Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 163-171.doi: 10.11978/2021173CSTR: 32234.14.2021173
• Marine Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Release potential of different forms of nitrogen extracted by chemical leaching in the surface sediments of the Bohai Sea
LI Zhen1( ), LI Yunkai1,2, LIU Yonghu3, CHENG Qian3, ZHANG Shuo1,2,4(
), LI Yunkai1,2, LIU Yonghu3, CHENG Qian3, ZHANG Shuo1,2,4( )
)
- 1. College of Marine Sciences, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
2. Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Education for the Sustainable Development of Ocean Fishery Resources, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
3. Dalian Modern Marine Ranch Research Institute, Dalian 116023, China
4. Joint Laboratory for Monitoring and Protection of Aquatic Organisms in the Yangtze River Estuary, Shanghai 201306, China
-
Received:2021-12-05Revised:2022-02-22Online:2022-07-10Published:2022-03-01 -
Contact:ZHANG Shuo E-mail:lz20181920@163.com;s-zhang@shou.edu.cn -
Supported by:Shanghai Talent Development Fund Support Project(B1-5404-19-0002);Local Capacity Building Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Science and Technology(21010502200)
CLC Number:
- P734.44
Cite this article
LI Zhen, LI Yunkai, LIU Yonghu, CHENG Qian, ZHANG Shuo. Release potential of different forms of nitrogen extracted by chemical leaching in the surface sediments of the Bohai Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 163-171.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
General parameters of sediments and overlying water"
| 项目 | 含量范围 | 均值±标准差 |
|---|---|---|
| 黏土/% | 2.42~23.5 | 12.23±5.17 |
| 粉砂/% | 8.66~74.98 | 50.65±17.38 |
| 砂/% | 5.43~88.92 | 37.1±21.45 |
| 有机质/(mg?kg-1) | 2575.89~50629.18 | 24945.31±11147.38 |
| 表层海水DIN/(mg?L-1) | 0.04~0.21 | 0.08 ±0.04 |
| 表层海水Chl a/(μg?L-1) | 0.80~2.81 | 1.60±0.49 |
| 底层海水DIN/(mg?L-1) | 0.06~0.19 | 0.09±0.03 |
| 底层海水Chl a/(μg?L-1) | 0.92~10.60 | 4.43±0.50 |
Tab. 2
Content and release capacity of each TTN"
| TTN形态 | 范围 | 均值±标准差 | |
|---|---|---|---|
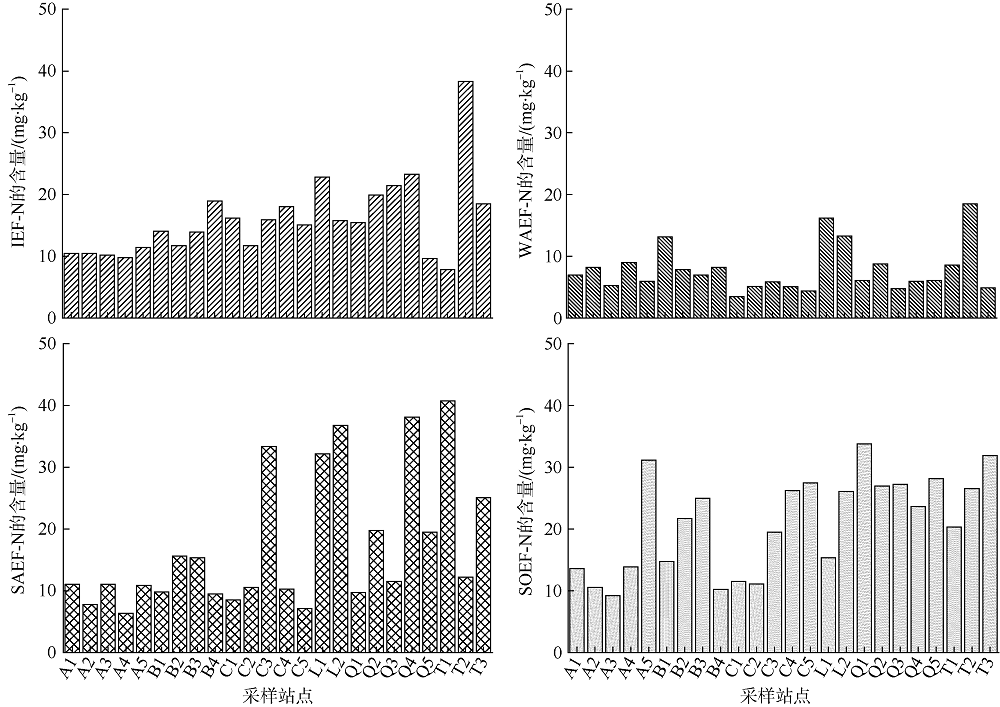
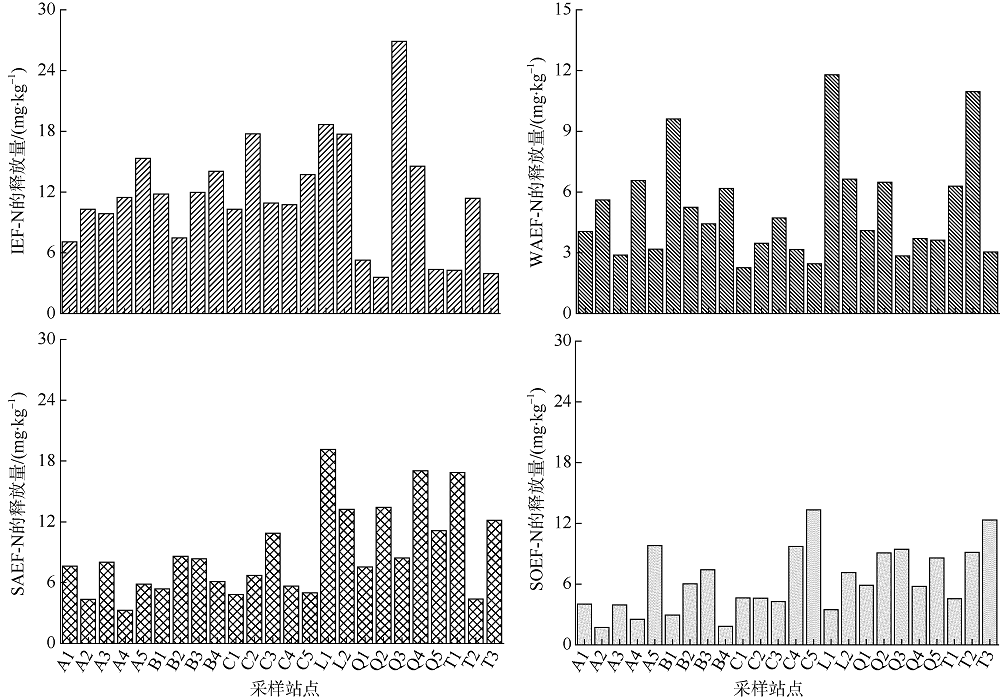
| 含量/(mg?kg-1) | IEF-N | 7.85~38.28 | 15.87±6.34 |
| WAEF-N | 3.44~18.48 | 7.86±3.72 | |
| SAEF-N | 6.36~40.72 | 17.19±10.71 | |
| SOEF-N | 9.21~33.76 | 21.07±7.60 | |
| 释放量/(mg?kg-1) | IEF-N | 3.57~26.89 | 11.40±5.26 |
| WAEF-N | 2.23~11.79 | 5.13±2.54 | |
| SAEF-N | 3.25~19.16 | 8.91±4.32 | |
