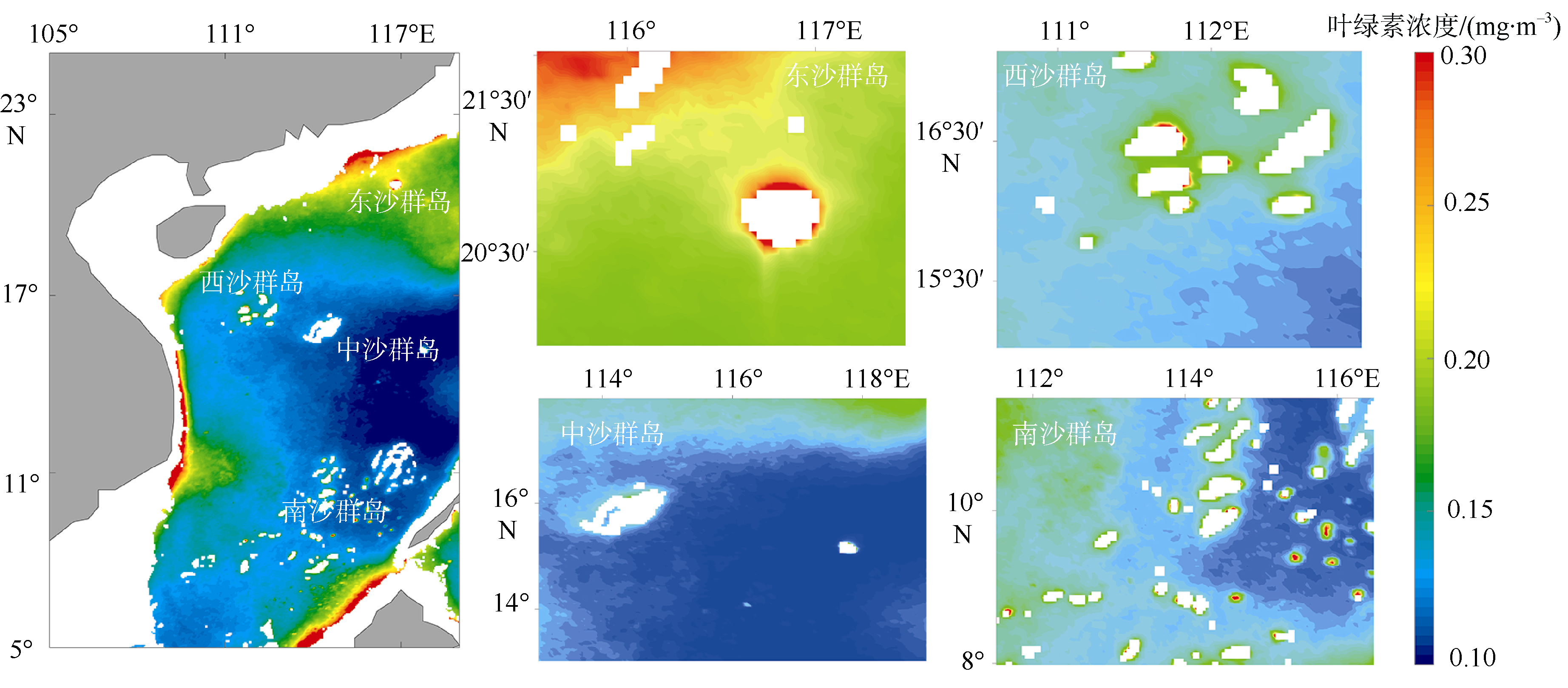
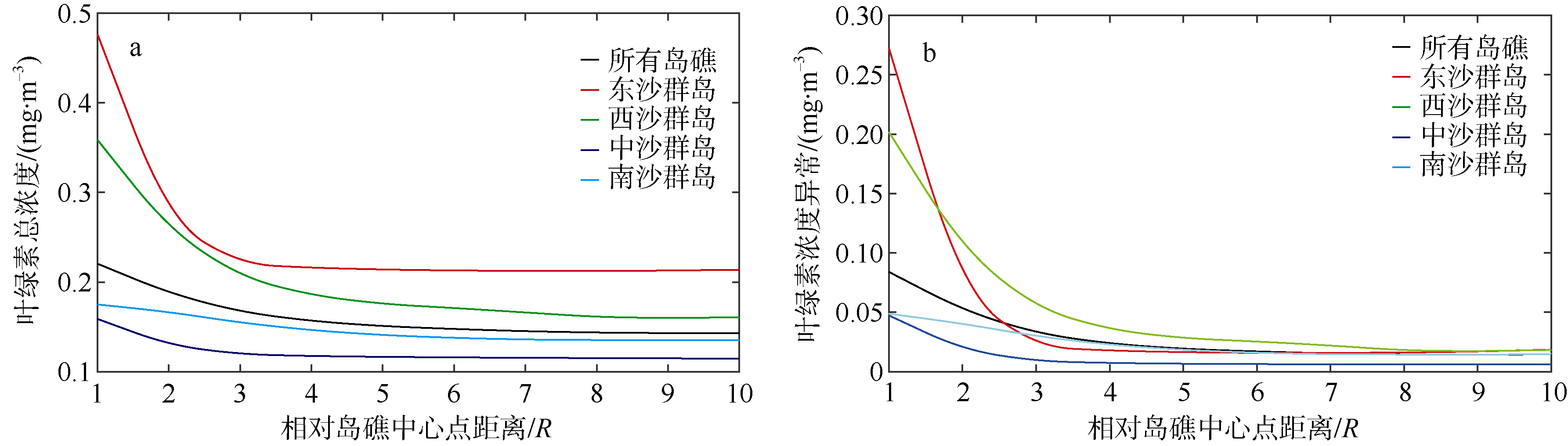
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 21-28.doi: 10.11978/2018135CSTR: 32234.14.2018135
Special Issue: 南海专题
• Marine Ecology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatial-temporal variation of sea surface chlorophyll around islands and reefs in the South China Sea
CHEN Wuyang, LI Junmin( ), HE Qingyou, TANG Shilin, SHI Ping
), HE Qingyou, TANG Shilin, SHI Ping
- State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2018-12-10Revised:2019-05-07Online:2019-11-20Published:2019-11-26 -
Contact:Junmin LI E-mail:jli@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA13030304);National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017YFC1405402);Key Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(KGZDEW60902);Innovation Group Program of State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology)(LTOZZ1701)
Cite this article
CHEN Wuyang, LI Junmin, HE Qingyou, TANG Shilin, SHI Ping. Spatial-temporal variation of sea surface chlorophyll around islands and reefs in the South China Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(6): 21-28.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
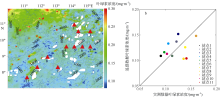
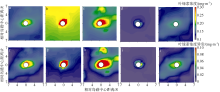
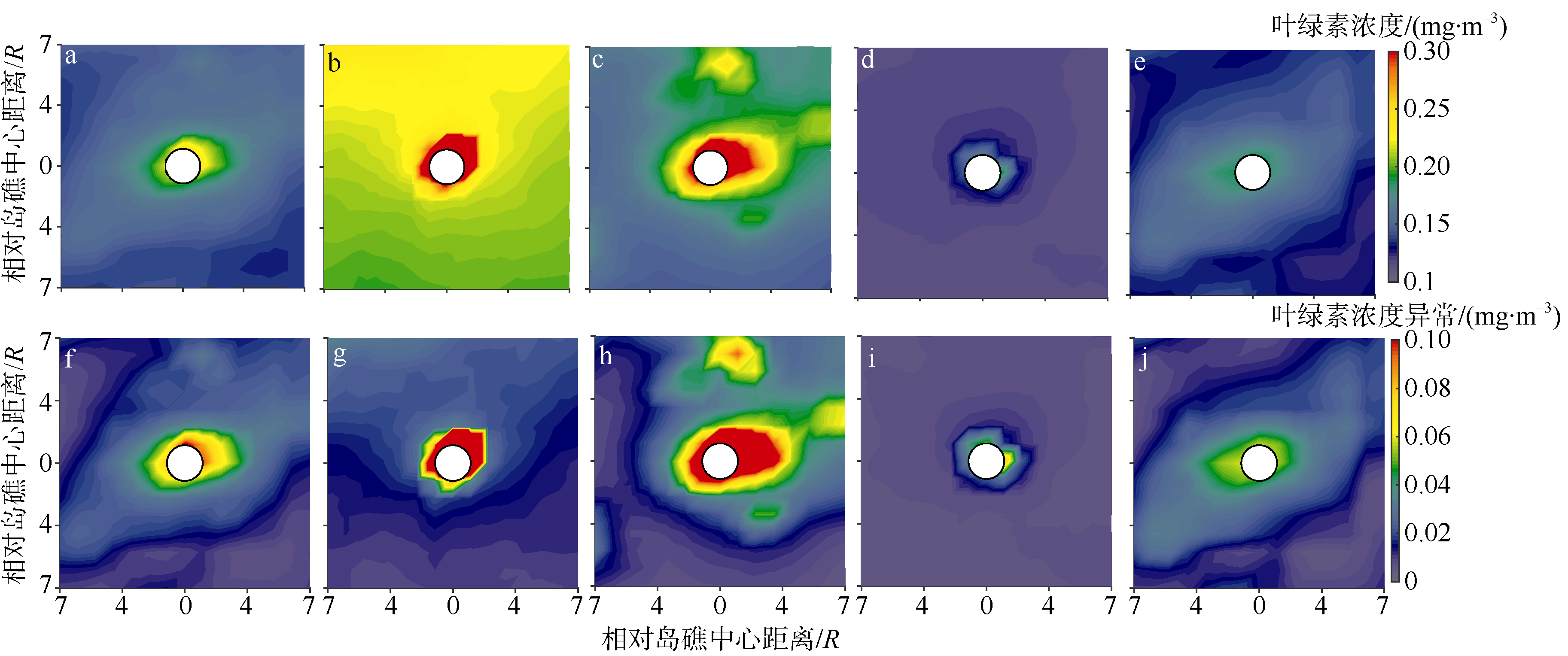
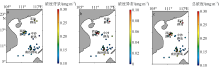
