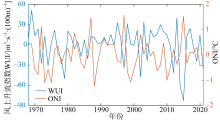
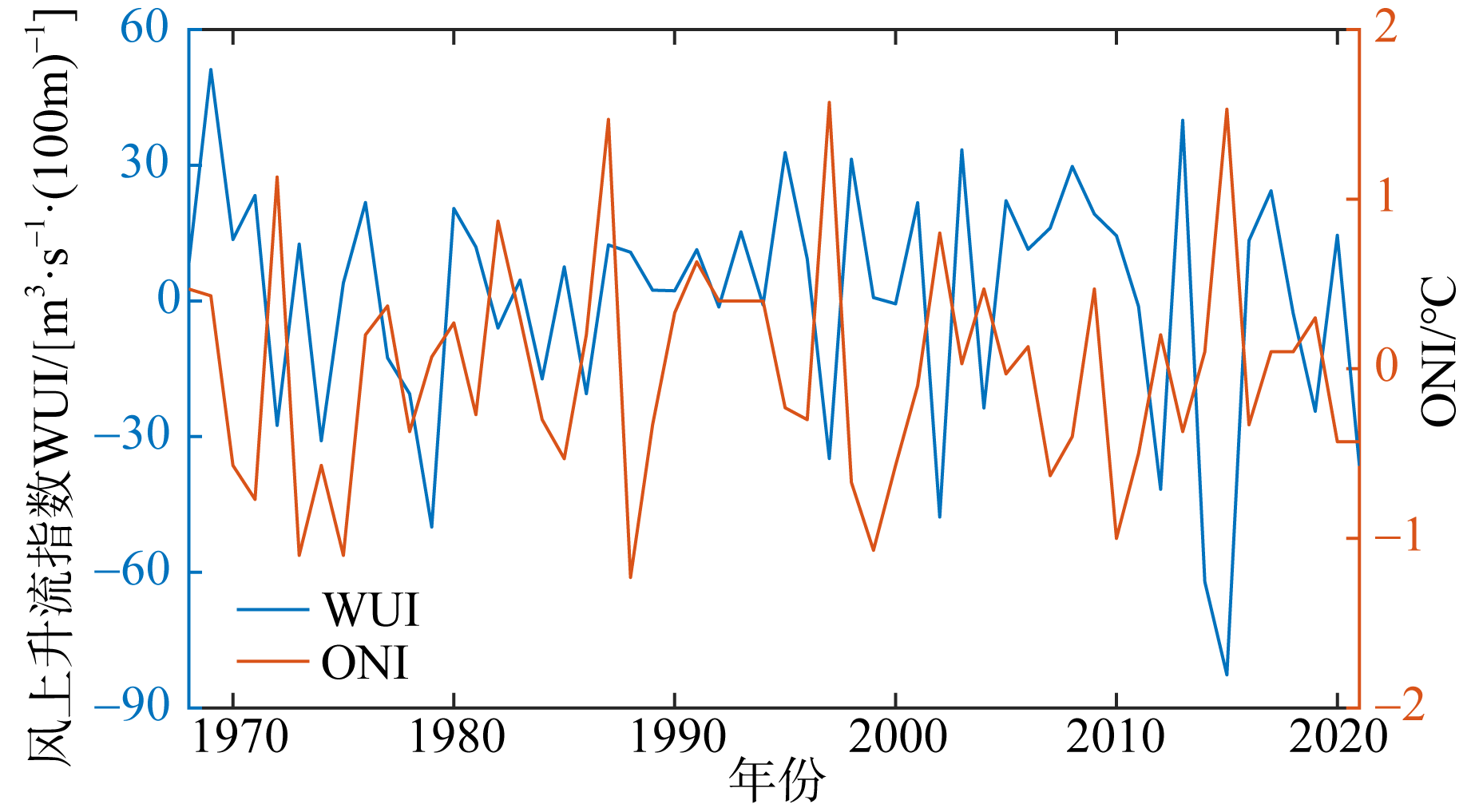
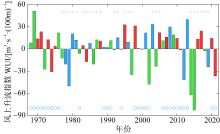
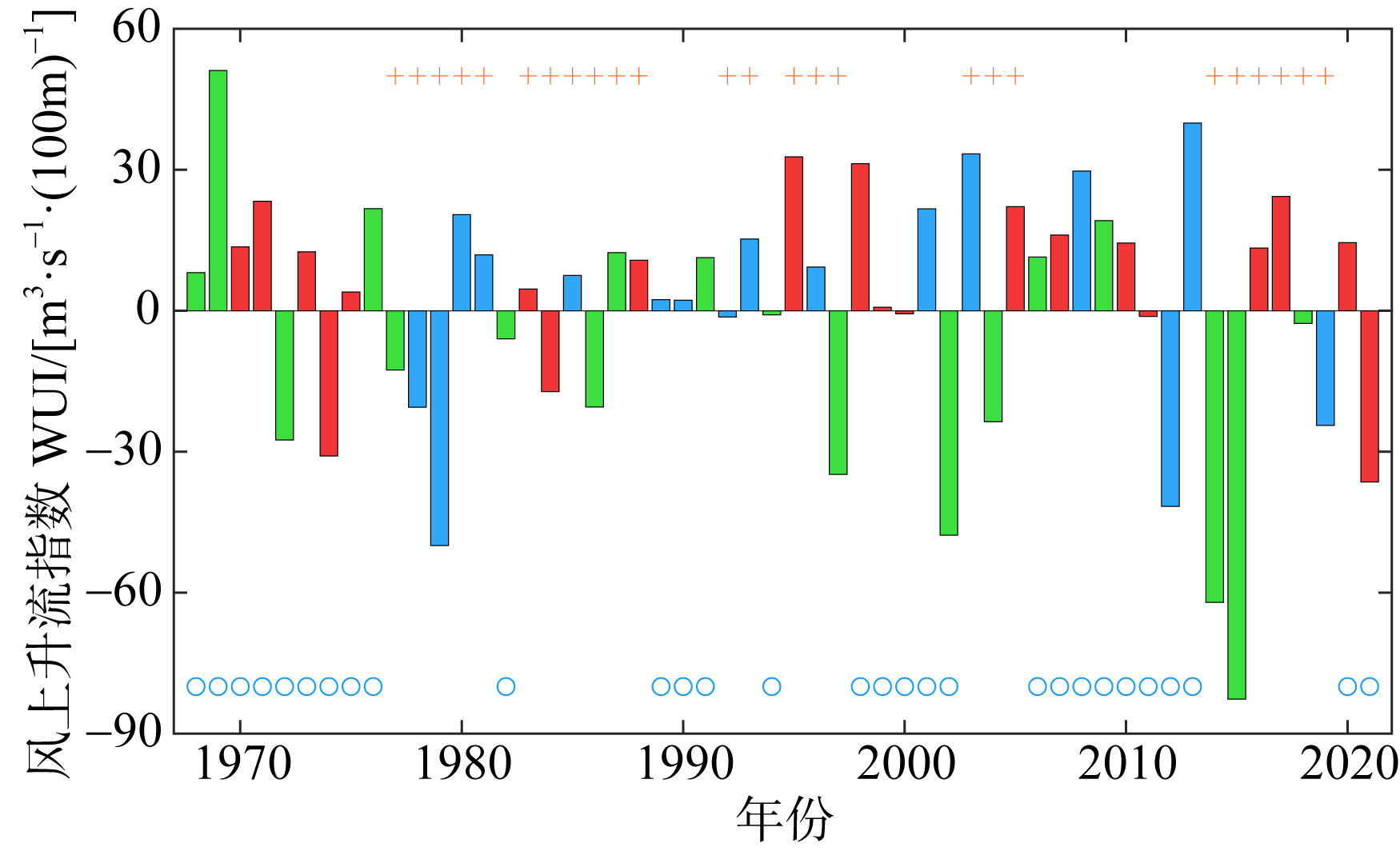
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2024, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 48-55.doi: 10.11978/2023026CSTR: 32234.14.2023026
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
The interannual variation of summer upwelling in Zhoushan Islands and its relationship with ENSO
QUAN Mengyuan( ), WANG Hui(
), WANG Hui( ), LI Wenshan, WANG Aimei, LUO Jingxin
), LI Wenshan, WANG Aimei, LUO Jingxin
- National Marine Data Information Center, Tianjin 300171, China
-
Received:2023-03-03Revised:2023-03-30Online:2024-01-10Published:2024-01-19
Cite this article
QUAN Mengyuan, WANG Hui, LI Wenshan, WANG Aimei, LUO Jingxin. The interannual variation of summer upwelling in Zhoushan Islands and its relationship with ENSO[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 48-55.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
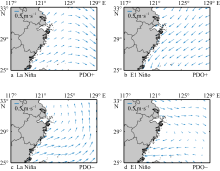
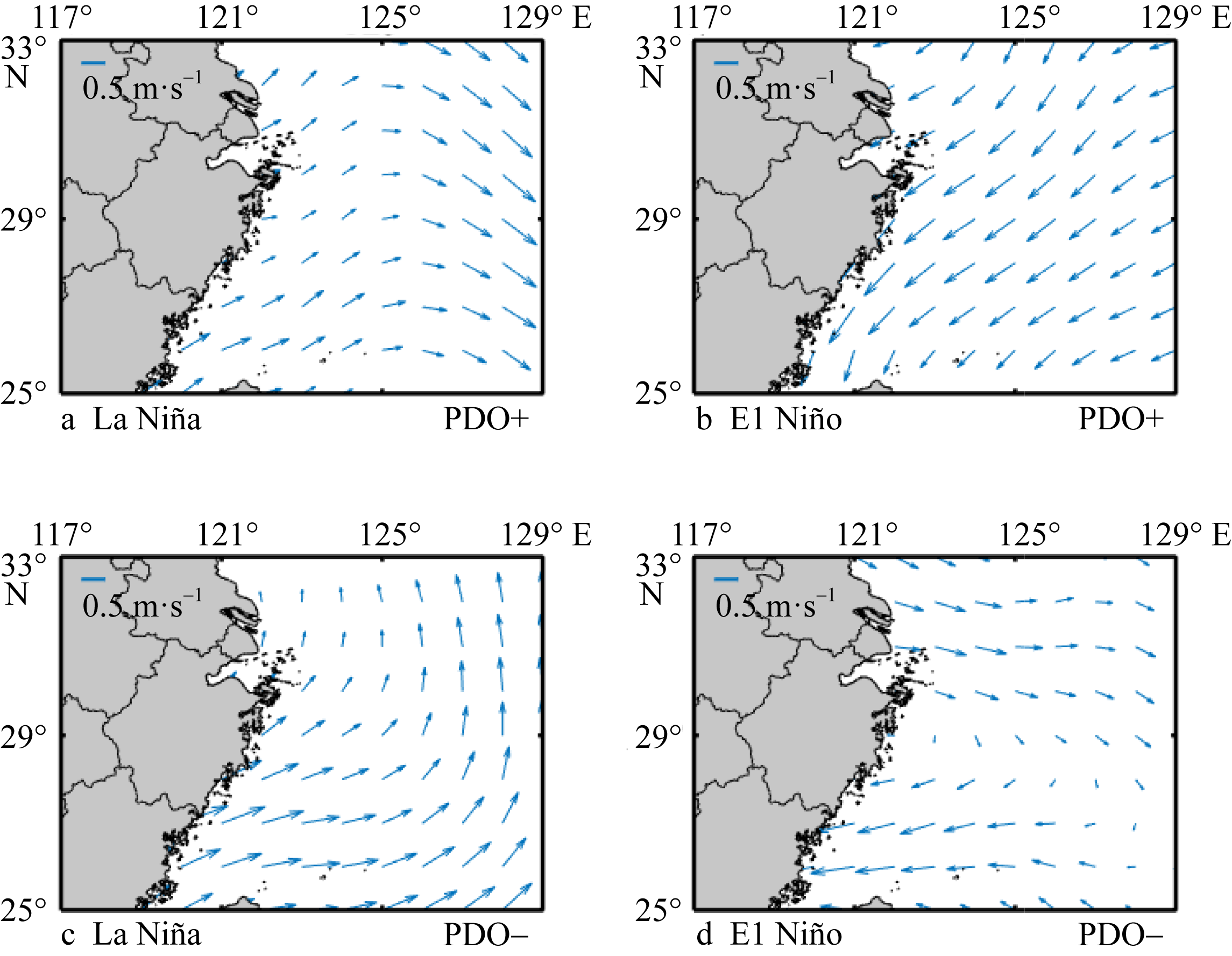
Tab. 1
El Niño years and La Niña years classified based on the different PDO phases"
