Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 54-64.doi: 10.11978/2019045CSTR: 32234.14.2019045
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of breeding density on the growth, metabolic enzyme activity and related gene expression level of juvenile Pampus argenteus
Jiahao NI1( ), Xiaojing ZHU1, Yiping JI1, Bin ZHOU1, Yajun WANG2, Shanliang XU2(
), Xiaojing ZHU1, Yiping JI1, Bin ZHOU1, Yajun WANG2, Shanliang XU2( ), Danli WANG1(
), Danli WANG1( )
)
- 1. School of Marine Sciences, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
2. Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biotechnology Ministry of Education, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
-
Received:2019-05-07Revised:2019-07-25Online:2020-03-10Published:2020-03-10 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(31772869);National Natural Science Foundation of China(31872586);Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province(LY15C190003);Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province(LY18C190008);Special Funds for Key Project of Science and Technology of Ningbo(2019C02059)
CLC Number:
- P735.541
Cite this article
Jiahao NI, Xiaojing ZHU, Yiping JI, Bin ZHOU, Yajun WANG, Shanliang XU, Danli WANG. Effects of breeding density on the growth, metabolic enzyme activity and related gene expression level of juvenile Pampus argenteus[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 54-64.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
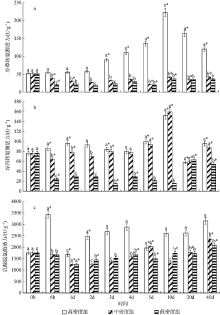
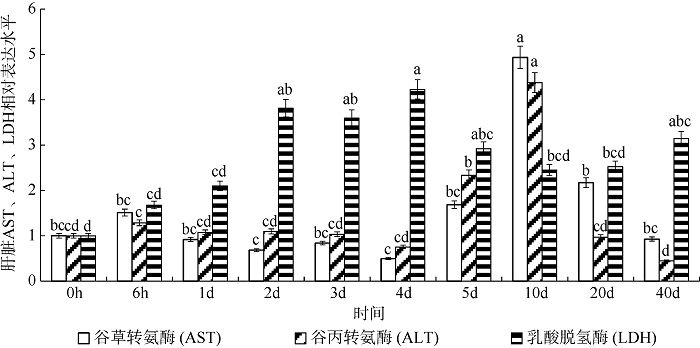
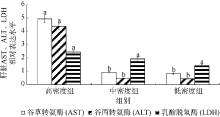
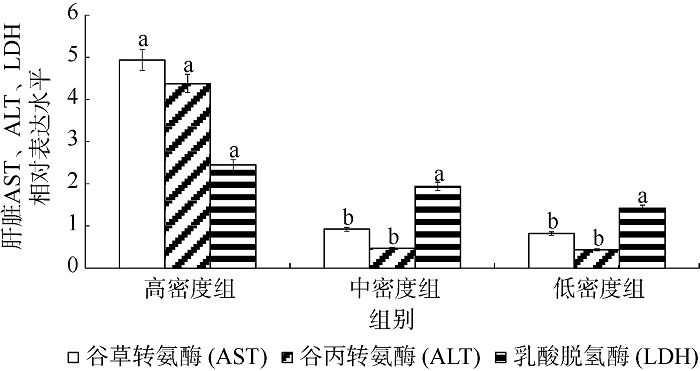
Fig. 1
Effect of density on liver AST (a), ALT (b) and LDH (c) activity of juvenile Pampus argenteus. * indicates significant difference between different treatment times at the same density (p<0.05), Different small letters above the bars indicate significant differences between different densities at the same time (p<0.05)"
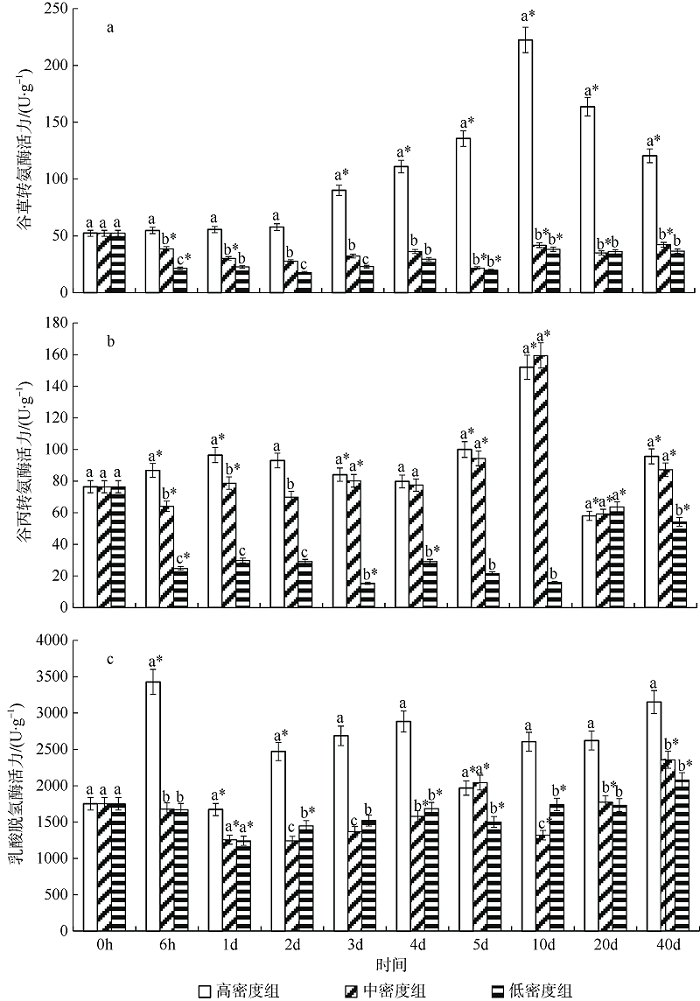
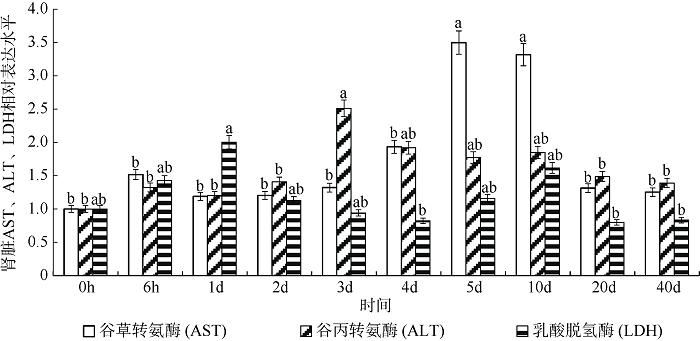
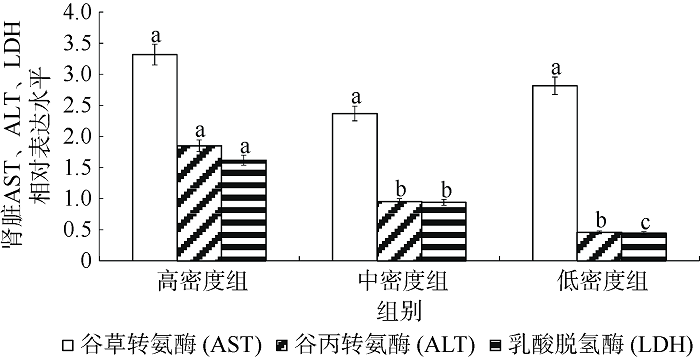
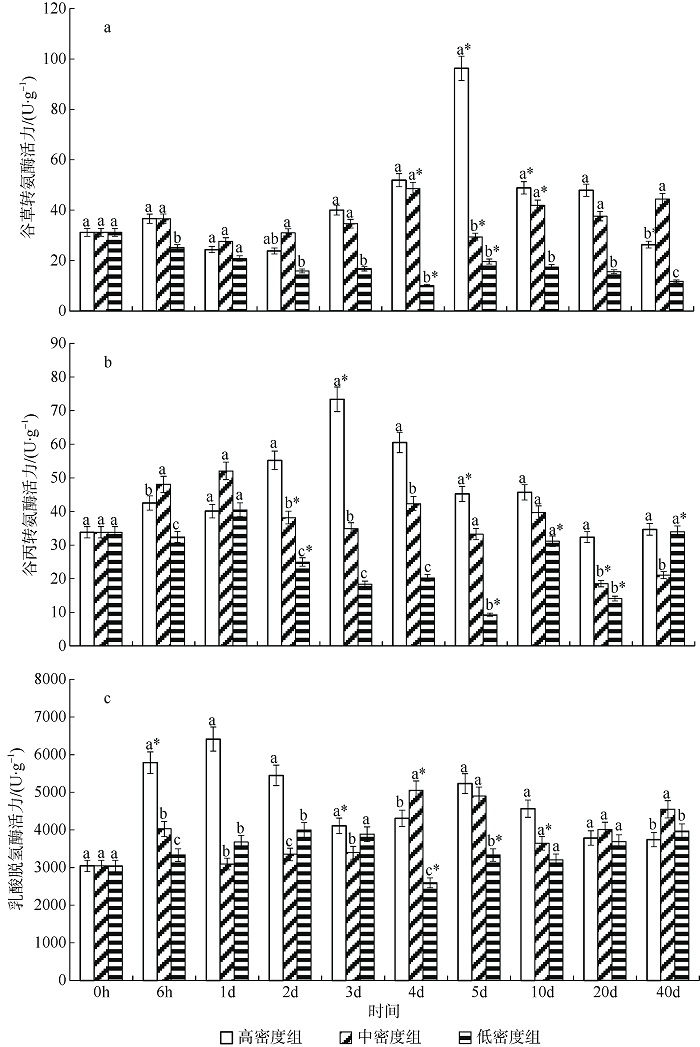
Fig. 2
Effect of density on kidney AST (a), ALT (b) and LDH (c) activity of juvenile Pampus argenteus. Asterisk (*) indicates significant difference between different treatment times at the same density (p<0.05), Different small letters above the bars indicate significant differences between different densities at the same time (p<0.05)"