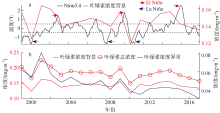
Fig. 2
Comparison between GlobColour and in-situ CHL data measured in Nansha region in December 2015. a) Spatial distributions of GlobColour CHL concentration (color), topography (contour) and cruise stations (triangle); b) in-situ data vs remote sensing data, with root mean squared error of 0.021 mg·m-3 and mean relative error of 16%"

Tab. 1
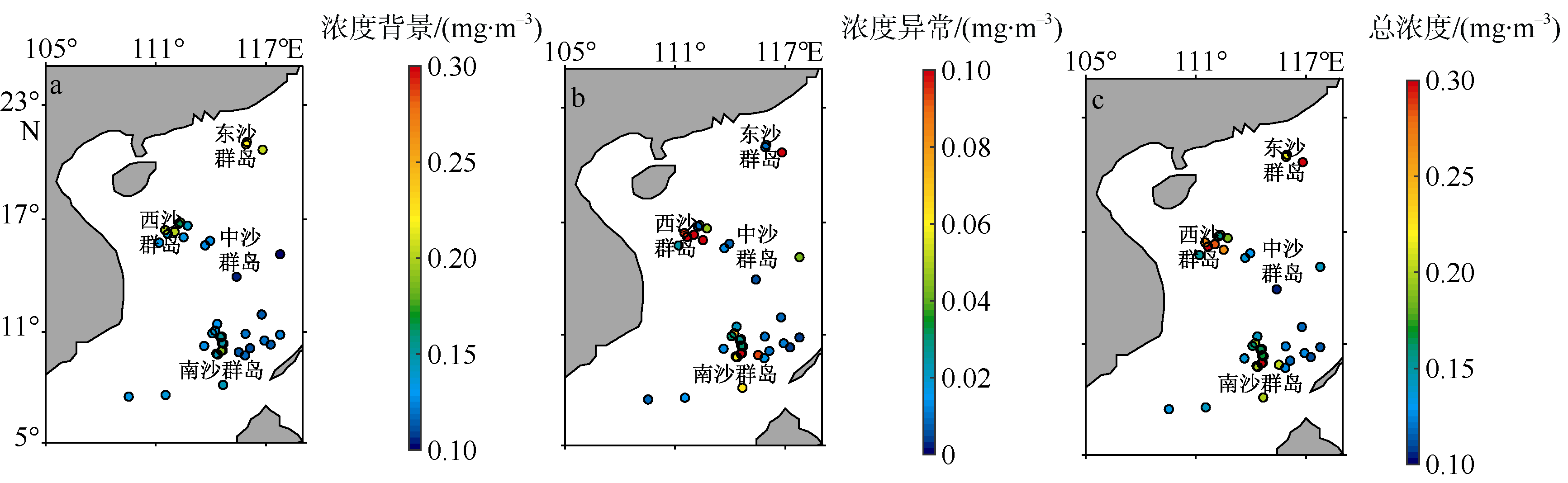
Islands and reefs analyzed in this paper"
| 海区 | 岛礁 | 经度 | 纬度 | R/km |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 东沙群岛 | 北卫滩 | 115°58′E | 21°04′N | 2.1 |
| 南卫滩 | 115°55′E | 20°58′N | 2.3 | |
| 东沙环礁 | 116°49′E | 20°40′N | 11.6 | |
| 西沙群岛 | 华光礁 | 111°40′E | 16°13′N | 12.9 |
| 中建岛 | 111°12′E | 15°46′N | 2.1 | |
| 永兴岛 | 112°20′E | 16°50′N | 2.3 | |
| 银砾滩 | 112°14′E | 16°46′N | 2.2 | |
| 玉琢礁 | 112°01′E | 16°20′N | 7.3 | |
| 浪花礁 | 112°31′E | 16°03′N | 8.2 | |
| 东岛 | 112°44′E | 16°40′N | 2.0 | |
| 金银岛 | 111°31′E | 16°27′N | 2.9 | |
| 中沙群岛 | 华夏暗沙 | 113°58′E | 15°52′N | 3.2 |
| 排洪滩 | 113°42′E | 15°37′N | 2.4 | |
| 中南暗沙 | 115°24′E | 13°57′N | 3.3 | |
| 黄岩岛 | 117°46′E | 15°09′N | 8.2 | |
| 南沙群岛 | 雄南礁 | 116°46′E | 11°55′N | 2.1 |
| 双子礁 | 114°21′E | 11°25′N | 5.9 | |
| 铁峙礁 | 114°14′E | 11°03′N | 5.4 | |
| 渚碧礁 | 114°05′E | 10°55′N | 2.8 | |
| 库归礁 | 114°35′E | 10°45′N | 4.3 | |
| 杨信沙洲 | 114°32′E | 10°42′N | 6.0 | |
| 舶兰礁 | 114°35′E | 10°24′N | 4.7 | |