| El Niño年 | La Niña年 | |
|---|---|---|
| PDO正位相 | 1977, 1986, 1987, 1997, 2004, 2014, 2015, 2018 | 1983, 1984, 1988, 1955, 2005, 2016, 2017 |
| PDO负位相 | 1968, 1969, 1972, 1976, 1982, 1991, 1994, 2002, 2006, 2009 | 1970, 1971, 1973, 1974, 1975, 1998, 1999, 2000, 2007, 2010, 2011, 2020, 2021 |
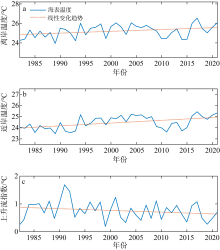
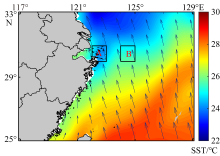
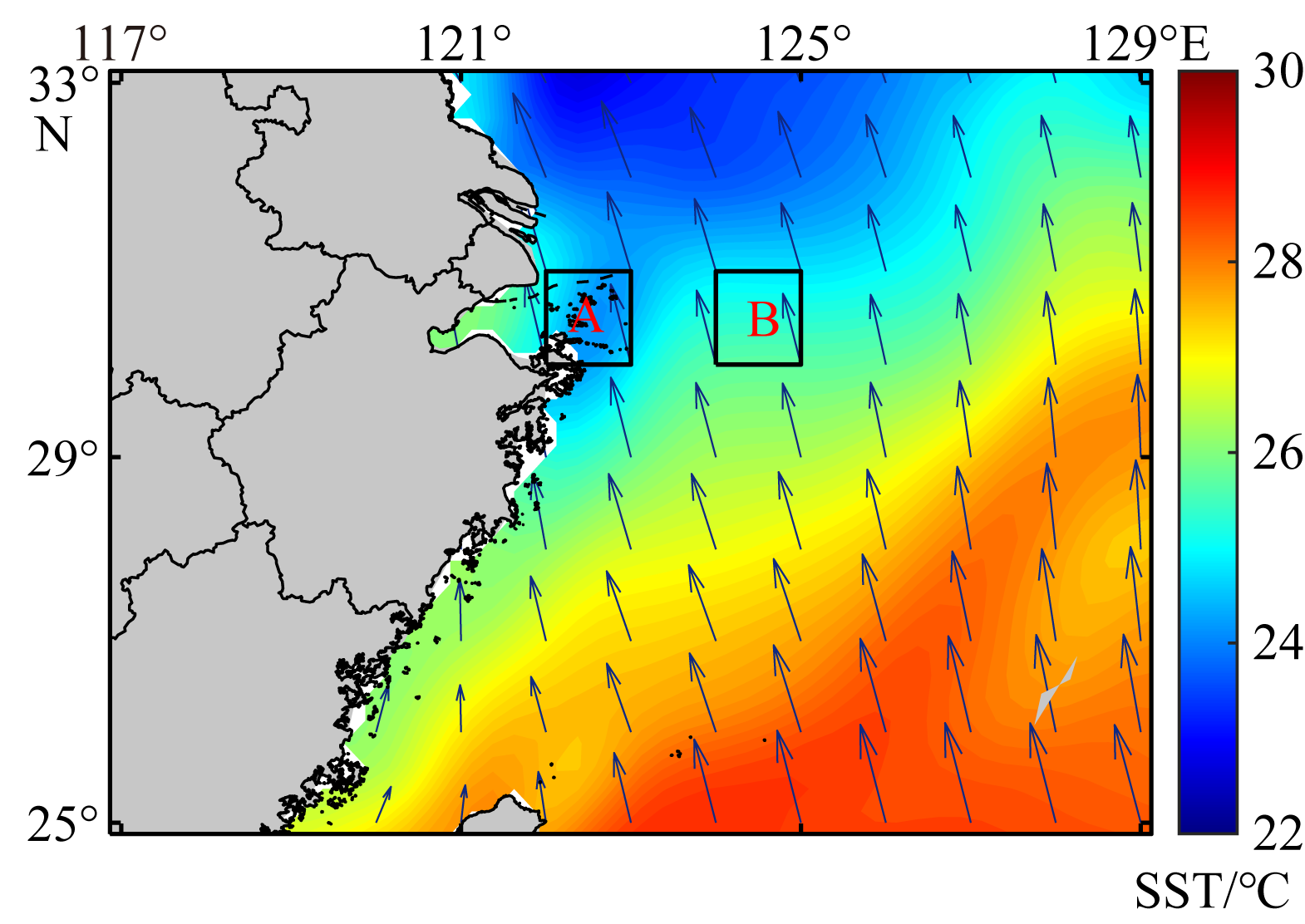
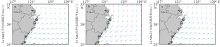
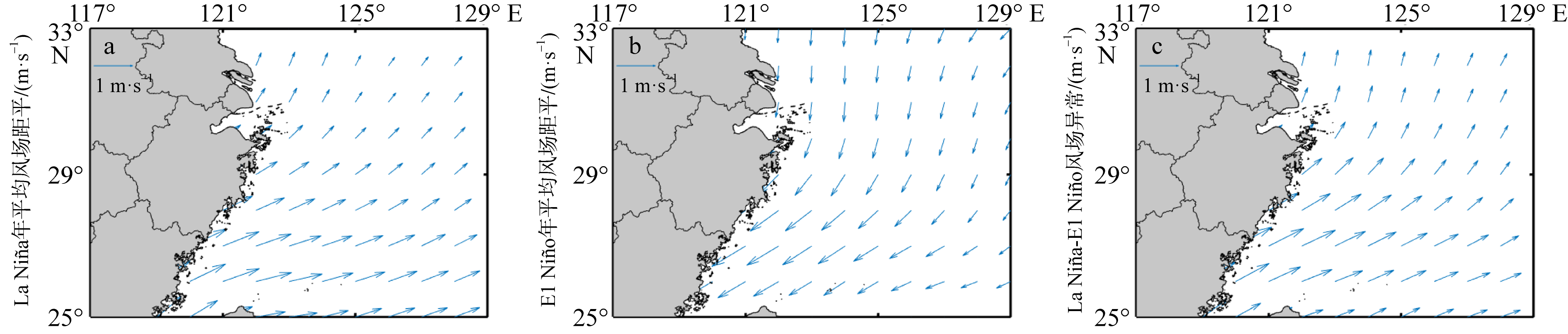
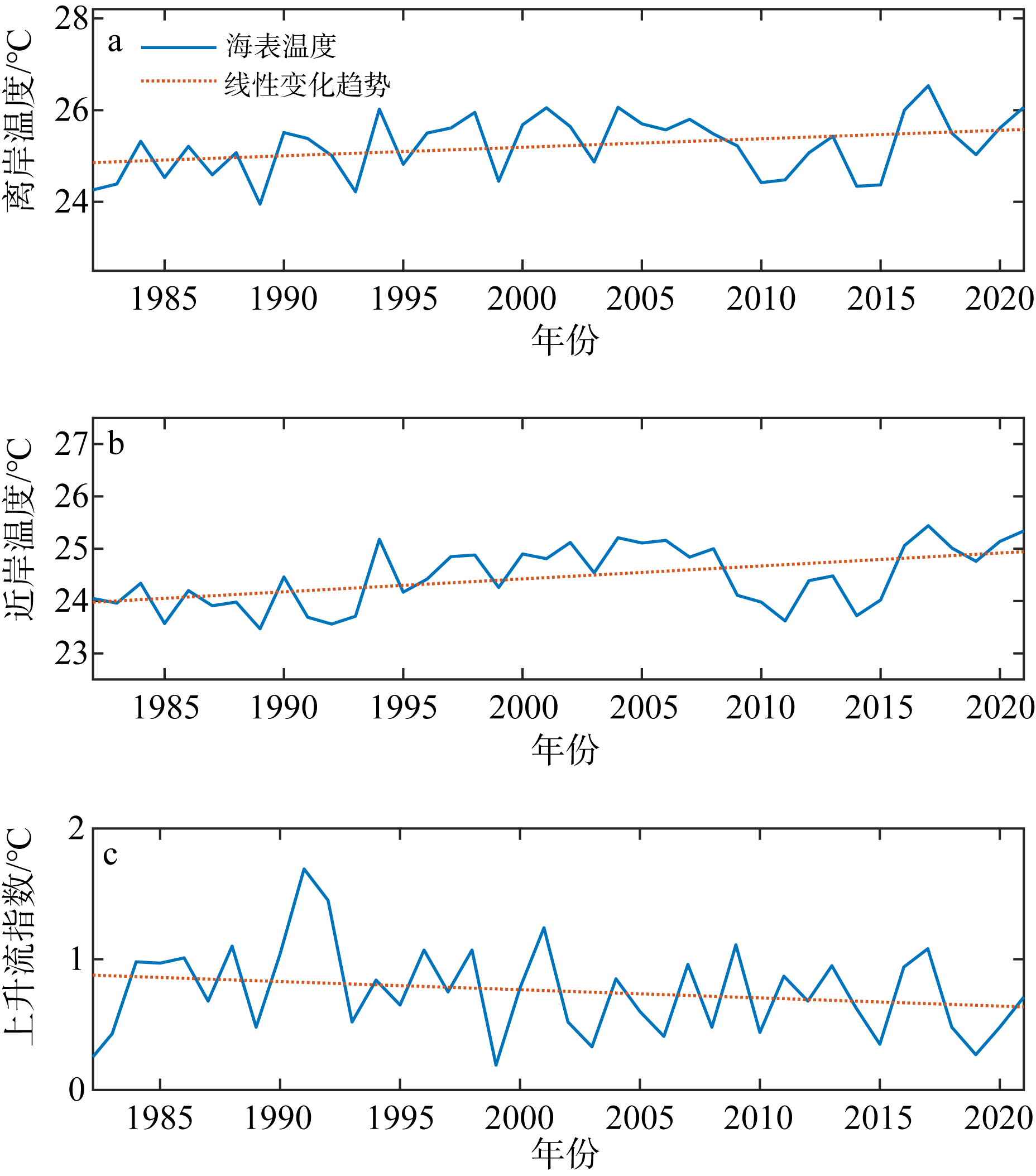
Fig. 2
Variations of averaged sea surface temperature (SST) and upwelling index in the study areas in summer of 1982—2021. (a) averaged SST in offshore background area; (b) averaged SST in nearshore upwelling area; (c) upwelling index is the difference between nearshore sea surface temperature and offshore sea surface temperature. Red dash lines show linear trends of the variation"
| [1] |
曹欣中, 1985. 浙江近海沿岸上升流与渔场的关系[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 1: 25-28.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
