Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 77-85.doi: 10.11978/2018120CSTR: 32234.14.2018120
• Oceanographic Research and Observation • Previous Articles Next Articles
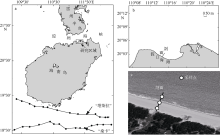
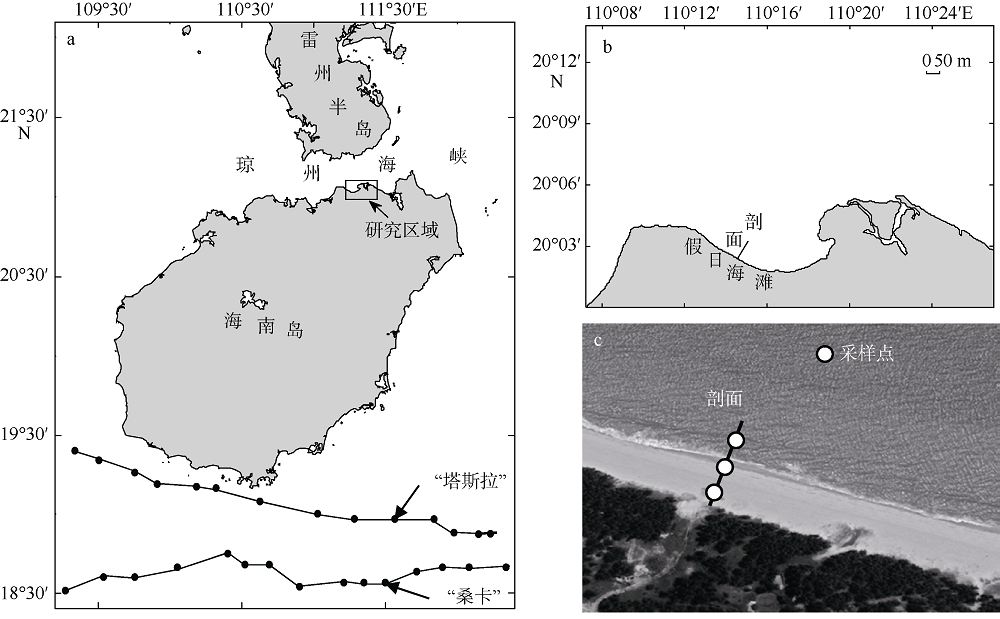
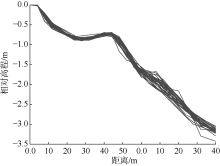
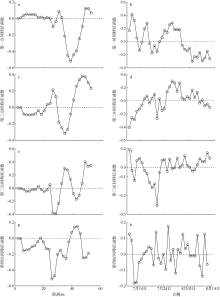
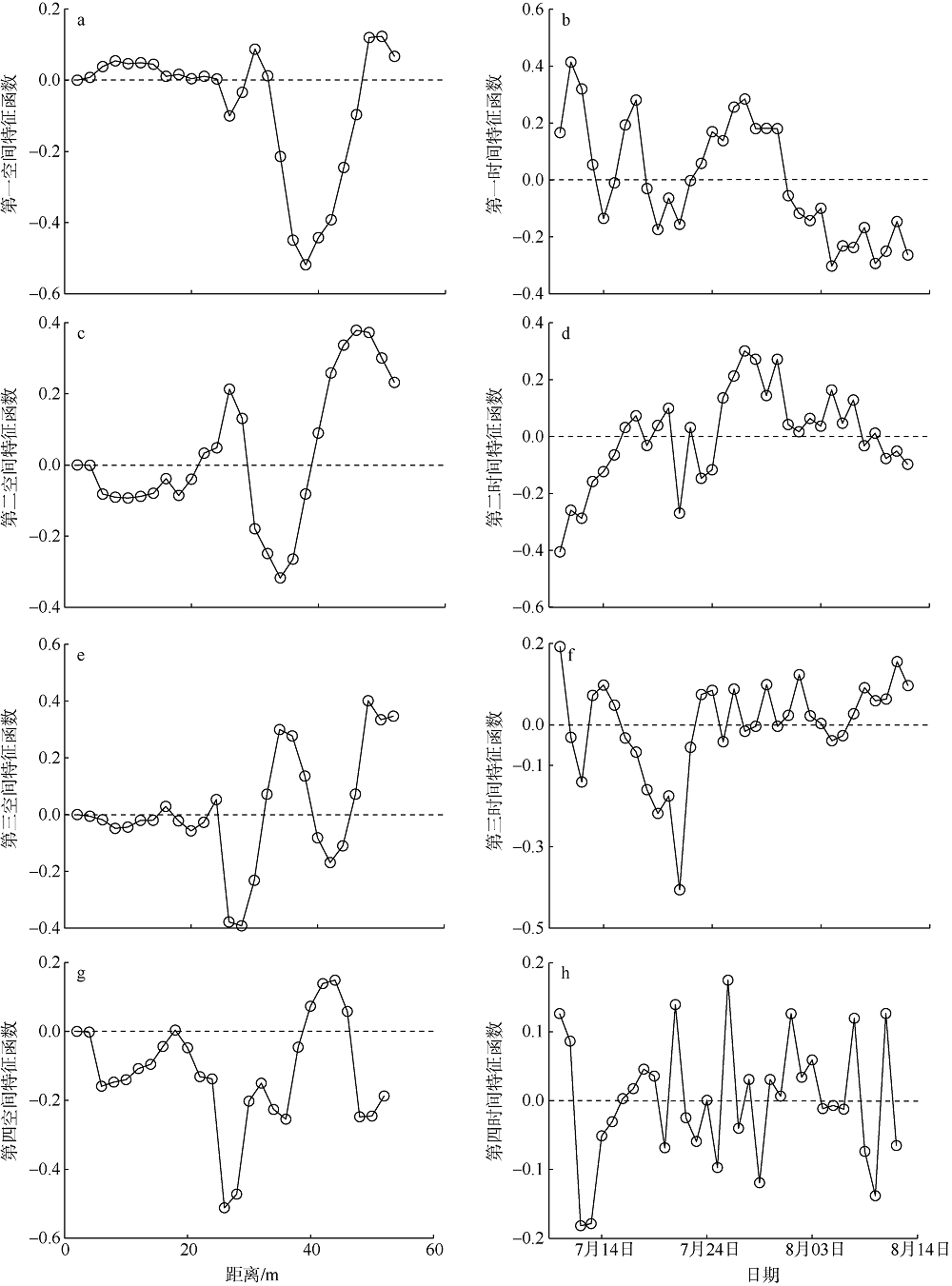
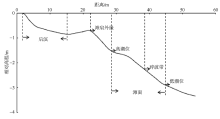
Analysis of short-term temporal and spatial changes and sedimentary dynamics at the middle section of Haikou Bay Beach *
Shibing ZHU,Danni HU,Huiling ZHANG,Chunhua ZENG,Zhehua LI,Zhiqiang LI( )
)
- College of Electronic and Information Engineering, College of Ocean Engineering, Guangdong Ocean University, Zhanjiang 524088, China
-
Received:2018-11-14Revised:2019-03-24Online:2019-09-20Published:2019-10-09 -
Contact:Zhiqiang LI E-mail:qiangzl1974@163.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41676079);Project of Enhancing School with Innovation of Guangdong Ocean University(Q18307)
CLC Number:
- P737.13
Cite this article
Shibing ZHU,Danni HU,Huiling ZHANG,Chunhua ZENG,Zhehua LI,Zhiqiang LI. Analysis of short-term temporal and spatial changes and sedimentary dynamics at the middle section of Haikou Bay Beach *[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 77-85.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
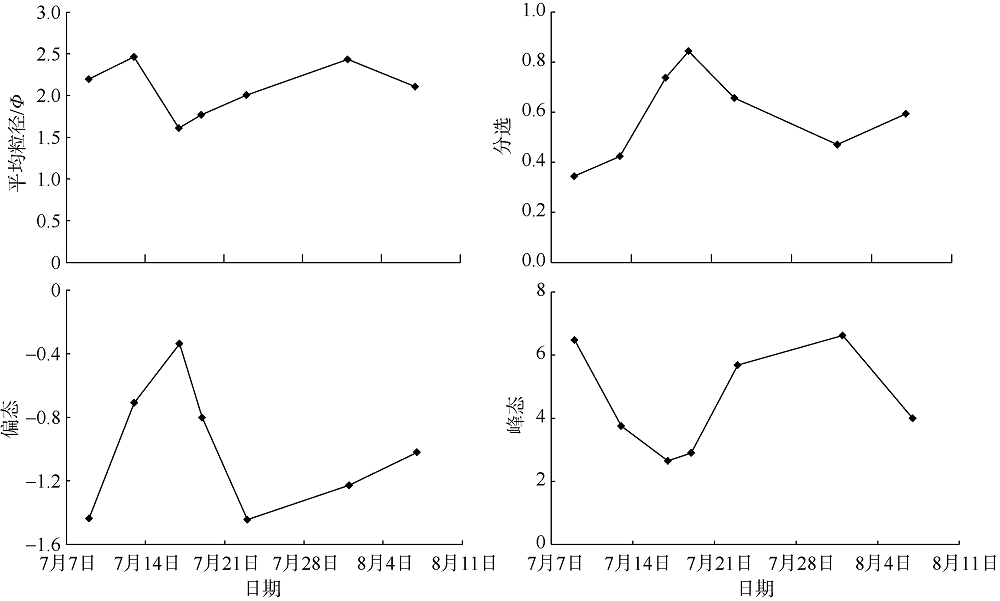
Tab. 2
Spatial distribution of beach sediments in the study area before and after the typhoon"
| Mz/Φ | σi | Sk | Kφ | 砂砾/% | 极粗砂/% | 粗砂/% | 中砂/% | 细砂/% | 极细砂/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 台 风 前 | 潮上带 | 2.45 | 0.45 | -2.31 | 6.81 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 1.71 | 16.23 | 78.46 | 3.53 |
| 潮间带 | 2.34 | 0.80 | -1.21 | 9.28 | 1.07 | 2.52 | 3.79 | 15.43 | 73.65 | 3.55 | |
| 潮下带 | 1.80 | 0.91 | -0.79 | 3.34 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 21.67 | 33.38 | 39.65 | 1.40 | |
| 平均值 | 2.20 | 0.72 | -1.00 | 6.48 | 0.95 | 1.12 | 9.06 | 21.68 | 63.92 | 2.83 | |
| 台 风 后 | 潮上带 | 1.98 | 0.66 | -0.64 | 2.69 | 2.43 | 15.49 | 15.45 | 35.03 | 31.25 | 0.35 |
| 潮间带 | 1.38 | 1.12 | -0.69 | 2.31 | 0.00 | 2.35 | 13.31 | 33.50 | 50.32 | 0.52 | |
| 潮下带 | 1.94 | 0.76 | -1.08 | 3.69 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 12.83 | 37.36 | 48.99 | 0.78 | |
