Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 62-70.doi: 10.11978/2020007CSTR: 32234.14.2020007
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Growth characteristics of four representative fishes and their responses to seagrass resource changes in typical tropical seagrass beds of Hainan Island
CHEN Qiming1,2,3,4( ), LIU Songlin1,2,4, ZHANG Chi5, CUI Lijun1,2,3,4, JIANG Zhijian1,2,4, WU Yunchao1,2,4, HUANG Xiaoping1,2,3,4(
), LIU Songlin1,2,4, ZHANG Chi5, CUI Lijun1,2,3,4, JIANG Zhijian1,2,4, WU Yunchao1,2,4, HUANG Xiaoping1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
5. College of Fisheries, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, China
-
Received:2020-01-12Revised:2020-03-09Online:2020-09-10Published:2020-03-19 -
Contact:Xiaoping HUANG E-mail:qmcxtzgg@163.com;xphuang@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41730529);National Natural Science Foundation of China(41806147);Key Special Project for Introduced Talents Team of Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou)(GML2019ZD0405);Guangzhou Science and Technology Program(201904010370);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018PY01);Innovation Academy of South China Sea Ecology and Environmental Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences(ISEE2018ZD02)
CLC Number:
- P735.121
Cite this article
CHEN Qiming, LIU Songlin, ZHANG Chi, CUI Lijun, JIANG Zhijian, WU Yunchao, HUANG Xiaoping. Growth characteristics of four representative fishes and their responses to seagrass resource changes in typical tropical seagrass beds of Hainan Island[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 62-70.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 2
Biological traits of Ehanlus acoroides in the three seagrass meadows of Tanmen Port, Xincun Bay and Li’an Port (x ± MSE, n = 6~10)"
| 海菖蒲海草生物学指标 | 潭门港 | 新村湾 | 黎安港 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 覆盖率/% | 24.60±2.75a | 47.60±3.04b | 61.20±6.97c |
| 茎枝密度/(株·m-2) | 147.20±5.99a | 214.40±13.00b | 256.00±25.30b |
| 海草根生物量/(g·m-2) | 192.26±81.12a | 222.59±28.74a | 539.19±227.24a |
| 海草茎生物量/(g·m-2) | 300.88±71.70a | 1300.85±182.35a | 2713.96±628.86b |
| 海草叶片生物量/(g·m-2) | 247.43±88.49a | 513.73±108.44a | 1121.80±127.07b |
Tab. 3
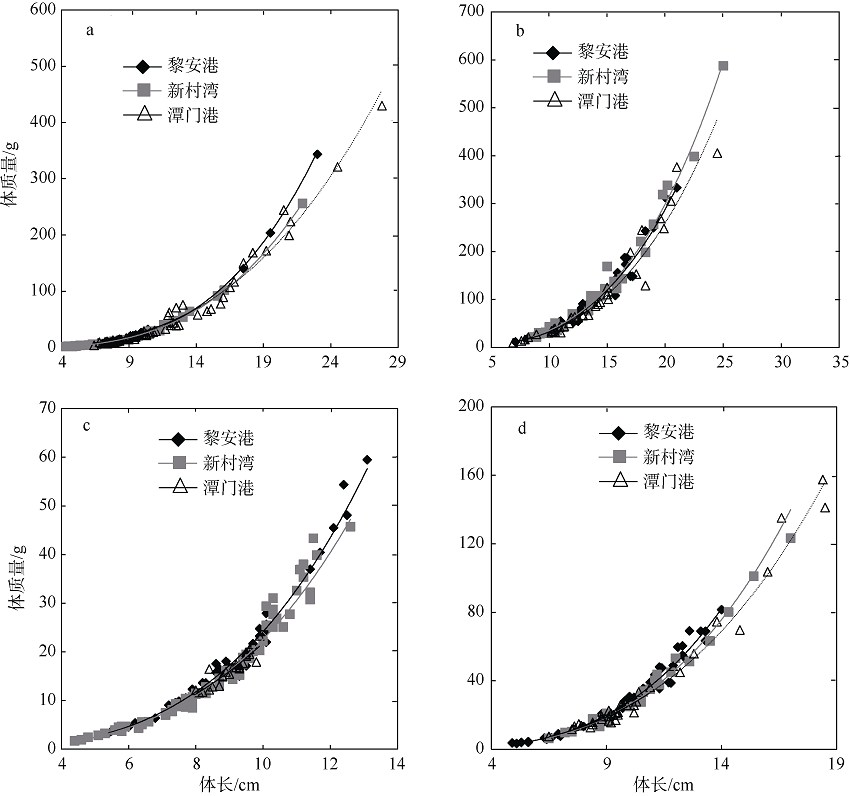
Parameters of body length-mass relationship for S. fuscessens, S. guttatus, P. quadrilineatus and T. jarbua in the seagrass meadows of Li’an Port, Xincun Bay and Tanmen Port"