| 1 | 李爱华 , 1997. 拥挤胁迫对草鱼血浆皮质醇、血糖及肝脏中抗坏血酸含量的影响[J]. 水生生物学报, 21(4):384-386. |
| LI AIHUA, 1997. Effects of crowding stress on plasma cortisol, glucose and liver ascorbic acid in grass carp(Ctenopharyngodon idellus)[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 21(4):384-386 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 2 | 李大鹏, 庄平, 严安生 , 等, 2004. 光照、水流和养殖密度对史氏鲟稚鱼摄食、行为和生长的影响[J]. 水产学报, 28(1):54-61. |
| LI DAPENG, ZHUANG PING, YAN ANSHENG, et al, 2004. The influences of illumination, water current and stocking density on feeding, behavior and growth in juveniles Acipenser schrenckii[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 28(1):54-61 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 3 | 梁从飞 , 2015. 尼罗罗非鱼耐盐碱选育一代耐受性、生长性能及鳃Na+/HCO3-共转运子、碳酸酐酶基因表达[D]. 硕士学位论文, 上海:上海海洋大学. |
| LIANG CONGFEI, 2015. Tolerance, growth and branchial mRNA expression of Na+/HCO3- cotransporter and CA of the first selected generation of Oreochromis niloticus in saline and alkaline water[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 4 | 逯尚尉 , 2010. 不同饵料、密度和光周期对点带石斑鱼(Epinephelus malabaricus)幼鱼的影响[D] . 硕士学位论文, 南京: 南京农业大学. |
| LU SHANGWEI, 2010. Effect of different diets, stocking densities and photoperiods on juvenile Epinephelus malabaricus[D] . Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 5 | 逯尚尉, 刘兆普, 余燕 , 2011. 密度胁迫对点带石斑鱼幼鱼生长、代谢的影响[J]. 中国水产科学, 18(2):322-328. |
| LU SHANGWEI, LIU ZHAOPU, YU YAN, 2011. Effects of density stress on growth and metabolism of juvenile Epinephelus malabaricus[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 18(2):322-328 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 6 | 彭士明, 施兆鸿, 孙鹏 , 等, 2010. 养殖密度对银鲳幼鱼生长及组织生化指标的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 29(7):1371-1376. |
| PENG SHIMING, SHI ZHAOHONG, SUN PENG, et al, 2010. Effects of breeding density on the growth and tissues biochemical indices of juvenile silver pomfret(Pampus argenteus)[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(7):1371-1376 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 7 | 亓成龙 , 2016. 养殖密度和亚硝酸盐胁迫对团头鲂幼鱼生理机能和肌肉品质的影响[D]. 硕士学位论文, 武汉: 华中农业大学. |
| QI CHENGLONG, 2016. Effect of stocking density and nitrite on physiological functions and muscle quality of blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala juveniles[D] . Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 8 | 强俊, 徐跑, 何杰 , 等, 2011. 氨氮与拥挤胁迫对吉富品系尼罗罗非鱼幼鱼生长和肝脏抗氧化指标的联合影响[J]. 水产学报, 35(12):1837-1848. |