| 安达礁 | 114°42′E | 10°21′N | 5.6 | |
| 牛轭礁 | 114°39′E | 09°59′N | 3.6 | |
| 主权礁 | 114°34′E | 09°58′N | 2.3 | |
| 华礁 | 114°18′E | 09°50′N | 4.2 | |
| 屈原礁 | 114°22′E | 09°47′N | 5.6 | |
| 和平暗沙 | 115°54′E | 10°53′N | 4.2 | |
| 海马滩 | 117°47′E | 10°50′N | 7.0 | |
| 东华礁 | 116°55′E | 10°32′N | 2.1 | |
| 莪兰暗沙 | 117°16′E | 10°19′N | 4.2 | |
| 半路礁 | 116°08′E | 10°07′N | 2.0 | |
| 美济礁 | 115°32′E | 09°54′N | 4.6 | |
| 仁爱礁 | 115°52′E | 09°44′N | 3.3 | |
| 浪口礁 | 114°40′E | 08°07′N | 16.1 | |
| 金盾暗沙 | 111°32′E | 07°35′N | 4.3 | |
| 福禄寺礁 | 113°38′E | 10°14′N | 2.2 | |
| 万安滩 | 109°31′E | 07°30′N | 5.3 |
| 1 | 陈楚群, 施平, 毛庆文 , 2001. 南海海域叶绿素浓度分布特征的卫星遥感分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 20(2):66-70. |
| CHEN CHUQUN, SHI PING, MAO QINGWEN , 2001. Satellite remotely-sensed analysis of distribution characters of chlorophyll concentration in South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 20(2):66-70 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 2 |
高永利, 黄晖, 练健生 , 等, 2014. 西沙群岛礁栖鱼类物种多样性及其食性特征[J]. 生物多样性, 22(5):618-623.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.14102 |
|
GAO YONGLI, HUANG HUI, LIAN JIANSHENG , et al, 2014. The species diversity and trophic structure of reef fishes in the waters of the Xisha Archipelago[J]. Biodiversity Science, 22(5):618-623 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.14102 |
|
