Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 48-57.doi: 10.11978/2018075CSTR: 32234.14.2018075
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Impact of simulated warming and nutrients input on plankton community metabolism in Daya Bay*
Fuwu XIE1,2( ), Xingyu SONG3(
), Xingyu SONG3( ), Yehui TAN3, Meiting TAN3, Yadong HUANG3, Huaxue LIU1(
), Yehui TAN3, Meiting TAN3, Yadong HUANG3, Huaxue LIU1( )
)
- 1. Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fishery Ecological Environment, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Guangzhou 510300, China
2. Hainan Academy of Ocean and Fisheries Sciences (Hainan Provincial Marine Development Plan and Design Research Institute), Haikou, 571126, China
3. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China;
-
Received:2018-07-25Revised:2018-09-10Online:2019-03-20Published:2019-04-15 -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0506302);National Basic Research Program (2015CB452904);National Natural Science Foundation of China (41276161)
CLC Number:
- P735.12
Cite this article
Fuwu XIE, Xingyu SONG, Yehui TAN, Meiting TAN, Yadong HUANG, Huaxue LIU. Impact of simulated warming and nutrients input on plankton community metabolism in Daya Bay*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 48-57.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 2
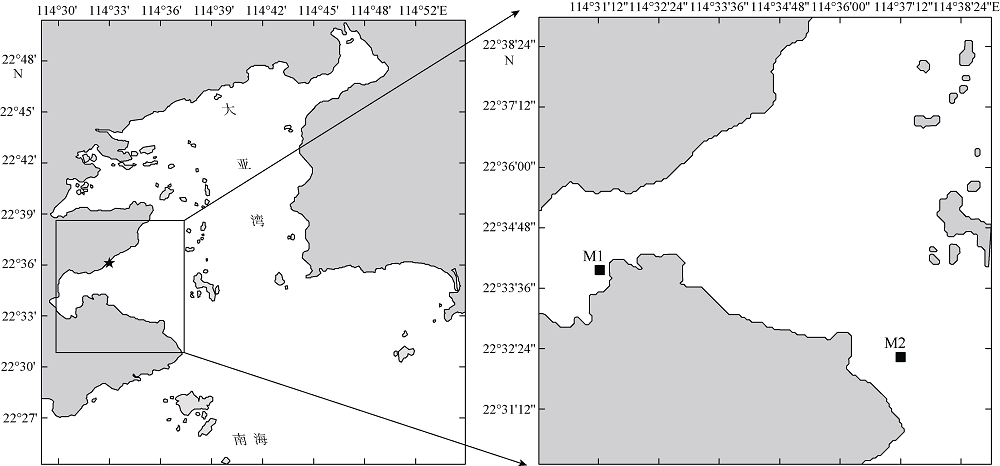
The environmental parameters of surface water in Daya Bay"
| 季节 | 站位 | 温度/℃ | 盐度/‰ | pH | Chl-a/(μg·L-1) | DIP/(μmol·L-1) | DIN/(μmol·L-1) | DIN/DIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 夏季 | M1 | 28.3 | 30.7 | 8.1 | 5.37 | 0.44 | 35.46 | 80.59 |
| M2 | 29.9 | 33.6 | 8.3 | 1.58 | 0.05 | 7.82 | 156.40 | |
| 冬季 | M1 | 18.4 | 29.1 | 8.0 | 0.63 | 0.51 | 12.50 | 24.51 |
| M2 | 17.9 | 29.9 | 8.0 | 1.43 | 0.30 | 10.62 | 35.40 |
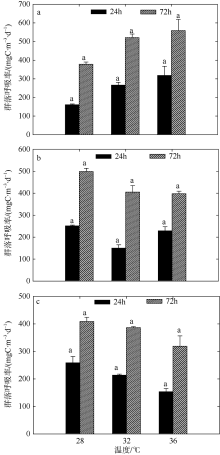
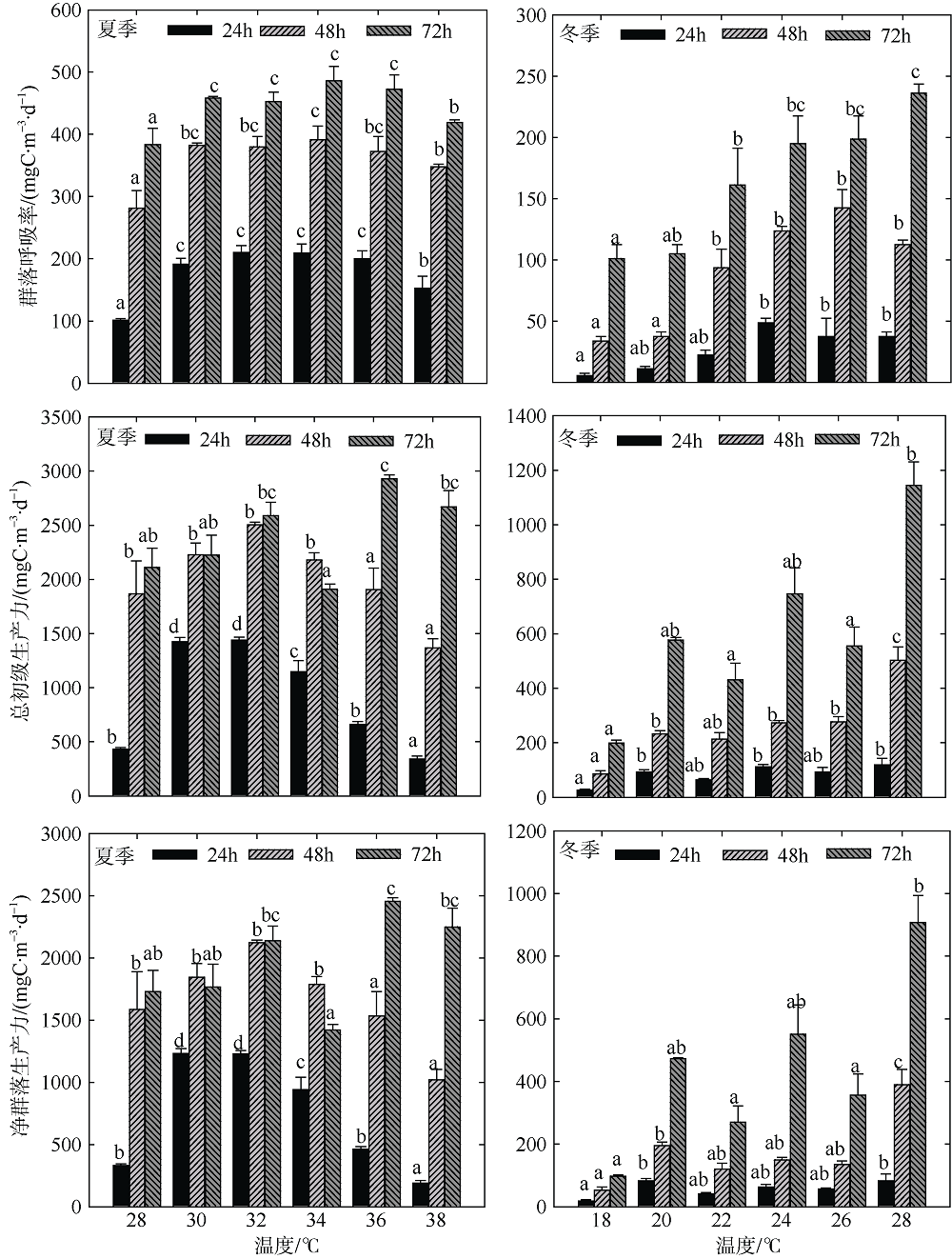
Fig. 3
Variation of plankton CR of two-factors simulated experiments in summer. Significant differences among the temperature groups are indicated by using different superscripts (p<0.05), while no significant difference is shown using the same superscript. LN: low nutrients, MN: medium nutrients, HN: high nutrients. Significant differences among the nutrients groups are marked by “*”, while no significant difference is shown without “*”"

