Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 104-113.doi: 10.11978/2023178CSTR: 32234.14.2023178
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Characteristics of carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of major fish species in coral reefs of the Nansha Islands in spring 2023
QIU Xingyu1,2( ), LIU Qingxia2, CHEN Zuozhi1,2, CAI Yancong2, HUANG Honghui1,2,3(
), LIU Qingxia2, CHEN Zuozhi1,2, CAI Yancong2, HUANG Honghui1,2,3( )
)
- 1. College of Fisheries and Life Science, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai 201306, China
2. South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fishery Ecology and Environment, Guangzhou 510300, China
3. Sanya Tropical Fisheries Research Institute, Sanya 572018, China
-
Received:2023-11-27Revised:2024-01-12Online:2024-11-10Published:2024-12-05 -
Contact:HUANG Honghui -
Supported by:Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS(2023TD15); Fund of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fishery Ecology and Environment(FEEL-2022-9); Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS(2021SD03); Financial Fund of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, P.R. China(NFZX2021)
CLC Number:
- Q958
Cite this article
QIU Xingyu, LIU Qingxia, CHEN Zuozhi, CAI Yancong, HUANG Honghui. Characteristics of carbon and nitrogen stable isotopes of major fish species in coral reefs of the Nansha Islands in spring 2023[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 104-113.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
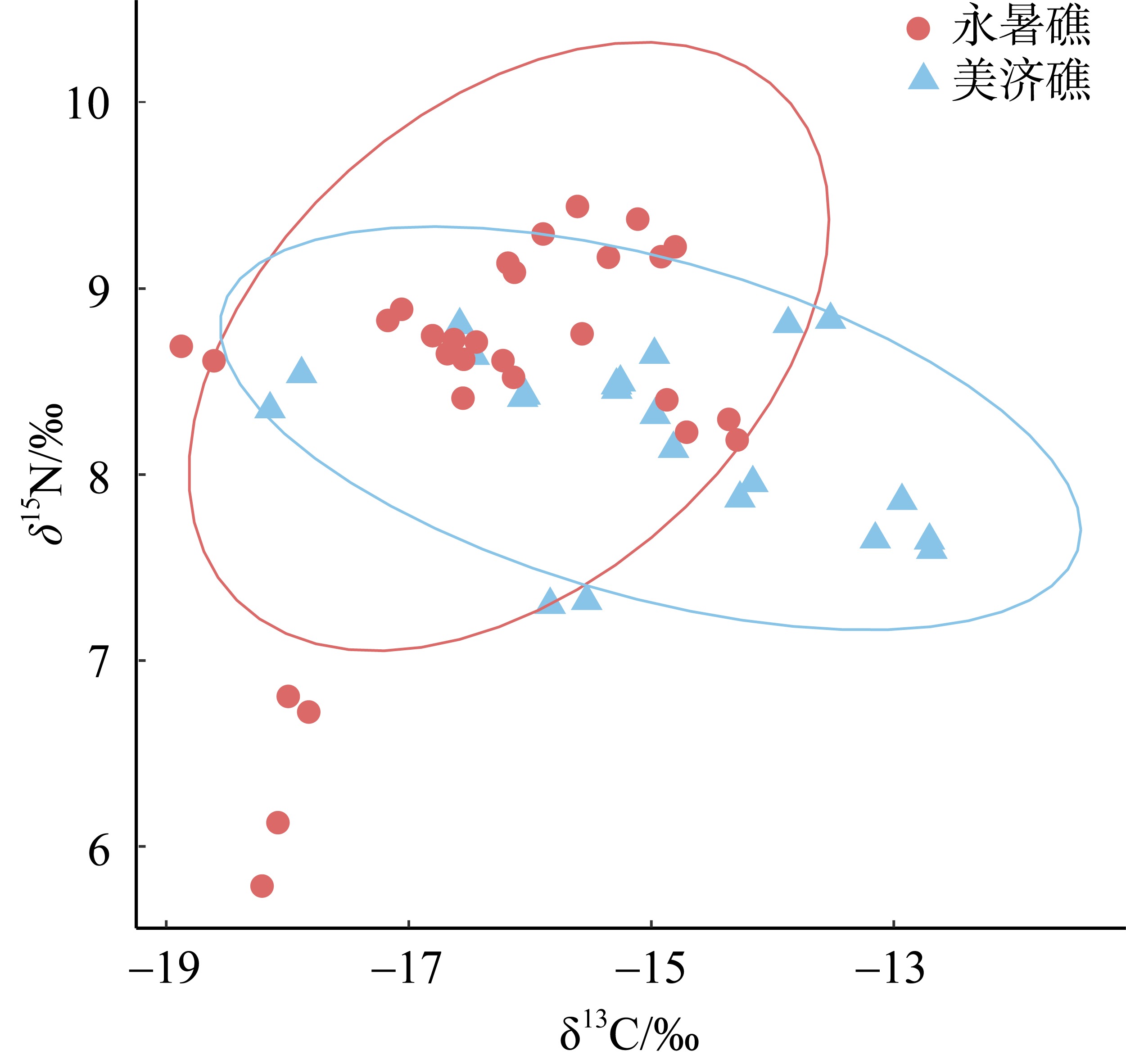
