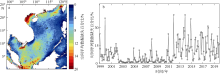
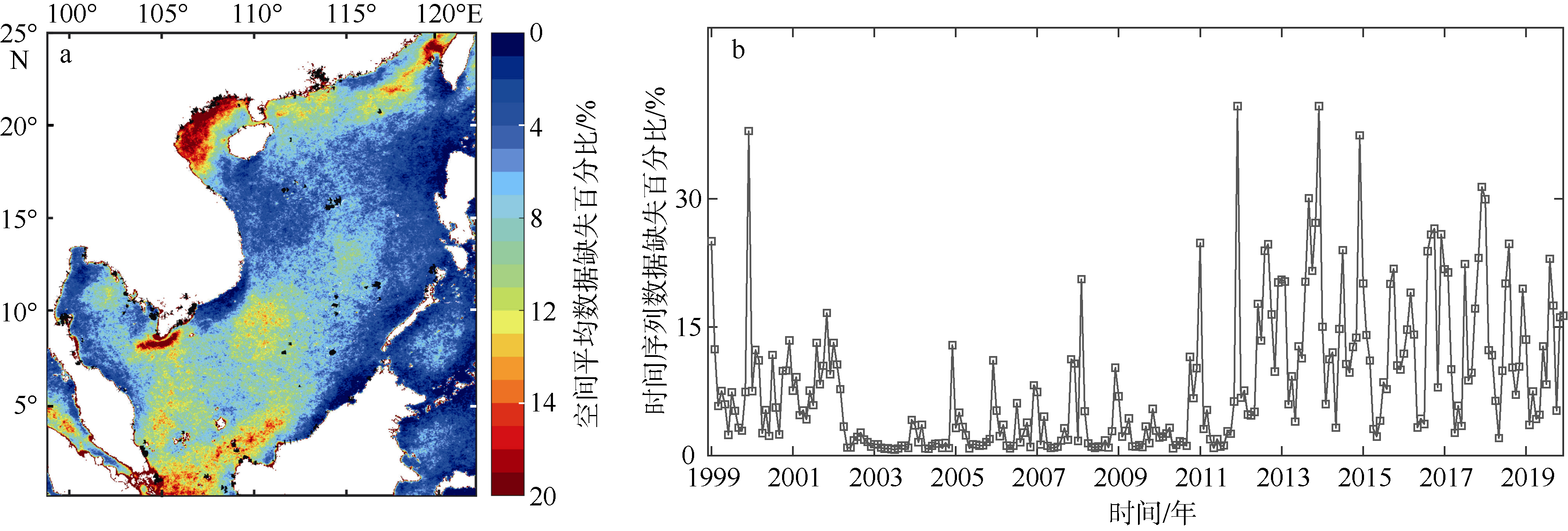
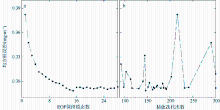
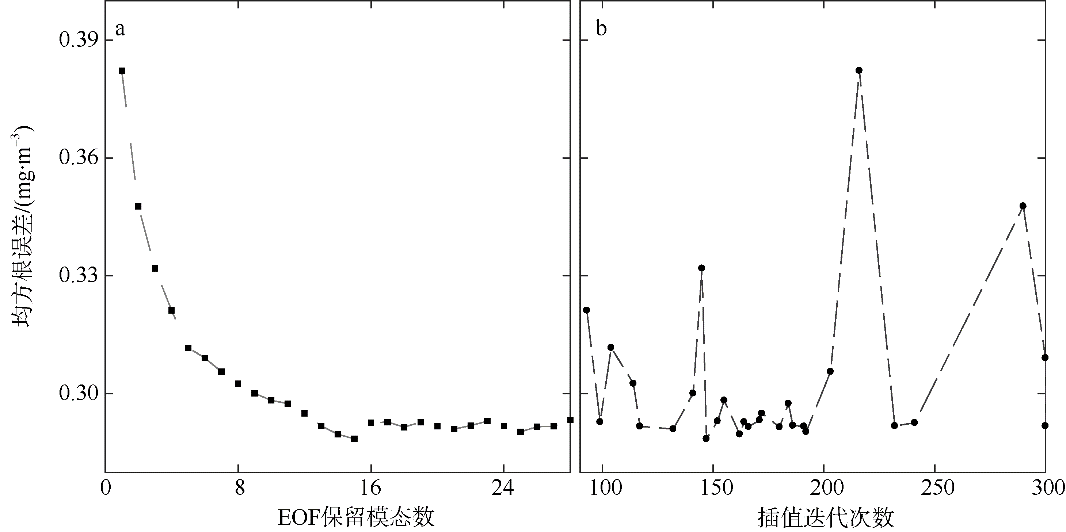
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 77-89.doi: 10.11978/2021048CSTR: 32234.14.2021048
Special Issue: 海洋大数据及应用
• Marine Remote Sensing • Previous Articles Next Articles
Spatiotemporal variation of water area with high chlorophyll a concentration in the South China Sea based on OC-CCI data*
LI Ao1,2( ), FENG Yang1,3, WANG Yuntao1,4, XUE Huijie1(
), FENG Yang1,3, WANG Yuntao1,4, XUE Huijie1( )
)
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
4. The Second Institute of Oceanology, Ministry of Natural Resources, Hangzhou 310000, China
-
Received:2021-04-12Revised:2021-07-24Online:2022-03-10Published:2021-07-30 -
Contact:XUE Huijie E-mail:liao@scsio.ac.cn;huijiexue@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:Subproject B of the Pilot Special Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDB42010201);Basic Research Funds of the Second Institute of Oceanology, Ministry of Natural Resources of China(HYGG2002)
