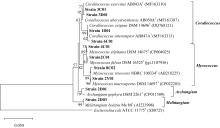
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 158-168.doi: 10.11978/2022142CSTR: 32234.14.2022142
• Marine Geology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Preliminary study on the culturable myxobacteria resources from the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi and their antibacterial activity
LU Tianmei1( ), GUAN jiasong1,2, QIN Shijing1, LIU Yonghong1,3, SU Zhiwei1(
), GUAN jiasong1,2, QIN Shijing1, LIU Yonghong1,3, SU Zhiwei1( )
)
- 1. Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
2. College of Agriculture, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China
3. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2022-06-23Revised:2022-08-24Online:2023-05-10Published:2022-09-01 -
Supported by:Scientific Research Foundation of Institute of Marine Drugs, GUCM(2018ZD005-A08); National Natural Science Foundation of China(32060098); Special Fund for Bagui Scholars to Yonghong Liu(05019055); Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education of GXUCM(YCSZ2022024); University Student Innovation Project(S202110600122); Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region(AB19259010)
Cite this article
LU Tianmei, GUAN jiasong, QIN Shijing, LIU Yonghong, SU Zhiwei. Preliminary study on the culturable myxobacteria resources from the Beibu Gulf, Guangxi and their antibacterial activity[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 158-168.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Details of samples"
| 样品编号 | 样品名称 | 采样区域 | 经纬度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1H | 木榄根际沉积物 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 2H | 木榄腐木 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 3H | 木榄胚轴 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 4H | 木榄树皮 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 5H | 木榄根际沉积物 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 6H | 白骨壤根际沉积物 | 珍珠湾 | 108°13′55″E, 21°36′27″N |
| 1D | 海蚀坑沉积物 | 涠洲岛 | 109°05′52″E, 21°00′04″N |
| 2D | 滩岩老鼠簕根际沉积物 | 涠洲岛 | 109°05′58″E, 21°00′42″N |
| 3D | 礁石地衣 | 涠洲岛 | 109°05′56″E, 21°00′39″N |
| 4D | 滩岩仙人掌根际沉积物 | 涠洲岛 | 109°05′55″E, 21°00′15″N |
| 1Y | 盐田淤泥 | 银海区 | 109°16′39″E, 21°26′35″N |
| 2Y | 盐田淤泥 | 银海区 | 109°16′22″E, 21°26′35″N |
| 3Y | 盐田淤泥 | 银海区 | 109°16′23″E, 21°26′35″N |
| 1C | 海草床沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°12′06″E, 21°34′14″N |
| 2C | 互花米草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′10″E, 21°35′11″N |
| 3C | 互花米草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°10′57″E, 21°34′33″N |
| 4C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′29″E, 21°34′59″N |
| 5C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′21″E, 21°34′53″N |
| 6C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′20″E, 21°34′51″N |
| 7C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′36″E, 21°34′58″N |
| 8C | 贝壳喜盐草根际沉积物 | 山心村 | 108°11′24″E, 21°34′51″N |
Tab. 2
Preliminary identification of myxobacteria according to morphological characteristics"
| 菌属 | 菌株数 | 子实体形态 | 菌落形态 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Myxococcus | 24 | 球状、卵球状, 单生, 多为橙色、白色或红粉色, 表面光滑柔软 | 圆形, 菌膜薄且呈同心圆扩展 |
| Corallococcus | 10 | 波浪状、肠状或珊瑚状, 单生或簇生, 多为淡黄色、粉色或乳白色, 表面不光滑、较硬 | 圆形, 菌膜薄且呈波浪纹扩展 |
| Archangium | 3 | 颗粒状, 簇生, 多为橘红色或棕色, 表面不光滑、较黏稠难挑 | 圆形, 菌膜薄、黏稠且呈放射状扩展 |
| Melittangium | 1 | 球状或扁平, 似蘑菇的菌伞, 分支生长, 黄褐色,表面不光滑 | 圆形, 菌膜薄、黏稠且呈放射状扩展 |
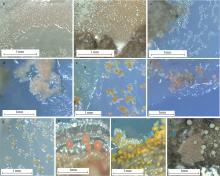
Fig. 1
The fruiting body of some myxobacteria strains from samples. (a) Corallococcus aberystwythensis; (b) Corallococcus interemptor; (c) Corallococcus exiguus; (d) Corallococcus exercitus; (e) Melittangium boletus; (f) Archangium gephyra; (g) Myxococcus macrosporus; (h) Myxococcus fulvus; (i) Myxococcus virescens; (j) Myxococcus stipitatus a. Corallococcus aberystwythensis; b. Corallococcus interemptor; c. Corallococcus exiguus; d. Corallococcus exercitus; e. Melittangium boletus; f. Archangium gephyra; g. Myxococcus macrosporus; h. Myxococcus fulvus; i. Myxococcus virescens; j. Myxococcus stipitatus"