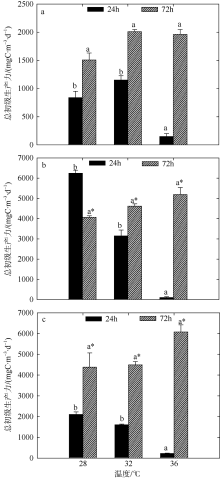
Fig. 4
Variation of plankton GPP of two-factors simulated experiments in summer. Significant differences among the temperature groups are indicated by using different superscripts (p<0.05), while no significant difference is shown using the same superscript. LN: low nutrients, MN: medium nutrients, HN: high nutrients. Significant differences among the nutrients groups are marked by “*”, while no significant difference is shown without “*”"
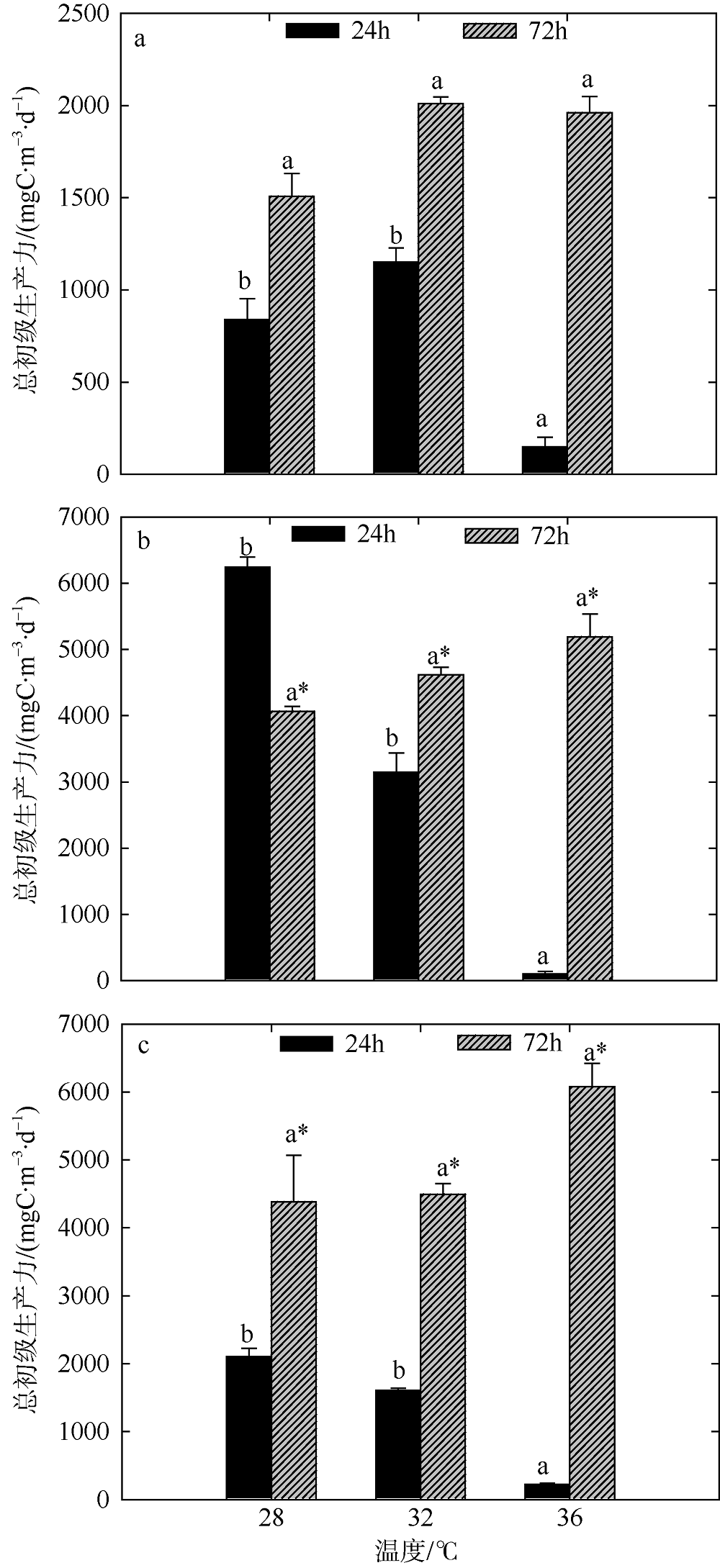
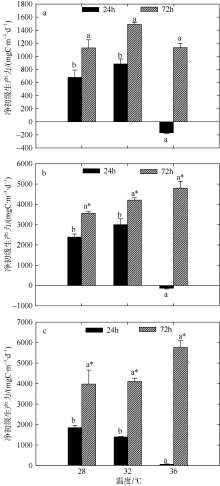
Fig. 5
Variation of plankton NCP of two-factors simulated experiments in summer. Significant differences among the temperature groups are indicated by using different superscripts (p<0.05), while no significant difference is shown using the same superscript. LN: low nutrients, MN: medium nutrients, HN: high nutrients. Significant differences among the nutrients groups are marked by “*”, while no significant difference is shown without “*”"