| 3 | 古园园, 王静, 储小青 , 等, 2017. 夏季南海西部叶绿素浓度高值带的年际变化[J]. 海洋学报, 39(6):1-9. |
| GU YUANYUAN, WANG JING, CHU XIAOQING , et al, 2017. Interannual variability of the high chlorophyll a concentration strip in the western South China Sea during summer[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 39(6):1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
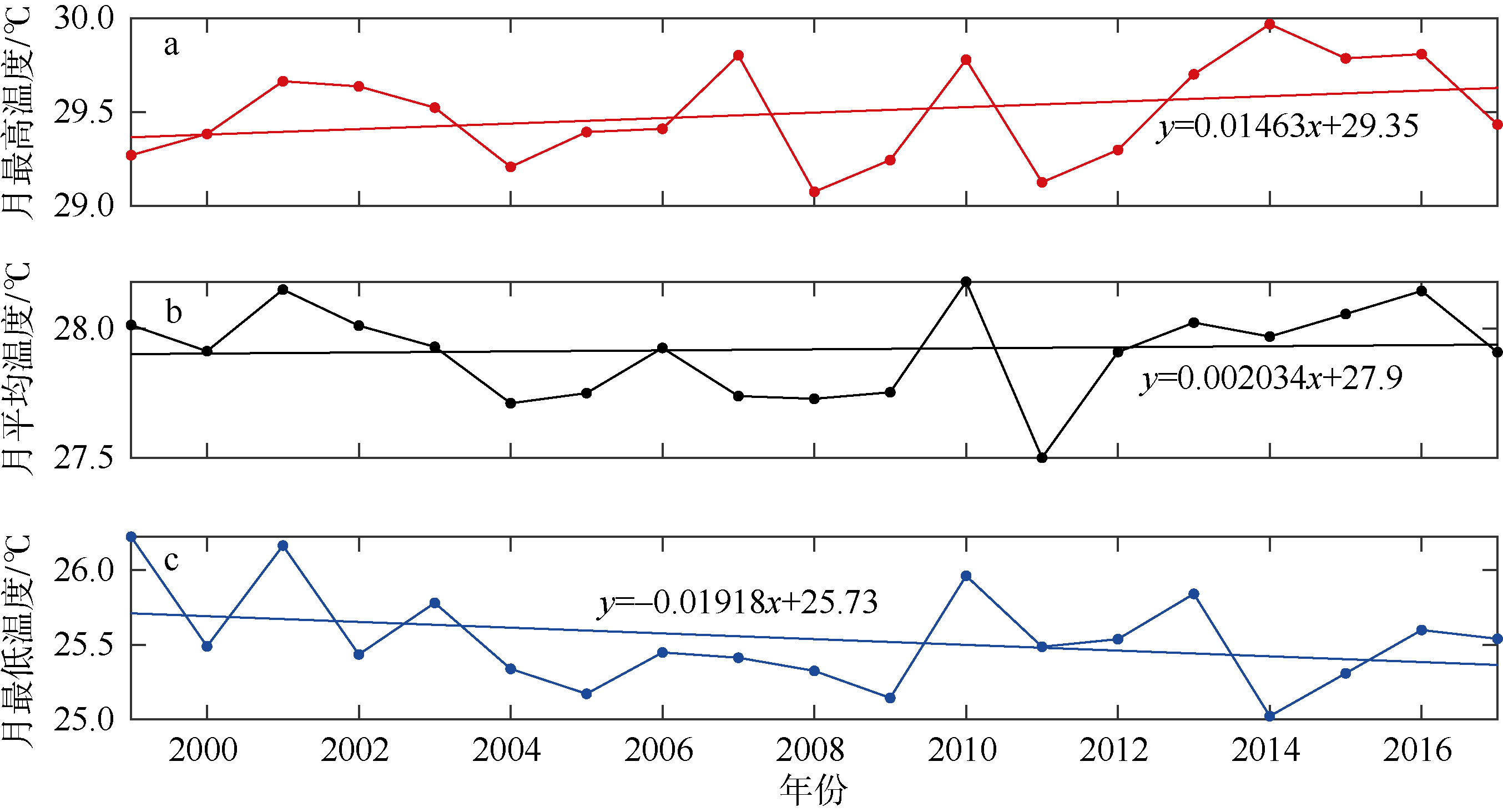
| 4 | 贾丹丹, 陈正华, 张威 , 等, 2018. 南海珊瑚礁区34年卫星遥感海表温度变化的时空特征分析[J]. 海洋学报, 40(3):112-120. |
| JIA DANDAN, CHEN ZHENGHUA, ZHANG WEI , et al, 2018. Analysis of temporal and spatial characteristics of sea surface temperature variabilities over the past 34 years in coral reef areas of the South China Sea[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 40(3):112-120 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 5 | 李永振, 史赟荣, 艾红 , 等, 2011. 南海珊瑚礁海域鱼类分类多样性大尺度分布格局[J]. 中国水产科学, 18(3):619-628. |
| LI YONGZHEN, SHI YUNRONG, AI HONG , et al, 2011. Large scale distribution patterns of taxonomic diversity of fish in coral reef waters, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 18(3):619-628 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 6 |
刘昕, 王静, 程旭华 , 等, 2012. 南海叶绿素浓度的时空变化特征分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 31(4):42-48.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.04.006 |
|
