Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 153-164.doi: 10.11978/2023130CSTR: 32234.14.2023130
• Marine Environmental Science • Previous Articles Next Articles
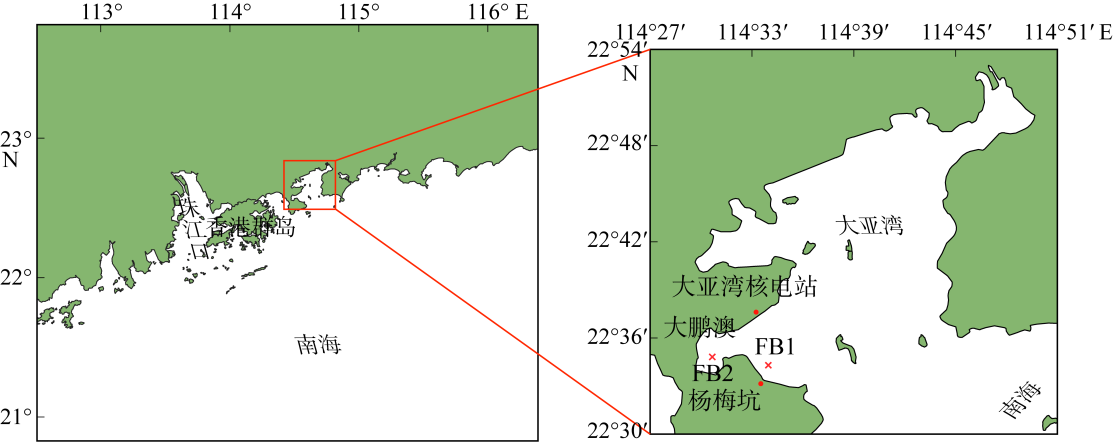
Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys
XI Chen1( ), LIN Zongxuan2, SA Rula3, DENG Xi1, LIU Qiang1, NI Liang1, LUO Laicai4, MA Teng5, XIE Zhijie6, CHEN Siruo2, CHEN Songze3(
), LIN Zongxuan2, SA Rula3, DENG Xi1, LIU Qiang1, NI Liang1, LUO Laicai4, MA Teng5, XIE Zhijie6, CHEN Siruo2, CHEN Songze3( )
)
- 1. China Nuclear Power Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd., Shenzhen 518000, China
2. Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Marine Archaea Geo-Omics, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China
3. Shenzhen Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Center of Guangdong Province, Shenzhen 518049, China
4. Shenzhen Lightsun Industry Co. Ltd., Shenzhen 518000, China
5. Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