| 鱼种 | 采样地点 | 样本量 | 长度范围/cm | a | b | r2 | t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 褐篮子鱼 | 黎安港 | 33 | 6.7~23.0 | 0.01 | 3.23 | 0.99 | 2.94** |
| 新村湾 | 33 | 4.3~21.9 | 0.02 | 3.03 | 0.99 | 1.73ns | |
| 潭门港 | 75 | 6.4~27.8 | 0.04 | 2.76 | 0.98 | 5.07** | |
| 点斑篮子鱼 | 黎安港 | 31 | 7.1~21.0 | 0.03 | 3.05 | 0.97 | 3.78** |
| 新村湾 | 30 | 8.6~25.0 | 0.04 | 3.08 | 0.99 | 10.31** | |
| 潭门港 | 40 | 6.9~24.5 | 0.06 | 2.81 | 0.96 | 5.86** | |
| 四带牙鯻 | 黎安港 | 40 | 5.4~13.1 | 0.01 | 3.32 | 0.99 | 8.59** |
| 新村湾 | 77 | 4.4~12.6 | 0.01 | 3.20 | 0.99 | 10.33** | |
| 潭门港 | 26 | 8.4~9.8 | 0.01 | 2.95 | 0.95 | 6.52** | |
| 细鳞鯻 | 黎安港 | 47 | 4.9~14.0 | 0.02 | 3.17 | 0.97 | 8.57** |
| 新村湾 | 25 | 6.5~15.4 | 0.02 | 3.05 | 0.98 | 4.81** | |
| 潭门港 | 31 | 6.5~16.0 | 0.03 | 2.91 | 0.97 | 4.61** |
Tab. 4
Comparison of allometric factors of S. fuscessens, S. guttatus, P. quadrilineatus, and T. jarbua among the seagrass meadows of Li’an Port, Xincun Bay and Tanmen Port"
| 对比区域 | 褐篮子鱼 | 点斑篮子鱼 | 四带牙鯻 | 细鳞鯻 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黎安港vs新村湾 | 0.95ns | 1.09ns | 0.13ns | 0.22ns |
| 黎安港vs潭门港 | 4.28* | 4.00* | 4.19* | 9.14** |
| 新村湾vs潭门港 | 3.37ns | 8.88** | 0.71ns | 3.25ns |
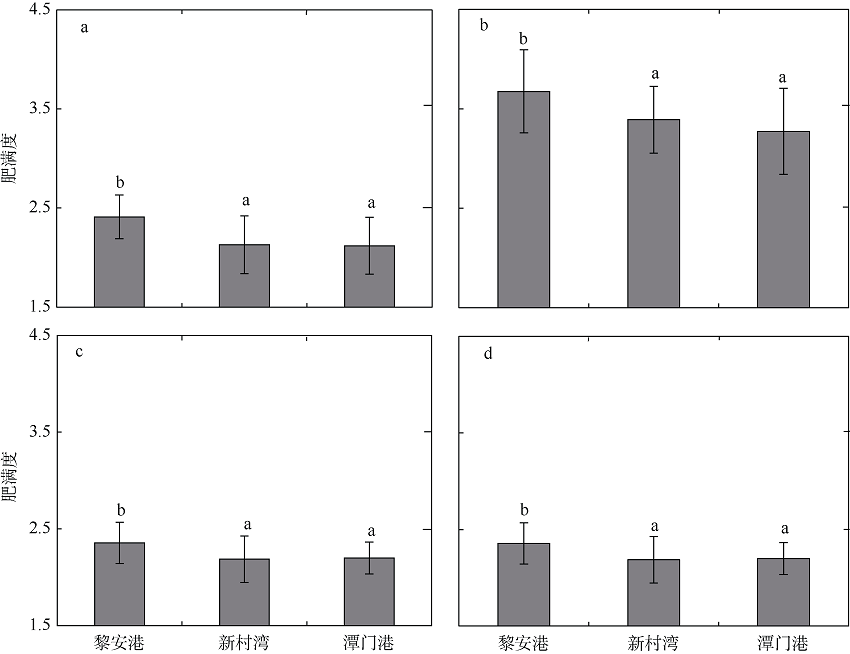
Fig. 2
Variation in relative fatness of S. fuscessens (a), S. guttatus (b), P. quadrilineatus (c), and T. jarbua (d) in the seagrass meadows of Li’an Port, Xincun Bay and Tanmen Port. Different capital letters over the bars indicate significant difference among different seagrass meadows (S-N-K test, p < 0.05)"
Tab. 5
Comparison of allometric factors of S. fuscessens, S. guttatus, P. quadrilineatus, and T. jarbua in global coastal areas"
| 研究区域 | 褐篮子鱼 | 点斑篮子鱼 | 四带牙鯻 | 细鳞鯻 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 菲律宾, 巴拉望岛 | 2.51 | ||||
| 菲律宾, 普哈达湾 | 3.01 | ||||
| 新喀里多尼亚 | 3.01 | ||||
| 菲律宾, 达沃湾 | 3.01 | 2.89 | |||
| 菲律宾, 本田湾 | 2.95 | ||||
| 日本, 冲绳海域 | 3.00 | Database of | |||
| 土耳其, 地中海 | 2.96 | ||||
| 泰国, 罗勇府 | 2.88 | ||||
| 南非, 河口 | 2.94 | ||||
| 也门, 亚丁湾 | 2.99 | ||||
| 中国北部湾 | 2.76 | ||||
| 中国湛江沿海 | 2.88 | ||||
| 中国香港西、南及东部水域 | 3.11 | ||||
| 中国海南岛海域 | 3.02 | 3.02 | 3.14 | 3.04 | 本研究 |
| [1] | 樊敏玲, 黄小平, 张大文, 等, 2011. 海南新村湾海草床主要鱼类及大型无脊椎动物的食源[J]. 生态学报, 31(1):31-38. |
| FAN MINLING, HUANG XIAOPING, ZHANG DAWEN, et al, 2011. Food sources of fish and macro-invertebrates in a tropical seagrass bed at Xincun Bay, Southern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(1):31-38 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 黄晓璇, 2010. 青岛近海方氏云鳚(Enedrias fangi Wang et Wang)渔业生物学初步研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学: 9-10. |