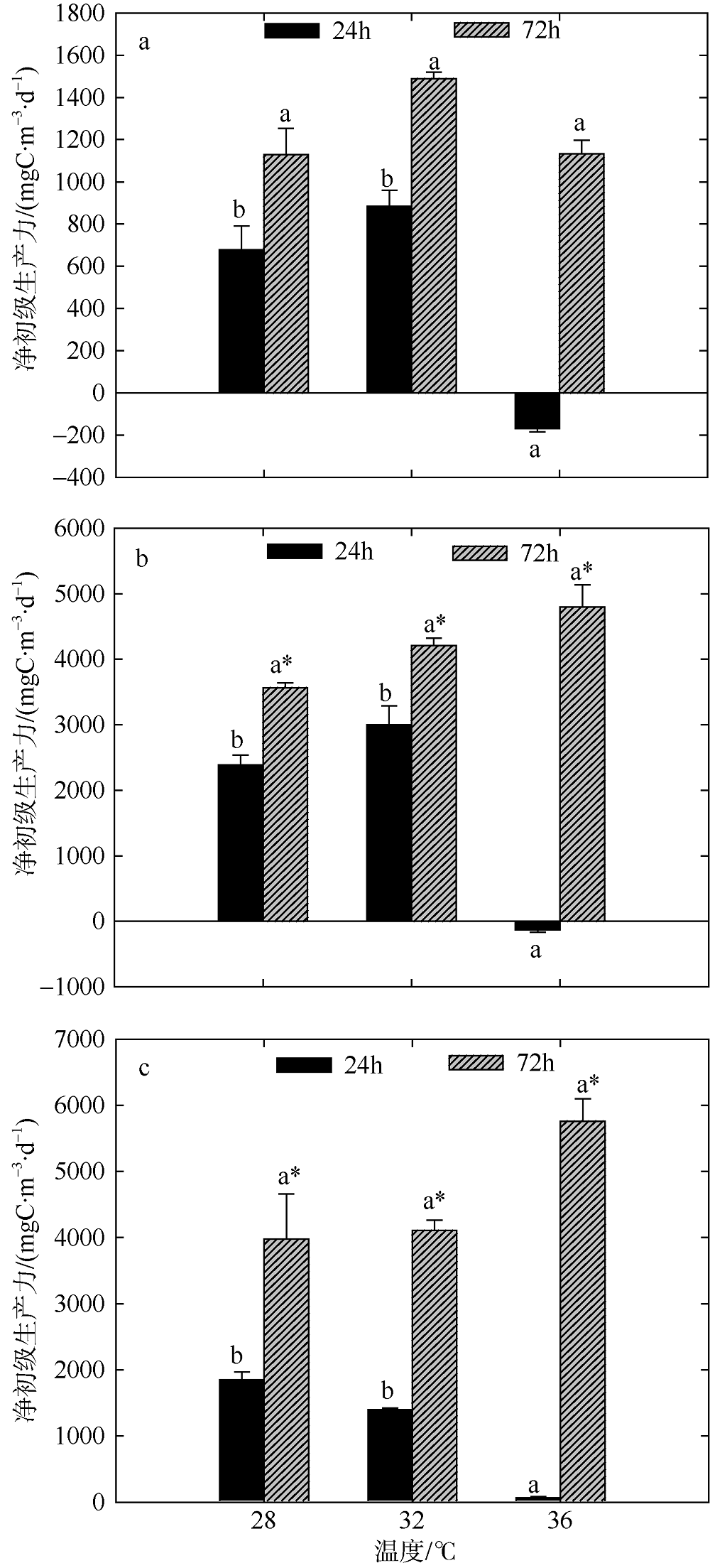
Tab. 3
Ratio of GPP/CR of two-factors simulated experiments during summer and winter"
| 营养盐 | 夏季 | 冬季 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28℃ | 32℃ | 36℃ | 均值 | 20℃ | 24℃ | 28℃ | 均值 | ||
| 24h | 低营养 | 5.21 | 4.32 | 0.47 | 3.33 | 5.38 | 2.78 | 1.76 | 3.31 |
| 中营养 | 10.50 | 21.00 | 0.44 | 10.65 | 2.63 | 2.60 | 2.37 | 2.53 | |
| 高营养 | 8.14 | 7.53 | 1.44 | 5.70 | 2.63 | 3.00 | 1.40 | 2.34 | |
| 均值 | 7.95 | 10.95 | 0.78 | 3.55 | 2.79 | 1.84 | |||
| 72h | 低营养 | 3.98 | 3.86 | 10.72 | 6.19 | 2.51 | 5.92 | 3.12 | 3.85 |
| 中营养 | 8.15 | 11.39 | 11.63 | 10.39 | 2.91 | 4.52 | 3.14 | 3.52 | |
| 高营养 | 10.72 | 13.18 | 19.07 | 14.32 | 2.95 | 4.00 | 4.41 | 3.79 | |
| 均值 | 7.62 | 9.48 | 13.81 | 2.79 | 4.81 | 3.56 | |||
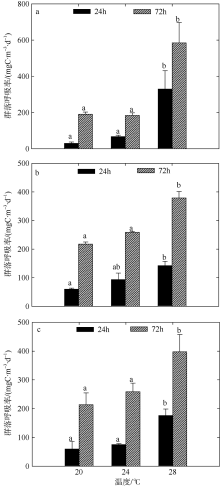
Fig. 6
Variation of plankton CR of two-factors simulated experiments in winter. Significant differences among the temperature groups are indicated by using different superscripts (p<0.05), while no significant difference is shown using the same superscript. LN: low nutrients, MN: medium nutrients, HN: high nutrients. Significant differences among the nutrients groups are marked by “*”, while no significant difference is shown without “*”"