6. Department of Ocean Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518005, China
-
Received:2023-08-29Revised:2023-09-26Online:2024-07-10Published:2024-07-22 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42141003); Key Program of Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund (Guangdong-Shenzhen Joint Fund)(2021B1515120080); Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Marine Archaea Geo-Omics, Southern University of Science and Technology(ZDSYS201802081843490); Special Funds for the Cultivation of Guangdong College Students’ Scientific and Technological Innovation(pdjh2022c0029)
Cite this article
XI Chen, LIN Zongxuan, SA Rula, DENG Xi, LIU Qiang, NI Liang, LUO Laicai, MA Teng, XIE Zhijie, CHEN Siruo, CHEN Songze. Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 153-164.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
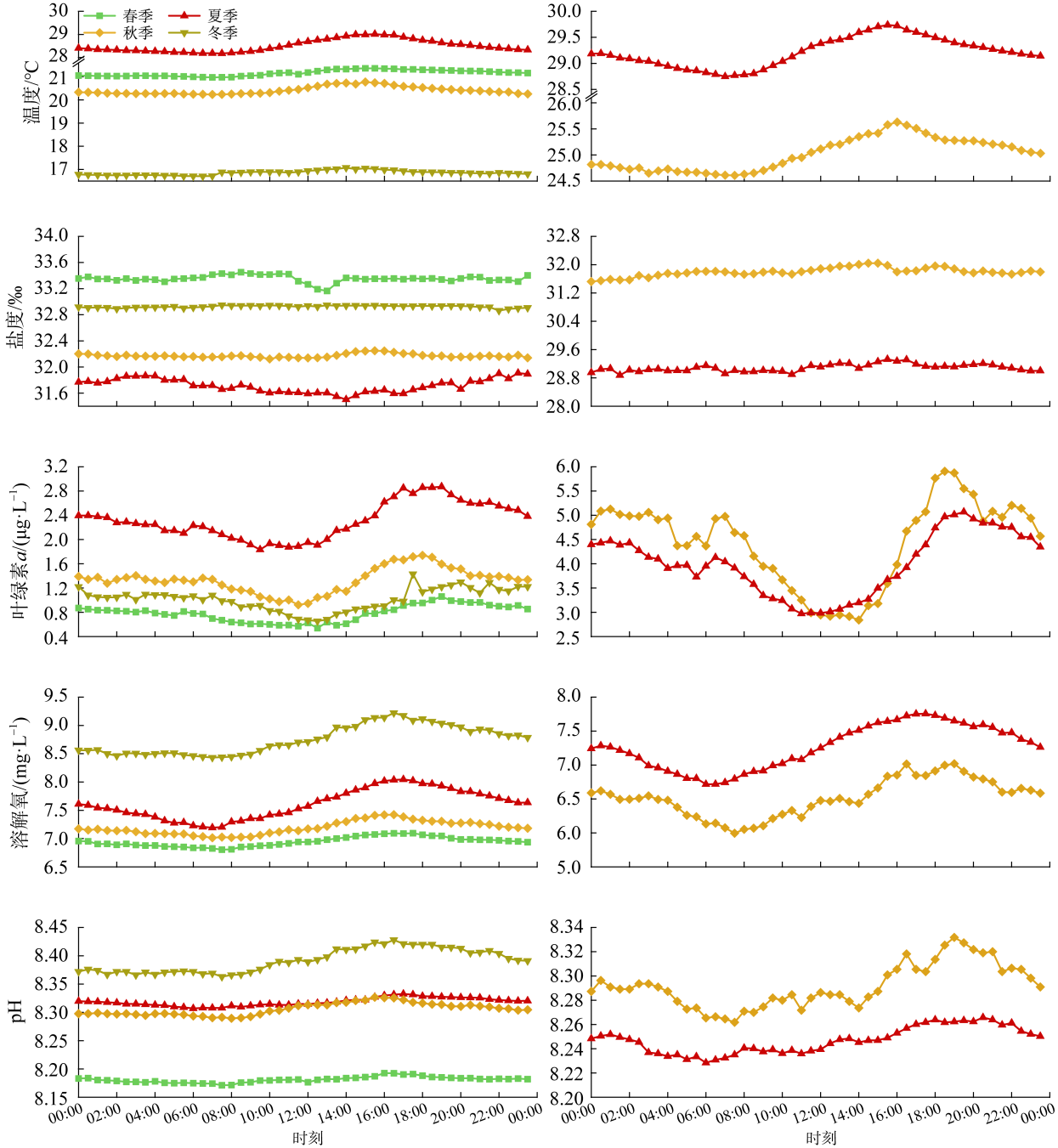
Tab. 2
Seasonal average values of environmental parameters of FB1"
| 季节 | 环境参数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | DO/(mg·L−1) | pH | Chl a/(μg·L−1) | |