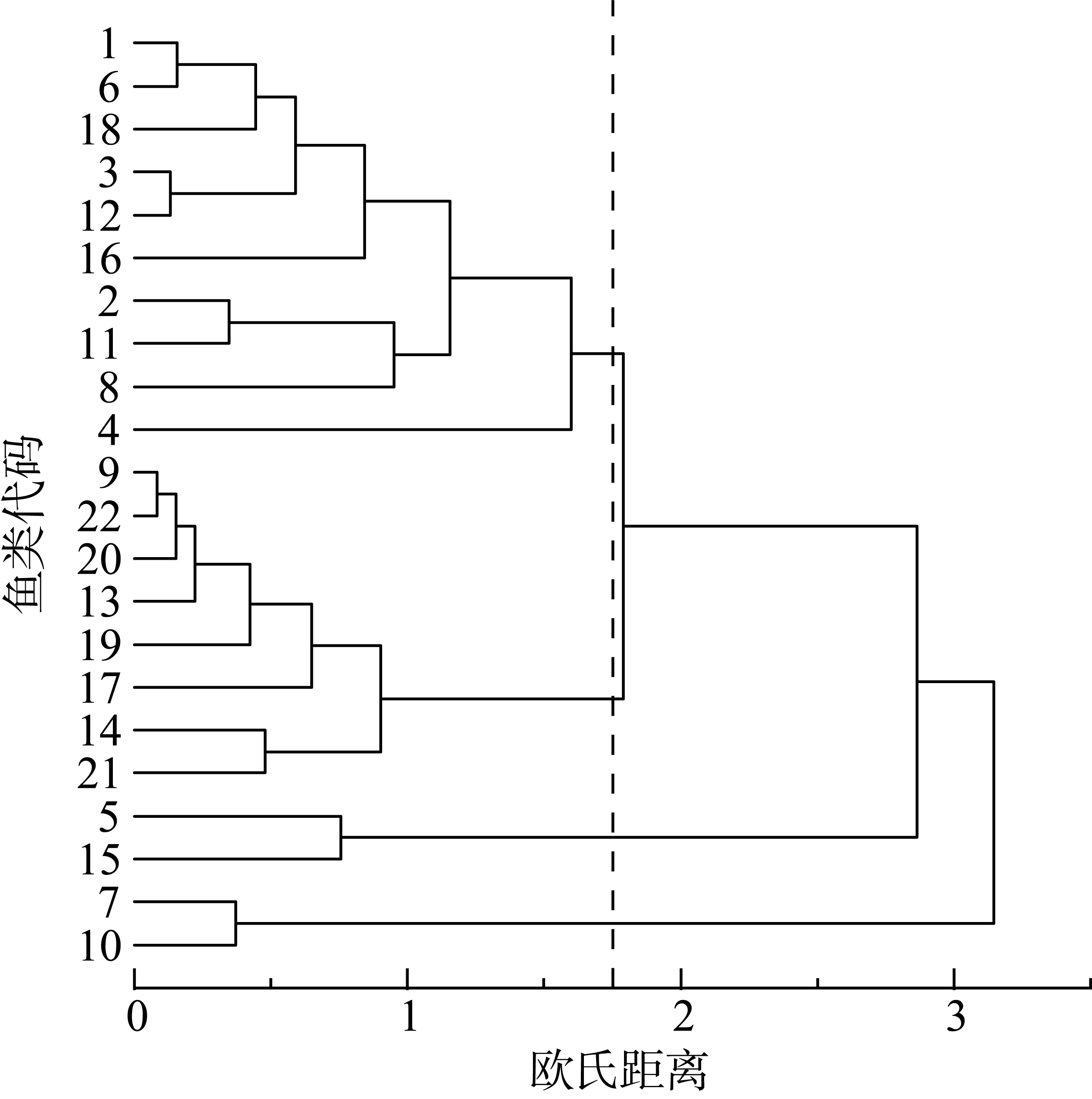
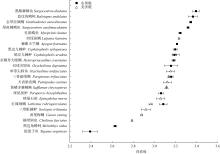
Tab. 2
Carbon and nitrogen stable isotope ratios and basic information of the main fish species in the Nansha coral island reefs"
| 珊瑚礁 | 代码 | 种类 | 科 | 属 | δ13 C/‰ | δ15 N/‰ | 体长范围/mm | 食性 | 主要食物来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 美济礁 | 1 | 单带尖唇鱼 Oxycheilinus unifasciatus | 隆头鱼科 | 尖唇鱼属 | -15.13±0.22 | 8.55±0.13 | 140~145 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、甲壳类 |
| 2 | 红裸颊鲷 Lethrinus rubrioperculatus | 裸颊鲷科 | 裸颊鲷属 | -14.22±0.07 | 7.91±0.06 | 154 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 3 | 蜂巢石斑 Epinephelus merra | 鮨科 | 石斑鱼属 | -14.89±0.11 | 8.23±0.13 | 124~127 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、小虾 | |
| 4 | 横带唇鱼 Cheilinus fasciatus | 隆头鱼科 | 尖唇鱼属 | -15.68±0.21 | 7.31±0.01 | 134 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物 | |
| 5 | 犬牙锥齿鲷 Pentapodus caninus | 金线鱼科 | 锥齿鲷属 | -18.01±0.18 | 8.45±0.13 | 133 | 肉食性 | 小鱼、浮游动物 | |
| 6 | 三带副绯鲤 Parupeneus trifasciatus | 羊鱼科 | 副绯鲤属 | -15.27±0.02 | 8.49±0.01 | 143~152 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 7 | 三带眶棘鲈 Scolopsis trilineata | 眶棘鲈科 | 眶棘鲈属 | -13.04±0.16 | 7.76±0.15 | 198 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 8 | 四线笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira | 笛鲷科 | 笛鲷属 | -13.7±0.25 | 8.82±0.02 | 145 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 9 | 尾纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis urodeta | 鮨科 | 石斑鱼属 | -16.52±0.08 | 8.72±0.12 | 92~126 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、甲壳类 | |