| 平均值 | 1.77 | 0.84 | -0.80 | 2.90 | 0.75 | 3.19 | 11.12 | 27.52 | 55.18 | 1.85 |
| [1] | 常瑞芳 , 1997. 海岸工程环境[M]. 青岛: 青岛海洋大学出版社: 178-181. |
| CHANG RUIFANG , 1997. Coastal engineering environment[M]. Qingdao: Qingdao Ocean University Press: 178-181(in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 陈子燊, 李春初 , 1993. 粤西水东弧形海岸海滩剖面的地貌状态[J]. 热带海洋, 12(2):61-68. |
| CHEN ZISHEN, LI CHUNCHU , 1993. Geomorphological states of beach profiles in an arc-shaped shore of Shuidong, Western Guangdong[J]. Tropic Oceanology, 12(2):61-68 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 陈子燊 , 2000. 海滩剖面时空变化过程分析[J]. 海洋通报, 19(2):42-48. |
| CHEN ZISHEN , 2000. Analysis on spatial and temporal processes of beach profile variations[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 19(2):42-48 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 戴志军, 陈子燊, 张清凌 , 2001. 波控岬间海滩剖面短期变化过程分析[J]. 热带地理, 21(3):266-269. |
| DAI ZHIJUN, CHEN ZISHEN, ZHANG QINGLING , 2001. An analysis on temporal variation process of a wave-dominated beach profile between headlands[J]. Tropical Geography, 21(3):266-269 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 黎树式, 戴志军, 葛振鹏 , 等, 2017. 强潮海滩响应威马逊台风作用动力沉积过程研究——以北海银滩为例[J]. 海洋工程, 35(3):89-98. |
| LI SHUSHI, DAI ZHIJUN, GE ZHENPENG , et al, 2017. Sediment dynamic processes of macro-tidal beach in response to Typhoon Rammasun action — A case study of Yintan, Beihai[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 35(3):89-98 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 李志龙, 陈子燊, 戴志军 , 2004. 粤东汕尾岬间海滩体积短期变化分析[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 43(2):112-116. |
| LI ZHILONG, CHEN ZISHEN, DAI ZHIJUN , 2004. Analysis of beach volume variations over a month for a beach between headlandsin Shanwei, Eastern Guangdong[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 43(2):112-116 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 刘志杰, 公衍芬, 周松望 , 等, 2013. 海洋沉积物粒度参数3种计算方法的对比研究[J]. 海洋学报, 35(3):179-188. |
| LIU ZHIJIE, GONG YANFEN, ZHOU SONGWANG , et al, 2013. A comparative study on the grain-size parameters of marine sediments derived from three different computing methods[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 35(3):179-188 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 田明, 李春初 . 1994. 海南岛南渡江干流河口泥沙转运与现代地貌过程[J]. 热带地理, 14(2):105-112. |