| 春季 | 21.16±2.18 | 33.35±1.28 | 6.95±0.74 | 8.18±0.20 | 0.79±0.36 |
| 夏季 | 28.51±2.48 | 31.72±2.82 | 7.61±0.86 | 8.32±0.16 | 2.31±1.52 |
| 秋季 | 20.41±2.63 | 32.17±0.81 | 7.19±0.67 | 8.31±0.10 | 1.33±1.15 |
| 冬季 | 16.82±0.59 | 32.93±0.06 | 8.75±1.14 | 8.39±0.10 | 1.03±0.45 |
| Z | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| P | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
Tab. 4
Average values of environmental parameters of FB1 and FB2 in summer and autumn"
| 季节 | 环境参数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | DO/(mg·L−1) | pH | Chl a/(μg·L−1) | |
| FB1_夏季 | 28.51±2.48 | 31.72±2.82 | 7.61±0.86 | 8.32±0.16 | 2.31±1.52 |
| FB1_秋季 | 20.41±2.63 | 32.17±0.81 | 7.19±0.67 | 8.31±0.10 | 1.33±1.15 |
| FB2_夏季 | 29.21±2.87 | 29.08±3.21 | 7.26±0.97 | 8.24±0.12 | 4.00±2.85 |
| FB2_秋季 | 25.02±0.52 | 31.80±0.87 | 6.52±0.76 | 8.29±0.05 | 4.45±1.97 |
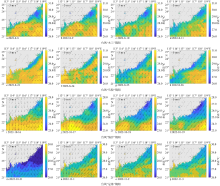
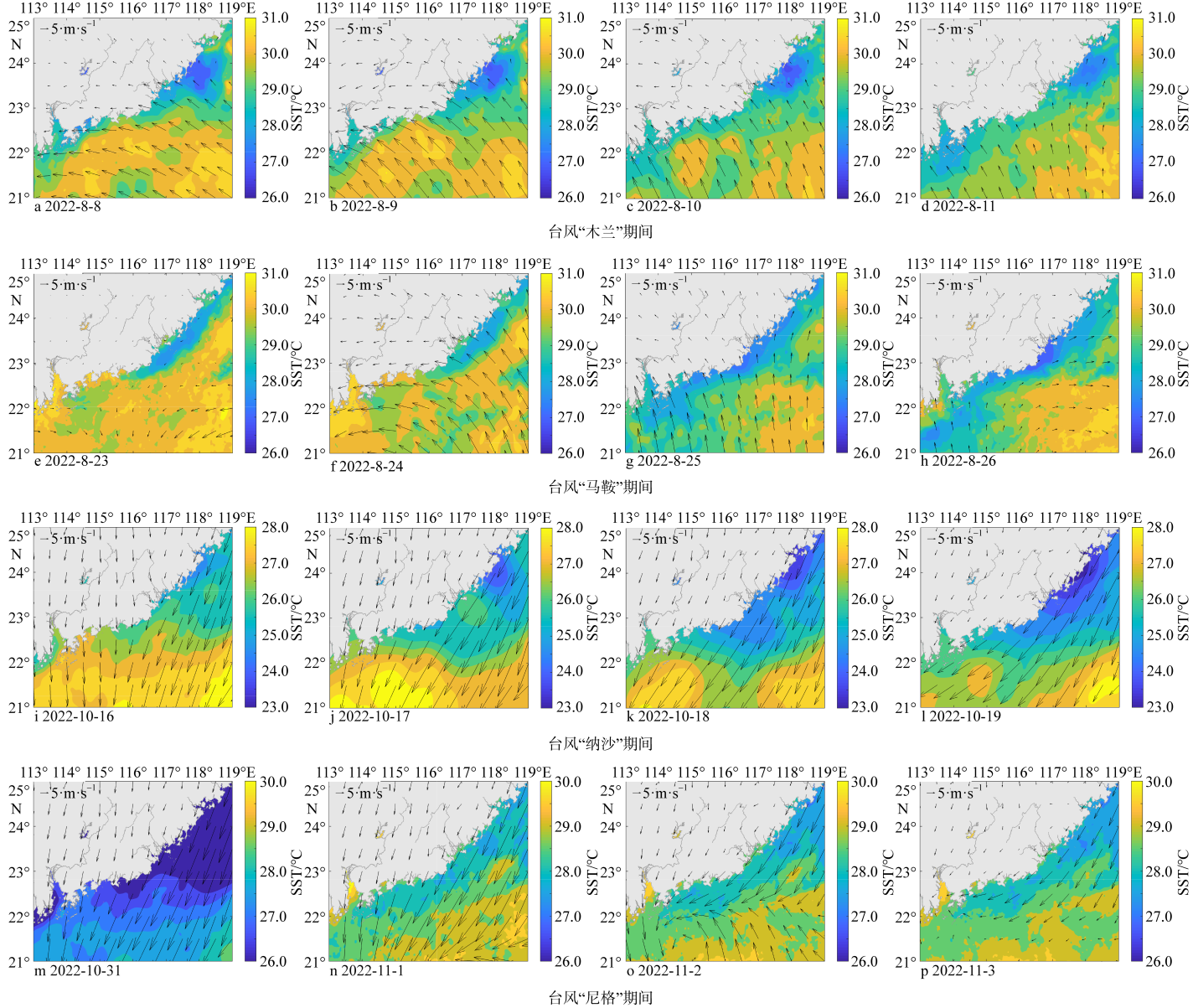
Fig. 3