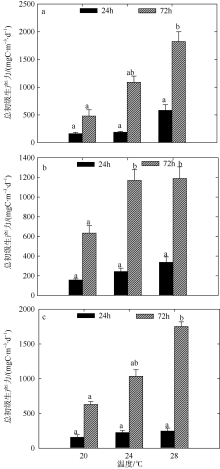
Fig. 7
Variation of plankton GPP of two-factors simulated experiments in winter. Significant differences among the temperature groups are indicated by using different superscripts (p<0.05), while no significant difference is shown using the same superscript. LN: low nutrients, MN: medium nutrients, HN: high nutrients. Significant differences among the nutrients groups are marked by “*”, while no significant difference is shown without “*”"
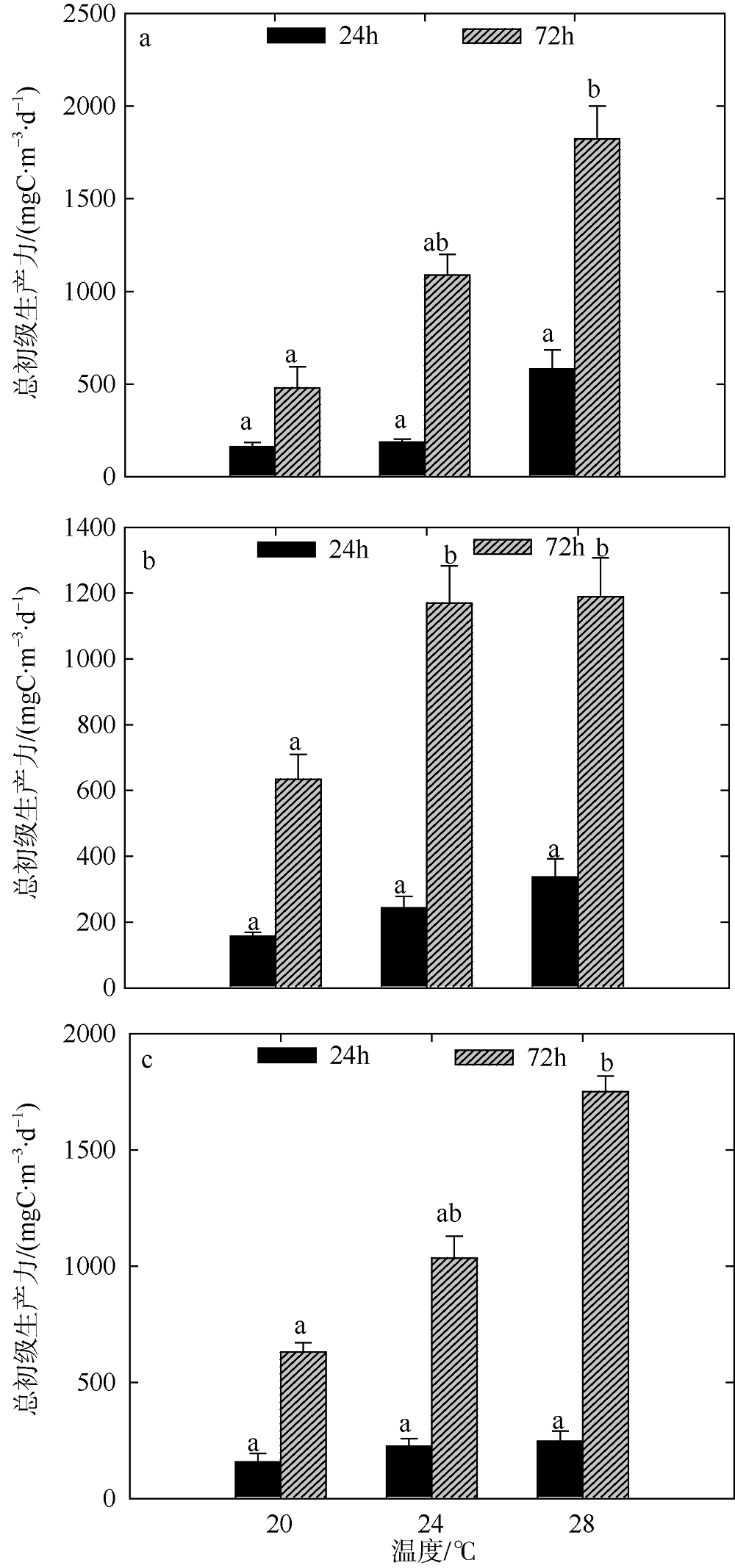
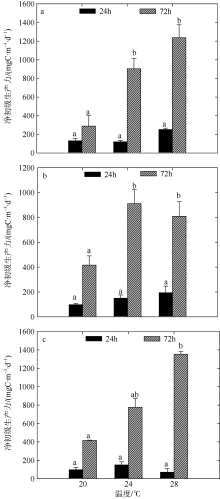
Fig. 8
Variation of plankton NCP of two-factors simulated experiments in winter. Significant differences among the temperature groups are indicated by using different superscripts (p<0.05), while no significant difference is shown using the same superscript. LN: low nutrients, MN: medium nutrients, HN: high nutrients. Significant differences among the nutrients groups are marked by “*”, while no significant difference is shown without “*”"

| [1] | 蔡泽富, 2011. 温排水对象山港浮游生态系统的影响及其围隔实验研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学. |
| CAI ZEFU, 2011. The study of affects of thermal effluent on pelagic ecosystem by mesocosm experiments in Xiang Shan Bay[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] |
丘耀文, 王肇鼎, 朱良生, 2005. 大亚湾海域营养盐与叶绿素含量的变化趋势及其对生态环境的影响[J]. 台湾海峡, 24(2): 131-139.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2005.02.001 |
|
QIU YAOWEN, WANG ZHAODING, ZHU LIANGSHENG, 2005. Variation trend of nutrient and chlorophyll contents and their effects on ecological environment in Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 24(2): 131-139 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2005.02.001 |
|
| [3] | 王娜, 2014. 南海及福建近岸水体中群落与细菌呼吸的研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学. |
| WANG NA, 2014. Community and bacterial respiration in the South China Sea and Fujian coastal waters[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] |
谢福武, 刘华雪, 黄洪辉, 等, 2018. 大亚湾浮游植物粒级结构对温排水和营养盐输入的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 37(3): 55-64.