| QIANG JUN, XU PAO, HE JIE, et al, 2011. The combined effects of external ammonia and crowding stress on growth and biochemical activities in liver of (GIFT) Nile tilapia juvenile(Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 35(12):1837-1848 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 9 | 强俊, 杨弘, 何杰 , 等, 2014. 3种品系尼罗罗非鱼生长及高密度胁迫后生理响应变化的比较[J]. 中国水产科学, 21(1):142-152. |
| QIANG JUN, YANG HONG, HE JIE, et al, 2014. Comparison on growth performance in three different strains of Nile tilapia and physiological responses after short-term high stocking density stress[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 21(1):142-152 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 10 | 任源远 , 2014. 养殖密度对施氏鲟大规格鱼种生长性能及血液生理生化组分的影响[D]. 硕士学位论文, 山东: 中国海洋大学. |
| REN YUANYUAN, 2014. Effects of stocking density on growth performance and blood physiological and biochemical components in large-sized juvenile Amur sturgeon[D]. Shandong: Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 11 | 石小涛 , 2006. 史氏鲟在拥挤胁迫中的应激反应[D]. 硕士学位论文, 华中农业大学, 2006. |
| SHI XIAOTAO, 2006. The stress-influences of rearing densities on juvenile Amur sturgeon, Acipenser schrenckii[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 12 | 孙大川, 谭洪新, 罗国芝 , 等, 2009. 养殖密度对宝石鲈生长性能和血液生化指标的影响[J]. 渔业现代化, 36(2):12-15. |
| SUN DACHUAN, TAN HONGXIN, LUO GUOZHI, et al, 2009. Effect of stocking density on growth and blood biochemical parameters of Scortum barcoo[J]. Fishery Modernization, 36(2):12-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 13 | 王春枝, 李忠, 梁宏伟 , 等, 2014. 低氧胁迫对鲢线粒体ATP酶活性及F1-δ基因表达的影响[J]. 中国水产科学, 21(3):454-463. |
| WANG CHUZHI, LI ZHONG, LIANG HONGWEI, et al, 2014. The effects of hypoxia stress on mitochondrial ATPase activity and the expression of F1-δ in Hypophthalmichthys molitrix[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 21(3):454-463 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 14 | 王文博, 汪建国, 李爱华 , 等, 2004. 拥挤胁迫后鲫鱼血液皮质醇和溶菌酶水平的变化及对病原的敏感性[J]. 中国水产科学, 11(5):408-412. |
| WANG WENBO, WANG JIANGUO, LI AIHUA, et al, 2004. Changes of cortisol and lysozyme levels in Carassius auratus blood after crowding stress and the fish sensitivity to pathogen[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 11(5):408-412 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 15 | 王跃斌, 胡成硕, 胡则辉 , 等, 2017. 养殖密度对日本黄姑鱼幼鱼生长及非特异性免疫的影响[J]. 海洋渔业, 39(1):51-57 . |