| SOEF-N | 1.71~13.31 | 6.34±3.17 | |
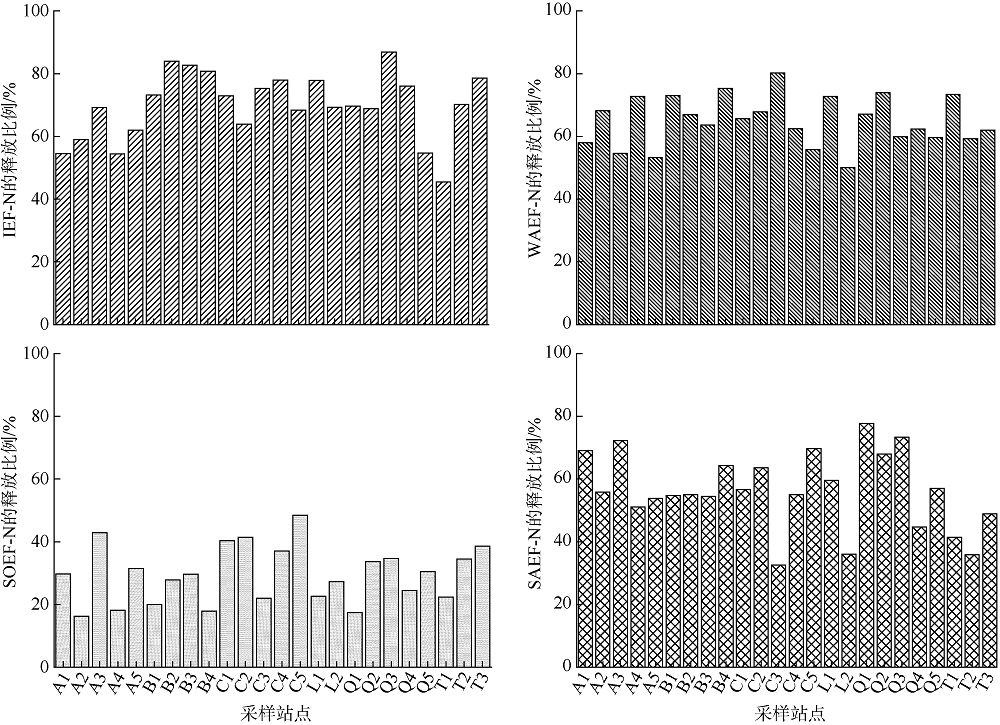
| 释放比例/% | IEF-N | 45.5~86.93 | 69.83±10.38 |
| WAEF-N | 50.03~80.28 | 64.93±7.68 | |
| SAEF-N | 32.63~77.79 | 56.27±12.01 | |
| SOEF-N | 16.23~48.47 | 29.56±8.83 |
Tab. 3
Correlation analysis between the nitrogen release capacity of each TTN and the physical and chemical properties of the sediment"
| RIEF-N | RWAEF-N | RSAEF-N | RSOEF-N | IEF-N | WAEF-N | SAEF-N | SOEF-N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIEF-N | 1 | 0.414* | 0.974** | 0.106 | 0.273 | |||
| RWAEF-N | 0.370 | 1 | 0.439* | 0.959** | 0.221 | -0.175 | ||
| RSAEF-N | 0.121 | 0.215 | 1 | 0.099 | 0.181 | 0.902** | 0.196 | |
| RSOEF-N | 0.296 | -0.340 | 0.024 | 1 | 0.295 | -0.213 | -0.002 | 0.822** |
| TN | -0.038 | 0.072 | -0.080 | -0.047 | 0.009 | 0.195 | 0.078 | -0.053 |
| 黏土 | 0.280 | 0.093 | 0.039 | 0.217 | 0.315 | 0.144 | 0.076 | 0.285 |
| 粉砂 | 0.208 | 0.100 | -0.173 | -0.162 | 0.201 | 0.089 | -0.157 | -0.169 |
| 砂 | -0.236 | -0.104 | 0.131 | 0.079 | -0.239 | -0.107 | 0.109 | 0.068 |
| OM | 0.404 | 0.131 | 0.055 | 0.239 | 0.402 | 0.201 | 0.063 | 0.194 |
Tab. 4
Correlation analysis of TTN and its release in the surface sediments on nutrients and Chl a in seawater"
| RIEF-N | RWAEF-N | RSAEF-N | RSOEF-N | IEF-N | WAEF-N | SAEF-N | SOEF-N | SDIN | SChl a | BChl a | BDIN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIEF-N | 1 | |||||||||||
| RWAEF-N | 0.370 | 1 | ||||||||||
| RSAEF-N | 0.121 | 0.215 | 1 | |||||||||
| RSOEF-N | 0.296 | -0.340 | 0.024 | 1 | ||||||||
| IEF-N | 0.414* | 0.959** | 0.181 | -0.213 | 1 | |||||||
| WAEF-N | 0.974** | 0.439* | 0.099 | 0.295 | 0.501* | 1 | ||||||
| SAEF-N | 0.106 | 0.221 | 0.902** | -0.002 | 0.226 | 0.107 | 1 | |||||
| SOEF-N | 0.273 | -0.175 | 0.196 | 0.822** | -0.070 | 0.276 | 0.197 | 1 | ||||
| SDIN | -0.147 | -0.004 | -0.079 | -0.178 | -0.098 | -0.212 | -0.027 | -0.171 | 1 | |||
| SChl a | 0.033 | 0.371 | 0.122 | -0.367 | 0.381 | -0.007 | 0.013 | -0.385 | -0.235 | 1 | ||
| BChl a | -0.267 | 0.264 | 0.146 | -0.464* | 0.221 | -0.270 | 0.021 | -0.471* | -0.121 | 0.803** | 1 | |
| BDIN | 0.086 | 0.166 | 0.064 | -0.197 | 0.101 | -0.005 | 0.047 | -0.137 | 0.831** | 0.002 | 0.103 | 1 |
| [1] | 戴纪翠, 宋金明, 郑国侠, 等, 2007. 胶州湾沉积物氮的环境生物地球化学意义[J]. 环境科学, 28(9): 1924-1928. |