LIU XIN, WANG JING, CHENG XUHUA , et al, 2012. The temporal and spatial evolution of chlorophyll-a concentration in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 31(4):42-48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.04.006 |
|
| 7 | 聂宝符, 陈特固, 梁美桃 , 等, 1997. 南沙群岛及其邻近礁区造礁珊瑚与环境变化的关系[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 5-28. |
| NIE BAOFU, CHEN TEGU, LIANG MEITAO , et al, 1997. The relationship between reef coral and environmental changes of Nansha Islands and adjacent regions[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 5-28(in Chinese). | |
| 8 |
王雪辉, 杜飞雁, 林昭进 , 等, 2011. 西沙群岛主要岛礁鱼类物种多样性及其群落格局[J]. 生物多样性, 19(4):463-469.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07267 |
|
WANG XUEHUI, DU FEIYAN, LIN ZHAOJIN , et al, 2011. Fish species diversity and community pattern in coral reefs of the Xisha Islands, South China Sea[J]. Biodiversity Science, 19(4):463-469 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2011.07267 |
|
| 9 | 谢石建, 朱首贤, 马疆 , 等, 2015. 基于NAO.99b资料对南海主要岛礁潮汐特征的分析[J]. 解放军理工大学学报(自然科学版), 16(6):593-599. |
| XIE SHIJIAN, ZHU SHOUXIAN, MA JIANG , et al, 2015. Tidal characteristics analysis of main islands, reefs and shoals in South China Sea by NAO.99b data[J]. Journal of PLA University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 16(6):593-599 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 10 | 余克服, 蒋明星, 程志强 , 等, 2004. 涠洲岛42年来海面温度变化及其对珊瑚礁的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 15(3):506-510. |
| YU KEFU, JIANG MINGXING, CHENG ZHIQIANG , et al, 2004. Latest forty two years’ sea surface temperature change of Weizhou Island and its influence on coral reef ecosystem[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 15(3):506-510 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 11 | 赵辉, 唐丹玲, 王素芬 , 2005. 南海西北部夏季叶绿素a浓度的分布特征及其对海洋环境的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 24(6):31-37. |
| ZHAO HUI, TANG DANLING, WANG SUFEN , 2005. Spatial distribution of chlorophyll a concentration in summer in western South China Sea and its response to oceanographic environmental factors[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 24(6):31-37 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| 12 |
ANDRADE I, SANGRÀ P, HORMAZABAL S , et al, 2014. Island mass effect in the Juan Fernández Archipelago (33°S), Southeastern Pacific[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 84:86-99.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2013.10.009 |
| 13 |
DOTY M S, OGURI M , 1956. The island mass effect[J]. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 22(1):33-37.
doi: 10.1093/icesjms/22.1.33 |
| 14 |
HASEGAWA D, LEWIS M R, GANGOPADHYAY A , 2009. How islands cause phytoplankton to bloom in their wakes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 36(20):L20605.
