Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2022, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 90-104.doi: 10.11978/2022013CSTR: 32234.14.2022013
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Phycosphere microbial communities of zooxanthellae cultures isolated from corals in Sanya Bay, South China Sea
HUANG Sijun1,2( ), QIU Chen1,3, LONG Chao1,2, LONG Lijuan1,2,4
), QIU Chen1,3, LONG Chao1,2, LONG Lijuan1,2,4
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou 511458, China
3. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
4. Sanya Institute of Ocean Eco-Environmental Engineering, Yazhou Scientific Bay, Sanya 572000, China
-
Received:2022-01-23Revised:2022-03-29Online:2022-11-10Published:2022-04-12 -
Contact:HUANG Sijun E-mail:huangsijun@scsio.ac.cn -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(41576126);National Natural Science Foundation of China(42176116);Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2017A030306020);Rising Star Foundation of the South China Sea Institute of Oceanology(NHXX2019ST0101);Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS(2018377)
CLC Number:
- Q938
Cite this article
HUANG Sijun, QIU Chen, LONG Chao, LONG Lijuan. Phycosphere microbial communities of zooxanthellae cultures isolated from corals in Sanya Bay, South China Sea[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 90-104.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
Source and taxonomic information of zooxanthellae strains"
| 藻株 | 宿主拉丁文名(中文名) | ITS2基因型 | 藻株分类(属级) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SYSC-2-1 | Acropora tenuis (柔枝鹿角珊瑚) | C1 | Cladocopium (C型) |
| SYSC-2-8 | Acropora tenuis (柔枝鹿角珊瑚) | E101 | Effrenium (E型) |
| SYSC-14-11 | Galaxea fascicularis (丛生盔形珊瑚) | E101 | Effrenium (E型) |