董小芳, 杨华玮, 张峦, 等, 2017. ENSO事件对上海降水中氢氧同位素变化的影响[J]. 环境科学, 38(12): 4991-5003.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
管秉贤, 陈上及, 1964. 中国近海的海流系统[R]// 中国科学技术委员会海洋组海洋综合调查办公室, 全国海洋综合调查报告. 北京: 海洋研究所:1-85 (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
何齐齐, 2017. 基于卫星遥感和数值模拟的夏季舟山沿岸上升流研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
何青青, 张春玲, 高郭平, 等, 2016. 舟山近海海域夏季上升流时空特征及其与风场的关系[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 25(1): 142-151.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
胡明娜, 赵朝方, 2007. 舟山及邻近海域上升流长周期的遥感观测与分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报: 自然科学版, 37(S1): 235-240.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
胡明娜, 赵朝方, 2008. 浙江近海夏季上升流的遥感观测与分析[J]. 遥感学报, 12(2): 297-304.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
柳沙沙, 赵骞, 王玉, 等, 2020. 辽东半岛顶端海域上升流长期变化特征及影响因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 51(1): 31-39.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
吕新刚, 乔方利, 夏长水, 等, 2007. 长江口外及浙江沿岸夏季上升流的潮生机制[J]. 中国科学D辑: 地球科学, 37(1): 133-144.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
苗馨, 胡建宇, 2011. 用沿岸上升流指数分析中国东南沿岸风生上升流的特征[J]. 海洋通报, 30(3): 258-265.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