| HUANG XIAOXUAN, 2010. Study on the fishery biology of Enedrias fangi Wang et Wang in the inshore waters of Qingdao[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China: 9-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 李忠炉, 2011. 黄渤海小黄鱼、大头鳕和黄鮟鱇种群生物学特征的年际变化[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所):11-19. |
| LI ZHONGLU, 2011. Interannual changes in biological characteristics of small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis, Pacific Cod Gadus microcephalus and Anglerfish Lophius litulon in the Bohai Sea and Yellow sea[D]. Beijing: The Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences: 11-19 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 刘松林, 江志坚, 吴云超, 等, 2015. 海草床育幼功能及其机理[J]. 生态学报, 35(24):7931-7940. |
| LIU SONGLIN, JIANG ZHIJIAN, WU YUNCHAO, et al, 2015. Nursery function of seagrass beds and its mechanisms[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(24):7931-7940 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 罗秉征, 1966. 浙江近海大黄鱼的季节生长[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 8(2):121-139. |
| LUO BINGZHENG, 1966. Seasonal growth of the large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea (Rich.) off Chekiang[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 8(2):121-139. | |
| [6] | 张健东, 宋蓓玲, 陈刚, 2002. 细鳞鯻年龄与生长的研究[J]. 海洋科学, 26(7):63-67. |
| ZHANG JIANDONG, SONG BEILING, CHEN GANG, 2002. Study on the age and growth of Therapon jarbua[J]. Marine Sciences, 26(7):63-67 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | BLACKWELL B G, BROWN M L, WILLIS D W, 2000. Relative weight (Wr) status and current use in fisheries assessment and management[J]. Reviews in Fisheries Science, 8(1):1-44. |
| [8] | BOLOGNA P A X, HECK K L, 2000. Impacts of seagrass habitat architecture on bivalve settlement[J]. Estuaries, 23(4):449-457. |
| [9] | CADIER C, FROUWS A, 2019. Experimental harvest in a tropical seagrass meadow leads to shift in associated benthic communities[J]. Community Ecology, 20(2):138-148. |
| [10] | CARROLL J M, PETERSON B J, 2013. Ecological trade-offs in seascape ecology: bay scallop survival and growth across a seagrass seascape[J]. Landscape Ecology, 28(7):1401-1413. |