| SYSC-17-3 | Galaxea fascicularis (丛生盔形珊瑚) | A6 | Symbiodinium (A型) |
| SYSC-24-3 | Platygyra verwyi (小叶扁脑珊瑚) | D1 | Durusdinium (D型) |
| SYSC-28-9 | Pavona decussate (十字牡丹珊瑚) | B1 | Breviolum (B型) |
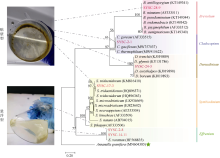
Fig. 1
Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree based on ITS2 sequences. The six strains of zooxanthellae in this experiment are marked in red. Ansanella granifera is used as the outgroup. The bootstrap value (%) with 1000 replicates is shown above the branch. The six zooxanthellae strains are classified into anchorage-dependent living lifestyle (SYSC-2-1, SYSC-17-3, SYSC-24-3, SYSC-28-9) and free-living lifestyle (SYSC-2-8 and SYSC-14-11), as indicated in the pictures"
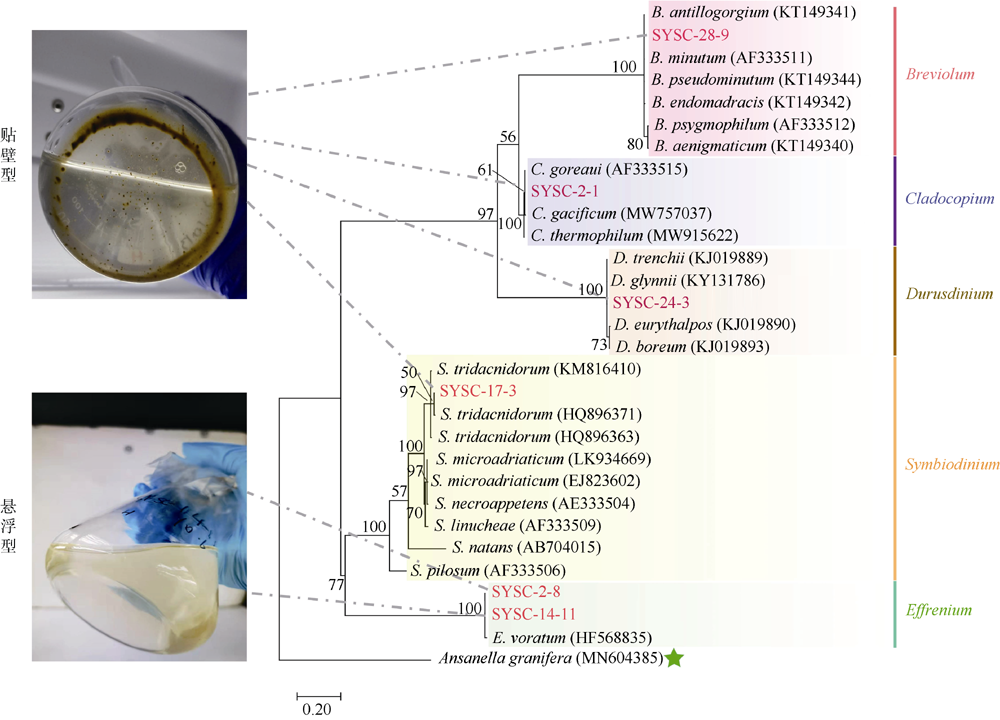
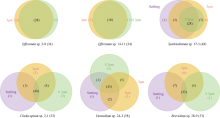
Fig. 2
The α diversity indices (Chao1, Shannon, Pielou) of phycosphere bacterial communities in six zooxanthellae strains, including 3 μm and 0.2 μm samples of all zooxanthellae strains, as well as “Settling” samples of four anchorage-dependent living algae. Significance code: ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05"
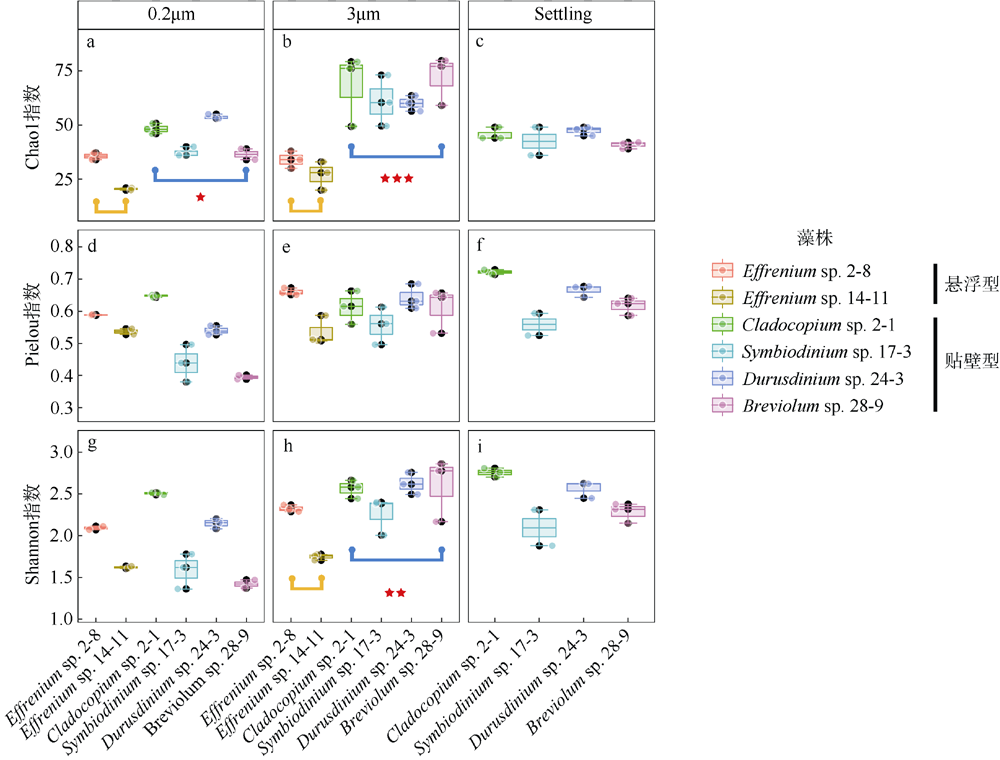
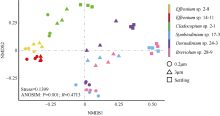
Fig. 3
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) analysis based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity among bacterial community of zooxanthellae. Three types of samples are represented by different shapes (circles for 0.2μm samples, triangles for 3μm samples, and squares for Settling samples). The ANOSIM analysis indicates the overall similarity among the six algal strains"
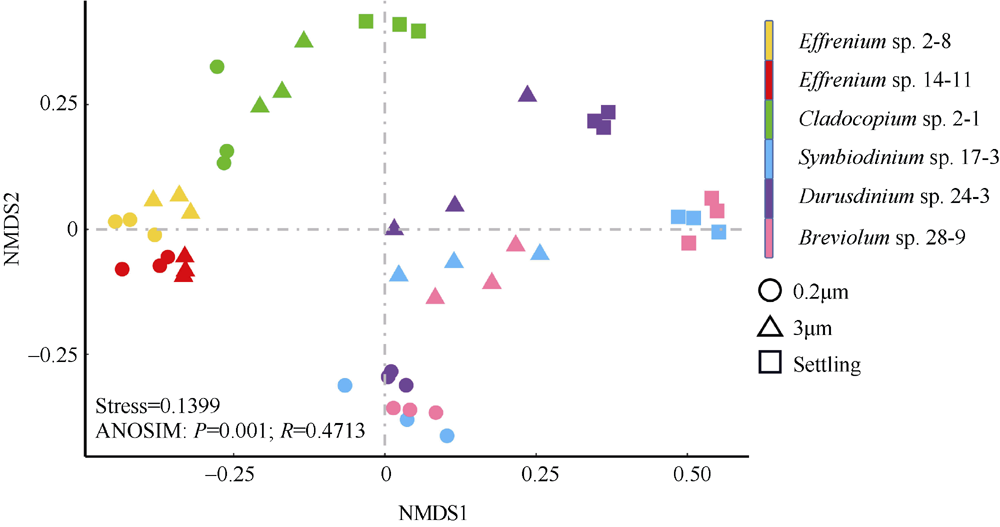
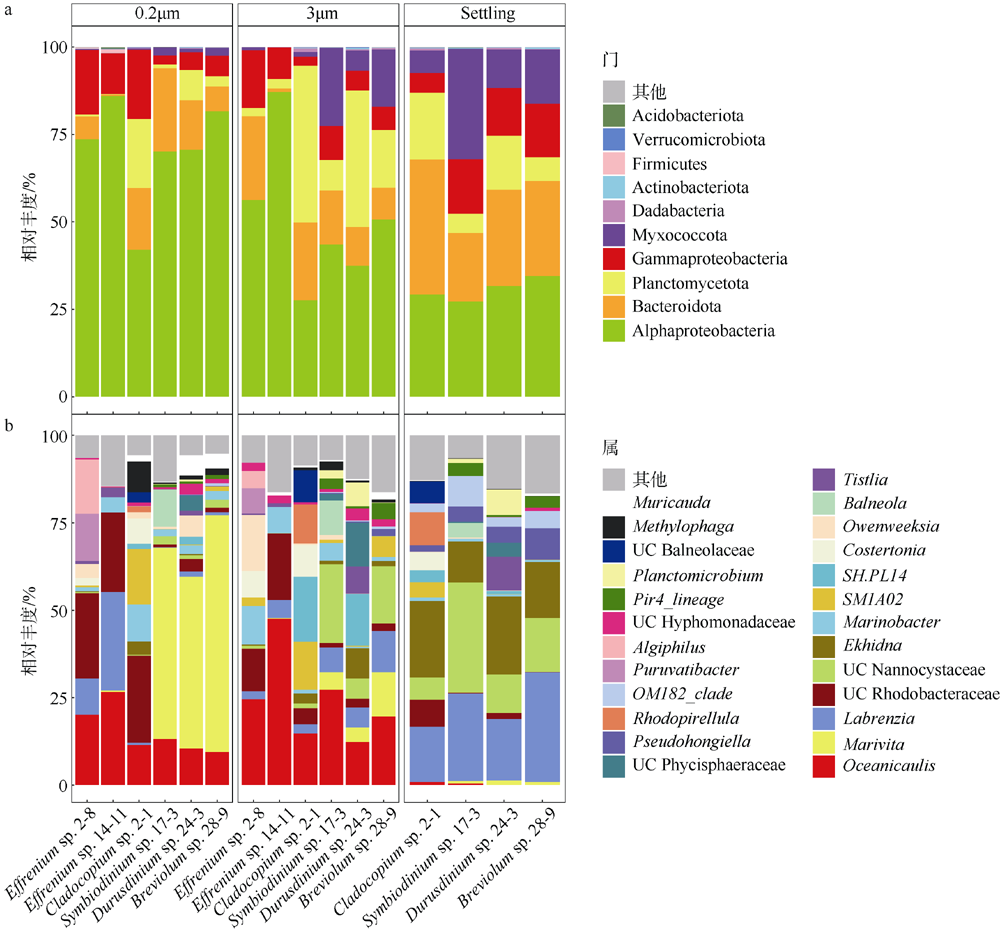
Fig. 4