| TIAN MING, LI CHUNCHU , 1994. Sediment bypassing and present geomorphic processes at the main stream estuary of the Nandujiang River in Hainan[J]. Tropical Geography, 14(2):105-112 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 王宝灿, 陈沈良, 龚文平 , 等, 2006. 海南岛港湾海岸的形成与演变[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 43-50(in Chinese). |
| [10] | 谢华亮, 戴志军, 吴莹 , 等, 2014. 海南岛南渡江河口动力沉积模式[J]. 沉积学报, 32(5):884-892. |
| XIE HUALIANG, DAI ZHIJUN, WU YING , et al, 2014. Sedimentation dynamic modes of the Nandujiang estuary’ Hainan island[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 32(5):884-892 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 于吉涛, 丁圆婷, 程璜鑫 , 等, 2015. 波控中等潮差海滩剖面时空变化过程研究[J]. 海洋通报, 34(5):540-546. |
| YU JITAO, DING YUANTING, CHENG HUANGXIN , et al, 2015. Spatial and temporal variability of the wave-dominated, meso-tidal beach profile[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 34(5):540-546 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] |
周晗宇, 陈沈良, 钟小菁 , 等, 2013. 海口湾西海岸海滩沉积物与海滩稳定性分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(1):26-34.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.01.004 |
|
ZHOU HANYU, CHEN SHENLIANG, ZHONG XIAOJING , et al, 2013. Sedimentary characteristics and stability analysis of the beach in west coast of Haikou Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(1):26-34 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.01.004 |
|
| [13] | BURVINGT O, MASSELINK G, RUSSELL P , et al, 2017. Classification of beach response to extreme storms[J]. Geomorphology, 295:722-737. |
| [14] | CHEN ZISHEN , 1995. Analysis of the dynamic characteristics and stochastic simulation on variations of beach volumes[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 14(3):393-403. |
| [15] | COLLIAS E E, RONA M R, MCMANUS D A , 1963. Machine processing of geological data[R]. University of Washington Technical Report Number 87. Seattle 5, Washington: University of Washington Department of Oceanalgraphy: 119-120. |
| [16] | ELIOT I G, CLARKE D J , 1986. Minor storm impact on the beachface of a sheltered sandy beach[J]. Marine Geology, 73(1-2):61-83. |