| WANG YUEBIN, HU CHENGSHUO, HU ZEHUI, et al, 2017. Effects of different stocking densities on growth performance and non-specific immunity of juvenile Nibea japonica[J]. Marine Fisheries, 39(1):51-57 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 16 | 夏华, 李威名, 陈阿琴 , 等, 2013. 两种养殖密度下鲫鱼生长和免疫酶活性的比较[J]. 广东农业科学, 40(12):130-133. |
| XIA HUA, LI WEIMING, CHENG AQIN, et al, 2013. Comarative analysis of growth and immune enzyme activities of Carassius auratus under two densities[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 40(12):130-133 (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| 17 | 薛宝贵, 楼宝, 徐冬冬 , 等, 2013. 密度胁迫对黄姑鱼幼鱼生长、代谢及非特异性免疫的影响[J]. 渔业科学进展, 34(2):45-51. |
| XUE BAOGUI, LOU BAO, XU DONGDONG, et al, 2013. Impact of density stress on growth, metabolism and non-specific immune functions of juvenile Nibea albiflora[J]. Progress in fishery sciences, 34(2):45-51 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 18 | 张建明, 郭柏福, 高勇 , 2013. 中华鲟幼鱼对慢性拥挤胁迫的生长、摄食及行为反应[J]. 中国水产科学, 20(3):592-598. |
| ZHANG JIANMING, GUO BOFU, GAO YONG, 2013. Effects of chronic crowding stress on growth, feeding, and behavior in Chinese sturgeon Acipenser sinensis F2 juveniles[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 20(3):592-598 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 19 | 于淼, 樊启学, 程鹏 , 等, 2008. 急性拥挤胁迫对鲤血液中皮质醇及几项生化指标的影响[J]. 淡水渔业, 38(4):20-24 . |
| YU MIAO, FAN QIXUE, CHENG PENG, et al, 2008. Effects of acute crowding stress on cortisol and several biochemical indexes in Cyprinus carpio serum[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 38(4):20-24 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 20 | 张磊, 樊启学, 赵志刚 , 等, 2007. 慢性拥挤胁迫对鲤生长及血液生化指标的影响[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 22(6):465-469. |
| ZHANG LEI, FAN QIXUE, ZHAO ZHIGANG, et al, 2007. The effects of chronic crowding stress on growth and blood Biochemical indexes in common carp Cyprinus carpio[J]. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 22(6):465-469 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 21 | 张廷军, 杨振才, 孙儒泳 , 1998. 鱼类对高密度环境的适应[J]. 水产科技情报, 25(3):110-113. |
| ZHANG TINGJUN, YANG ZHENCAI, SUN RUYONG, 1998. The Acclimation of Fishes to High Stocking Density[J]. Fisheries Science & Technology Information, 25(3):110-113 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 22 | 张曦文, 吴垠, 贺茹靖 , 等, 2012. 循环水养殖模式下养殖密度对青石斑鱼生长及生理指标的影响[J]. 大连海洋大学学报, 27(6):518-522. |