Changes of environmental parameters of FB2 during typhoon blue and yellow dotted lines are the time when Meteorological Bureau of Shenzhen Municipality issued typhoon blue and yellow warning, and black dotted lines are the time when the typhoon was downgraded by the National Meteorological Center"
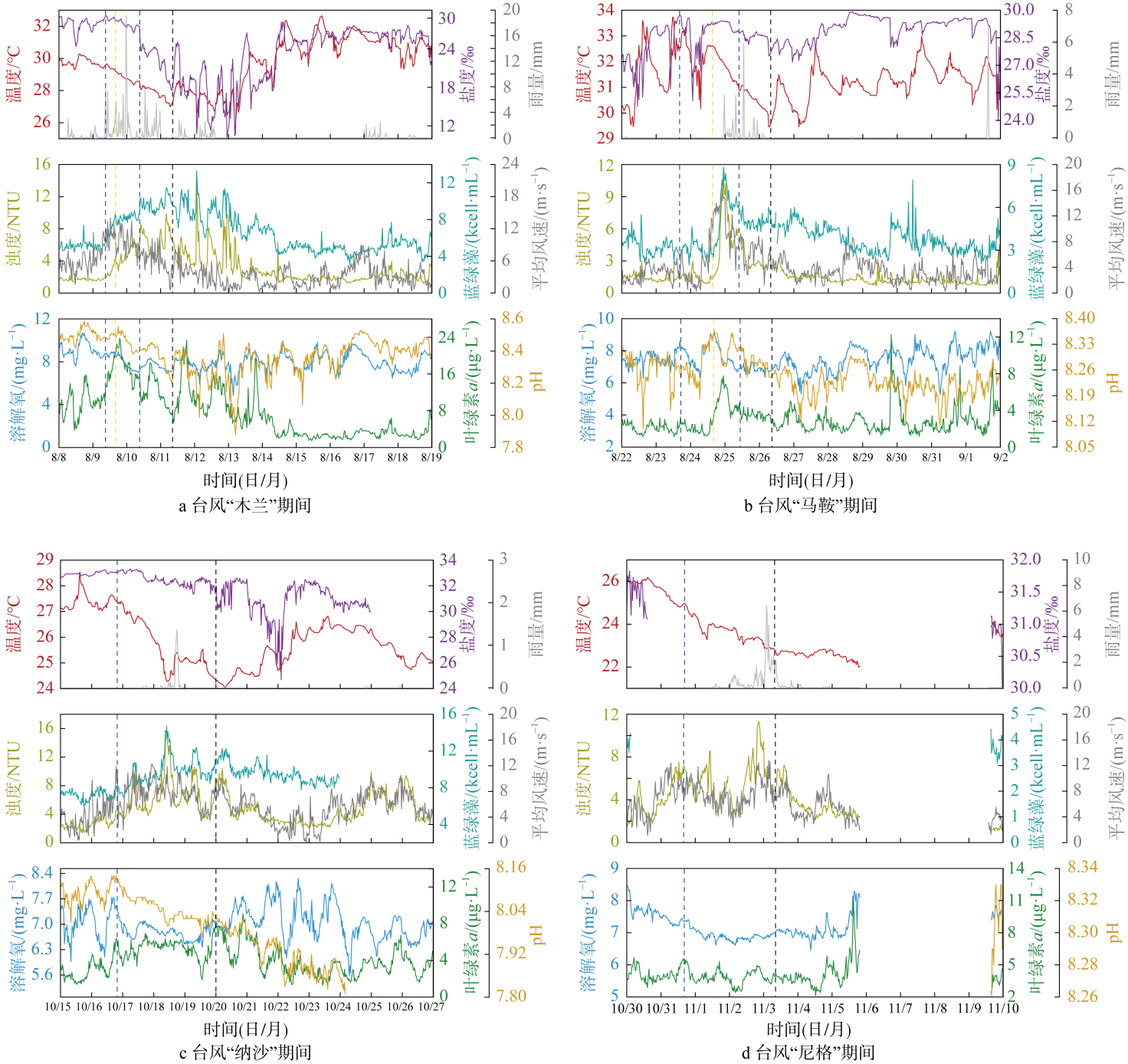
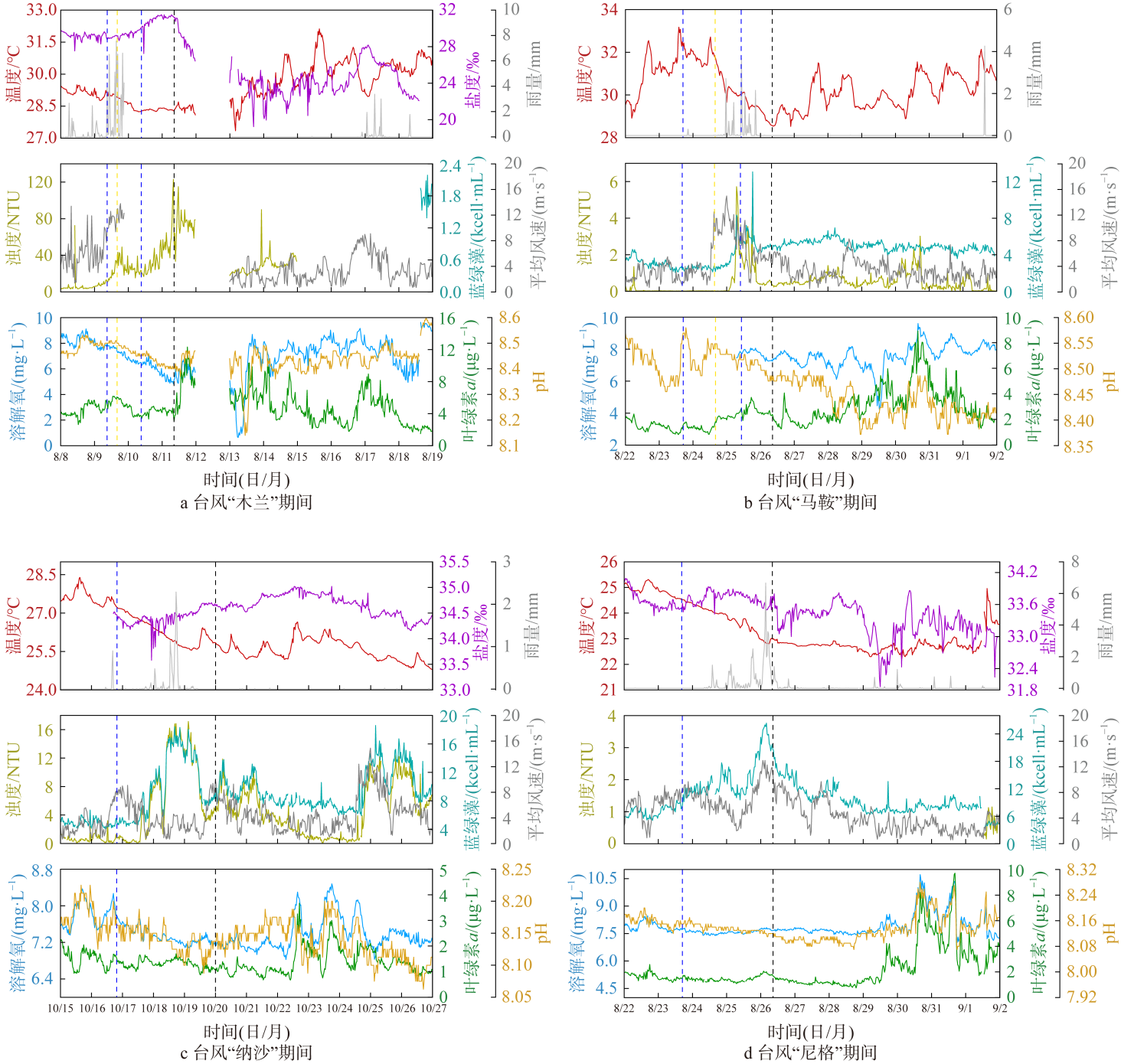
Fig. 4
Changes of environmental parameters of FB1 during typhoon (blue and yellow dotted lines are the time when Meteorological Bureau of Shenzhen Municipality issued typhoon blue and yellow warning, and black dotted lines are the time when the typhoon was downgraded by the National Meteorological Center)"
| [1] |
曹公平, 宋金宝, 樊伟, 2013. 2007年长江口邻近海域夏季上升流演变机制研究[J]. 海洋科学, 37(1): 102-112.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈飞羽, 2016. 大鹏澳海域微表层与次表层浮游植物光合色素时空分布特征研究[D]. 广州: 暨南大学.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈其焕, 庄亮钟, 陈兴群, 1990. 大亚湾叶绿素a与初级生产力[C]// 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 自然资源部第三海洋研究所:198-209.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
