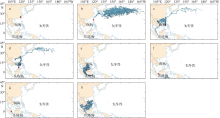
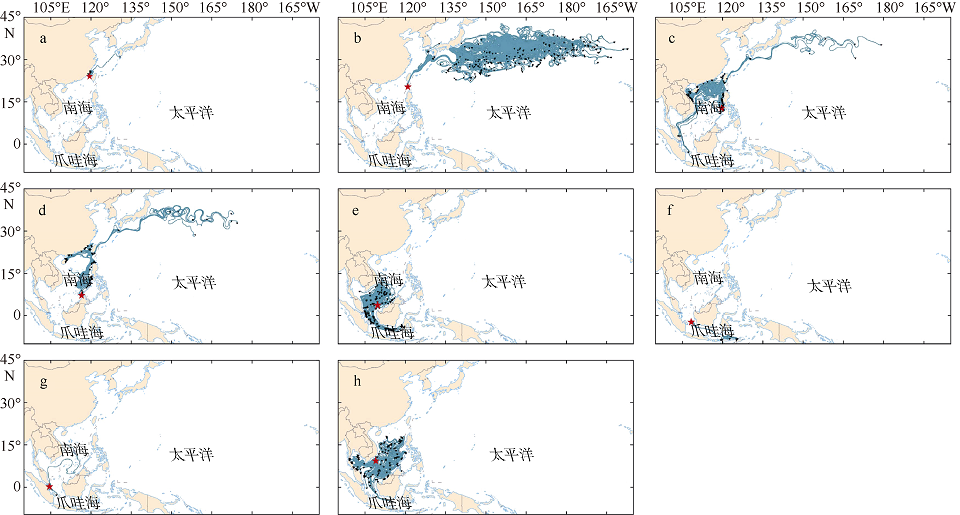
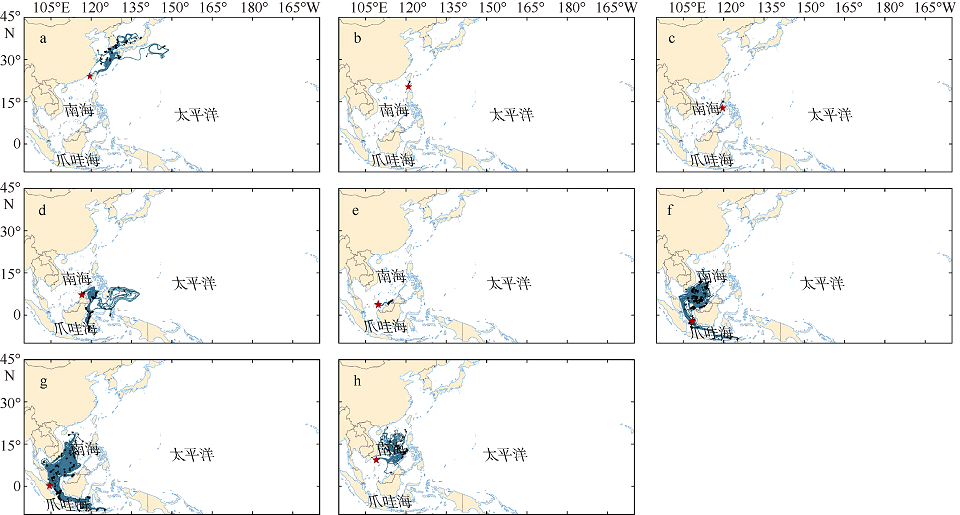
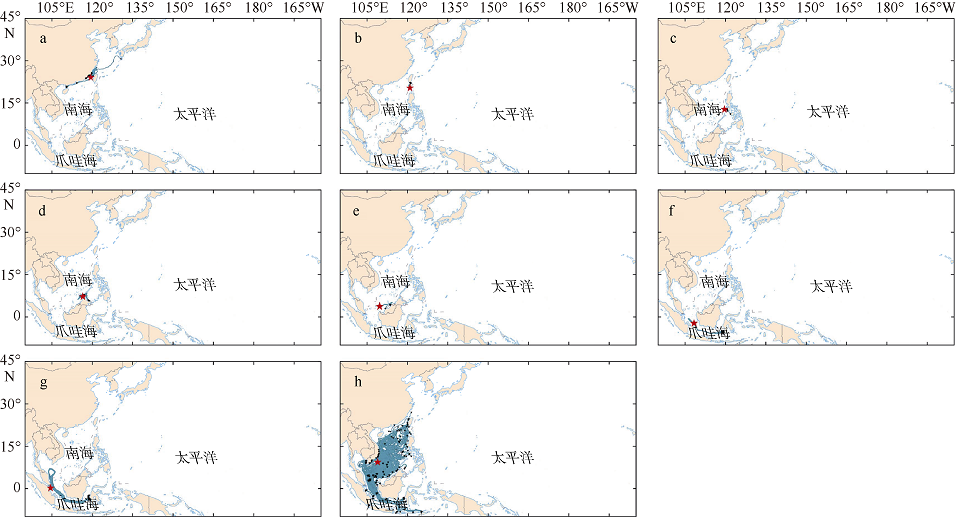
| [1] |
BJORNDAL K A, BOLTEN A B, LAGUEUX C J, 1994. Ingestion of marine debris by juvenile sea turtles in coastal Florida habitats[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 28(3):154-158.