| [11] | DORENBOSCH M, GROL M G G, DE GROENE A, et al, 2009. Piscivore assemblages and predation pressure affect relative safety of some back-reef habitats for juvenile fish in a Caribbean bay[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 379:181-196. |
| [12] | FROESE R, 2006. Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: history, meta-analysis and recommendations[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 22(4):241-253. |
| [13] | GUMANAO G S, SACEDA-CARDOZA M M, MUELLER B, et al, 2016. Length-weight and length-length relationships of 139 Indo-Pacific fish species (Teleostei) from the Davao Gulf, Philippines[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 32(2):377-385. |
| [14] | HARRISON T D, 2001. Length-weight relationships of fishes from South African estuaries[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 17(1):46-48. |
| [15] | HEMMINGA M A, DUARTE C M, 2000. Seagrass ecology[M]. London: Cambridge University Press: 20-22. |
| [16] | HERKÜL K, KOTTA J, 2009. Effects of eelgrass (Zostera marina) canopy removal and sediment addition on sediment characteristics and benthic communities in the Northern Baltic Sea[J]. Marine Ecology, 30(S1):74-82. |
| [17] | HORINOUCHI M, 2007. Distribution patterns of benthic juvenile gobies in and around seagrass habitats: effectiveness of seagrass shelter against predators[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 72(4):657-664. |
| [18] | HOVEL K A, FONSECA M S, 2005. Influence of seagrass landscape structure on the juvenile blue crab habitat-survival function[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 300:179-191. |
| [19] | IGFA, 2009. Database of IGFA angling records until 2009[DB]. IGFA, Fort Lauderdale, USA. http://wrec.igfa.org/. |
| [20] | JUMAWAN-NANUAL B, METILLO E B, 2008. Population structure and reproductive biology of Siganus fuscescens Houttuyn 1782 (Perciformes, Siganidae) in Pujada Bay, Southeastern Mindanao, Philippines[J]. The Philippine Scientist, 2008,45:62-79. |
| [21] | KANOU K, SANO M, KOHNO H, 2004. Food habits of fishes on unvegetated tidal mudflats in Tokyo Bay, central Japan[J]. Fisheries Science, 70(6):978-987. |
| [22] | KUITER R H, TONOZUKA T, 2001. Pictorial guide to Indonesian reef fishes[M]. Australia: Zoonetics Press: 100-893. |
| [23] |
LAMB J B, VAN DE WATER J A J M, BOURNE D G, et al, 2017. Seagrass ecosystems reduce exposure to bacterial pathogens of humans, fishes, and invertebrates[J]. Science, 355(6326):731-733.