| 10 | 黄尾梅鲷 Caesio cuning | 乌尾鮗科 | 梅鲷属 | -12.7±0.01 | 7.62±0.04 | 170 | 肉食性 | 浮游动物 | |
| 黄鳍多棘鳞鲀 Sufflamen chrysopterus | 鳞鲀科 | 鳞鲀属 | -16.05±0.04 | 9.219±0.17 | 152 | 杂食性 | 鱼类、藻类、底栖生物 | ||
| 永暑礁 | 11 | 斑尾拟鲈 Parapercis hexophthalma | 拟鲈科 | 拟鲈属 | -14.33±0.05 | 8.24±0.08 | 146~149 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物、浮游动物 |
| 12 | 红裸颊鲷 Lethrinus rubrioperculatus | 裸颊鲷科 | 裸颊鲷属 | -14.79±0.12 | 8.32±0.12 | 208 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 13 | 黑边九棘鲈 Cephalopholis spiloparaea | 鮨科 | 石斑鱼属 | -16.74±0.09 | 8.7±0.07 | 78~104 | 肉食性 | 鱼类 | |
| 14 | 黑鮨棘鳞鱼 Sargocentron diadema | 金鳞鱼科 | 棘鳞鱼属 | -15.75±0.2 | 9.37±0.1 | 127 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 15 | 灰鳍异大眼鲷 Heteropriacanthus cruentatus | 大眼鲷科 | 异大眼鲷属 | -18.74±0.19 | 8.65±0.06 | 95~141 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 16 | 金带齿颌鲷 Gnathodentex aureolineatus | 裸颊鲷科 | 裸颊鲷属 | -14.86±0.08 | 9.2±0.04 | 127~158 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 17 | 孔锯鳞鱼 Myripristis kuntee | 金鳞鱼科 | 棘鳞鱼属 | -17.12±0.08 | 8.86±0.04 | 83~114 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物 | |
| 18 | 棘眼天竺鲷 Apogon fraenatus | 天竺鲷科 | 天竺鲷属 | -15.57±0 | 8.76±0 | 108 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物 | |
| 19 | 三带副绯鲤 Parupeneus trifasciatus | 羊鱼科 | 副绯鲤属 | -16.18±0.06 | 8.57±0.06 | 111~145 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 20 | 双线尖唇鱼 Oxycheilinus digramma | 隆头鱼科 | 尖唇鱼属 | -16.5±0.08 | 8.56±0.21 | 180~192 | 肉食性 | 底栖生物 | |
| 21 | 尾斑棘鳞鱼 Sargocentron caudimaculatum | 金鳞鱼科 | 棘鳞鱼属 | -16.16±0.04 | 9.11±0.03 | 154 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、底栖生物 | |