| DAI JICUI, SONG JINMING, ZHENG GUOXIA, et al, 2007. Environmental biogeochemical significance of nitrogen in Jiaozhou Bay sediments[J]. Environmental Science, 28(9): 1924-1928. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [2] | 何桐, 谢健, 余汉生, 等, 2009. 大亚湾表层沉积物中氮的形态分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 28(2): 86-91. |
| HE TONG, XIE JIAN, YU HANSHENG, et al, 2009. Distribution characteristics of different forms of nitrogen in surface sediments of Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 28(2): 86-91. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 黄欣嘉, 何少华, 王赛, 2017. 湘江衡阳段沉积物对硝态氮的吸附特性研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 17(5): 1922-1926. |
| HUANG XINJIA, HE SHAOHUA, WANG SAI, 2017. Characteristics of adsorption of nitrate nitrogen for the sediment substances in Hengyang section of Xiang River[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 17(5): 1922-1926. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] | 黄小平, 郭芳, 岳维忠, 2006. 南海北部沉积物间隙水中营养盐研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 25(5): 43-48. |
| HUANG XIAOPING, GUO FANG, YUE WEIZHONG, 2006. Studies on nutrients in sediment interstitial water in northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 25(5): 43-48. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [5] | 姜双城, 林培梅, 林建伟, 等, 2014. 厦门湾沉积物中磷的形态特征及环境意义[J]. 热带海洋学报, 33(3): 72-78. |
| JIANG SHUANGCHENG, LIN PEIMEI, LIN JIANWEI, et al, 2014. Distribution characteristics of phosphorus and its environmental significance in the surface sediments of Xiamen Gulf[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 33(3): 72-78. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [6] | 姜霞, 王书航, 等, 2012. 沉积物质量调查评估手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 27-30. (in Chinese) |
| [7] | 吕晓霞, 宋金明, 袁华茂, 等, 2004. 南黄海表层沉积物中氮的潜在生态学功能[J]. 生态学报, 24(8): 1635-1642. |
| LÜ XIAOXIA, SONG JINMING, YUAN HUAMAO, et al, 2004. The potential ecological roles of nitrogen in the surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 24(8): 1635-1642. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [8] | 马红波, 宋金明, 吕晓霞, 等, 2003. 渤海沉积物中氮的形态及其在循环中的作用[J]. 地球化学, 32(1): 48-54. |
| MA HONGBO, SONG JINMING, LÜ XIAOXIA, et al, 2003. Nitrogen forms and their functions in recycling of the Bohai Sea sediments[J]. Geochimica, 32(1): 48-54. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [9] | 裴佳瑶, 冯民权, 2020. 环境因子对雁鸣湖沉积物氮磷释放的影响[J]. 环境工程学报, 14(12): 3447-3459. |