Tab. 3
Relevant information and salt-tolerance abilities of strains"
| 种名 | 菌株编号 | 相似度/% | 耐盐能力/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corallococcus aberystwythensis | 3C01 | 99.61 | 1 |
| Corallococcus exercitus | 3D01 | 98.97 | 1 |
| Corallococcus exiguus | 6C01 | 98.85 | 1 |
| Melittangium boletus | 2D03 | 99.49 | <1 |
| Archangium gephyra | 2D01 | 100.00 | 1 |
| 1Y01 | 99.74 | 2 | |
| 4D01 | 99.15 | 1 | |
| Corallococcus interemptor | 1C01 | 100.00 | 1 |
| 1D01 | 100.00 | 1 | |
| 2D02 | 100.00 | 1 | |
| 6C02 | 99.87 | 1 | |
| 8C01 | 99.87 | 1.5 | |
| 1C02 | 99.74 | 1 | |
| 4H01 | 99.35 | 1 | |
| Myxococcus fulvus | 2C01 | 99.87 | 1 |
| 1H02 | 99.74 | <1 | |
| 5C01 | 99.36 | 1 | |
| 6H01 | 99.36 | 1 | |
| 1C04 | 98.85 | 1 | |
| 1D02 | 98.59 | 1 | |
| Myxococcus macrosporus | 2Y01 | 100.00 | 1.5 |
| 5H01 | 99.87 | 1.5 | |
| 1H01 | 99.74 | 1 | |
| 4H02 | 99.36 | <1 | |
| 3Y01 | 99.10 | 2 | |
| 3H01 | 98.97 | 2 | |
| 1C03 | 98.87 | 1 | |
| Myxococcus stipitatus | 4C01 | 99.87 | 1 |
| 7C01 | 99.74 | <1 | |
| 1C06 | 99.74 | <1 | |
| 3D02 | 99.62 | 1 | |
| 1H03 | 99.50 | 1 | |
| 5H02 | 99.49 | 1 | |
| 1C05 | 99.49 | 1 | |
| Myxococcus virescens | 8C02 | 99.49 | 2 |
| 1Y02 | 99.36 | 2 | |
| 2H01 | 99.36 | 2 | |
| 1C07 | 99.10 | 1.5 |
Tab. 5
Antibacterial activity of extracts from fermentation of myxobacteria"
| 菌种 | 编号 | 抑菌圈直径/mm | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G+ | G- | |||||||||
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | ||
| C. aberystwythensis | 3C01 | - | - | - | - | 12.03±0.32 | 12.58±0.44 | - | - | - |
| C. exiguus | 6C01 | - | - | - | - | - | 9.28±0.14 | - | - | - |
| A. gephyra | 1Y01 | - | - | - | - | 12.07±0.04 | - | - | - | - |
| C. interemptor | 1C01 | - | - | - | - | 11.95±0.01 | - | - | - | - |
| 1D01 | - | - | - | - | 13.43±0.40 | 8.64±0.09 | 12.25±0.29 | - | - | |
| 2D02 | - | - | 9.53±0.25 | - | 11.83±0.25 | 11.10±0.16 | - | - | - | |
| 6C02 | - | - | - | - | - | 9.97±0.05 | - | - | - | |
| 1C02 | - | - | - | 10.57±0.05 | 15.97±0.06 | - | - | - | - | |
| M. fulvus | 2C01 | - | - | - | 10.33±0.32 | 14.93±0.11 | 11.54±0.44 | - | - | - |
| 5C01 | - | 7.67±0.42 | - | - | - | 12.79±0.18 | - | - | - | |
| 1C04 | 10.82±0.04 | 7.34±0.02 | 12.03±0.65 | 12.23±0.24 | 15.79±0.05 | 14.05±0.20 | 10.91±0.17 | 11.14±0.07 | 13.78±0.06 | |
| 1D02 | - | - | 8.40±0.30 | - | - | 13.76±0.08 | - | - | - | |
| M. macrosporus | 1H01 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 18.16±0.24 | - | 9.65±0.03 |
| 4H02 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10.39±0.51 | |
| 1C03 | - | - | - | - | 14.19±0.05 | - | - | - | - | |
| M. stipitatus | 7C01 | - | - | - | 14.77±0.15 | - | 9.89±0.62 | - | - | - |
| 1C06 | 9.76±0.47 | 9.14±0.03 | - | 13.70±0.02 | 12.24±0.04 | 10.22±0.05 | 9.75±0.08 | 8.01±0.04 | - | |
| 3D02 | 14.33±0.14 | 13.87±0.12 | 11.90±0.10 | 14.57±0.60 | 19.74±0.29 | 16.61±0.04 | 13.74±0.08 | 8.43±0.08 | - | |
| 1H03 | 11.22±0.05 | 12.15±0.18 | 11.86±0.09 | 10.75±0.02 | 17.36±0.07 | 8.65±0.06 | 12.94±0.09 | - | - | |
| 1C05 | 12.90±0.36 | - | - | - | - | 15.99±0.27 | 12.38±0.22 | - | - | |
| M. virescens | 8C02 | - | - | - | - | - | 14.00±0.26 | - | - | - |
| 1Y02 | 13.90±0.36 | 8.72±0.08 | 10.50±0.30 | 13.10±0.44 | 11.31±0.27 | 15.66±0.47 | - | - | - | |
| 2H01 | 10.03±0.09 | 7.54±0.13 | 10.15±0.13 | 11.59±0.03 | 12.25±0.03 | 10.09±0.12 | - | - | - | |
| 1C07 | - | - | - | - | 15.59±0.03 | - | - | - | - | |
| 氨苄青霉素钠 | - | 19.46±0.30 | 10.40±0.15 | 14.33±0.38 | 20.17±0.23 | 22.10±0.19 | 17.11±0.56 | 17.02±0.03 | 15.72±0.02 | 18.39±0.12 |
| 空白对照 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [1] |
韩敏敏, 李蜜, 刘昕明, 等, 2020. Khai岛和Pathiu岛珊瑚礁沉积物细菌多样性及细菌粗提物延缓秀丽隐杆线虫衰老活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 39(5): 19-29.