Zooxanthellae associated bacteria community composition profiles in different samples(3 μm, 0.2 μm, Settling). (a) Bacteria community composition profiles at phylum level. Relative abundance <0.01% was classified into others. Phylum Proteobacteria was subdivided into α-Proteobacteria, β-Proteobacteria and γ-Proteobacteria. (b) Bacteria community composition profiles at genus level. Relative abundance <1% was classified into others"
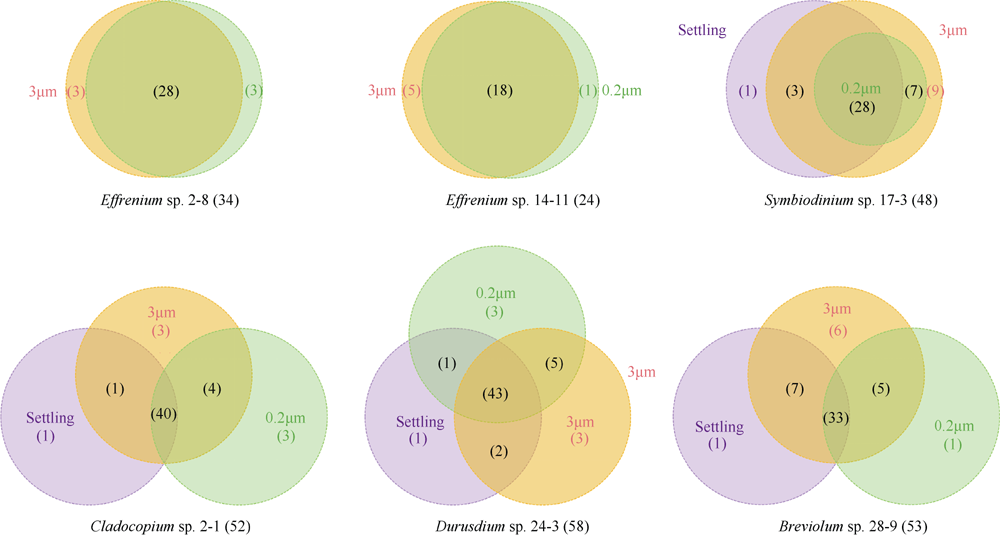
Tab. 2
The ratio of shared ASVs between different zooxanthellae strains"
| 藻株1 | 藻株2 | 两藻株共有ASVs数(取交集)/两藻株总ASVs数(取并集) | 所占比例/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 24-3 | 28-9 | 35/76 | 46.05 |
| 17-3 | 24-3 | 33/73 | 45.21 |
| 17-3 | 28-9 | 30/71 | 42.25 |
| 2-8 | 14-11 | 16/42 | 38.10 |
| 2-1 | 28-9 | 23/82 | 28.05 |
| 2-1 | 24-3 | 24/86 | 27.91 |
| 17-3 | 2-1 | 20/80 | 25.00 |
| 14-11 | 2-1 | 14/62 | 22.58 |
| 2-8 | 24-3 | 15/71 | 21.13 |
| 14-11 | 28-9 | 11/66 | 16.67 |
| 2-8 | 24-3 | 13/79 | 16.46 |
| 14-11 | 17-3 | 10/62 | 16.13 |
| 14-11 | 24-3 | 11/71 | 15.49 |
| 2-8 | 28-9 | 10/77 | 12.99 |
| 2-8 | 17-3 | 9/73 | 12.33 |

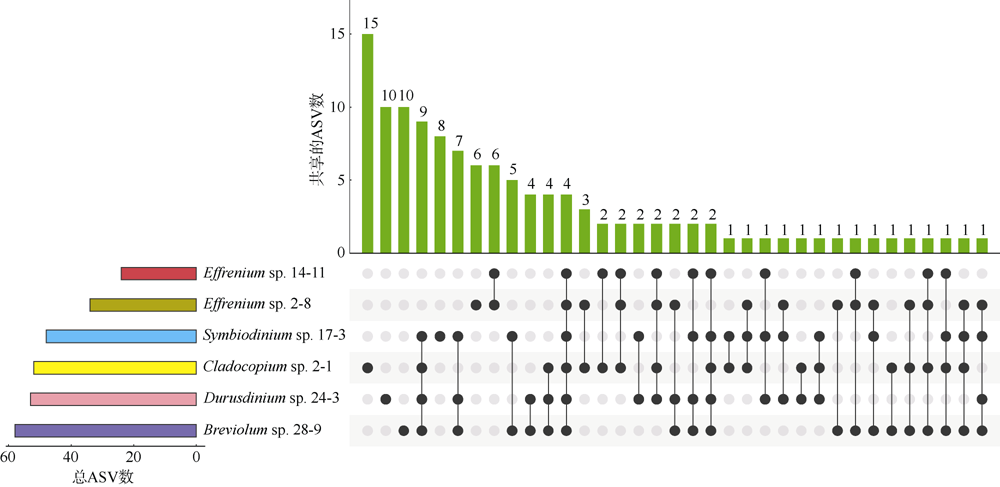
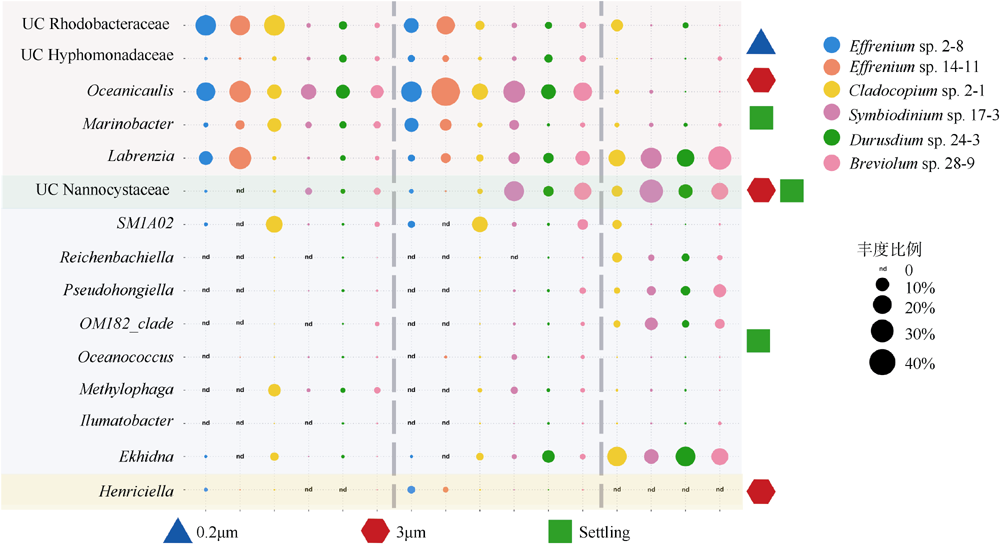
Fig. 7
Comparing the core genera in 0.2μm, 3μm, and Settling samples of 6 zooxanthellae strains. Four different colored area blocks correspond to 4 types of core genera, from top to bottom: core genera of 0.2 μm, 3 μm and Settling samples; core genera of 3μm and Settling samples; core genera of Settling samples; core genera of 3μm samples"
| [1] | 李淑, 余克服, 陈天然, 等, 2011. 珊瑚共生虫黄藻密度的季节变化及其与珊瑚白化的关系——以大亚湾石珊瑚为例[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(2): 39-45. |
|