| [17] | HEGGE B, ELIOT I, HSU J . 1996. Sheltered sandy beaches of Southwestern Australia[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 12(3):748-760. |
| [18] | LARSON M, CAPOBIANCO M, JANSEN H , et al, 2003. Analysis and modeling of field data on coastal morphological evolution over yearly and decadal time scales. Part 1: background and linear techniques[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 19(4):760-775. |
| [19] | LARSON M, HANSON H, KRAUS N C , et al, 1999. Short- and long-term responses of beach fills determined by EOF analysis[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 125(6):285-293. |
| [20] | LI Y, LARK M, REEVE D , 2005. Multi-scale variability of beach profiles at Duck: a wavelet analysis[J]. Coastal Engineering, 52(12):1133-1153. |
| [21] | ROSEN P S , 1978. Beach processes and sedimentation[J]. The Journal of Geology, 86(1):155. |
| [22] | SHENOI S S C, MURTY C S, VEERAYYA M , 1987. Monsoon-induced seasonal variability of sheltered versus exposed beaches along the west coast of India[J]. Marine Geology, 76:117-130. |
| [1] | SUN Zeming, HAN Shuzong, WANG Mingjie, SU Hanxiang. Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 17-31. |
| [2] | SHANG Jie, WU Ying, ZOU Yike, MA Jingwen. Retrieval of typhoon precipitation rate over ocean surface based on FY-3D/MWRI Data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 32-40. |
| [3] | CHEN Jie, BIAN Cheng, JIANG Changbo, YAO Zhen, JIANG Chao, LIANG Hai. Advances in the characterization of bioclastic sediment motion [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 33-41. |
| [4] | MO Danyang, NING Zhiming, YANG Bin, XIA Ronglin, LIU Zhijin. Response of dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in coral reef sediments of the Weizhou island to temperature changes [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [5] | GAO Jie, YU Kefu, XU Shendong, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Biao, WANG Yonggang. Content and source analysis of organic carbon in the outer slope sediments of the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zheran, HU Junyang, ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Penghui, XING Jiuxing, CHEN Shengli. Storm surge simulations of the coastal area of Shenzhen using different types of typhoon meteorological fields—a case study of Typhoon Mangkhut* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