| 22 | 尾纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis urodeta | 鮨科 | 石斑鱼属 | -16.59±0.06 | 8.67±0.07 | 91~112 | 肉食性 | 鱼类、甲壳类 | |
| 波纹钩鳞鲀 Balistapus undulatus | 鳞鲀科 | 鳞鲀属 | -15.23±0.17 | 9.27±0.14 | 175 | 杂食性 | 藻类、底栖生物、鱼类 | ||
| 黑边角鳞鲀 Melichthys vidua | 鳞鲀科 | 鳞鲀属 | -17.91±0.12 | 6.77±0.06 | 140~147 | 杂食性 | 藻类、底栖生物、鱼类 | ||
| 银篮子鱼 Siganus argenteus | 篮子鱼科 | 篮子鱼属 | -18.14±0.09 | 5.96±0.24 | 190~192 | 植食性 | 藻类 |
Tab. 3
The index parameters of trophic structure of the main fish communities in Yongshu Reef and Meiji Reef"
| 参数指数 | 含义 | 美济礁 | 永暑礁 |
|---|---|---|---|
| δ15N范围(δ15N range, NR) | 指示生态系统中营养长度和多样性 | 1.51 | 3.41 |
| δ13C范围(δ13C range, CR) | 指示食物来源多样性 | 5.32 | 4.42 |
| 凸包总面积(total area, TA) | 表示食物网中营养多样性的总程度 | 5.15 | 8.40 |
| 到质心平均距离(average distance of centroid, CD) | 根据每个群落组成部分到质心的欧几里得距离计算, 表示生态位宽度和物种间距 | 1.31 | 1.27 |
| 平均最邻近距离(mean nearest neighbour distance, MNND) | 指示群落物种聚集的密度的均匀度, 表示营养生态位分布 | 0.64 | 0.52 |
| 最邻近距离标准差(standard deviation of nearest neighbour distance, SDNND) | 指群落物种空间密度均匀度参数, 表示营养冗余度 | 0.44 | 0.38 |
Tab. 4
Comparison of trophic structure indexes of fishery organisms in the South China Sea and coastal waters"
| 区域 | CR | NR | MNND | SDNND |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南海中西部海域(黄佳兴 等, | 3.49 | 4.91 | 1.69 | 0.74 |
| 南沙群岛(宁加佳 等, | 3.4 | 4.3 | 0.37 | 0.43 |
| 大亚湾西南海域(张婉茹 等, | 2.83 | 4.18 | 0.31 | 0.23 |
| 南海中西部海域(孔业富 等, | 2.28 | 4.15 | - | - |
| 大亚湾珊瑚礁(朱文涛 等, | 5.92 | 3.72 | - | - |
| 华南典型海湾(张文博 等, | 4.45 | 4.66 | 0.6 | 0.54 |
| 大亚湾海域(汪慧娟 等, | 4.47 | 4.38 | 0.33 | 0.23 |
| 美济礁珊瑚岛礁(本研究) | 5.32 | 1.51 | 0.64 | 0.44 |