| PEI JIAYAO, FENG MINQUAN, 2020. Effects of environmental factors on the release of nitrogen and phosphorus from the sediment of the Yanming Lake, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 14(12): 3447-3459. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [10] | 孙晓杰, 舒航, 刘云江, 等, 2021. 环境因子对黄河甘宁蒙段表层沉积物中磷吸附-解吸的影响[J]. 水资源保护, 37(4): 51-60. |
| SUN XIAOJIE, SHU HANG, LIU YUNJIANG, et al, 2021. Effects of environmental factors on phosphorus adsorption and desorption in surface sediments of Gansu-Ningxia-Inner Mongolia section of the Yellow River[J]. Water Resources Protection, 37(4): 51-60. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [11] | 王功芹, 朱珠, 张硕, 2016. 海州湾表层沉积物中氮的赋存形态及其生态意义[J]. 环境科学学报, 36(2): 450-457. |
| WANG GONGQIN, ZHANG SHUO, 2016. Nitrogen forms in the surface sediment of Haizhou Bay and their ecological significance[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 36(2): 450-457. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [12] |
张嘉雯, 魏健, 刘利, 等, 2020. 衡水湖沉积物营养盐形态分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 41(12): 5389-5399.
doi: 10.1021/es070722r |
|
ZHANG JIAWEN, WEI JIAN, LIU LI, et al, 2020. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of nutrients in Hengshui Lake sediments[J]. Environmental Science, 41(12): 5389-5399. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.1021/es070722r |
|
| [13] |
张小勇, 孙耀, 石晓勇, 等, 2013. 黄海、东海陆架区沉积物中氮的形态分布及与浮游植物总量的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 35(1): 111-120.
doi: 10.1007/s13131-016-0932-8 |
|
ZHANG XIAOYONG, SUN YAO, SHI XIAOYONG, et al, 2013. The distribution of nitrogen forms and the relationship with the total phytoplankton in the Huanghai Sea and the East China Sea continental shelf[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(1): 111-120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.1007/s13131-016-0932-8 |
|
| [14] | 赵晨英, 臧家业, 刘军, 等, 2016. 黄渤海氮磷营养盐的分布、收支与生态环境效应[J]. 中国环境科学, 36(7): 2115-2127. |
| ZHAO CHENYING, ZANG JIAYE, LIU JUN, et al, 2016. Distribution and budget of nitrogen and phosphorus and their influence on the ecosystem in the Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea[J]. China Environmental Science, 36(7): 2115-2127. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [15] | 赵海超, 王圣瑞, 焦立新, 等, 2013. 洱海沉积物中不同形态氮的时空分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 26(3): 235-242. |
