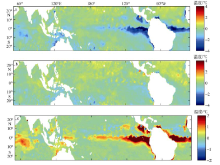
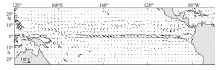
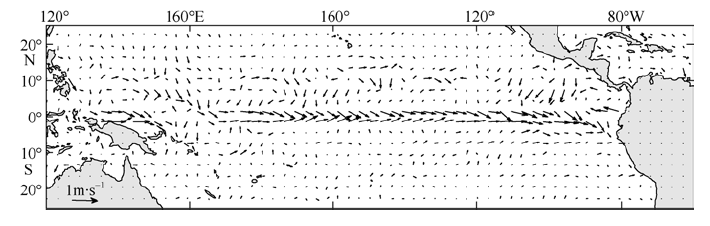
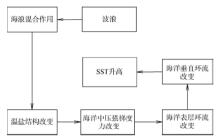
| [1] |
胡好国, 袁业立, 万振文, 2004. 海浪混合参数化的渤海、黄海、东海水动力环境数值模拟[J]. 海洋学报, 26(4): 19-32.
|
|
HU HAOGUO, YUAN YELI, WAN ZHENWEN, 2004. Study on hydrodynamic environment of the Bohai Sea, the Huanghai Sea and the East China Sea with wave-current coupled numerical model[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 26(4): 19-32 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [2] |
刘欣, 韦骏, 2014. 热带气旋与海洋暖涡间的海—气相互作用[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 50(3): 456-466.
|
|
LIU XIN, WEI JUN, 2014. Air-sea interaction between tropical cyclone and ocean warm core ring[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 50(3): 456-466 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [3] |
乔方利, 马建, 夏长水, 等, 2004. 波浪和潮流混合对黄海、东海夏季温度垂直结构的影响研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 14(12): 1434-1441.
|
| [4] |
宋振亚, 乔方利, 杨永增, 等, 2006. 波致混合对热带太平洋海气耦合模式中冷舌模拟的改进[J]. 自然科学进展, 16(9): 1138-1145.
|
| [5] |
宋振亚, 乔方利, 雷晓燕, 等, 2007. 大气-海浪-海洋环流耦合数值模式的建立及北太平洋SST模拟[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 22(5): 543-548.
|
|
SONG ZHENYA, QIAO FANGLI, LEI XIAOYAN, et al, 2007. The establishment of an atmosphere-wave-ocean circulation coupled numerical model and its application in the North Pacific SST simulation[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 22(5): 543-548 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [6] |
吴望一, 1983. 流体力学(下)[M]. 北京大学出版社, 1-493.
|
| [7] |
张洪生, 辜俊波, 王海龙, 等, 2013. 利用WAVEWATCH和SWAN嵌套计算珠江口附近海域的风浪场[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(1): 8-17.
|
|
ZHANG HONGSHENG, GU JUNBO, WANG HAILONG, et al, 2013. Simulating wind wave field near the Pearl River Estuary with SWAN nested in WAVEWATCH[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(1): 8-17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [8] |
周良明, 吴伦宇, 郭佩芳, 等, 2007. 应用WAVEWATCH-Ⅲ模式对南海的波浪场进行数值计算、统计分析和研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 26(5): 1-8.
|
|
ZHOU LIANGMING, WU LUNYU, GUO PEIFANG, et al, 2007. Simulation and study of wave in South China Sea using WAVEWATCH Ⅲ[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 26(5): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| [9] |
BLUMBERG A F, MELLOR G L, 1987. A description of a three-dimensional coastal ocean circulation model[C]// HEAPS N S. Three-Dimensional Coastal Ocean Models. Washington DC: American Geophysical Union: 1-16.
|
| [10] |
COVEY C, ACHUTARAO K M, CUBASCH U, et al, 2003. An overview of results from the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 37(1-2): 103-133.
|
| [11] |
DAVEY M, HUDDLESTON M, SPERBER K, et al, 2002. STOIC: A study of coupled model climatology and variability in tropical ocean regions[J]. Climate Dynamics, 18(5): 403-420.
|
| [12] |
JORDI A, WANG DONGPING, 2012. sbPOM: A parallel implementation of Princenton Ocean Model[J]. Environmental Modeling & Software, 38: 59-61.
|
| [13] |
MA C C, MECHOSO C R, ROBERTSON A W, et al, 1996. Peruvian stratus clouds and the tropical Pacific circulation: A coupled ocean-atmosphere GCM study[J]. Journal of Climate, 9(7): 1635-1645.
|
| [14] |
MECHOSO C R, ROBERTSON A W, BARTH N, et al, 1995. The seasonal cycle over the tropical Pacific in coupled ocean-atmosphere general circulation models[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 123(9): 2825-2838.
|
| [15] |
QIAO FANGLI, YUAN YELI, YANG YONGZENG, et al, 2004. Wave-induced mixing in the upper ocean: Distribution and application to a global ocean circulation model[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(11): L11303.
|
| [16] |
SONG ZHENYA, QIAO FANGLI, SONG YAJUAN, 2012. Response of the equatorial basin-wide SST to non-breaking surface wave-induced mixing in a climate model: An amendment to tropical bias[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C11): C00J26.
|
| [17] |
SONG XIAOLIANG, ZHANG GUANGJUN, 2009. Convection parameterization, tropical pacific double ITCZ, and upper-ocean biases in the NCAR CCSM3. Part I: Climatology and atmospheric feedback[J]. Journal of Climate, 22(16): 4299-4315.
|
| [18] |
TOLMAN H L, 1991. A third-generation model for wind waves on slowly varying, unsteady, and inhomogeneous depths and currents[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 21(6): 782-797.
|
| [19] |
UPPALA S M, KÅLLBERG P W, SIMMONS A J, et al, 2005. The ERA-40 re-analysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 131(612): 2961-3012.
|
| [20] |
WU LICHUAN, RUTGERSSON A, SAHLÉE E, 2015. Upper-ocean mixing due to surface gravity waves[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 120(12): 8210-8228.
|
| [21] |
WANG JIZHAO, ZHANG JIE, YANG JUNGANG, 2014. Numerical simulation and preliminary analysis on ocean waves during Typhoon Nesat in South China Sea and adjacent areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 32(3): 665-680.
|
| [22] |
ZHANG GUANGJUN, SONG XIAOLIANG, 2010. Convection parameterization, tropical Pacific double ITCZ, and upper-ocean biases in the NCAR CCSM3. Part II: Coupled feedback and the role of ocean heat transport[J]. Journal of Climate, 23(3): 800-812.
|
 ), Jian SHI(
), Jian SHI( ), Guorong JIANG, Lin XIAO
), Guorong JIANG, Lin XIAO