| 永暑礁珊瑚岛礁(本研究) | 4.42 | 3.41 | 0.52 | 0.38 |
Tab. 5
Dominant fish species in the Yongshu Reef and Meiji Reef from 2016 to 2018"
| 永暑礁优势种鱼类 | 美济礁优势种鱼类 |
|---|---|
| 四带笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira* | 四带笛鲷 Lutjanus kasmira* |
| 红牙鳞鲀Odonus niger | 长棘银鲈Gerres filamentosus |
| 金带齿颌鲷 Gnathodentex aureolineatus* | 无斑拟羊鱼Mulloidichthys vanicolensis* |
| 小鲔Euthynnus alletteratus | 蜂巢石斑鱼Epinephelus merra* |
| 榄色细齿笛鲷Aphareus furca* | 犬牙锥齿鲷 Pentapodus caninus* |
| 黑边角鳞鲀 Melichthys vidua* | 角棘鳞鱼Sargocentron cornutum* |
| 短吻弱棘鱼Malacanthus brevirostris | 黑斑条尾魟Taeniura melanospilos |
| 黄鳍多棘鳞鲀 Sufflamen chrysopterus | 太平洋裸颊鲷Lethrinus atkinsoni |
| 丝尾鼻鱼 Naso vlamingii | 红裸颊鲷 Lethrinus rubrioperculatus* |
| 黑边九棘鲈Cephalopholis spiloparaea* | 双带似天竺鲷Apogonichthyoides taeniatus* |
| 尾纹九棘鲈 Cephalopholis urodeta* | 尖吻棘鳞鱼argocentron spiniferum* |
| 桔带裸颊鲷 Lethrinus obsole | |
| 羽鳃鲐Rastrelliger kanagurta | |
| 隆背笛鲷 Lutjanus gibbus | |
| 三带眶棘鲈Scolopsis lineata* | |
| 三带副绯鲤 Parupeneus trifasciatus* | |
| 彼氏眶棘鲈Scolopsis affinis | |
| 横带唇鱼 Cheilinus fasciatus* |
| [1] |
陈玲, 王凯, 周曦杰, 等, 2016. 岛礁水域海藻场食物网基准生物的选择[J]. 海洋渔业, 38(4): 364-373.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈明强, 陈旭, 李有宁, 等, 2018. 美济礁合浦珠母贝吊笼养殖试验[J]. 水产科学, 37(3): 379-383.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈绍勇, 周伟华, 吴云华, 等, 2001. 南沙珊湖礁生态系生物体中δ13C的分布[J]. 海洋科学, 25(6): 4-7.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
何志成, 2001. 南沙美济礁鱼类养殖试验获得成功[J]. 中国水产, (3): 26 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
黄佳兴, 龚玉艳, 徐姗楠, 等, 2019. 南海中西部渔场主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 38(1): 76-84.