doi: 10.11978/2017083 |
|
XIE FUWU, LIU HUAXUE, HUANG HONGHUI, et al, 2018. Effects of thermal discharge and nutrients input on size structure of phytoplankton in Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 37(3): 55-64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2017083 |
|
| [5] | 徐姗楠, 陈作志, 何培民, 2008. 杭州湾北岸大型围隔海域人工生态系统的能量流动和网络分析[J]. 生态学报, 28(5): 2065-2072. |
| XU SHANNAN, CHEN ZUOZHI, HE PEIMIN, 2008. Energy flux and network analysis for an artificial ecosystem of a large enclosed sea area in North Hangzhou Bay[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(5): 2065-2072 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 余立华, 2006. 秋季长江口不同辐照和氮、磷浓度水平下浮游植物营养盐吸收动力学及生长变化研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学. |
| YU LIHUA, 2006. Nutrient absorbing kinetics and growth changes of phytoplankton controlled by different irradiance, Nitrate and phosphate concentration levels on autumn in Yangtze River estuary[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | CHEN ZUOZHI, QIU YONGSONG, XU SHANNAN, 2011. Changes in trophic flows and ecosystem properties of the Beibu Gulf ecosystem before and after the collapse of fish stocks[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 54(8): 601-611. |
| [8] | CULLER L E, 2013. Temperature effects on consumer-resource species interactions: Integrating thermal physiology and community ecology[D]. Dartmouth: Dartmouth College. |
| [9] | DUCKLOW H W, MCCALLISTER S L, 2005. The biogeochemistry of carbon dioxide in the coastal oceans[M]//ROBINSON A R, BRINK K H. The Sea. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 13: 269-315. |
| [10] |
EL-SABAAWI R, HARRISON P J, 2006. Interactive effects of irradiance and temperature on the photosynthetic physiology of the pennate diatom Pseudo-nitzschia granii (bacillariophyceae) from the Northeast subarctic Pacific[J]. Journal of Phycology, 42(4): 778-785.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.2006.42.issue-4 |
| [11] |
FU MINGZHU, WANG ZONGLING, LI YAN, et al, 2016. Phytoplankton biomass size structure and its regulation in the Southern Yellow Sea (China): seasonal variability[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 29(18): 2178-2194.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.08.010 |
| [12] |
GARCÍA-MARTÍN E E, SERRET P, LEAKEY R J G, 2014. Plankton community and bacterial metabolism in Arctic sea ice leads during summer 2010[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 92: 152-161.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2014.06.007 |
| [13] |
JIANG ZHAOYU, WANG YOUSHAO, CHENG HAO, et al, 2015. Spatial variation of phytoplankton community structure in Daya Bay, China[J]. Ecotoxicology, 24(7-8): 1450-1458.
doi: 10.1007/s10646-015-1471-3 |
| [14] |
KIM Y H, AHN J K, YOON H D, et al, 2007. Effects of heated effluents on the intertidal macroalgal community near Gori Nuclear Power Plant[J]. Algae, 22(4): 297-304.
doi: 10.4490/ALGAE.2007.22.4.297 |
| [15] |
KIRKWOOD D S, AMINOT A, CARLBERG S R, 1996. The 1994 quasimeme laboratory performance study: nutrients in seawater and standard solutions[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 32(8-9): 640-645.
doi: 10.1016/0025-326x(96)00076-8 |
| [16] |
LEWANDOWSKA A M, BOYCE D G, HOFMANN M, et al, 2014. Effects of sea surface warming on marine plankton[J]. Ecology Letters, 17(5): 614-623.
doi: 10.1111/ele.12265 pmid: 24575918 |
| [17] |
LIU HUAXUE, SONG XINGYU, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2011. Diurnal variation of phytoplankton community in a high frequency area of HABs: Daya Bay, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 29(4): 800-806.
doi: 10.1007/s00343-011-0509-5 |
| [18] |
NGUYEN D, MARANGER R, TREMBLAY J É, et al, 2012. Respiration and bacterial carbon dynamics in the Amundsen Gulf, western Canadian Arctic[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C9): C00G16.
doi: 10.1029/2011JC007343 |
| [19] | PARSONS T R, MAITA Y, LALLI C M, 1984. A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis[M]. Oxford: Pergamon Press: 158-161. |
| [20] |
REGAUDIE‐DE‐GIOUX A, DUARTE C M, 2012. Temperature dependence of planktonic metabolism in the ocean[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 26(1): GB1015.
doi: 10.1029/2010GB003907 |
| [21] |
SONG XINGYU, HUANG LIANGMIN, ZHANG JIANLIN, et al, 2009. Harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Daya Bay, China: An in situ study of primary production and environmental impacts[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 58(9): 1310-1318.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2009.04.030 |
| [22] |
SONG XINGYU, LIU HUAXUE, ZHONG YU, et al, 2015. Bacterial growth efficiency in a partly eutrophicated bay of South China Sea: Implication for anthropogenic impacts and potential hypoxia events[J]. Ecotoxicology, 24(7-8): 1529-1539.
