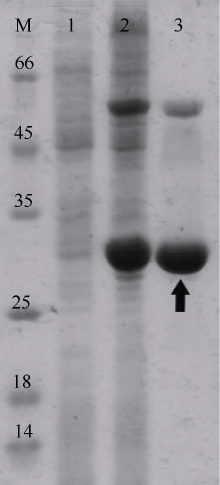
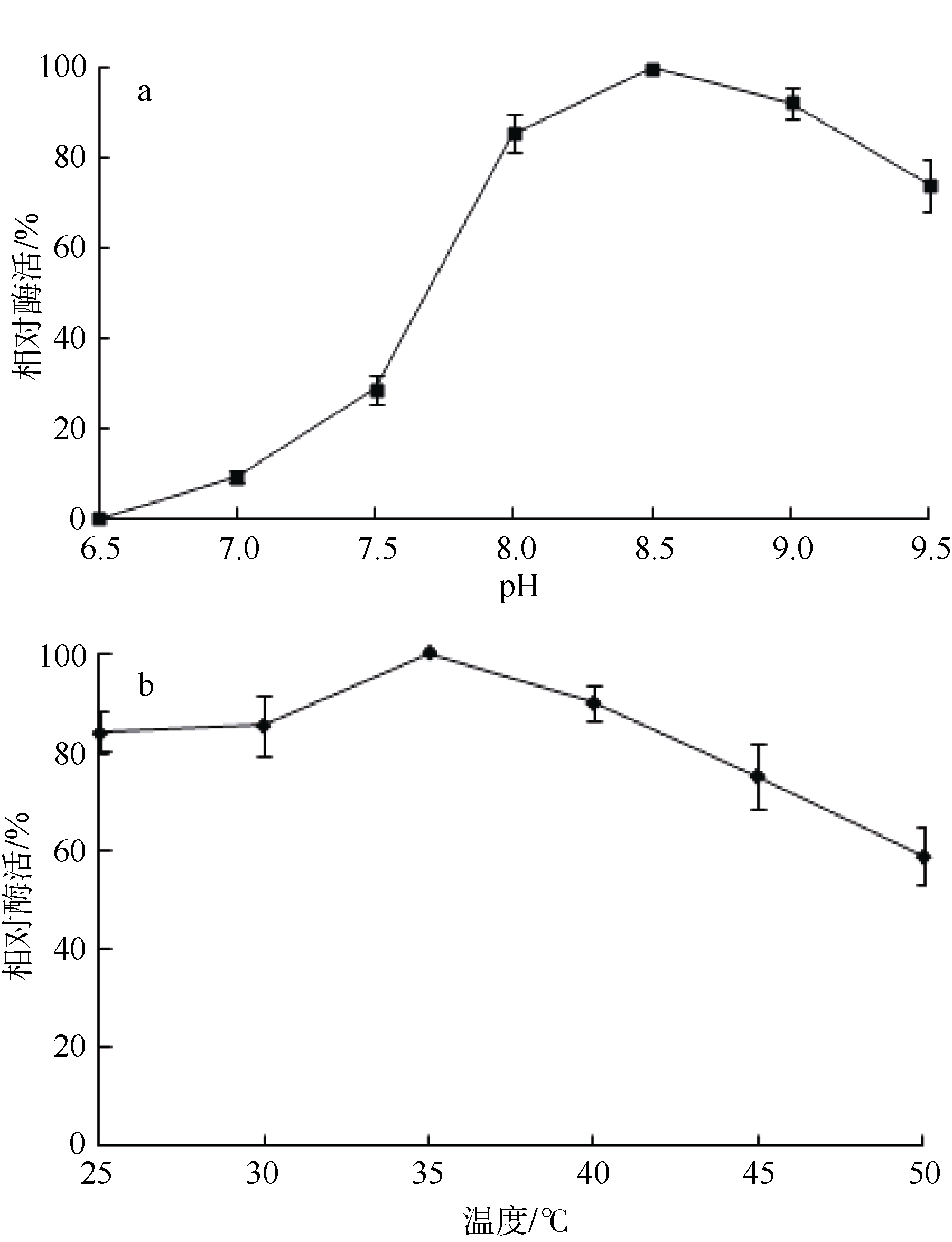
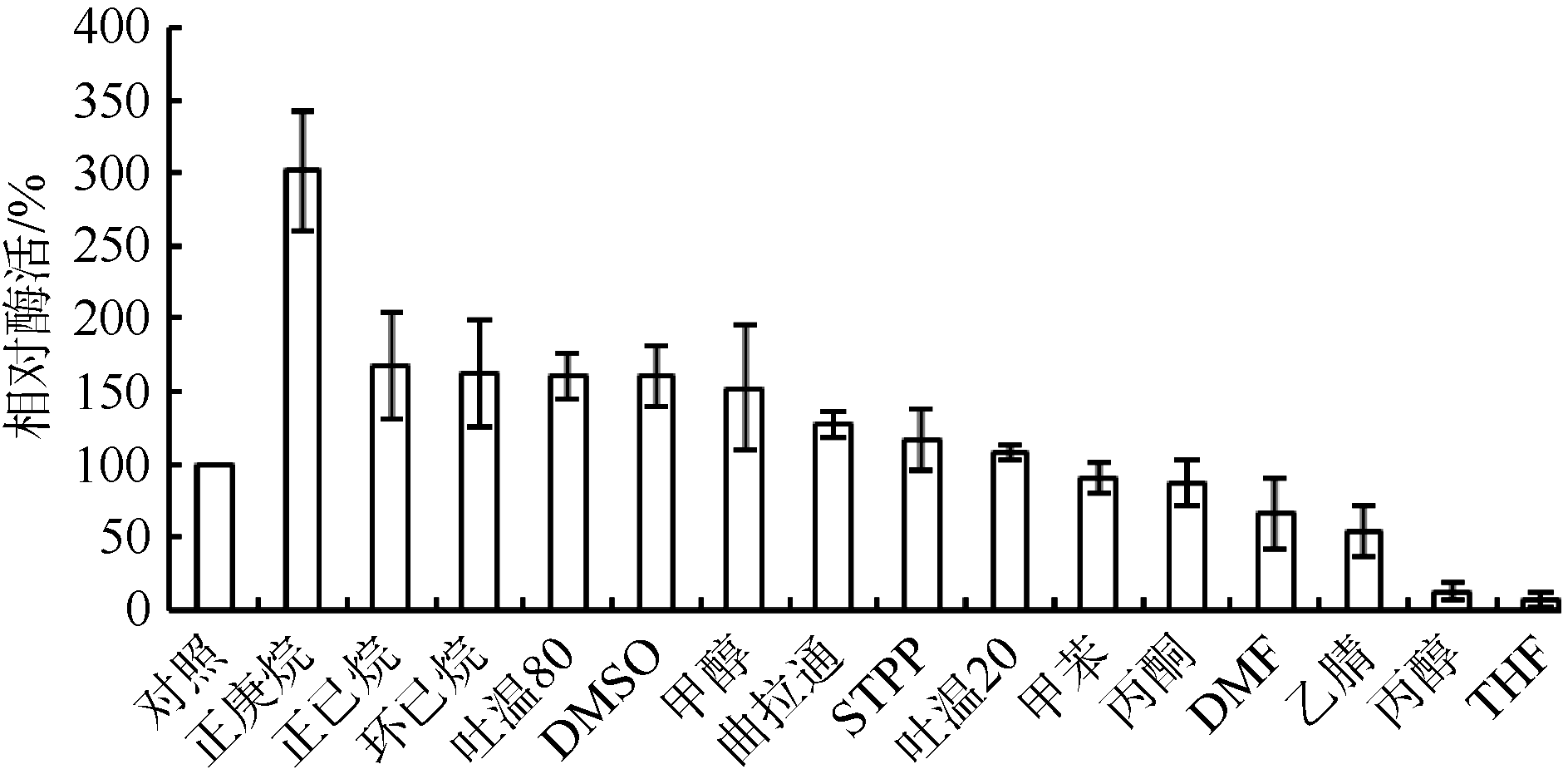
| 1 |
周明芳, 2014. (R)-2-[4-(6-氯-2-苯并噁唑氧基)苯氧基丙酸的合成工艺研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学.
|
|
ZHOU MINGFANG, 2014. Study on synthesis of (R)-2-[4-(6-Chlor-2- benzoxazolyloxy)-phenoxy]-propionic acid[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science & Technology (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 2 |
AQAR D Y, RAHMANIAN N, MUJTABA I M, 2016. Methyl lactate synthesis using batch reactive distillation: Operational challenges and strategy for enhanced performance[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 158: 193-203.
|
| 3 |
CHANG P C, TSAI W S, TSAI C L, et al, 2004. Cloning and characterization of two thermostable xylanases from an alkaliphilic Bacillus firmus[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 319(3): 1017-1025.