| ZHAO HAICHAO, WANG SHENGRUI, JIAO LIXIN, et al, 2013. Characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution of the nitrogen forms in the sediments of Erhai Lake[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 26(3): 235-242. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [16] | 郑国侠, 宋金明, 孙云明, 等, 2006. 南海深海盆表层沉积物氮的地球化学特征与生态学功能[J]. 海洋学报, 28(6): 44-51. |
| ZHENG GUOXIA, SONG JINMING, SUN YUNMING, et al, 2006. Geochemical characteristics and ecological functions of nitrogen in the abyssal basin surface sediments, South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 28(6): 44-51. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [17] | 周美玲, 张鉴达, 杨小雨, 等, 2018. 昌黎黄金海岸自然保护区海域表层沉积物中氮赋存形态分布特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 37(5): 691-698. |
| ZHOU MEILING, ZHANG JIANDA, YANG XIAOYU, et al, 2018. Distribution of nitrogen in surface sediments of the Golden Beach Ocean Nature reserve, Changli[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 37(5): 691-698. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [18] | 周睿, 袁旭音, BAWK M J, 等, 2018. 不同湖泊入湖河流沉积物可转化态氮的空间分布及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 39(3): 1122-1128. |
| ZHOU RUI, YUAN XUYIN, BAWK M J, et al, 2018. Spatial distributions of transferable nitrogen forms and influencing factors in sediments from inflow rivers in different lake basins[J]. Environmental Science, 39(3): 1122-1128. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [19] | 朱元荣, 张润宇, 吴丰昌, 2011. 滇池沉积物中氮的地球化学特征及其对水环境的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 31(6): 978-983. |
| ZHU YUANRONG, ZHANG RUNYU, WU FENGCHANG, 2011. Geochemical characteristics and influence to overlying water of nitrogen in the sediments from Dianchi Lake[J]. China Environmental Science, 31(6): 978-983. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [20] | 邹景忠, 董丽萍, 秦保平, 1983. 渤海湾富营养化和赤潮问题的初步探讨[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2(2): 41-54. (in Chinese) |
| [21] |
AIGARS J, CARMAN R, 2001. Seasonal and spatial variations of carbon and nitrogen distribution in the surface sediments of the Gulf of Riga, Baltic Sea[J]. Chemosphere, 43(3): 313-320.
doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00150-8 |
| [22] |
BRISTOW L A, MOHR W, AHMERKAMP S, et al, 2017. Nutrients that limit growth in the ocean[J]. Current Biology, 27(11): R474-R478.
doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2017.03.030 |
| [23] |
COWAN J L W, PENNOCK J R, BOYNTON W R, 1996. Seasonal and interannual patterns of sediment-water nutrient and oxygen fluxes in Mobile Bay, Alabama (USA): regulating factors and ecological significance[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 141: 229-245.