LI SHU, YU KEFU, CHEN TIANRAN, et al, 2011. Seasonal patterns of densities of symbiotic zooxanthellae in scleractinian corals from Daya Bay, northern South China Sea, and relation to coral bleaching[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 30(2): 39-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.02.039 |
|
| [2] | 吴家法, 李洁, 张偲, 2015. 鹿回头岸礁区4种造礁珊瑚中可培养细菌的多样性[J]. 广东农业科学, 42(2): 146-151. |
| WU JIAFA, LI JIE, ZHANG SI, 2015. Diversity of culturable bacteria associated with four scleractinian corals located in Luhuitou fringing reef[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 42(2): 146-151. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [3] | 张增虎, 唐丽丽, 张永雨, 2018. 海洋中藻菌相互关系及其生态功能[J]. 微生物学通报, 45(9): 2043-2053. |
| ZHANG ZENGHU, TANG LILI, ZHANG YONGYU, 2018. Algae-bacteria interactions and their ecological functions in the ocean[J]. Microbiology China, 45(9): 2043-2053. (in Chinese with English abstract) | |
| [4] |
AINSWORTH T D, KRAUSE L, BRIDGE T, et al, 2015. The coral core microbiome identifies rare bacterial taxa as ubiquitous endosymbionts[J]. The ISME Journal, 9(10): 2261-2274.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.39 |
| [5] |
ALTSCHUL S F, GISH W, MILLER W, et al, 1990. Basic local alignment search tool[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 215(3): 403-410.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2 pmid: 2231712 |
| [6] |
AMIN S A, GREEN D H, HART M C, et al, 2009. Photolysis of iron-siderophore chelates promotes bacterial-algal mutualism[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(40): 17071-17076.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905512106 pmid: 19805106 |
| [7] |
BANASZAK A T, LAJEUNESSE T C, TRENCH R K, 2000. The synthesis of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) by cultured, symbiotic dinoflagellates[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 249(2): 219-233.