| [7] | XING Nannan, REN Runxin, TANG Zhenzhou, LUO Zhihong, XIA Chenxi, LIU Yonghong, PENG Liang, CHEN Xianqiang. Study on the secondary metabolites of fungus Aspergillus sp. GXIMD02003 derived from marine sediment in the Weizhou island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 154-160. |
| [8] | SUN Cuici, YUE Weizhong, ZHAO Wenjie, WANG Youshao. Distribution of the microbial Carbohydrate-Active enzymes genes in the surface sediment of the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [9] | LI Junmin, LI Bo, CHEN Wuyang, LIU Junliang. Observation characteristics of coastal waves in Sanya and their responses to typhoon processes [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 25-35. |
| [10] | YANG Xialing, LI Shushi, XU Shanshan, YU Chongxi, PAN Jie. Variations in water and sediments of the Nanliu River flowing into the sea under the influence of extreme weather in the past 60 years [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 91-103. |
| [11] | ZHANG Min, WU Hangxing, LU Yibin, LU Diwen, MI Jie, ZHU Donglin, CHEN Bo. Impact of the coastal reclamations on topography evolution in the Qinzhou Bay, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 124-131. |
| [12] | GAO Na, ZHAO Mingli, MA Yi, XU Wanming, ZHAN Haigang, CAI Shuqun. Effect of typhoon on storm surge in the Pearl River Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 32-42. |
| [13] | TANG Chaoli, TAO Xinhua, WEI Yuanyuan, DAI Congming, WEI Heli. Spatiotemporal modal analysis and prediction of surface temperature in East Asia and the Western Pacific* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 183-192. |
| [14] | YANG Hongqiang, TAN Fei, XU Huilong, ZHANG Xiyang, SHI Qi, TAO Shichen. Reconstruction of the tropical cyclones activity in the Nansha Islands since the Little Ice Age from the atoll lagoon sediments [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 171-182. |
| [15] | SHU Aiqing, XU Dongmei, LI Hong, WU Haiying, SHEN Feifei, DEND Hua, BAI Yawen. Assimilating MWHS-2 radiance of FY-3D satellite and its influence on the forecast of Typhoon Mitag* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 17-28. |
|
||