|
| [2] |
CÓZAR A, ECHEVARRÍA F, GONZÁLEZ-GORDILLO J I, et al, 2014. Plastic debris in the open ocean[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(28):10239-10244.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1314705111
|
| [3] |
CÓZAR A, MARTÍ E, DUARTE C M, et al, 2017. The Arctic Ocean as a dead end for floating plastics in the North Atlantic branch of the Thermohaline Circulation[J]. Science Advances, 3(4):e1600582.
pmid: 28439534
|
| [4] |
CHIBA S, SAITO H, FLETCHER R, et al, 2018. Human footprint in the abyss: 30 year records of deep-sea plastic debris[J]. Marine Policy, 96:204-212.
|
| [5] |
ERIKSEN M, LEBRETON L C M, CARSON H S, et al, 2014. Plastic pollution in the World’s oceans: more than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250000 Tons Afloat at Sea[J]. PLoS ONE, 9(12):e111913.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111913
pmid: 25494041
|
| [6] |
GEYER R, JAMBECK J R, LAW K L, 2017. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made[J]. Science Advances, 3(7):e1700782.
pmid: 28776036
|
| [7] |
HAND E, 2014. Arctic sea ice traps floating plastic[J]. Science, 344(6187):985.
|
| [8] |
HU JIANYU, KAWAMURA H, HONG HUASHENG, et al, 2000. A review on the currents in the South China Sea: seasonal circulation, South China Sea warm current and Kuroshio intrusion[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 56(6):607-624.
|
| [9] |
HURLEY R, WOODWARD J, ROTHWELL J J, 2018. Microplastic contamination of river beds significantly reduced by catchment-wide flooding[J]. Nature Geoscience, 11(4):251-257.
|
| [10] |
JAMBECK J R, GEYER R, WILCOX C, et al, 2015. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean[J]. Science, 347(6223):768-771.
doi: 10.1126/science.1260352
pmid: 25678662
|
| [11] |
LAMB J B, WILLIS B L, FIORENZA E A, et al, 2018. Plastic waste associated with disease on coral reefs[J]. Science, 359(6374):460-462.
pmid: 29371469
|
| [12] |
LAVERS J L, BOND A L, 2017. Exceptional and rapid accumulation of anthropogenic debris on one of the world’s most remote and pristine islands[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(23):6052-6055.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1619818114
pmid: 28507128
|
| [13] |
LEBRETON L C M, VAN DER ZWET J, DAMSTEEG J W, et al, 2017. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans[J]. Nature Communications, 8:15611.
pmid: 28589961
|
| [14] |
MASUMOTO Y, SASAKI H, KAGIMOTO T, et al, 2004. A fifty-year eddy-resolving simulation of the world ocean — Preliminary outcomes of OFES (OGCM for the Earth Simulator)[J]. Journal of the Earth Simulator, 1:35-56.
|
| [15] |
MAXIMENKO N, HAFNER J, NIILER P, 2012. Pathways of marine debris derived from trajectories of Lagrangian drifters[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 65(1-3):51-62.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.04.016
pmid: 21696778
|
| [16] |
SASAI Y, ISHIDA A, YAMANAKA Y, et al, 2004. Chlorofluorocarbons in a global ocean eddy-resolving OGCM: pathway and formation of Antarctic bottom water[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(12):L12305.
|
| [17] |
SASAKI H, NONAKA M, MASUMOTO Y, et al, 2008. An eddy-resolving hindcast simulation of the quasiglobal ocean from 1950 to 2003 on the Earth Simulator[M]// HAMILTON K, OHFUCHI W. High Resolution Numerical Modelling of the Atmosphere and Ocean. New York, NY: Springer, 157-185.
|
| [18] |
SASAKI H, SASAI Y, KAWAHARA S, et al, 2004. A series of eddy-resolving ocean simulations in the world ocean-OFES (OGCM for the Earth Simulator) project[C]// Oceans ’04 MTS/IEEE Techno-Ocean ’04 (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37600). Kobe, Japan: IEEE, 3:1535-1541.
|
| [19] |
SAVOCA M S, WOHLFEIL M E, EBELER S E, et al, 2016. Marine plastic debris emits a keystone infochemical for olfactory foraging seabirds[J]. Science Advances, 2(11):e1600395.
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1600395
pmid: 28861463
|
| [20] |
VAN SEBILLE E, ENGLAND M H, FROYLAND G, 2012. Origin, dynamics and evolution of ocean garbage patches from observed surface drifters[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 7(4):044040.
|
| [21] |
WALLER C L, GRIFFITHS H J, WALUDA C M, et al, 2017. Microplastics in the Antarctic marine system: an emerging area of research[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 598:220-227.
pmid: 28441600
|
| [22] |
YAMASHITA R, TANIMURA A, 2007. Floating plastic in the Kuroshio Current area, western North Pacific Ocean[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54(4):485-488.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.11.012
pmid: 17275038
|
 ), LI Ning5, GUAN Yuping1,2,4(
), LI Ning5, GUAN Yuping1,2,4( ), FENG Yang1,2
), FENG Yang1,2