邵贤, 2014. 舟山群岛新区海洋工程环境管理研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋学院.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
沈萌, 缪明芳, 王舒瑜, 等, 2020. 2018年夏季舟山海域上升流特征及形成机制分析[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 59(S1): 18-23.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
宋晨, 孟周, 王晓波, 等, 2022. 2019-2020年夏季舟山海域浮游动物优势种生态位及其生态分化[J]. 海洋学报, 44(10): 127-139.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
孙轶, 2016. 浙江与加州沿岸上升流的季节和年际变化研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
谢玲玲, 张书文, 赵辉, 2012. 琼东上升流研究概述[J]. 热带海洋学报, 31(4): 35-41.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.04.005 |
|
|
|
| [16] |
谢玲玲, 宗晓龙, 伊小飞, 等, 2016. 琼东上升流的年际变化及长期变化趋势[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 47(1): 43-51.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
张俊鹏, 旷芳芳, 万小芳, 等, 2019. ENSO发展期琼东上升流的动力过程响应差异[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 38(3): 307-317.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
张茹, 2022. 基于多源数据的辽东半岛顶端上升流研究[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
张雯, 董啸, 薛峰, 等, 2020. 不同PDO位相下El Niño发展年和La Niña年东亚夏季风的季节内变化[J]. 大气科学, 44(2): 390-406.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