CLC Number:
- P735.52
Cite this article
LI Ao, FENG Yang, WANG Yuntao, XUE Huijie. Spatiotemporal variation of water area with high chlorophyll a concentration in the South China Sea based on OC-CCI data*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 77-89.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
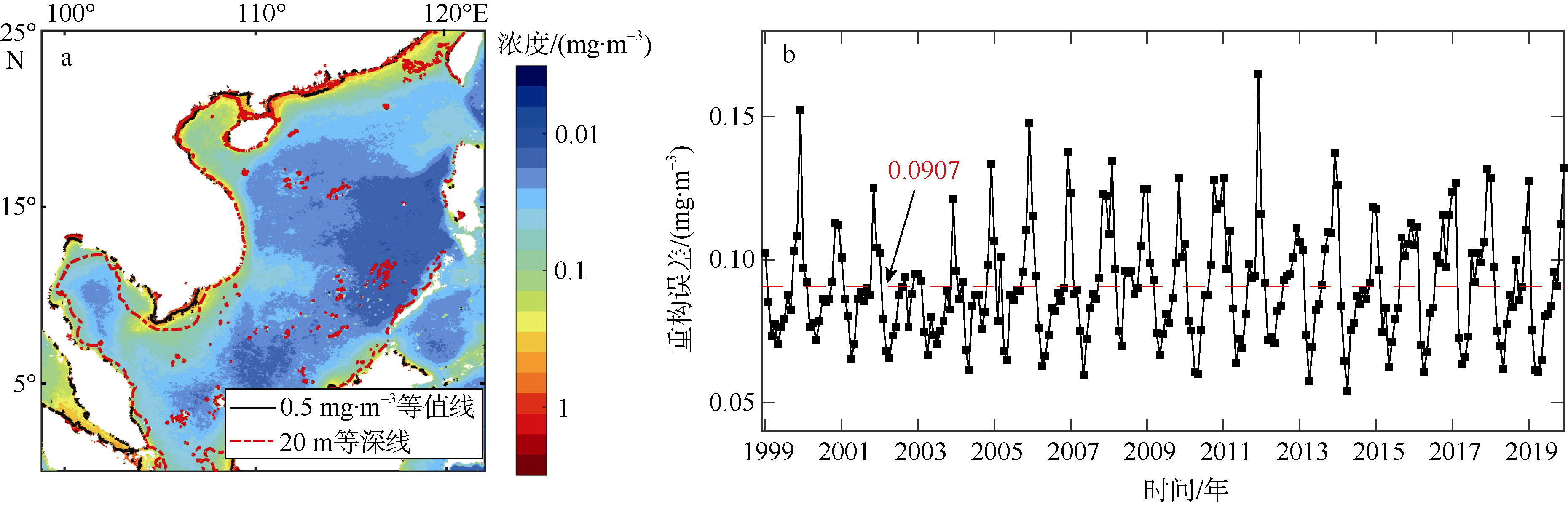
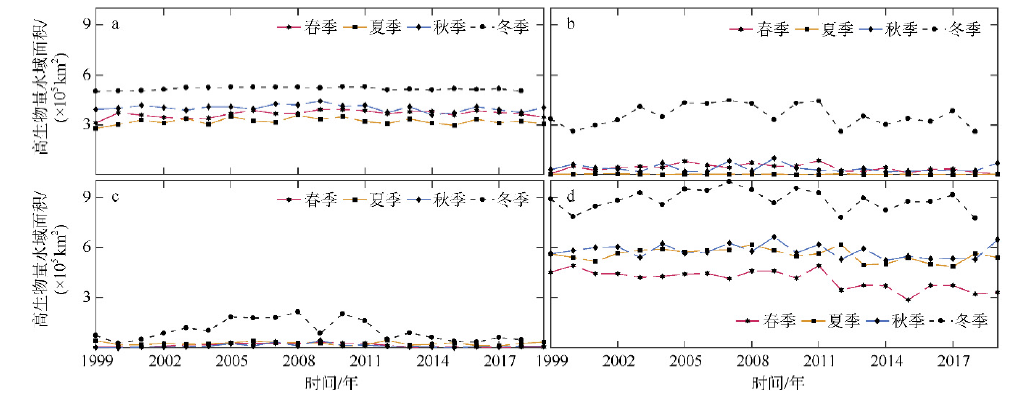
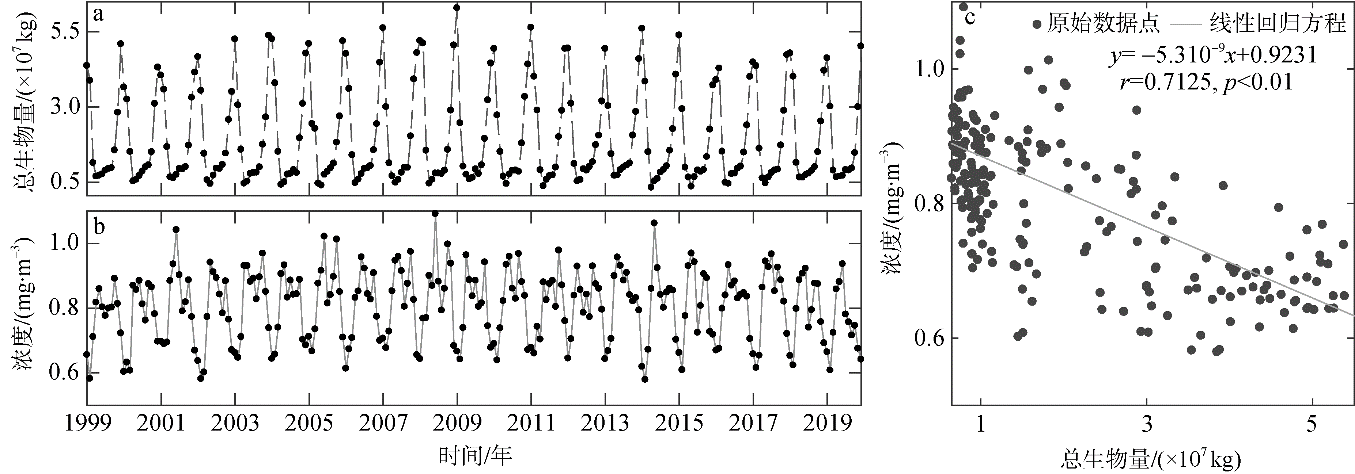
Fig. 9
Biomass of high chlorophyll a concentration waters and chlorophyll a concentration of high chlorophyll a concentration waters in the South China Sea. (a) estimated biomass of mixed layer in high chlorophyll a concentration waters; (b) the concentration of chlorophyll a on the surface of high chlorophyll a concentration waters; (c) regression analysis between the biomass of the mixed layer and the chlorophyll a concentration at the surface with high chlorophyll a concentration"
| [1] | 陈兴群, 陈其焕, 庄亮钟, 1989. 南海中部叶绿素a分布和光合作用及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋学报, 11(3): 349-355. |
| CHEN XINGQUN, CHEN QIHUAN, ZHUANG LIANGZHONG, 1990. Distribution of chlorophyll a, photosynthesis and their relations to the environmental factors in the Central South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 9(4): 611-624. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 倪晓波, 黄大吉, 2006. 海洋次表层叶绿素最大值的分布和形成机制研究[J]. 海洋科学, 30(5): 58-64, 70. |
| NI XIAOBO, HUANG DAJI, 2006. Subsurface chlorophyll maximum: its temporal-spatial distribution and formation mechanism in the ocean[J]. Marine Sciences, 30(5): 58-64, 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 赵辉, 齐义泉, 王东晓, 等, 2005. 南海叶绿素浓度季节变化及空间分布特征研究[J]. 海洋学报, 27(4): 45-52. |
| ZHAO HUI, QI YIQUAN, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2005. Study on the features of chlorophyll-a derived from SeaWiFS in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 27(4): 45-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] |
BECKERS J M, RIXEN M, 2003. EOF calculations and data filling from incomplete oceanographic datasets[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 20(12): 1839-1856.