陈希荣, 2019. 2015年夏季珠江口区域水文特征的观测与分析[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
黄云峰, 江涛, 冯佳和, 等, 2012. 珠江口广州海域叶绿素a分布特征及环境调控因素[J]. 海洋环境科学, 31(3): 379-384, 404.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
孔祥鹏, 2014. 辽东湾顶自净能力季节变化与排污调控策略[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
李立, 曾刚, 许金殿, 1990a. 大亚湾1987年夏季冷水的入侵现象[C]// 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 自然资源部第三海洋研究所:95-99.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李立, 张炳凯, 曾刚, 1990b. 大亚湾的海流特征[C]// 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 自然资源部第三海洋研究所:87-94.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李禹辉, 邱云, 杨龙奇, 等, 2021. 大亚湾及其邻近海域夏季温度、盐度的分布特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 40(2): 284-292.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
林凯荣, 何艳虎, 雷旭, 等, 2013. 深圳市1960-2009年降雨时空变化分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 3(3): 18-23.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
林志兰, 2006. 海湾富营养化非点源污染的评估与控制研究——以福建罗源湾为例[D]. 厦门: 国家海洋局第三海洋研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
牟新悦, 陈敏, 张琨, 等, 2017. 夏季大亚湾悬浮颗粒有机物碳、氮同位素组成及其物源指示[J]. 海洋学报, 39(2): 39-52.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
宋国栋, 石晓勇, 祝陈坚, 2007. 春季黄海溶解氧的平面分布特征及主要影响因素初探[J]. 海洋环境科学, 26(6): 534-536.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
孙丽华, 陈浩如, 彭云辉, 等, 2003. 大亚湾大鹏澳周边河流中营养盐的分布及入海通量的估算[J]. 台湾海峡, 22(2): 211-217.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
田媛, 李涛, 胡思敏, 等, 2020. 广东省沿岸海域藻华发生的时空特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 39(1): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
王盼盼, 2015. 长江口及邻近海域沉积物再悬浮对水体营养盐的影响研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
王友绍, 王肇鼎, 黄良民, 2004. 近20年来大亚湾生态环境的变化及其发展趋势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 23(5): 85-95.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
吴仁豪, 蔡树群, 王盛安, 等, 2007. 大亚湾海域潮流和余流的三维数值模拟[J]. 热带海洋学报, 26(3): 18-23.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
谢福武, 刘华雪, 黄洪辉, 等, 2018. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构对温排水和营养盐输入的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(3): 55-64.