doi: 10.11978/2019126 |
|
|
|
| [2] |
蒋莲秀, 吴越, 陈建宏, 等, 2017. 具有广谱抗菌活性的红树林稀有放线菌的分离及鉴定[J]. 中国抗生素杂志, 42(4): 311-317.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
鞠建华, 杨镇业, 李青连, 等, 2021. 微生物药物研究开发现状与思考[J]. 山东大学学报, 59(9): 43-50+63.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
李艳群, 陈柔雯, 林宗豪, 等, 2021. 一株群体感应抑制活性海洋放线菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(1): 75-81.
doi: 10.11978/2020011 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020011 |
|
| [5] |
骆宁宁, 2015. 粘球菌通过mts基因簇调控社会性细胞行为以适应海水生境的分子机制[D]. 济南: 山东大学: 1-123.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
马丽丽, 田新朋, 李桂菊, 等, 2021. 海洋微生物来源天然产物研究现状与态势[J]. 热带海洋学报, 40(5): 134-146.
doi: 10.11978/2020104 |
|
doi: 10.11978/2020104 |
|
| [7] |
邱智军, 李越中, 张勇, 等, 2003. 海水盐离子对耐盐粘球菌生长和发育的影响[J]. 微生物学杂志, (3): 8-11.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
沙国萌, 陈冠军, 陈彤, 等, 2020. 抗生素耐药性的研究进展与控制策略[J]. 微生物学通报, 47(10): 3369-3379.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
宋腾飞, 2019. 海洋青霉菌(Penicillium sp. ZZ380)的代谢产物及其生物活性的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学: 1-116.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
王春玲, 冯广达, 姚青, 等, 2019. 粘细菌基因组学研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 46(9): 2394-2403.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
王春玲, 吕颖颖, 姚青, 等, 2021. 粘细菌资源挖掘与多相分类研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报, 48(8): 2870-2880.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王聪, 王坤, 姜明国, 等, 2019. 广西北部湾放线菌的分离筛选及活性产物的鉴定[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 31(7): 1170-1176.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王婷, 2018. 新型生防粘细菌Myxococcus sp. BS的分离及粘细菌对细菌性软腐病菌的捕食机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学: 1-85.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
王雪寒, 2019. 内蒙古东部地区的可培养粘细菌及其抗菌活性的初步检测[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学: 1-79.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
吴姝鸽, 2021. 湖泊沉积物微生物的多样性、分离培养及四株新菌的分类鉴定[D]. 济南: 山东大学: 1-105.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
杨少娟, 陈雪梅, 沈锐, 等, 2021. 广西北部湾局部海域海洋沉积物细菌多样性及生物活性评估[J]. 广西科学, 28(5): 460-472.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
蚁烁星, 周杨, 张鲜姣, 等, 2020. 不同分离方法对子实体形成和粘细菌分离的影响[J]. 微生物学报, 61(4): 923-934.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
周秀文, 2013. 土壤中粘细菌群落的调查及领地性行为的分子机制的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学: 1-183.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.3390/md16060209 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.3390/md16090314 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1007/s10482-010-9460-2 pmid: 20582471 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020196 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.040501-0 |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1007/s10295-009-0683-z pmid: 20033830 |
| [25] |
doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1102-1108.1991 pmid: 2059035 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.2471/BLT.16.181743 pmid: 27516629 |
| [27] |
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00194.x |
| [28] |
pmid: 11997170 |
| [29] |
doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00424-7 |
| [30] |
doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000250 |
| [31] |
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6030084 |
| [32] |
doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6030073 |
| [33] |
doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.09.010 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-8843-6 pmid: 29455386 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.3390/v10070374 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/s00248-006-9169-y |
| [39] |
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238769 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00012-21 |
| [41] |