doi: 10.11978/2018041 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2018041 |
|
| [6] |
孔业富, 吴忠鑫, 颜云榕, 等, 2020. 基于碳氮稳定同位素的南海中西部海域春季中上层渔业生物群落营养结构[J]. 应用生态学报, 31(10): 3559-3567.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202010.038 |
|
|
|
| [7] |
刘华雪, 徐军, 李纯厚, 等, 2015. 南海南部浮游动物稳定同位素研究——氮稳定同位素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 34(2): 32-38.
|
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2015.02.005 |
|
| [8] |
刘胜, 林先智, 张黎, 等, 2021. 南沙群岛珊瑚礁鱼类生态图册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社 (in Chinese).
|
| [9] |
宁加佳, 杜飞雁, 王雪辉, 等, 2016. 南沙群岛西南部陆架区底层鱼类营养结构研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(2): 468-475.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
石娟, 李纯厚, 王腾, 等, 2023. 万山群岛黄斑篮子鱼与云斑海猪鱼的营养生态位特征[J/OL]. 水产学报: 1-13. (2023-10-27)
|
|
[ 2023-11-26. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/31.1283.S.20231027.1614.002.
|
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
汪慧娟, 张文博, 黄洪辉, 等, 2021. 基于碳、氮稳定同位素的大亚湾渔业生物群落营养结构[J]. 南方水产科学, 17(5): 101-109.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王静, 蒋日进, 胡翠林, 等, 2021. 基于胃含物分析和稳定同位素技术研究鳀的摄食生态[J]. 应用生态学报, 32(6): 2035-2044.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202106.029 |
|
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202106.029 |
|
| [13] |
王腾, 刘永, 李纯然, 等, 2022. 南沙美济礁海域隆背笛鲷繁殖和食性的初步研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 18(6): 78-84.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
徐雯, 杨蕊, 陈淦, 等, 2022. 基于胃含物和碳、氮稳定同位素研究浙江南部近海蓝圆鲹的摄食生态[J]. 应用生态学报, 33(11): 3097-3104.
doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.202212.029 |
|
|
|
| [15] |
杨国欢, 孙省利, 侯秀琼, 等, 2012. 基于稳定同位素方法的珊瑚礁鱼类营养层次研究[J]. 中国水产科学, 19(1): 105-115.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
尹洪洋, 朱文涛, 马文刚, 等, 2022. 三亚蜈支洲岛海洋牧场区域夏季食物网研究[J]. 生态学报, 42(8): 3241-3253.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
张俊, 陈作志, 蔡研聪, 等, 2021. 南海美济礁瀉湖区鱼类优势种和生物多样性的长期变化[J]. 中国水产科学, 28(11): 1466-1476.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
张婉茹, 刘庆霞, 黄洪辉, 等, 2022. 2020年冬季大亚湾西南海域主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 41(3): 147-155.
doi: 10.11978/2021108 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2021108 |
|
| [19] |
张文博, 黄洪辉, 李纯厚, 等, 2019. 华南典型海湾主要渔业生物碳氮稳定同位素研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 15(5): 9-14.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
赵焕庭, 宋朝景, 朱袁智, 1992. 南沙群岛“危险地带”腹地珊瑚礁的地貌与现代沉积特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 12(4): 368-377.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
周天成, 张琛, 刘胜, 等, 2022. 南海珊瑚礁鱼的食性探究[J]. 大自然, (4): 40-47 (in Chinese).