周楠, 2021. 舟山海域上升流时空变化及其原因研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<2205:TABTIO>2.0.CO;2 |
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
pmid: 17813287 |
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [1] | YUAN Yu, XU Haiming, MA Jing, ZHANG Tong. Impact of Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on interannual relationship between ENSO and early summer marine heatwaves in the Western Pacific* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 1-16. |
| [2] | WANG Xu, QU Ke, WANG Zijun, YANG Yuanping, WANG Chao, ZHANG Liangbin. Numerical simulation study on the effect of wind on the hydrodynamic characteristics of undular tidal bores seawall [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 116-130. |
| [3] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [4] | HAN Dingyan, LI Min, HU Rui, XIE Lingling. Variation and mechanisms of autumn tropical cyclones landed in Guangdong [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 64-78. |
| [5] | ZHANG Liangbin, QU Ke, HUANG Jingxuan, WANG Xu, GUO Lei. Numerical simulation study of the influences of onshore wind on overtopping characteristics of coastal seawall under focused wave [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 63-73. |
| [6] | LIN Shaowen, REN Hengye, LU Wenfang. Intra-seasonal regulation and mechanism on sea surface chlorophyll in the upwelling off the coast of Vietnam [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 113-124. |
| [7] | LI Chengyong, MENG Xiangfeng, XIE Ruihuang. Interdecadal modulation of ENSO asymmetry by the Pacific Decadal Oscillation and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 36-46. |
| [8] | CHU Xiaoqing, PENG Qihua. The role of alongshore wind and ocean wave in generating the northward Somali Current [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 1-8. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yuhong, ZHANG Lianyi, DU Yan. Tropical ocean-atmosphere coupling modes and their relationship with ENSO during spring* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 34-44. |
| [10] | ZHANG Qi, LIAN Tao. Low-frequency wind stress forcing reduces El Niño diversity in numerical model [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 1-9. |
| [11] | GU Jinghua, ZHU Jianrong, JIN Zhi. Numerical simulation of oil film drift and diffusion after oil spill accident at the Baosteel wharf in the Changjiang Estuary [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 159-170. |
| [12] | YANG Shaoqiong, CHENG Dan, CHEN Guangyao, LUO Chenyi, NIU Wendong, MA Wei, FA Shuai. Review on the application of underwater gliders for observing typical ocean phenomena [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 54-74. |
| [13] | CHEN Kehai, XIE Xuetong, ZHANG Jinlan, ZHENG Yan. An SST dependent geophysical model function for HY-2A scatterometer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 90-102. |
| [14] | XIN Hongyu, XIE Qiang, WANG Weiqiang. Seasonal variation of East India Coastal Current and its transports of heat and salt [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 38-51. |
| [15] | CAI Shuqun, NIU Jianwei, HE Yinghui, CHEN Xuebin, ZHANG Yongkang, XU Jiexin, CHEN Zhiwu, LIN Shicheng, XIE Jieshuo. A view on constructing synchronous real-time in-situ observational system of marine hydrology based on offshore wind power field [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(3): 96-102. |
|
||