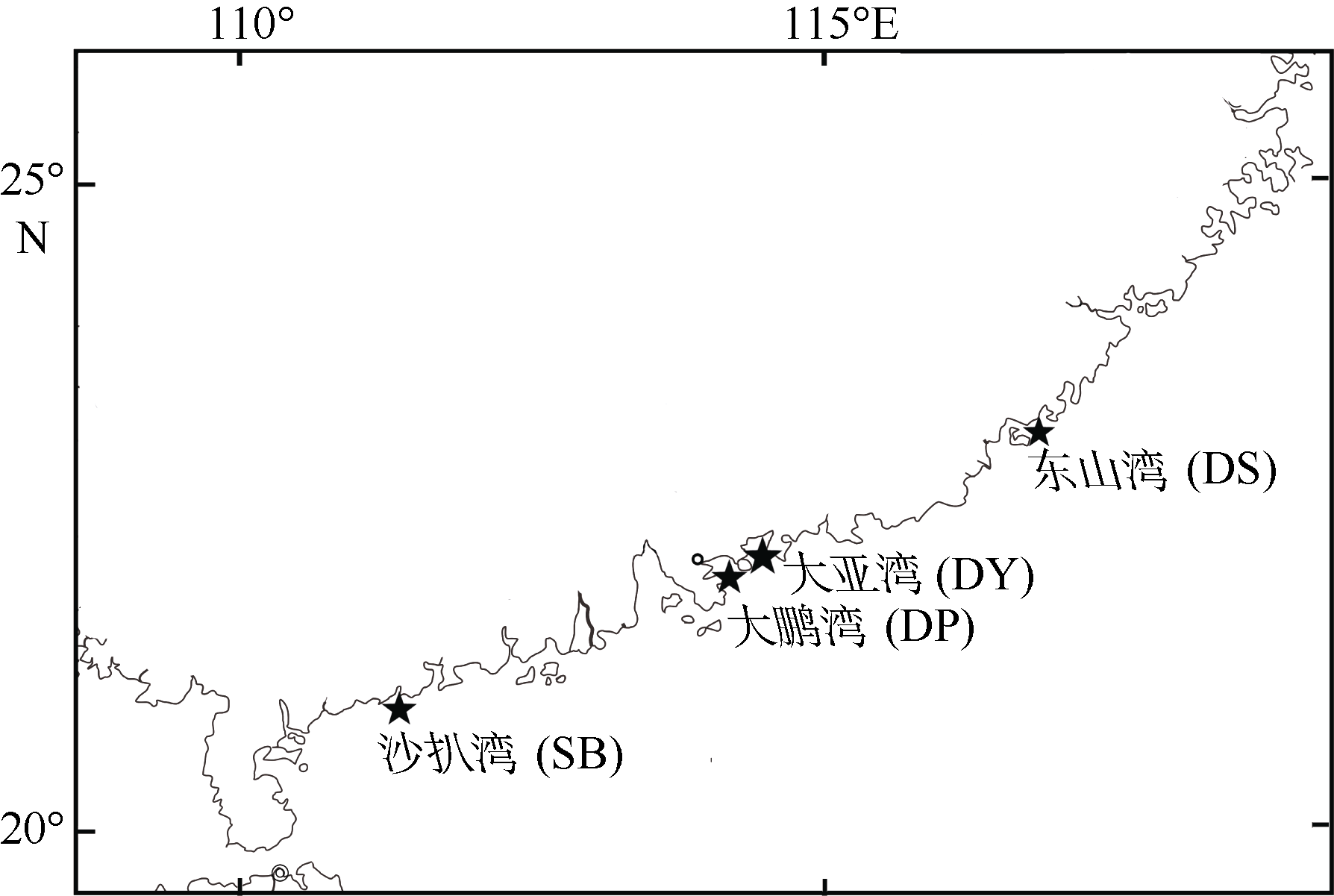
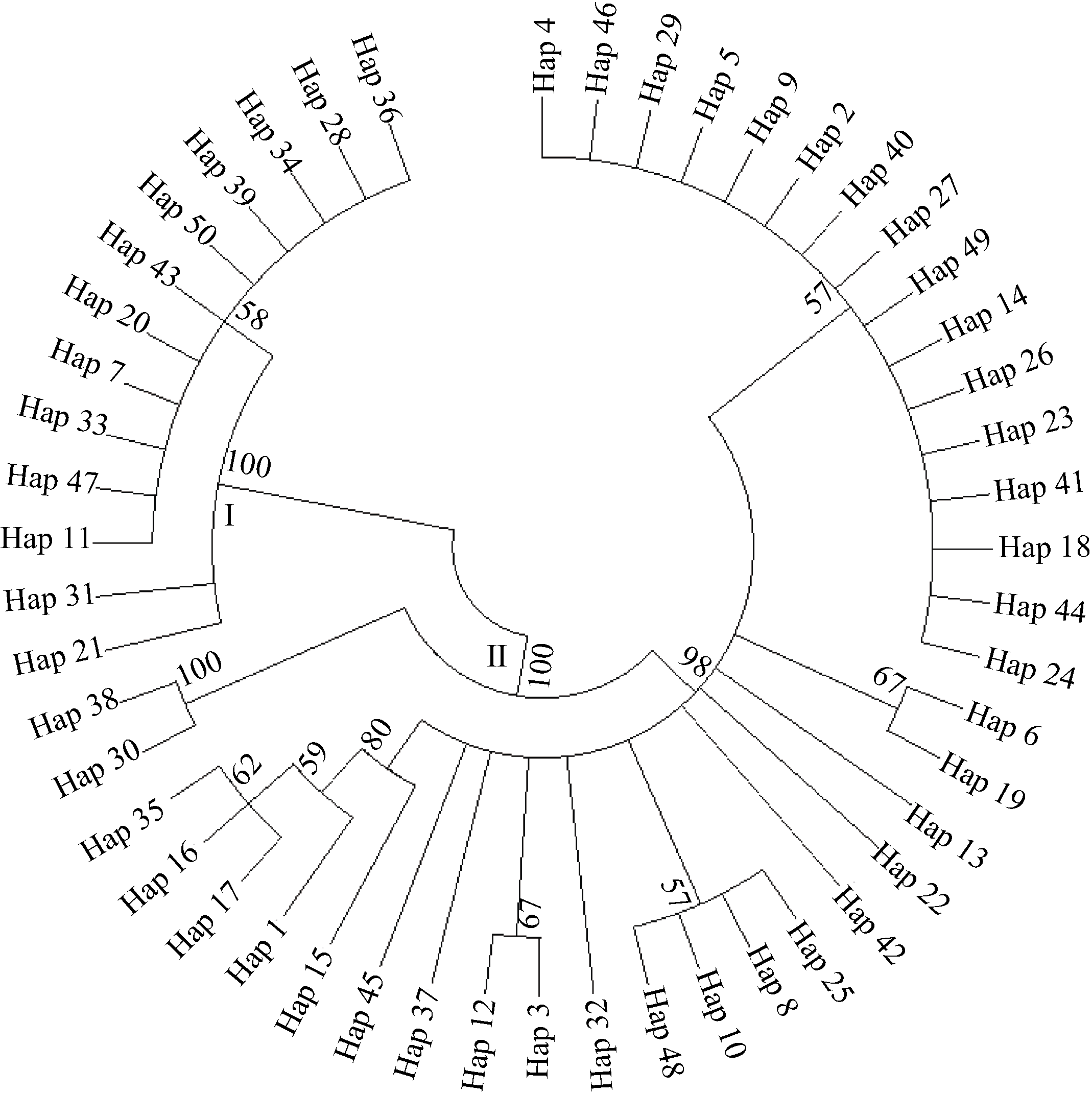
| 1 |
高天翔, 毕潇潇, 赵林林, 等, 2013. 基于线粒体Cytb基因全序列的松江鲈群体遗传结构分析[J]. 水生生物学报, 37(2): 199-207.
|
|
GAO TIANXIANG, BI XIAOXIAO, ZHAO LINLIN, et al, 2013. Population genetic structure of roughskin sculpin Trachidermus fasciatus based on the mitochondrial Cytb sequence[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 37(2): 199-207 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 2 |
龚金波, 2006. 中国近海两种鲷科鱼类遗传结构及遗传多样性分析[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 24-25.