doi: 10.3354/meps141229 |
| [24] |
FISHER N S, COWDELL R A, 1982. Growth of marine planktonic diatoms on inorganic and organic nitrogen[J]. Marine Biology, 72(2): 147-155.
doi: 10.1007/BF00396915 |
| [25] |
GARDNER W S, YANG L Y, COTNER J B, et al, 2001. Nitrogen dynamics in sandy freshwater sediments (Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron)[J]. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 27(1): 84-97.
doi: 10.1016/S0380-1330(01)70624-7 |
| [26] | LI H, WANG Y, SHI L Q, et al, 2012. Distribution and fractions of phosphorus and nitrogen in surface sediments from Dianchi Lake, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research, 6(1): 195-208. |
| [27] |
LIU SUMEI, LI LINGWEI, ZHANG ZHINAN, 2011. Inventory of nutrients in the Bohai[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 31(16): 1790-1797.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.08.004 |
| [28] |
LÜ XIAOXIA, SONG JINMING, LI XUEGANG, et al, 2005. Geochemical characteristics of nitrogen in the southern Yellow Sea surface sediments[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 56(1-2): 17-27.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2004.06.009 |
| [29] |
OLSEN S, JEPPESEN E, MOSS B, et al, 2015. Factors influencing nitrogen processing in lakes: an experimental approach[J]. Freshwater Biology, 60(4): 646-662.
doi: 10.1111/fwb.12511 |
| [30] | SCHINDLER D W, HECKY R E, FINDLAY D L, et al, 2008. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: Results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(32): 11254-11258. |
| [31] |
WANG SHENGRUI, JIN XIANGCAN, JIAO LIXIN, et al, 2008. Nitrogen fractions and release in the sediments from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River area, China[J]. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 187(1-4): 5-14.
doi: 10.1007/s11270-007-9453-6 |
| [32] | YANG WANQIU, XIAO HAN, LI YE, et al, 2017. Vertical distribution and release characteristics of nitrogen fractions in sediments in the estuaries of Dianchi Lake, China[J]. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability, 29(1): 110-119. |
| [33] |
YE HONGMENG, YANG HAO, HAN NIAN, et al, 2019. Risk assessment based on nitrogen and phosphorus forms in watershed sediments: A case study of the upper reaches of the Minjiang Watershed[J]. Sustainability, 11(20): 5565.