doi: 10.3390/md17120698 |
| [42] |
doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3331-3336.2005 |
| [1] | WANG Jiaxi, LU Humu, QI Xin, GAO Chenghai, LIU Yonghong, LUO Xiaowei. Study on the secondary metabolites from the Weizhou Island coral Acropora austera associated fungus Arachniotus ruber GXIMD 02510 and their antibacterial activity [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 174-180. |
| [2] | SUN Manman, ZENG Yanbo, XU Han, YAO Ligong, GUO Yuewei, SU Mingzhi. Chemical composition and antibacterial activities of the soft coral Lobophytum sp. from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 189-197. |
| [3] | LIU Ying, XIAO Yang, ZHU Zhenxin, LIU Hongcun, JIANG Mingguo, ZHU Yuzhang, LIN Kun, WU Jincheng, LU Xiaomei, HUANG Xiaoning, LIANG Haina, LU Wensen, YANG Lifang. Study on the Secondary Metabolites of Marine Streptomyces Sporoverrucosus 33510 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 128-134. |
| [4] | ZENG Buyan, LIANG Zhifeng, LUO Qinqin, ZENG Ling, YANG Changgeng, WANG Liyun, SUN Yulin. Molecular identification, secondary metabolites and biological activities of a deep-sea-derived fungus 101#* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 104-114. |
| [5] | YE Yuxiu, LUO Xiaowei, YANG Bin, LIN Xiuping, LIU Yonghong, ZHOU Xuefeng. Study on the secondary metabolites of reef habitat algae-derived fungus Pestalotiopsis neglecta SCSIO41403 from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 186-190. |
| [6] | XU Yixiao, HE Xilin, ZHANG Teng, LAN Wenlu. Causative species of Phaeocystis blooms in Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 122-130. |
| [7] | Yanfeng WANG,Jing YU,Pimao CHEN,Jie YU,Zhunan LIU. Relationship between spatial-temporal distribution of light falling-net fishing ground and marine environments * [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 68-76. |
| [8] | Xiangqing HUANG, Zhen’ang CUI, Kai LIANG, Huayang GAN, Zhen XIA, Zhenhai HUO. The primary sedimentary characteristics of Warm Pool in Beibu Gulf and its environmental indication* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2018, 37(1): 72-89. |
| [9] | Jiannan SUN, Ying LIU, Weitian XIE, Chunhou XU. Isolation and identification of marine Rhodotorula in a coastal area near Leizhou Peninsula [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(4): 87-92. |
| [10] | ZHANG Kui, CHEN Zuozhi, WANG Yuezhong, SUN Dianrong, QIU Yongsong. Population structure of Priacanthus macracanthus in the Beibu Gulf, and parameters for its growth, mortality and maturity [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(5): 20-28. |
| [11] | SUN Longqi, LIN Yuanshao, CHEN Lixiao, CAO Wenqing, ZHENG Lianming. Analysis of ecosystem structure and function in the northern Beibu Gulf Ⅶ: Nutrition structure and keystone species selection based on Ecopath with Ecosim [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(4): 51-62. |
| [12] | LI Zili, CAO Hongyan, JIA Chunyang. Observation of wind field in the Beibu Gulf during Typhnoon Usagi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(4): 31-34. |
| [13] | YANG Lu, CAO Wenqing, LIN Yuanshao, CHEN Yinghan, LIN Zhaojin, WANG Xuehui. Preliminary study on feeding habits and trophic niche of nine economic fish species in Beibu Gulf in summer [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2016, 35(2): 66-75. |
| [14] | WANG Fu-jing, LIN Yuan-shao, CAO Wen-qing, ZHANG Wen-jing, ZHENG Lian-ming, YANG Wei-di, WANG Yu-jie. The relationship between nutrients and phytoplankton community structure in northern Beibu Gulf [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(6): 73-85. |
| [15] | TANG Bo, LONG Jiang-ping, JIN Lu, XU Dong, LI Tuan-jie. The contrast of heavy metals’ ecological risks in marine sediments between the Beibu Gulf and the Pearl River Delta [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2015, 34(3): 75-81. |
|
||