| ZHANG XI WEN, WU YIN, HE RUJING, et al, 2012. The effects of stocking density on growth and physiological indices of grouper Epinephelus awoara in recirculating aquaculture[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 27(6):518-522 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 23 | Allen K O , 1974. Effects of stocking density and water exchange rate on growth and survival of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus in circular tanks[J]. Aquaculture, 4:29-39. |
| 24 | Baker R F, Ayles G B , 1990. The effects of varying density and loading level on the growth of arctic charr (Aalvelinus alpinus L.) and rainbow trout[J]. Journal of the World Aquaculture Society, 121, 313-326. |
| 25 | Demeal N A , 1978. Some characteristics of carbohydrate metabolism in fish[J]. Oceanis (Doc. Oceanogr.), 4:359-365. |
| 26 | Hoener, G, Rosenthal H, Kruener G , 1987. Social interaction of juvenile Sarotherodon galilaeus in laboratory aquaria[J]. Journal of Aquaculture in the Tropics, 2(1):45-58. |
| 27 | Jørgensen E H, Christiansen J S, Jobling M , 1993. Effects of stocking density on food intake, growth performance and oxygen consumption in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus)[J]. Aquaculture, 110(2):191-204. |
| 28 | Shelbourn J E, Brett J R, Shirahata S , 1973. Effect of Temperature and Feeding Regime on the Specific Growth Rate[J]. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 30(8):1191-1194. |
| 29 | Tejpal C S, Pal A K, Sahu N P , et al, 2009. Dietary supplementation of L-tryptophan mitigates crowding stress and augments the growth in Cirrhinus mrigala fingerlings[J]. Aquaculture, 293(3-4):272-277. |
| 30 | Vijayan M M, Ballantyne J S, Leatherland J F , 1990. High stocking density alters the energy metabolism of brook charr, Salvelinus fontinalis[J]. Aquaculture, 88(3):371-381. |
| [1] | SUN Zeming, HAN Shuzong, WANG Mingjie, SU Hanxiang. Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 17-31. |
| [2] | ZHAO Zhongwei, WU Lingyun, GAO Weijian, LI Wei. A study of the effect of shore platform morphology on coastal erosion of rocky cliffs in the Wucaiwan Bay, E’man, Hainan Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 106-115. |
| [3] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [4] | CHEN Jie, BIAN Cheng, JIANG Changbo, YAO Zhen, JIANG Chao, LIANG Hai. Advances in the characterization of bioclastic sediment motion [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 33-41. |