|
|
GONG JINBO, 2006. Genetic structure and genetic diversity of two sparidae in Chinese coastal waters[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 24-25 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 3 |
李敏, 张鹏, 李玉芳, 等, 2015. 南海扁舵鲣种群遗传结构和遗传多样性评价[J].南方水产科学, 11(5): 82-89.
|
|
LI MIN, ZHANG PENG, LI YUFANG, et al, 2015. Population genetic structure and genetic diversity of frigate tuna (Auxis thazard) in the South China Sea[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 11(5): 82-89 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 4 |
孟庆闻, 苏锦祥, 缪学祖, 1995. 鱼类分类学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社: 898-900 (in Chinese).
|
| 5 |
谭杰, 孙慧玲, 刘萍, 等. 2007. 仿刺参自然群体和养殖群体间遗传变异的微卫星标记研究[J]. 海洋水产研究, 28(3): 38-43.
|
|
TAN JIE, SUN HUILING, LIU PING, et al.2007. Microsatellites analysis of genetic variation between natural and culture populations of Apostichopus japonicus[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 28(3): 38-43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 6 |
唐文乔, 胡雪莲, 杨金权, 2007. 从线粒体控制区全序列变异看短颌鲚和湖鲚的物种有效性[J]. 生物多样性, 15(3): 224-231.
|
|
TANG WENQIAO, HU XUELIAN, YANG JINQUAN, 2007. Species validities of Coilia brachygnathus and C. Nasus taihuensis based on sequence variations of complete mtDNA control region[J]. Biodiversity Science, 15(3): 224-231 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 7 |
徐汗福, 黄鹤忠, 范皖苏, 等, 2011. 乌苏里拟鲿野生群体和人工养殖群体遗传多样性的比较研究[J]. 海洋科学, 35(3): 17-22.
|
|
XU HANFU, HUANG HEZHONG, FAN WANSU, et al, 2011. Genetic diversity analyses of wild and cultured Pseudobagrus ussuriensis populations[J]. Marine Sciences, 35(3): 17-22 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 8 |
徐树德, 刘雪兵, 王树启, 等, 2014. 不同类型饲料对黄斑篮子鱼幼鱼生长及肌肉蛋白质和脂肪酸组成的影响[J]. 海洋渔业, 36(6): 529-535.
|
|
XU SHUDE, LIU XUEBING, WANG SHUQI, et al, 2014. Effects of different diets on growth performance and flesh protein and fatty acid composition in juvenile Siganus canaliculatus[J]. Marine Fisheries, 36(6): 529-535 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 9 |
赵亮, 张洁, 刘志瑾, 等, 2010. 乔氏新银鱼基于细胞色素b序列的种群遗传结构和种群历史[J]. 生物多样性, 18(3): 251-261.
|
|
ZHAO LIANG, ZHANG JIE, LIU ZZHIJIN, et al, 2010. Population genetic structure and demographic history of Neosalanx jordani based on cytochrome b sequences[J]. Biodiversity Science, 18(3): 251-261 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 10 |
中国科学院动物研究所, 中国科学院海洋研究所, 上海水产学院, 1962. 南海鱼类志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 733 (in Chinese).
|
| 11 |
庄平, 宋超, 章龙珍, 等, 2008. 黄斑篮子鱼肌肉营养成分与品质的评价[J]. 水产学报, 32(1): 77-83.
|
|
ZHUANG PING, SONG CHAO, ZHANG LONGZHEN, et al, 2008. Evaluation of nutritive quality and nutrient components in the muscle of Siganus oramin[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 32(1): 77-83 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 12 |
CANTATORE P, ROBERTI M, PESOLE G, et al, 1994. Evolutionary analysis of cytochrome b sequences in some Perciformes: Evidence for a slower rate of evolution than in mammals[J]. Journal of Molecular Evolution, 39(6): 589-597.
|
| 13 |
CHAN K M, 1995. Concentrations of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead in rabbitfish (Siganus oramin) collected in Victoria Harbour, Hong Kong[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31(4-12): 277-280.
|
| 14 |
FU Y X, 1997. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection[J]. Genetics, 147(2): 915-925.
|
| 15 |
HAN ZHIQIANG, GAO TIANXIANG, YANAGIMOTO T, et al, 2008. Genetic population structure of Nibea albiflora in Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Fisheries Science, 74(3): 544-552.
|
| 16 |
HEWITT G, 2000. The genetic legacy of the quaternary ice ages[J]. Nature, 405(6789): 907-913.