pmid: 10841936 |
| [8] |
BAYER T, NEAVE M J, ALSHEIKH-HUSSAIN A, et al, 2013. The microbiome of the red sea coral Stylophora pistillata is dominated by tissue-associated Endozoicomonas bacteria[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(15): 4759-4762.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.00695-13 |
| [9] |
BEHRINGER G, OCHSENKÜHN M A, FEI CONG, et al, 2018. Bacterial communities of diatoms display strong conservation across strains and time[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9: 659.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00659 pmid: 29681892 |
| [10] |
BLACKALL L L, WILSON B, VAN OPPEN M J H, 2015. Coral—the world's most diverse symbiotic ecosystem[J]. Molecular Ecology, 24(21): 5330-5347.
doi: 10.1111/mec.13400 |
| [11] |
BLANK R J, HUSS V A R, 1989. DNA divergency and speciation in Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae)[J]. Plant Systematics and Evolution, 163(3): 153-163.
doi: 10.1007/BF00936511 |
| [12] |
BLANK R J, TRENCH R K, 1985. Speciation and symbiotic dinoflagellates[J]. Science, 229(4714): 656-658.
pmid: 17739379 |
| [13] |
BOLYEN E, RIDEOUT J R, DILLON M R, et al, 2019. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 37(8): 852-857.
doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9 pmid: 31341288 |
| [14] |
BONGAERTS P, RIGINOS C, RIDGWAY T, et al, 2010. Genetic divergence across habitats in the widespread coral Seriatopora hystrix and its associated Symbiodinium[J]. PLoS One, 5(5): e10871.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010871 |
| [15] |
BOSCH T C G, 2013. Cnidarian-microbe interactions and the origin of innate immunity in metazoans[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 67: 499-518.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-092412-155626 pmid: 23808329 |
| [16] |
BOURNE D, IIDA Y, UTHICKE S, et al, 2008. Changes in coral-associated microbial communities during a bleaching event[J]. The ISME Journal, 2(4): 350-363.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2007.112 |
| [17] |
BOURNE D G, MORROW K M, WEBSTER N S, 2016. Insights into the coral microbiome: underpinning the health and resilience of reef ecosystems[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 70: 317-340.
doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095440 pmid: 27482741 |
| [18] |
CAMP E F, KAHLKE T, NITSCHKE M R, et al, 2020. Revealing changes in the microbiome of Symbiodiniaceae under thermal stress[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 22(4): 1294-1309.
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14935 pmid: 31997503 |
| [19] |
CURSON A R J, LIU JI, MARTÍNEZ A B, et al, 2017. Dimethylsulfoniopropionate biosynthesis in marine bacteria and identification of the key gene in this process[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2(5): 17009.
doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.9 pmid: 28191900 |
| [20] |
EIGEMANN F, HILT S, SALKA I, et al, 2013. Bacterial community composition associated with freshwater algae: species specificity vs. dependency on environmental conditions and source community[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 83(3): 650-663.
doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12022 pmid: 23030046 |
| [21] |
FREUDENTHAL H D, 1962. Symbiodinium gen. nov. and Symbiodinium microadriaticum sp. nov., a zooxanthella: taxonomy, life cycle, and morphology[J]. The Journal of Protozoology, 9(1): 45-52.
doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1962.tb02579.x |
| [22] | FROMMLET J C, SOUSA M L, ALVES A, et al, 2015. Coral symbiotic algae calcify ex hospite in partnership with bacteria[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(19): 6158-6163. |
| [23] |
GARDNER S G, RAINA J B, NITSCHKE M R, et al, 2017. A multi-trait systems approach reveals a response cascade to bleaching in corals[J]. BMC Biology, 15(1): 117.
doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0459-2 pmid: 29216891 |
| [24] |
GARREN M, WALSH S M, CACCONE A, et al, 2006. Patterns of association between Symbiodinium and members of the Montastraea annularis species complex on spatial scales ranging from within colonies to between geographic regions[J]. Coral Reefs, 25(4): 503-512.
doi: 10.1007/s00338-006-0146-1 |
| [25] |
GORDON B R, LEGGAT W, 2010. Symbiodinium-invertebrate symbioses and the role of metabolomics[J]. Marine Drugs, 8(10): 2546-2568.
doi: 10.3390/md8102546 pmid: 21116405 |
| [26] |
GROSSART H P, LEVOLD F, ALLGAIER M, et al, 2005. Marine diatom species harbour distinct bacterial communities[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 7(6): 860-873.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00759.x |
| [27] |
GROTTOLI A G, MARTINS P D, WILKINS M J, et al, 2018. Coral physiology and microbiome dynamics under combined warming and ocean acidification[J]. PLoS One, 13(1): e0191156.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191156 |
| [28] |
GUIDI F, PEZZOLESI L, VANUCCI S, 2018. Microbial dynamics during harmful dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata growth: bacterial succession and viral abundance pattern[J]. MicrobiologyOpen, 7(4): e00584.
doi: 10.1002/mbo3.584 |
| [29] |
HERNANDEZ-AGREDA A, GATES R D, AINSWORTH T D, 2017. Defining the core microbiome in corals' microbial soup[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 25(2): 125-140.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.11.003 |
| [30] |
HIROSE M, REIMER J D, HIDAKA M, et al, 2008. Phylogenetic analyses of potentially free-living Symbiodinium spp. isolated from coral reef sand in Okinawa, Japan[J]. Marine Biology, 155(1): 105-112.
doi: 10.1007/s00227-008-1011-2 |
| [31] |
ISHIKURA M, HAGIWARA K, TAKISHITA K, et al, 2004. Isolation of new Symbiodinium strains from tridacnid giant clam (Tridacna crocea) and sea slug (Pteraeolidia ianthina) using culture medium containing giant clam tissue homogenate[J]. Marine Biotechnology, 6(4): 378-385.