pmid: 28209895 |
| [24] | LAVERGNE E, ZAJONZ U, SELLIN L, 2013. Length-weight relationship and seasonal effects of the Summer Monsoon on condition factor of Terapon jarbua (Forsskål, 1775) from the wider Gulf of Aden including Socotra Island[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 29(1):274-277. |
| [25] | LETOURNEUR Y, KULBICKI M, LABROSSE P, 1998. Length-weight relationship of fishes from coral reefs and lagoons of New Caledonia: an update[J]. Naga, the ICLARM Quarterly, 21(4):39-46. |
| [26] | LIESKE E, MYERS R, 1998. Coral reef fishes: caribbean, indian ocean and pacific ocean including the red sea[M]. New Jersey: Princeton University Press: 300-359. |
| [27] | LIN H J, SHAO K T, KUO S R, et al, 1999. A trophic model of a sandy barrier lagoon at Chiku in southwestern Taiwan[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 48(5):575-588. |
| [28] |
LIU SONGLIN, JIANG ZHIJIAN, ZHANG JINGPING, et al, 2017. Sediment microbes mediate the impact of nutrient loading on blue carbon sequestration by mixed seagrass meadows[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 599-600:1479-1484.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.06.105 pmid: 23870498 |
| [29] | MERCY T V A, JACOB E, BHASKAR R K, 2008. Length-weight relationship of sixteen species of indigenous ornamental fishes of the Western Ghats of India[J]. Indian Journal of Fisheries, 55(4):337-339. |
| [30] | NAKAMURA Y, HORINOUCHI M, NAKAI T, et al, 2003. Food habits of fishes in a seagrass bed on a fringing coral reef at Iriomote Island, southern Japan[J]. Ichthyological Research, 50(1):15-22. |
| [31] | PALLA H P, PAGLIAWAN H B, RODRIGUEZ E F, et al, 2018. Length-weight relationship of marine fishes from Palawan, Philippines[J]. The Palawan Scientist, 10(1):17-28. |
| [32] | PERKINS M J, MAK Y K Y, LAW C S W, et al, 2019. Length‐weight relationships of 79 marine fish species from the coastal waters of Hong Kong[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 35(3):779-788. |
| [33] |
PHELAN B A, GOLDBERG R, BEJDA A J, et al, 2000. Estuarine and habitat-related differences in growth rates of young-of-the-year winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus) and tautog (Tautoga onitis) in three northeastern US estuaries[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 247(1):1-28.
pmid: 10727685 |
| [34] | REIMER O, 1999. Increased gonad ratio in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis, exposed to starfish predators[J]. Aquatic Ecology, 33(2):185-192. |
| [35] | ROOKER J R, HOLT G J, HOLT S A, 1998. Vulnerability of newly settled red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) to predatory fish: is early-life survival enhanced by seagrass meadows?[J]. Marine Biology, 131(1):145-151. |
| [36] | SOGARD S M, 1992. Variability in growth rates of juvenile fishes in different estuarine habitats[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 85(1):35-53. |
| [37] | STUNZ G W, MINELLO T J, LEVIN P S, 2002. Growth of newly settled red drum Sciaenops ocellatus in different estuarine habitat types[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 238:227-236. |
| [38] | TAKASUKA A, AOKI I, 2006. Environmental determinants of growth rates for larval Japanese anchovy Engraulis japonicus in different waters[J]. Fisheries Oceanography, 15(2):139-149. |
| [39] | TASKAVAK E, BILECENOGLU M, 2001. Length-weight relationships for 18 Lessepsian (Red Sea) immigrant fish species from the eastern Mediterranean coast of Turkey[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 81(5):895-896. |
| [40] | TSOUMANI M, LIASKO R, MOUTSAKI P, et al, 2006. Length-weight relationships of an invasive cyprinid fish (Carassius gibelio) from 12 Greek lakes in relation to their trophic states[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 22(4):281-284. |
| [41] | VERWEIJ M C, NAGELKERKEN I, HANS I, et al, 2008. Seagrass nurseries contribute to coral reef fish populations[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 53(4):1540-1547. |
| [42] | WANG X H, QIU Y S, ZHU G P, et al, 2011. Length-weight relationships of 69 fish species in the Beibu Gulf, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Applied Ichthyology, 27(3):959-961. |
| [43] |
WAYCOTT M, DUARTE C M, CARRUTHERS T J B, et al, 2009. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(30):12377-12381.