|
| [22] |
朱文涛, 秦传新, 马鸿梅, 等, 2020. 大亚湾珊瑚礁生态系统简化食物网的稳定同位素[J]. 水产学报, 44(7): 1112-1123.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00348-w pmid: 34697332 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2007)88[42:csirpf]2.0.co;2 pmid: 17489452 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [1] | XIE Hongyu, LIU Yong, LI Chunhou, ZHAO Jinfa, SUN Jinhui, SHEN Jianzhong, SHI Juan, WANG Teng. Species composition and evolutionary characteristics of coral reef fish in the Langhua Reef, Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(6): 114-128. |
| [2] | LIN Xianzhi, ZHOU Yanyan, LIN Haoye, HU Simin, HUANG Hui, ZHANG Li, LIU Sheng. Diet analysis of the parrotfish (Scarus globiceps) in coral reefs of the Nansha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 100-108. |
| [3] | LEI Mingfeng, YU Kefu, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Biao, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Xiaoyan. The rapid ecological degradation and its impact on fish of the Yinyu Island in the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [4] | LAN Zhenqiang, ZHENG Jitao, CHEN Yun, CHEN Nan, WANG Shuhong. Copulation, embryonic and post-embryonic development of Sphaeramia nematoptera [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 116-125. |
| [5] | YANG Bin, SALENDRA Limbadri, LIU Juan, LIU Yonghong. Alkaloids from the Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus SCSIO41214 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 195-201. |
| [6] | WANG Zihan, ZENG Cong, JIANG Ziyu, CAO Ling. Conservation gap analysis of threatened fish in the East China Sea and adjacent sea areas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 66-86. |
| [7] | ZHANG Wanru, LIU Qingxia, HUANG Honghui, QIN Xiaoqing, LI Jiajun, CHEN Jianhua. Study on stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen of main fishery organisms in the southwestern waters of Daya Bay, South China Sea in winter 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [8] | LI Kaizhi, KE Zhixin, WANG Junxing, TAN Yehui. Preliminary study on the community structure of zooplankton in coral reef waters of Xisha Islands* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [9] | DU Chong, HE Jun, SUN Tingting, WANG Lei, WANG Fanghan, DONG Zhijun. Molecular identification on the causative species jellyfish blooms in the northern South China Sea in 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 142-148. |
| [10] | HONG Xiaofan, CHEN Zuozhi, JIANG Yane, ZHANG Jun, WANG Huanhuan, LI Yuanjie, LI Gang. Biological characteristics of Cephalopholis spiloparaea of reef waters in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 50-62. |
| [11] | HUANG Jianzhong, WEI Yuheng, GU Zhifeng, WU Chuanliang, XU Qiang, WANG Aiming, LI Xiubao. Coral community change and its influencing factors in Ximaozhou Island of Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 103-113. |
| [12] | CHEN Qiming, LIU Songlin, ZHANG Chi, CUI Lijun, JIANG Zhijian, WU Yunchao, HUANG Xiaoping. Growth characteristics of four representative fishes and their responses to seagrass resource changes in typical tropical seagrass beds of Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 62-70. |
| [13] | Min LI, Xiaolan KONG, Youwei XU, Zuozhi CHEN. Genetic polymorphism of the Brushtooth lizardfish Saurida undosquamis based on mitochondrial D-loop sequences [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 42-49. |
| [14] | Mengna LIU, Lei XU, Xuehui WANG, Yu LIU, Miaodi WANG, Yongsong QIU, Jiangfeng ZHU, Yinglin HE, Weilie BEI, Feiyan DU. Study on food contents of Uroteuthis chinensis and Sthenoteuthis oualaniensis based on COI sequence [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 61-69. |
| [15] | Danfeng ZHAO, Zhou HUANG, Qiang XU, Dongmei HUANG. Competitive pressure inquiry and resource allocation of coral fishes based on LSH method [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 118-126. |
|
||