doi: 10.1007/s10126-004-1800-7 |
| [32] |
JEONG H J, YOO Y D, KANG N S, et al, 2012. Heterotrophic feeding as a newly identified survival strategy of the dinoflagellate Symbiodinium[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109(31): 12604-12609.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204302109 |
| [33] |
KIMBREL J A, SAMO T J, WARD C, et al, 2019. Host selection and stochastic effects influence bacterial community assembly on the microalgal phycosphere[J]. Algal Research, 40: 101489.
doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2019.101489 |
| [34] |
KROHN-MOLT I, ALAWI M, FÖRSTNER K U, et al, 2017. Insights into microalga and bacteria interactions of selected phycosphere biofilms using metagenomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic approaches[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 1941.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01941 |
| [35] |
KUMAR S, STECHER G, LI M, et al, 2018. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 35(6): 1547-1549.
doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096 pmid: 29722887 |
| [36] |
LAJEUNESSE T C, BHAGOOLI R, HIDAKA M, et al, 2004. Closely related Symbiodinium spp. differ in relative dominance in coral reef host communities across environmental, latitudinal and biogeographic gradients[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 284: 147-161.
doi: 10.3354/meps284147 |
| [37] |
LAJEUNESSE T C, PARKINSON J E, GABRIELSON P W, et al, 2018. Systematic revision of Symbiodiniaceae highlights the antiquity and diversity of coral endosymbionts[J]. Current Biology, 28(16): 2570-2580.e6.
doi: S0960-9822(18)30907-2 pmid: 30100341 |
| [38] |
LAWSON C A, RAINA J B, KAHLKE T, et al, 2018. Defining the core microbiome of the symbiotic dinoflagellate, Symbiodinium[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 10(1): 7-11.
doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12599 |
| [39] |
LI JIE, CHEN QI, LONG LIJUAN, et al, 2014. Bacterial dynamics within the mucus, tissue and skeleton of the coral Porites lutea during different seasons[J]. Scientific Reports, 4: 7320.
doi: 10.1038/srep07320 |
| [40] |
LIU MIN, LIU LEMIAN, CHEN HUIHUANG, et al, 2019. Community dynamics of free-living and particle-attached bacteria following a reservoir Microcystis bloom[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 660: 501-511.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.414 |
| [41] |
MAIRE J, GIRVAN S K, BARKLA S E, et al, 2021. Intracellular bacteria are common and taxonomically diverse in cultured and in hospite algal endosymbionts of coral reefs[J]. The ISME Journal, 15(7): 2028-2042.
doi: 10.1038/s41396-021-00902-4 |
| [42] |
MATTHEWS J L, RAINA J B, KAHLKE T, et al, 2020. Symbiodiniaceae-bacteria interactions: rethinking metabolite exchange in reef-building corals as multi-partner metabolic networks[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 22(5): 1675-1687.
doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14918 pmid: 31943674 |
| [43] |
MIZUYAMA M, IGUCHI A, IIJIMA M, et al, 2020. Comparison of Symbiodiniaceae diversities in different members of a Palythoa species complex (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Zoantharia)—implications for ecological adaptations to different microhabitats[J]. PeerJ, 8: e8449.
doi: 10.7717/peerj.8449 |
| [44] |
MÖNNICH J, TEBBEN J, BERGEMANN J, et al, 2020. Niche-based assembly of bacterial consortia on the diatom Thalassiosira rotula is stable and reproducible[J]. The ISME Journal, 14(6): 1614-1625.
doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-0631-5 |
| [45] |
MOORE R B, FERGUSON K M, LOH W K W, et al, 2003. Highly organized structure in the non-coding region of the psbA minicircle from clade C Symbiodinium[J]. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 53(Pt 6): 1725-1734.
doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02594-0 |
| [46] |
MORROW K M, MOSS A G, CHADWICK N E, et al, 2012. Bacterial associates of two Caribbean coral species reveal species-specific distribution and geographic variability[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(18): 6438-6449.
doi: 10.1128/AEM.01162-12 pmid: 22773636 |
| [47] | MOTONE K, TAKAGI T, ABURAYA S, et al, 2020. A zeaxanthin-producing bacterium isolated from the algal phycosphere protects coral endosymbionts from environmental stress[J]. mBio, 11(1): e01019-19. |
| [48] |
MUSCATINE L, PORTER J W, 1977. Reef corals: mutualistic symbioses adapted to nutrient-poor environments[J]. BioScience, 27(7): 454-460.
doi: 10.2307/1297526 |
| [49] | MUSCATINE L, 1990. The role of symbiotic algae in carbon and energy flux in reef corals[J]. Ecosystems of the World, 25: 75-87. |
| [50] |
NEAVE M J, RACHMAWATI R, XUN LIPING, et al, 2017. Differential specificity between closely related corals and abundant Endozoicomonas endosymbionts across global scales[J]. The ISME Journal, 11(1): 186-200.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.95 |
| [51] |
NG T Y, ANG P, 2016. Low symbiont diversity as a potential adaptive strategy in a marginal non-reefal environment: a case study of corals in Hong Kong[J]. Coral Reefs, 35(3): 941-957.
doi: 10.1007/s00338-016-1458-4 |
| [52] |
NISSIMOV J, ROSENBERG E, MUNN C B, 2009. Antimicrobial properties of resident coral mucus bacteria of Oculina patagonica[J]. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 292(2): 210-215.
doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01490.x |
| [53] |
POCHON X, PAWLOWSKI J, ZANINETTI L, et al, 2001. High genetic diversity and relative specificity among Symbiodinium-like endosymbiotic dinoflagellates in soritid foraminiferans[J]. Marine Biology, 139(6): 1069-1078.
doi: 10.1007/s002270100674 |
| [54] |
POCHON X, GATES R D, 2010. A new Symbiodinium clade (Dinophyceae) from soritid foraminifera in Hawai’i[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 56(1): 492-497.
doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.03.040 |
| [55] |
POOTAKHAM W, MHUANTONG W, YOOCHA T, et al, 2021. Taxonomic profiling of Symbiodiniaceae and bacterial communities associated with Indo-Pacific corals in the Gulf of Thailand using PacBio sequencing of full-length ITS and 16S rRNA genes[J]. Genomics, 113(4): 2717-2729.
doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.06.001 pmid: 34089786 |
| [56] |
QIN ZHENJUN, YU KEFU, CHEN BIAO, et al, 2019. Diversity of Symbiodiniaceae in 15 coral species from the southern South China sea: potential relationship with coral thermal adaptability[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 10: 2343.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02343 pmid: 31681208 |
| [57] |
QUAST C, PRUESSE E, YILMAZ P, et al, 2013. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 41(D1): D590-D596.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1219 |
| [58] |
RÄDECKER N, POGOREUTZ C, VOOLSTRA C R, et al, 2015. Nitrogen cycling in corals: the key to understanding holobiont functioning?[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 23(8): 490-497.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2015.03.008 pmid: 25868684 |
| [59] |
RAINA J B, DINSDALE E A, WILLIS B L, et al, 2010. Do the organic sulfur compounds DMSP and DMS drive coral microbial associations?[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 18(3): 101-108.
doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.12.002 |
| [60] |
REICHMAN J R, VIZE P D, 2014. Separate introns gained within short and long soluble peridinin-chlorophyll a-protein genes during radiation of Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae) clade A and B lineages[J]. PLoS One, 9(10): e110608.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110608 |
| [61] |
RODRIGUEZ-LANETTY M, KRUPP D A, WEIS V M, 2004. Distinct ITS types of Symbiodinium in Clade C correlate with cnidarian/dinoflagellate specificity during onset of symbiosis[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 275: 97-102.
doi: 10.3354/meps275097 |
| [62] |
ROHWER F, BREITBART M, JARA J, et al, 2001. Diversity of bacteria associated with the Caribbean coral Montastraea franksi[J]. Coral Reefs, 20(1): 85-91.
doi: 10.1007/s003380100138 |
| [63] |
ROHWER F, SEGURITAN V, AZAM F, et al, 2002. Diversity and distribution of coral-associated bacteria[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 243: 1-10.
doi: 10.3354/meps243001 |
| [64] |
ROWAN R, POWERS D A, 1991. Molecular genetic identification of symbiotic dinoflagellates (zooxanthellae)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress, 71(1): 65-73.
doi: 10.3354/meps071065 |
| [65] |
SAKAMOTO T, BRYANT D A, 1997. Growth at low temperature causes nitrogen limitation in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 169(1): 10-19.
doi: 10.1007/s002030050535 |
| [66] | SCHOENBERG D A, TRENCH R K, 1980. Genetic variation in Symbiodinium (= Gymnodinium) microadriaticum Freudenthal, and specificity in its symbiosis with marine invertebrates. Ⅲ. Specificity and inlfectivity of Symbiodinium microadriaticum[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 207(1169): 445-460. |
| [67] |
SEYMOUR J R, AMIN S A, RAINA J B, et al, 2017. Zooming in on the phycosphere: the ecological interface for phytoplankton-bacteria relationships[J]. Nature Microbiology, 2(7): 17065.
doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.65 pmid: 28555622 |
| [68] |
SHADE A, HANDELSMAN J, 2012. Beyond the Venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 14(1): 4-12.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02585.x pmid: 22004523 |
| [69] |
SHARP K H, DISTEL D, PAUL V J, 2012. Diversity and dynamics of bacterial communities in early life stages of the Caribbean coral Porites astreoides[J]. The ISME Journal, 6(4): 790-801.
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2011.144 |
| [70] | SHARPE G C, GIFFORD S M, SEPTER A N, 2020. A model Roseobacter, Ruegeria pomeroyi DSS-3, employs a diffusible killing mechanism to eliminate competitors[J]. mSystems, 5(4): e00443-20. |
| [71] |
SHI TUO, NIU GAOFENG, KVITT H, et al, 2021. Untangling ITS2 genotypes of algal symbionts in zooxanthellate corals[J]. Molecular Ecology Resources, 21(1): 137-152.
doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13250 |
| [72] | SPALDING M D, RAVILIOUS C, GREEN E P, 2001. World atlas of coral reefs[M]. Berkeley: University of California Press. |
| [73] |
SUBRAMANIAN B, GAO SHENGHAN, LERCHER M J, et al, 2019. Evolview v3: a webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 47(W1): W270-W275.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz357 |
| [74] |
SUNDA W, KIEBER D J, KIENE R P, et al, 2002. An antioxidant function for DMSP and DMS in marine algae[J]. Nature, 418(6895): 317-320.
doi: 10.1038/nature00851 |
| [75] |
TAKABAYASHI M, SANTOS S R, COOK C B, 2004. Mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of the symbiotic dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium, Dinophyta)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 40(1): 160-164.
doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3646.2003.03-097.x |
| [76] |
TRENCH R K, THINH L V, 1995. Gymnodinium linucheae sp. nov.: the dinoflagellate symbiont of the jellyfish Linuche unguiculata[J]. European Journal of Phycology, 30(2): 149-154.
doi: 10.1080/09670269500650911 |
| [77] |
TURNBAUGH P J, LEY R E, HAMADY M, et al, 2007. The human microbiome project[J]. Nature, 449(7164): 804-810.
doi: 10.1038/nature06244 |
| [78] |
VAN OPPEN M J H, PALSTRA F P, PIQUET A M T, et al, 2001. Patterns of coral-dinoflagellate associations in Acropora: significance of local availability and physiology of Symbiodinium strains and host-symbiont selectivity[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 268(1478): 1759-1767.