doi: 10.1175/1520-0426(2003)020<1839:ECADFF>2.0.CO;2 |
| [5] |
CHEN C C, SHIAH F K, CHUNG S W, et al, 2006. Winter phytoplankton blooms in the shallow mixed layer of the South China Sea enhanced by upwelling[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 59(1-2): 97-110.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2005.09.002 |
| [6] | CHEN Y L L, 2005. Spatial and seasonal variations of nitrate-based new production and primary production in the South China Sea. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 52(2): 319-340. |
| [7] |
DEE D P, UPPALA S M, SIMMONS A J, et al, 2011. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 137(656): 553-597.
doi: 10.1002/qj.v137.656 |
| [8] |
GUO LIN, XIU PENG, CHAI FEI, et al, 2017a. Enhanced chlorophyll concentrations induced by Kuroshio intrusion fronts in the northern South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 44(22): 11565-11572.
doi: 10.1002/grl.v44.22 |
| [9] |
GUO MINGXIAN, CHAI FEI, XIU PENG, et al, 2015. Impacts of mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea on biogeochemical cycles[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 65(9): 1335-1352.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-015-0867-1 |
| [10] |
GUO MINGXIAN, XIU PENG, LI SHIYU, et al, 2017b. Seasonal variability and mechanisms regulating chlorophyll distribution in mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122(7): 5329-5347.
doi: 10.1002/jgrc.v122.7 |
| [11] |
HUYNH H N T, ALVERA-AZCÁRATE A, BECKERS J M, 2020. Analysis of surface chlorophyll a associated with sea surface temperature and surface wind in the South China Sea[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 70(1): 139-161.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-019-01308-9 |
| [12] |
LIU XIAOMING, WANG MENGHUA, 2019. Filling the gaps of missing data in the merged VIIRS SNPP/NOAA-20 ocean color product using the DINEOF method[J]. Remote Sensing, 11(2): 178.
doi: 10.3390/rs11020178 |
| [13] |
LOISEL H, VANTREPOTTE V, OUILLON S, et al, 2017. Assessment and analysis of the chlorophyll-a concentration variability over the Vietnamese coastal waters from the MERIS ocean color sensor (2002-2012)[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 190: 217-232.
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.12.016 |
| [14] | NING X, CHAI FEI, XUE HUIJIE, et al, 2004. Physical-biological oceanographic coupling influencing phytoplankton and primary production in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 109(C10): C10005. |
| [15] | PALACZ A P, XUE HUIJIE, ARMBRECHT C, et al, 2011. Seasonal and inter-annual changes in the surface chlorophyll of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C9): C09015. |
| [16] |
QUAN QI, XUE HUIJIE, QIN HUILING, et al, 2016. Features and variability of the South China Sea western boundary current from 1992 to 2011[J]. Ocean Dynamics, 66(6-7): 795-810.
doi: 10.1007/s10236-016-0951-1 |
| [17] |
SHIH Y Y, HUNG C C, HUANG S Y, et al, 2020. Biogeochemical variability of the upper ocean response to typhoons and storms in the northern South China Sea[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 7: 151.
doi: 10.3389/fmars.2020.00151 |
| [18] |
TANG DANLING, NI I H, KESTER D R, et al, 1999. Remote sensing observations of winter phytoplankton blooms southwest of the Luzon Strait in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 191: 43-51.
doi: 10.3354/meps191043 |
| [19] |
TANG DANLING, KAWAMURA H, LEE M A, et al, 2003. Seasonal and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a concentrations and water conditions in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 85(4): 475-483.
doi: 10.1016/S0034-4257(03)00049-X |
| [20] |
TANG DANLING, KAWAMURA H, VAN DIEN T, et al, 2004. Offshore phytoplankton biomass increase and its oceanographic causes in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 268: 31-41.
doi: 10.3354/meps268031 |
| [21] | TANG DANLING, KAWAMURA H, SHI PING, et al, 2006. Seasonal phytoplankton blooms associated with monsoonal influences and coastal environments in the sea areas either side of the Indochina Peninsula[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 111(G1): G01010. |
| [22] |
TANG SHILIN, DONG QING, LIU FENFEN, 2011. Climate-driven chlorophyll-a concentration interannual variability in the South China Sea[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 103: 229-237.
doi: 10.1007/s00704-010-0295-6 |
| [23] | TANG SHILIN, LIU FENFEN, CHEN CHUQUN, 2014. Seasonal and intraseasonal variability of surface chlorophyll a concentration in the South China Sea[J]. Aquatic Ecosystem Health & Management, 17(3): 242-251. |
| [24] |
TANG SHILIN, LIU FENFEN, 2020. Remote sensing of phytoplankton decline during the late 1980s and early 1990s in the South China Sea[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 41(15): 6010-6021.