doi: 10.1007/s10646-015-1497-6 pmid: 26024618 |
| [23] |
TEIXEIRA T P, NEVES L M, ARAÚJO F G, 2012. Thermal impact of a nuclear power plant in a coastal area in Southeastern Brazil: effects of heating and physical structure on benthic cover and fish communities[J]. Hydrobiologia, 684(1): 161-175.
doi: 10.1007/s10750-011-0980-1 |
| [24] |
VAQUER-SUNYER R, DUARTE C M, 2013. Experimental evaluation of the response of coastal mediterranean planktonic and benthic metabolism to warming[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 36(4): 697-707.
doi: 10.1007/s12237-013-9595-2 |
| [25] | VAQUER-SUNYER R, CONLEY D J, MUTHUSAMY S, et al, 2015. Dissolved organic nitrogen inputs from wastewater treatment plant effluents increase responses of planktonic metabolic rates to warming[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 49(19): 11411-11420. |
| [26] |
VAQUER-SUNYER R, READER H E, MUTHUSAMY S, et al, 2016. Effects of wastewater treatment plant effluent inputs on planktonic metabolic rates and microbial community composition in the Baltic Sea[J]. Biogeosciences, 13(16): 4751-4765.
doi: 10.5194/bg-13-4751-2016 |
| [27] |
WOHLERS J, ENGEL A, ZÖLLNER E, et al, 2009. Changes in biogenic carbon flow in response to sea surface warming[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(17): 7067-7072.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812743106 pmid: 19359482 |
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | XI Chen, LIN Zongxuan, SA Rula, DENG Xi, LIU Qiang, NI Liang, LUO Laicai, MA Teng, XIE Zhijie, CHEN Siruo, CHEN Songze. Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [3] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [4] | HUANG Yuan, CEN Jingyi, LIANG Qianyan, LYU Songhui, WANG Jianyan. Study on the community structure of eukaryotic phytoplankton in the Shenzhen Bay based on high-throughput sequencing technology [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 21-33. |
| [5] | SUN Cuici, YUE Weizhong, ZHAO Wenjie, WANG Youshao. Distribution of the microbial Carbohydrate-Active enzymes genes in the surface sediment of the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lanlan, CHENG Xiawen, XIANG Rong, QIU Zhuoya, CHANG Hu. Changes of radiolarian community structure with depth in the central Bay of Bengal in spring 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [7] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [8] | LI Ruofei, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, LIU Jiaxin, TAN Yehui. Vertical distribution of zooplankton in the “Haima” cold seep region based on ZooScan image analysis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 87-96. |
| [9] | ZHAO Hongwuyi, ZHOU Wen, ZENG Kai, DENG Lin, LIAO Jianzu, CAO Wenxi. A study of the regional size-fractionated primary production algorithm based on phytoplankton absorption coefficient and photosynthetically active radiation in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 43-55. |
| [10] | JIANG Xun, WU Wen, SONG Dehai. Identification and quantitative analysis of key controlling factors of water quality response to human activities in the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 182-191. |
| [11] | CHEN Jingfu, ZHONG Yu, WANG Lei, GUO Yupei, QIU Dajun. Noctiluca scintillans effects on eukaryotic plankton community structure using Environmental DNA analysis in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [12] | ZHOU Wen, WEI Panpan, LI Cai, WANG Guifen, ZHENG Wendi, DENG Lin, ZHAO Hongwuyi, YU Linghui, CAO Wenxi. Particle backscattering as a function of chlorophyll a concentration off the eastern Hainan coast in the South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 29-37. |
| [13] | ZHANG Wanru, LIU Qingxia, HUANG Honghui, QIN Xiaoqing, LI Jiajun, CHEN Jianhua. Study on stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen of main fishery organisms in the southwestern waters of Daya Bay, South China Sea in winter 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [14] | YIN Tianqi, WANG Qing, YANG Yufeng, CEN Jingyi. Comparative study on zooplankton community structure in Pearl River Estuary based on morphological and DNA identification [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 172-185. |
| [15] | YIN Jianqiang, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui. Bathyconchoecia nanshaensis sp. nov. (Myodocopa, Halocyprididae), a new species of ostracod from the southern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 193-197. |
|
||