doi: 10.11978/2017083 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2017083 |
|
| [20] |
许金电, 黄奖, 邱云, 等, 2015. 浙闽沿岸水的空间结构特征及生消过程[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(1): 1-7.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.01.001 |
|
|
|
| [21] |
杨文超, 黄道建, 陈继鑫, 等, 2020. 大亚湾海域2009-2018年重金属时空分布及污染评价[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 52(5): 65-75.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
殷建平, 王友绍, 徐继荣, 等, 2006. 大亚湾温跃层形成及其对有关环境要素的影响[J]. 海洋通报, 25(4): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
曾流明, 1986. 粤东沿岸上升流迹象的初步分析[J]. 热带海洋, 5(1): 68-73.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
张炳楷, 曾刚, 李立, 1990. 大亚湾的水温和盐度[C]// 大亚湾海洋生态文集(Ⅱ). 北京: 海洋出版社, 自然资源部第三海洋研究所: 67-74.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
郑利涛, 2019. 深圳大亚湾水质模拟与风险扩散预测研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
郑哲昊, 庄伟, 孙振宇, 等, 2020. 大亚湾及其邻近海域冬季温度、盐度的分布及日变化特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 39(1): 71-79.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
钟保粦, 1995. 用5天滑动平均气温作深圳市的四季划分[J]. 气象, 21(6): 22-23.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
朱明, 张学成, 茅云翔, 等, 2003. 温度、盐度及光照强度对海链藻(Thalassiosira sp. )生长的影响[J]. 海洋科学, 27(12): 58-61.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
pmid: 15361622 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [1] | ZHANG Zheran, HU Junyang, ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Penghui, XING Jiuxing, CHEN Shengli. Storm surge simulations of the coastal area of Shenzhen using different types of typhoon meteorological fields—a case study of Typhoon Mangkhut* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
| [2] | SUN Cuici, YUE Weizhong, ZHAO Wenjie, WANG Youshao. Distribution of the microbial Carbohydrate-Active enzymes genes in the surface sediment of the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [3] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [4] | JIANG Xun, WU Wen, SONG Dehai. Identification and quantitative analysis of key controlling factors of water quality response to human activities in the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 182-191. |
| [5] | CHEN Jingfu, ZHONG Yu, WANG Lei, GUO Yupei, QIU Dajun. Noctiluca scintillans effects on eukaryotic plankton community structure using Environmental DNA analysis in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [6] | SU Jinzhu, ZOU Jiashu, SU Yuping, ZHANG Mingfeng, WENG Zhenzhou, Yang Xiaoqiang. Study on the early warning model of red tide in the offshore area of Pingtan, Fujian province [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 172-180. |
| [7] | ZHANG Wanru, LIU Qingxia, HUANG Honghui, QIN Xiaoqing, LI Jiajun, CHEN Jianhua. Study on stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen of main fishery organisms in the southwestern waters of Daya Bay, South China Sea in winter 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [8] | LI Ao, FENG Yang, WANG Yuntao, XUE Huijie. Spatiotemporal variation of water area with high chlorophyll a concentration in the South China Sea based on OC-CCI data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 77-89. |
| [9] | LI Yao, XIANG Chenhui, JIANG Zhijian, SONG Xingyu. Production and metabolism characteristics of planktonic community and their influencing factors in Daya Bay during summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 83-92. |
| [10] | XIANG Chenhui, LIU Jiaxing, KE Zhixin, ZHOU Linbin, TAN Yehui. Phytoplankton responses to Dan’ao River estuary water enrichment in terms of size structure and community composition* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(2): 49-60. |
| [11] | HUANG Jianzhong, WEI Yuheng, GU Zhifeng, WU Chuanliang, XU Qiang, WANG Aiming, LI Xiubao. Coral community change and its influencing factors in Ximaozhou Island of Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 103-113. |
| [12] | ZHANG Liming, TAN Yehui, LI Jiajun, HUANG Xiaoping, LIU Jiaxing. Characteristics of the phytoplankton community and its response to Dan’ao River input in Daya Bay in summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [13] | ZHANG Xin, CHEN Mingyu. Analysis of characteristics of brightness temperature relative power spectrum before and after typhoon landfall in Guangdong coastal area [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(6): 29-40. |
| [14] | Hui WANG,Hengxiang LI,Lu LI,Yan YAN. The population distribution of Hyale grandicornis in macroalgae canopies of Daya Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 52-58. |
| [15] | Fuwu XIE, Xingyu SONG, Yehui TAN, Meiting TAN, Yadong HUANG, Huaxue LIU. Impact of simulated warming and nutrients input on plankton community metabolism in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 48-57. |
|
||