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2020.1718241 |
| [25] | WANG GUIHUA, LI JIAXUN, WANG CHUNZAI, et al, 2012. Interactions among the winter monsoon, ocean eddy and ocean thermal front in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 117(C8): C08002. |
| [26] |
XING XIAOGANG, QIU GUOQIANG, BOSS E, et al, 2019. Temporal and vertical variations of particulate and dissolved optical properties in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 124(6): 3779-3795.
doi: 10.1029/2018JC014880 |
| [27] | XIU PENG, CHAI FEI, 2011. Modeled biogeochemical responses to mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 116(C10): C10006. |
| [28] |
XIU PENG, DAI MINHAN, CHAI FEI, et al, 2019. On contributions by wind-induced mixing and eddy pumping to interannual chlorophyll variability during different ENSO phases in the northern South China Sea[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 64(2): 503-514.
doi: 10.1002/lno.v64.2 |
| [29] |
YU YI, XING XIAOGANG, LIU HAILONG, et al, 2019. The variability of chlorophyll-a and its relationship with dynamic factors in the basin of the South China Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 200: 103230.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2019.103230 |
| [30] |
ZU TINGTING, XUE HUIJIE, WANG DONGXIAO, et al, 2019. Interannual variation of the South China Sea circulation during winter: intensified in the southern basin[J]. Climate Dynamics, 52(3): 1917-1933.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-018-4230-3 |
| [31] |
ZU TINGTING, Wang DONGXIAO, WANG QIANG, et al, 2020. A revisit of the interannual variation of the South China Sea upper layer circulation in summer: correlation between the eastward jet and northward branch[J]. Climate Dynamics, 54(1): 457-471.
doi: 10.1007/s00382-019-05007-5 |
| [1] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 3. data sharing service and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [2] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, HE Yunkai, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 1. data reorganization technology and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [3] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, XU Xiaolu, YUAN Li. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 2. data curation and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [4] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [5] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [6] | JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [7] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [8] | HUANG Yuan, CEN Jingyi, LIANG Qianyan, LYU Songhui, WANG Jianyan. Study on the community structure of eukaryotic phytoplankton in the Shenzhen Bay based on high-throughput sequencing technology [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 21-33. |
| [9] | ZHAO Minghui, YUAN Ye, ZHANG Jiazheng, ZHANG Cuimei, GAO Jinwei, WANG Qiang, SUN Zhen, CHENG Jinhui. New developments on the rift-breakup of the continent-ocean transition zone in the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [10] | HUANG Yu, WANG Lin, MAI Zhimao, LI Jie, ZHANG Si. Isolation and characterization of sand fixation ability of bacteria in biological soil crusts of the tropical islands, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [11] | WANG Chenyan, SHI Jingwen, YAN Annan, KANG Yaru, WANG Yuxuan, QIN Suli, HAN Minwei, ZHANG Ruijie, YU Kefu. Bioaccumulation characteristics and source apportionment of organophosphate esters in Acanthaster planci from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
| [12] | LI Niu, DI Pengfei, FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu. The impact of cold seepage on geochemical indices for redox conditions of marine sediments ―Site F active seep site in the northeastern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
| [13] | ZHANG Zhisheng, XIE Lingling, LI Junyi, LI Qiang. Comparative analysis of mesoscale eddy evolution during life cycle in marginal sea and open ocean: South China Sea and Kuroshio Extension [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 63-76. |
| [14] | YANG Lei, WEN Jinhui, WANG Qiang, LUO Xi, HUANG Huaming, HE Yunkai, CHEN Ju. Recent research progress in the influence of tropical cyclones on the Luzon Strait transport* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 40-51. |
| [15] | ZHAO Zhongxian, SUN Zhen, MAO Yunhua, ZHANG Huodai. Heterogeneous extension and pulsed tectonic subsidence in the northern South China Sea margin* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 96-115. |
|
||