doi: 10.1029/2009GL039743 |
| 15 |
LEE CHEN Y-L , 2005. Spatial and seasonal variations of nitrate-based new production and primary production in the South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 52(2):319-340.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr.2004.11.001 |
| 16 |
MARITORENA S, D’ANDON O H F, MANGIN A , et al, 2010. Merged satellite ocean color data products using a bio-optical model: characteristics, benefits and issues[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 114(8):1791-1804.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.04.002 |
| 17 | ROUND F E , 1981. The ecology of algae[M]. London: Cambridge University Press. |
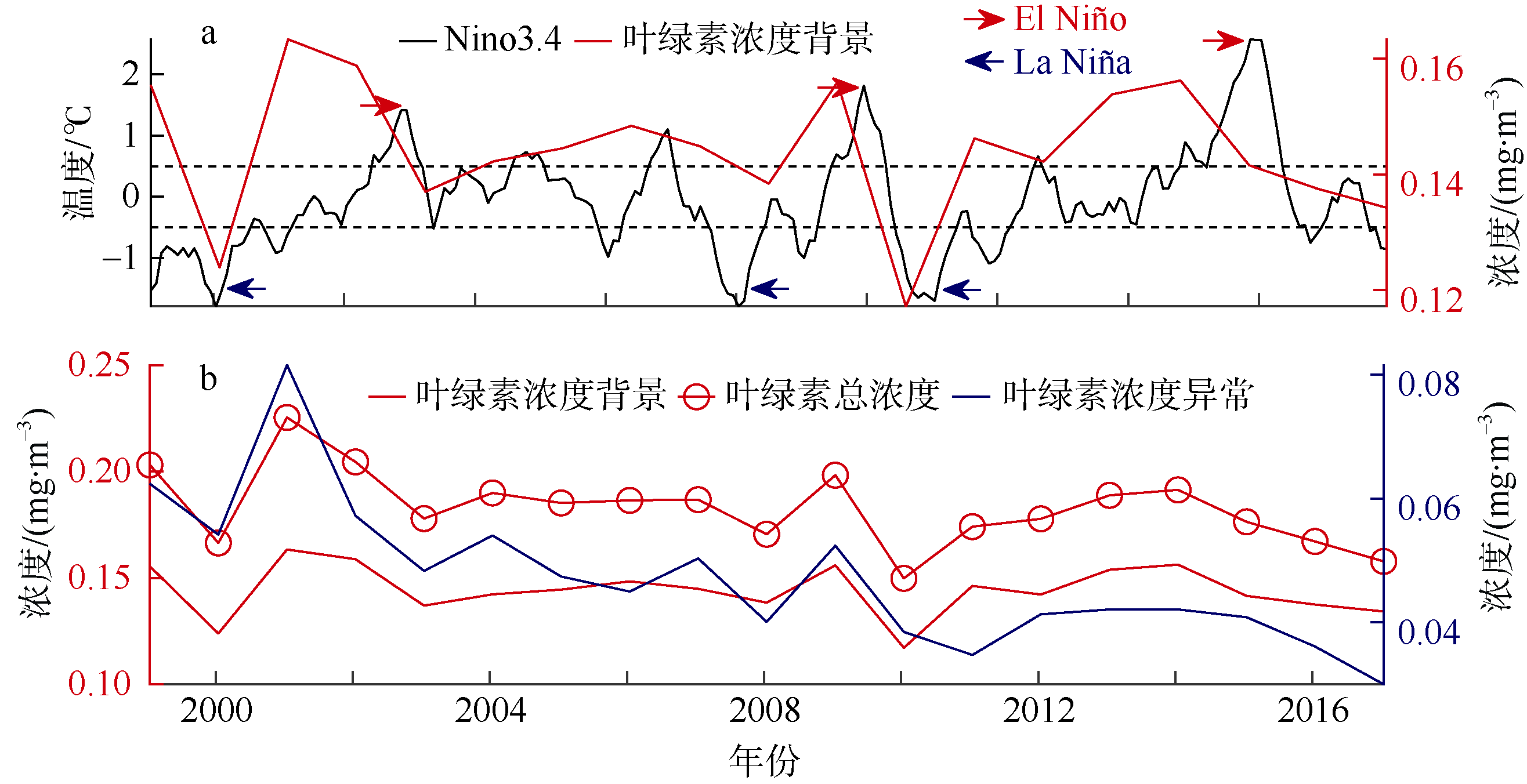
| 18 | WANG CHUNZAI, WANG WEIQIANG, WANG DONGXIAO , et al, 2006. Interannual variability of the South China Sea associated with El Niño[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 111(C3):C03023. |
| 19 | ZHAO HUI, TANG DANLING , 2007. Effect of 1998 El Niño on the distribution of phytoplankton in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 112(C2):C02017. |
|
||