pmid: 19587236 |
| [44] | WEBSTER P J, ROWDEN A A, ATTRILL M J, 1998. Effect of shoot density on the infaunal macro-invertebrate community within a Zostera marina Seagrass bed[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 47(3):351-357. |
| [45] | WHITFIELD A K, 2016. The role of seagrass meadows, mangrove forests, salt marshes and reed beds as nursery areas and food sources for fishes in estuaries[J]. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries, 27(1):75-110. |
| [46] | WOODLAND D J, 1990. Revision of the fish family Siganidae with descriptions of two new species and comments on distribution and biology[J]. Indo-Pacific Fishes, (19):136 |
| [47] | YAMAGAWA H, 1994. Length-weight relationship of Gulf of Thailand fishes[J]. Naga, 17(4):48-52. |
| [1] | LIN Xianzhi, ZHOU Yanyan, LIN Haoye, HU Simin, HUANG Hui, ZHANG Li, LIU Sheng. Diet analysis of the parrotfish (Scarus globiceps) in coral reefs of the Nansha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 100-108. |
| [2] | LEI Mingfeng, YU Kefu, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Biao, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Xiaoyan. The rapid ecological degradation and its impact on fish of the Yinyu Island in the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [3] | LAN Zhenqiang, ZHENG Jitao, CHEN Yun, CHEN Nan, WANG Shuhong. Copulation, embryonic and post-embryonic development of Sphaeramia nematoptera [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 116-125. |
| [4] | YANG Bin, SALENDRA Limbadri, LIU Juan, LIU Yonghong. Alkaloids from the Jellyfish-Derived Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus SCSIO41214 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 195-201. |
| [5] | WANG Zihan, ZENG Cong, JIANG Ziyu, CAO Ling. Conservation gap analysis of threatened fish in the East China Sea and adjacent sea areas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 66-86. |
| [6] | ZHANG Wanru, LIU Qingxia, HUANG Honghui, QIN Xiaoqing, LI Jiajun, CHEN Jianhua. Study on stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen of main fishery organisms in the southwestern waters of Daya Bay, South China Sea in winter 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [7] | DU Chong, HE Jun, SUN Tingting, WANG Lei, WANG Fanghan, DONG Zhijun. Molecular identification on the causative species jellyfish blooms in the northern South China Sea in 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 142-148. |
| [8] | HONG Xiaofan, CHEN Zuozhi, JIANG Yane, ZHANG Jun, WANG Huanhuan, LI Yuanjie, LI Gang. Biological characteristics of Cephalopholis spiloparaea of reef waters in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 50-62. |
| [9] | Min LI, Xiaolan KONG, Youwei XU, Zuozhi CHEN. Genetic polymorphism of the Brushtooth lizardfish Saurida undosquamis based on mitochondrial D-loop sequences [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 42-49. |
| [10] | Mengna LIU, Lei XU, Xuehui WANG, Yu LIU, Miaodi WANG, Yongsong QIU, Jiangfeng ZHU, Yinglin HE, Weilie BEI, Feiyan DU. Study on food contents of Uroteuthis chinensis and Sthenoteuthis oualaniensis based on COI sequence [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(4): 61-69. |
| [11] | Danfeng ZHAO, Zhou HUANG, Qiang XU, Dongmei HUANG. Competitive pressure inquiry and resource allocation of coral fishes based on LSH method [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 118-126. |
| [12] | Sixuan HE,Binyuan HE. Study on fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 86-97. |
| [13] | Shenglong YANG,Xiumei FAN,Fenghua TANG,Tianfei CHEN,Wei FAN. Relationship between spatial-temporal distribution of Scomber australasicus and environmental factors in the Arabian Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 91-100. |
| [14] | Jiaxing HUANG, Yuyan GONG, Shannan XU, Huanhuan WANG, Kui ZHANG, Jun ZHANG, Zuozhi CHEN. Characteristics of stable carbon and nitrogen isotopes of major fishery organisms in the fishing ground of central western South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(1): 76-84. |
| [15] | Qinwei HAO, Xiangrong XU, Hui CHEN, Shan LIU, Jun CHEN, Shuangshuang LIU, Guangguo YING. Residual antibiotics in the Nansha aquaculture area of Guangzhou [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(1): 106-113. |
|
||