|
| 17 |
ISHIKAWA S, AOYAMA J, TSUKAMOTO K, et al, 2001. Population structure of the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica as examined by mitochondrial DNA sequencing[J]. Fisheries Science, 67(2): 246-253.
|
| 18 |
JIANG BIAO, WANG JING, LUO HENGLI, et al, 2017. L-amino acid oxidase expression profile and biochemical responses of rabbitfish (Siganus oramin) after exposure to a high dose of Cryptocaryon irritans[J]. Fish & Shellfish Immunology, 69: 85-89.
|
| 19 |
KURIIWA K, HANZAWA N, YOSHINO T, et al, 2007. Phylogenetic relationships and natural hybridization in rabbitfishes (Teleostei: Siganidae) inferred from mitochondrial and nuclear DNA analyses[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 45(1): 69-80.
|
| 20 |
LAMBECK K, ESAT T M, POTTER E K, 2002. Links between climate and sea levels for the past three million years[J]. Nature, 419(6903): 199-206.
|
| 21 |
LIU JINXIAN, GAO TIANXIANG, WU SHIFANG, et al, 2007. Pleistocene isolation in the Northwestern Pacific marginal seas and limited dispersal in a marine fish, Chelon haematocheilus (Temminck & Schlegel, 1845)[J]. Molecular Ecology, 16(2): 275-288.
|
| 22 |
LIU JINXIAN, GAO TIANXIANG, YOKOGAWA K, et al, 2006. Differential population structuring and demographic history of two closely related fish species, Japanese sea bass (Latolabrax japonicus) and spotted sea bass (Lateolabrax maculatus) in Northwestern Pacific[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 39(3): 799-811.
|
| 23 |
LIU Y X, MA CHUNYAN, MA HONGYU, et al, 2015. Discovery and characterization of a first set of polymorphic microsatellite markers in Siganus oramin[J]. Genetics and Molecular Research, 14(4): 15320-15324.
|
| 24 |
ROLDAN M I, PERROTTA G R, CORTEY M, et al, 2000. Molecular and morphologic approaches to discrimination of variability patterns in chub mackerel, Scomber japonicus[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 253(1): 63-74.
|
| 25 |
ROSEL P E, DIZON A E, HAYGOOD M G, 1995. Variability of the mitochondrial control region in populations of the harbour porpoise, Phocoena, on interoceanic and regional scales[J]. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 52(6): 1421-1429.
|
| 26 |
SHAKLEE J B, 1982. Speciation and evolution of marine fishes studied by the electrophoretic analysis of proteins[J]. Pacific Science, 36(2): 141-157.
|
| 27 |
TABATA K, TANIGUCHI N, 2000. Differences between Pagrus major and Pagrus auratus through mainly mtDNA control region analysis[J]. Fisheries Science, 66(1): 9-18.
|
| 28 |
TUDELA S, GARCÍA-MARÍN L, PLA C, 1999. Genetic structure of the European anchovy, Engraulis encrasicolus l, in the north-west Mediterranean[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 234(1): 95-109.
|
| 29 |
WRIGHT S, 1951. The genetical structure of populations[J]. Annals of Eugenics, 15(1): 323-354.
|
| 30 |
XIAO YONGSHUANG, ZHANG YAN, GAO TIANXIANG, et al, 2009. Genetic diversity in the mtDNA control region and population structure in the small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis[J]. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 85(4): 303-314.
|
| 31 |
YOUSIF O M, OSMAN M F, ANAWHI A A, et al, 1996. Optimum protein-to-energy ratio for two size groups of rabbitfish, Siganus canaliculatus (Park)[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition, 2(4): 229-233.
|
| 32 |
ZHOU LIBIN, XIE ZHENZHEN, ZHANG YONG, 2016. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Siganus canaliculatus (Perciformes: Siganidae)[J]. Mitochondrial DNA, 27(2): 1111-1112.
|
 ), Wenjun LI1, Heizhao LIN1,2(
), Wenjun LI1, Heizhao LIN1,2( ), Yukai YANG1,2, Tao LI1,2, Wei YU1,2, Zhong HUANG1,2
), Yukai YANG1,2, Tao LI1,2, Wei YU1,2, Zhong HUANG1,2