doi: 10.3390/su11205565 |
| [34] |
ZHAO HAICHAO, ZHAO HAIXIANG, WANG SHENGRUI, et al, 2020. Coupling characteristics and environmental significance of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic carbon in the sediments of Erhai Lake[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(16): 19901-19914.
doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-08120-9 |
| [35] |
ZHENG GUOXIA, SONG JINMING, SUN YUNMING, et al, 2008. Characteristics of nitrogen forms in the surface sediments of southwestern Nansha Trough, South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 26(3): 280-288.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-008-0280-4 |
| [1] | CHEN Jie, BIAN Cheng, JIANG Changbo, YAO Zhen, JIANG Chao, LIANG Hai. Advances in the characterization of bioclastic sediment motion [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 33-41. |
| [2] | MO Danyang, NING Zhiming, YANG Bin, XIA Ronglin, LIU Zhijin. Response of dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in coral reef sediments of the Weizhou island to temperature changes [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [3] | GAO Jie, YU Kefu, XU Shendong, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Biao, WANG Yonggang. Content and source analysis of organic carbon in the outer slope sediments of the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [4] | XING Nannan, REN Runxin, TANG Zhenzhou, LUO Zhihong, XIA Chenxi, LIU Yonghong, PENG Liang, CHEN Xianqiang. Study on the secondary metabolites of fungus Aspergillus sp. GXIMD02003 derived from marine sediment in the Weizhou island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 154-160. |
| [5] | SUN Cuici, YUE Weizhong, ZHAO Wenjie, WANG Youshao. Distribution of the microbial Carbohydrate-Active enzymes genes in the surface sediment of the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [6] | YANG Xialing, LI Shushi, XU Shanshan, YU Chongxi, PAN Jie. Variations in water and sediments of the Nanliu River flowing into the sea under the influence of extreme weather in the past 60 years [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 91-103. |
| [7] | ZHANG Min, WU Hangxing, LU Yibin, LU Diwen, MI Jie, ZHU Donglin, CHEN Bo. Impact of the coastal reclamations on topography evolution in the Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 124-131. |
| [8] | YANG Hongqiang, TAN Fei, XU Huilong, ZHANG Xiyang, SHI Qi, TAO Shichen. Reconstruction of the tropical cyclones activity in the Nansha Islands since the Little Ice Age from the atoll lagoon sediments [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 171-182. |
| [9] | HUANG Zuming, ZHOU Xiaoyan, DAI Zhijun, CHE Zhiwei. Analysis of the variations of suspended sediment concentration in vertical profile near the bed of Aegiceras corniculatum tidal flat [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 38-50. |
| [10] | LI Weihua, LI Jiufa, ZHANG Wenxiang. Research progress in the continuous measurement technology of suspended sediment concentration [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 20-30. |
| [11] | WANG Zhaohui, ZHANG Yuning, WANG Wenting, XIE Changliang, CHEN Jiazhuo, ZHENG Hu, WANG Junxing. Distribution of dinoflagellate cysts in surface sediments on the Dongshan Bay, Fujian province, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 154-162. |
| [12] | SHANG Bowen, WU Yunchao, JIANG Zhijian, LIU Songlin, HUANG Xiaoping. Characteristics and sources of organic matter in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary: Carbon storage implications [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 16-28. |
| [13] | CHEN Qiong, TANG Shilin, WU Jie. Spatial-temporal variation of suspended sediment in the Pearl River Estuary retrieved from GF-4 satellite data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 65-76. |
| [14] | LI Huawei, XU Xiangrong. Pollution characteristics of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and alternative brominated flame retardants in sediments from typical mangrove wetlands of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 117-130. |
| [15] | NI Yugen, LI Jianguo, XI Long. Discussion on grain-size grading scale and sediment classification for marine sand and gravel [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 143-151. |
|
||