|
| 4 |
CHEN C S, FUJIMOTO Y, GIRDAUKAS G, et al, 1982. Quantitative analyses of biochemical kinetic resolutions of enantiomers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 104(25): 7294-7299.
|
| 5 |
FAULDS C B, PÉREZ-BOADA M, MARTÍNEZ Á T, 2011. Influence of organic co-solvents on the activity and substrate specificity of feruloyl esterases[J]. Bioresource Technology, 102(8): 4962-4967.
|
| 6 |
HUANG JINLONG, ZHANG YUN, HU YUNFENG, 2016. Functional characterization of a marine Bacillus esterase and its utilization in the stereo-selective production of D-methyl lactate[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(8): 1467-1481.
|
| 7 |
HUY N C, THIYAGARAJAN S, KIM D H, et al, 2013. Cloning and characterization of a novel bifunctional acetyl xylan esterase with carbohydrate binding module from Phanerochaete chrysosporium[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 115(5): 507-513.
|
| 8 |
KWON M, SONG J, PARK H S, et al, 2016. Characterization of heterologously expressed acetyl xylan esterase1 isolated from the anaerobic rumen fungus Neocallimastix frontalis PMA02[J]. Asian-Australas Journal of Animal Sciences, 29(11): 1576-1584.
|
| 9 |
MILLAR R, RAHMANPOUR R, YUAN E W J, et al, 2016. Esterase EstK from Pseudomonas putida mt-2: An enantioselective acetylesterase with activity for deacetylation of xylan and poly (vinylacetate)[J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 64(6): 803-809.
|
| 10 |
MØLGAARD A, KAUPPINEN S, LARSEN S, 2000. Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase elucidates the structure and function of a new family of hydrolases[J]. Structure, 8(4): 373-383.
|
| 11 |
NAVARRO-FERNÁNDEZ J, MARTÍNEZ-MARTÍNEZ I, MONTORO-GARCÍA S, et al, 2008. Characterization of a new rhamnogalacturonan acetyl esterase from Bacillus halodurans C-125 with a new putative carbohydrate binding domain[J]. Journal of Bacteriology, 190(4): 1375-1382.
|
| 12 |
REDDY C R, LATHA B, WARUDIKAR K, et al, 2016. Total synthesis of a piperidine alkaloid, microcosamine A[J]. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry, 14(1): 251-258.
|
| 13 |
REMOROZA C, WAGENKNECHT M, GU F, et al, 2014. A Bacillus licheniformis pectin acetylesterase is specific for homogalacturonans acetylated at O-3[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 107: 85-93.
|
| 14 |
RICHARD G, NOTT K, NICKS F, et al, 2013. Use of lipases for the kinetic resolution of lactic acid esters in heptane or in a solvent free system[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 97: 289-296.
|
| 15 |
TIAN QIANQIAN, SONG PING, JIANG LING, et al, 2014. A novel cephalosporin deacetylating acetyl xylan esterase from Bacillus subtilis with high activity toward cephalosporin C and 7-aminocephalosporanic acid[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98(5): 2081-2089.
|
| 16 |
TONG XIAOXUE, LANGE L, GRELL M N, et al, 2015. Hydrolysis of wheat arabinoxylan by two acetyl xylan esterases from Chaetomium thermophilum[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 175(2): 1139-1152.
|
| 17 |
WANG YILONG, ZHANG YUN, HU YUNFENG, 2016. Functional characterization of a robust marine microbial esterase and its utilization in the stereo-selective preparation of ethyl (S)-3-hydroxybutyrate[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 180(6): 1196-1212.
|
| 18 |
YAMANE H, SASAI K, 2003. Effect of the addition of poly (D-lactic acid) on the thermal property of poly (L-lactic acid)[J]. Polymer, 44(8): 2569-2575.
|
| 19 |
ZHOU WEI, LIU XIAOHUI, YE LI, et al, 2014. The biotransformation of astragalosides by a novel acetyl esterase from Absidia corymbifera AS2[J]. Process Biochemistry, 49(9): 1464-1471.
|
 ), Jifu ZHANG2(
), Jifu ZHANG2( ), Jieying HU4, Jianliu GUAN4, Yun ZHANG1,3, Aijun SUN1,3, Yunfeng HU1,3(
), Jieying HU4, Jianliu GUAN4, Yun ZHANG1,3, Aijun SUN1,3, Yunfeng HU1,3( )
)