| [5] | XI Chen, LIN Zongxuan, SA Rula, DENG Xi, LIU Qiang, NI Liang, LUO Laicai, MA Teng, XIE Zhijie, CHEN Siruo, CHEN Songze. Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [6] | WU Tao, PAN Ying, LIU Yiming, LIAN Changpeng, XU Bingjie, WANG Chaoqi, YANG Ling. Testis development, spermatogenesis and sperm ultrastructure of Lutraria sieboldii in the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 69-80. |
| [7] | XU Bingjie, LIU Yiming, LIAN Changpeng, WU Tao, PAN Ying. Ovarian development, oocyte and yolk production of Paphia textile in Beibu Gulf, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 48-58. |
| [8] | XU Bingjie, LIU Yiming, XING Qinggan, LIAN Changpeng, WU Tao, PAN Ying. Spermary development, spermatogenesis and sperm ultrastructure of Paphia textile in the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 59-68. |
| [9] | DING Yiting, DONG Dibo. Study on comprehensive risk assessment of storm surges for Fujian Province from the perspective of resilience [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 126-136. |
| [10] | ZHAO Jie, LIN Yanjiang, LIU Ran, DU Rong. Prediction of mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea based on the PredRNN++ model [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 16-27. |
| [11] | WU Tongren, LIU Pei, YU Jitao, WEN Tingting. Comparative study on different tide level correction methods in remote sensing extraction of coastline under balanced profile model* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 52-62. |
| [12] | WU Tao, PAN Ying, LIAN Changpeng, LIU Yiming, XU Bingjie, WANG Chaoqi, YANG Ling. The study on ovarian development, oogenesis and vitellogenesis of Lutraria sieboldii in Beibu Gulf of Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 137-149. |
| [13] | ZHANG Zheran, HU Junyang, ZHOU Kai, ZHANG Penghui, XING Jiuxing, CHEN Shengli. Storm surge simulations of the coastal area of Shenzhen using different types of typhoon meteorological fields—a case study of Typhoon Mangkhut* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 1-14. |
| [14] | TIAN Cheng, LI Xin, DU Yang, LI Ming, XIE Yong, XIA Jilu. Assessment of tropical cyclone disaster risk based on the Bayesian network and GIS [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 17-29. |
| [15] | WANG Chenyan, SHI Jingwen, YAN Annan, KANG Yaru, WANG Yuxuan, QIN Suli, HAN Minwei, ZHANG Ruijie, YU Kefu. Bioaccumulation characteristics and source apportionment of organophosphate esters in Acanthaster planci from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
|
||