doi: 10.1098/rspb.2001.1733 |
| [79] |
WAGNER-DÖBLER I, BIEBL H, 2006. Environmental biology of the marine Roseobacter lineage[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology, 60: 255-280.
doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.60.080805.142115 |
| [80] | WALTERS W, HYDE E R, BERG-LYONS D, et al, 2015. Improved bacterial 16S rRNA gene (V4 and V4-5) and fungal internal transcribed spacer marker gene primers for microbial community surveys[J]. mSystems, 1(1): e00009-15. |
| [81] |
WEGLEY L, EDWARDS R, RODRIGUEZ-BRITO B, et al, 2007. Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community associated with the coral Porites astreoides[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 9(11): 2707-2719.
doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01383.x |
| [82] |
XIANG TINGTING, HAMBLETON E A, DENOFRIO J C, et al, 2013. Isolation of clonal axenic strains of the symbiotic dinoflagellate Symbiodinium and their growth and host specificity[J]. Journal of Phycology, 49(3): 447-458.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.12055 |
| [83] |
YANG FANGFANG, LONG CHAO, WEI ZHANGLIANG, et al, 2020. Optimization of medium using response surface methodology to enhance the growth of Effrenium voratum (Symbiodiniaceae, Dinophyceae)[J]. Journal of Phycology, 56(5): 1208-1215.
doi: 10.1111/jpy.13007 |
| [84] |
YANG QINGSONG, ZHANG YING, AHMAD M, et al, 2021. Microbial community structure shifts and potential Symbiodinium partner bacterial groups of bleaching coral Pocillopora verrucosa in South China Sea[J]. Ecotoxicology, 30(5): 966-974.
doi: 10.1007/s10646-021-02380-y |
| [85] |
ZHAO MEIXIA, YU KEFU, ZHANG QIAOMIN, et al, 2012. Long-term decline of a fringing coral reef in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 28(5): 1088-1099.
doi: 10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-10-00172.1 |
| [86] |
ZHOU GUOWEI, HUANG HUI, 2011. Low genetic diversity of symbiotic dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium) in scleractinian corals from tropical reefs in southern Hainan Island, China[J]. Journal of Systematics and Evolution, 49(6): 598-605.
doi: 10.1111/j.1759-6831.2011.00161.x |
| [87] |
ZHOU GUOWEI, HUANG HUI, LIAN JIANSHENG, et al, 2012. Habitat correlation of Symbiodinium diversity in two reef-building coral species in an upwelling region, eastern Hainan Island, China[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 92(6): 1309-1316.
doi: 10.1017/S0025315411001548 |
| [88] |
ZHOU GUOWEI, CAI LIN, LI YUANCHAO, et al, 2017. Temperature-driven local acclimatization of Symbiodnium hosted by the coral Galaxea fascicularis at Hainan Island, China[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 8: 2487.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02487 |
| [1] | SUN Manman, ZENG Yanbo, XU Han, YAO Ligong, GUO Yuewei, SU Mingzhi. Chemical composition and antibacterial activities of the soft coral Lobophytum sp. from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 189-197. |
| [2] | MO Danyang, NING Zhiming, YANG Bin, XIA Ronglin, LIU Zhijin. Response of dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in coral reef sediments of the Weizhou island to temperature changes [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [3] | JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [4] | JIA Nan, ZHOU Tiancheng, HU Simin, ZHANG Chen, HUANG Hui, LIU Sheng. Difference in the feeding contents of three hermit crabs in the coral reefs of the Nansha Islands, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 109-121. |
| [5] | PENG Erman, YAO Yu, LI Zhuangzhi, XU Conghao. Numerical study of the hydrodynamic characteristics of reef coast under the combined effects of waves and currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 187-194. |
| [6] | LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [7] | HUANG Hui, YUAN Xiangcheng, SONG Yan, LI Yingxin, ZHOU Weihua, LONG Aimin. Carbon sequestration process and carbon storage mechanism of reef ecosystem in South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 13-21. |
| [8] | WANG Yongzhi, XU Lijia, HUANG Baiqiang, YANG Tianjian, QI Shibin, CHEN Hui, YANG Jing. Physiological responses to light limitation of reef-building corals in the Yongle Atoll of the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 31-39. |
| [9] | HUANG Hui, YU Xiaolei, HUANG Lintao, JIANG Lei. Current status and prospects of coral reef ecology research [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 3-12. |
| [10] | GAO Jie, YU Kefu, XU Shendong, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Biao, WANG Yonggang. Content and source analysis of organic carbon in the outer slope sediments of the Yongle Atoll, Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yuyang, LIU Chengyue, YU Xiaolei, LUO Yong, ZHOU Tiancheng, LIAN Jiansheng, HUANG Hui. Study on relocation effect of scleractinian coral in the Fenghuang Island, Sanya* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 177-186. |
| [12] | LEI Mingfeng, YU Kefu, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Biao, HUANG Xueyong, CHEN Xiaoyan. The rapid ecological degradation and its impact on fish of the Yinyu Island in the Xisha Islands [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 87-99. |
| [13] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [14] | LIANG Yuxian, LIU Chengyue, YU Xiaolei, ZHANG Yuyang, LIAN Wenke, CHEN Lunju, HUANG Hui. Focusing on supplementing and restoring degraded coral reefs with key groups of reef-building coral - paradigms in the restoration of Xidao Island’s coral reef [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 166-176. |
| [15] | ZHAO Jinfa, LIU Yong, LI Chunhou, WANG Teng, SHI Juan, XIAO Yayuan, WU Peng, SONG Xiaoyu. Study on species composition and distribution of fish eggs in Yongle Atoll and Dongdao Island by high-throughput sequencing technology [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 127-136. |
|
||