Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2025, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 18-29.doi: 10.11978/2024095CSTR: 32234.14.2024095
• Marine Hydrology • Previous Articles Next Articles
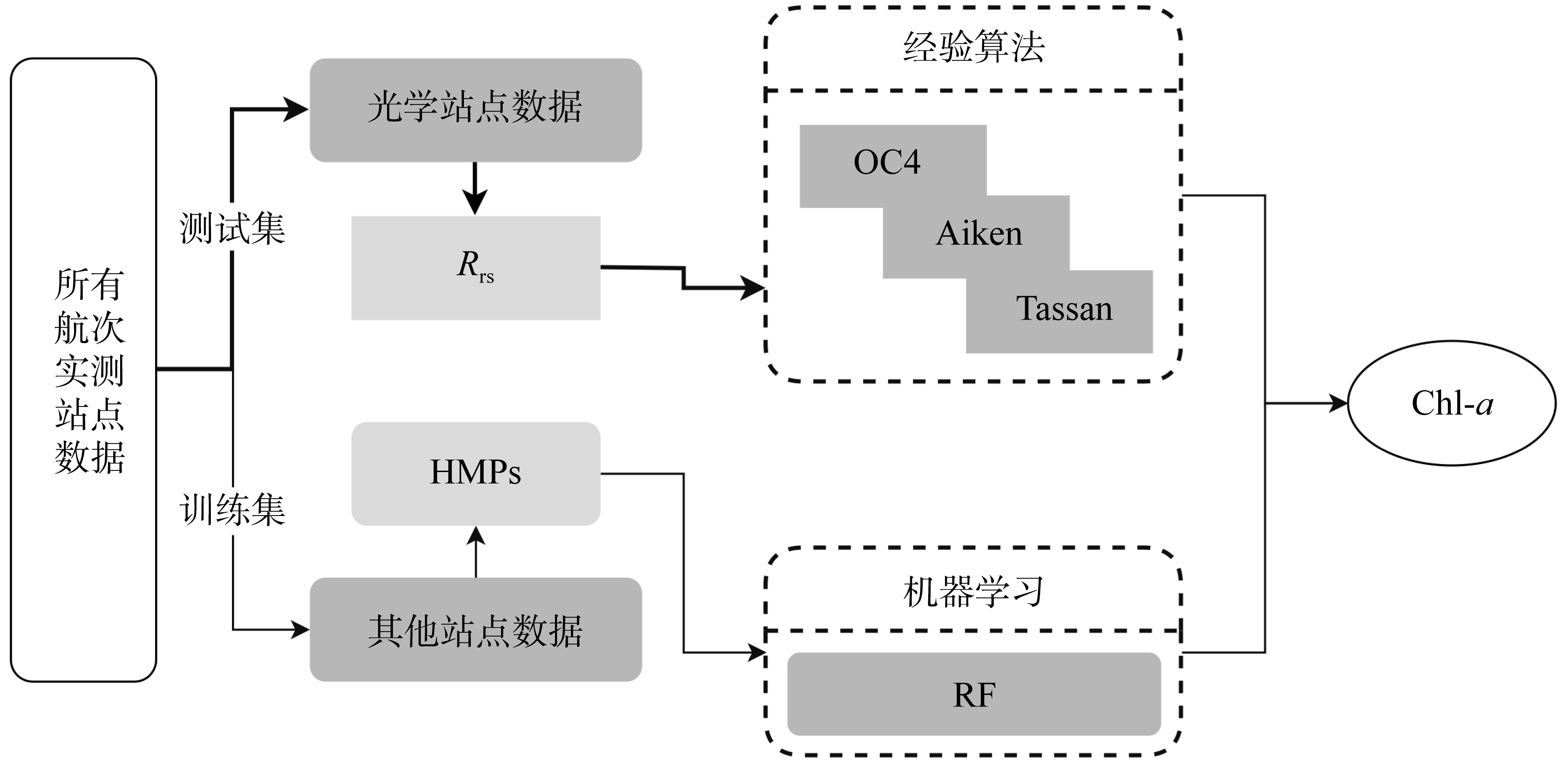
Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in the western South China Sea based on hydro-meteorological parameters*
ZHENG Yuanning1,2( ), LI Cai1(
), LI Cai1( ), ZHOU Wen1, XU Zhantang1, SHI Zhen1, ZHANG Xianqing1,2, LIU Cong1,2, ZHAO Jincheng1,2
), ZHOU Wen1, XU Zhantang1, SHI Zhen1, ZHANG Xianqing1,2, LIU Cong1,2, ZHAO Jincheng1,2
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Tropical Oceanography (South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2024-04-26Revised:2024-06-19Online:2025-03-10Published:2025-04-11 -
Contact:LI Cai -
Supported by:Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation(2023A1515240073); Science and Technology Planning Project of Science and Technology Planning Project of Nansha District, Guangzhou(2022ZD001); National Key Research and Development Program of China(2016YFC1400603); National Key Research and Development Program of China(2017YFC0506305)
CLC Number:
- P731.3
Cite this article
ZHENG Yuanning, LI Cai, ZHOU Wen, XU Zhantang, SHI Zhen, ZHANG Xianqing, LIU Cong, ZHAO Jincheng. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in the western South China Sea based on hydro-meteorological parameters*[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(2): 18-29.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
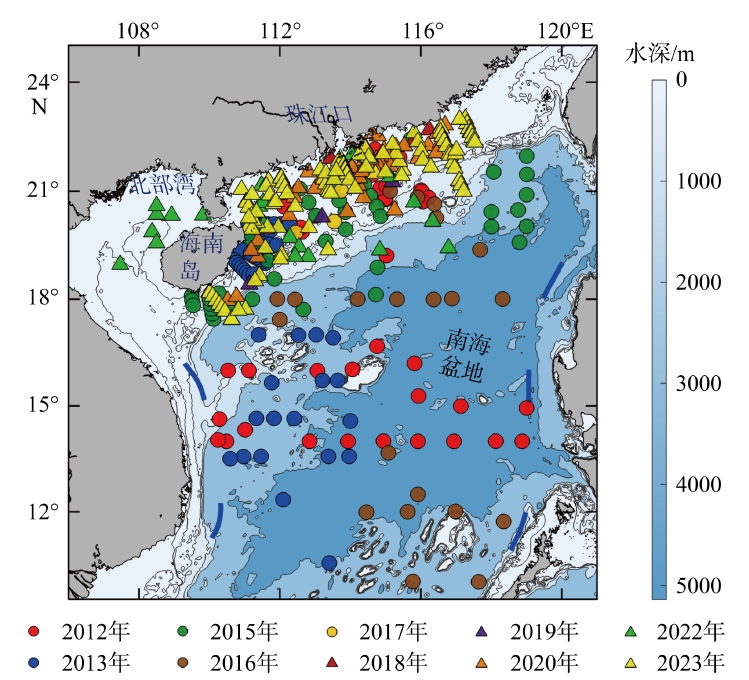
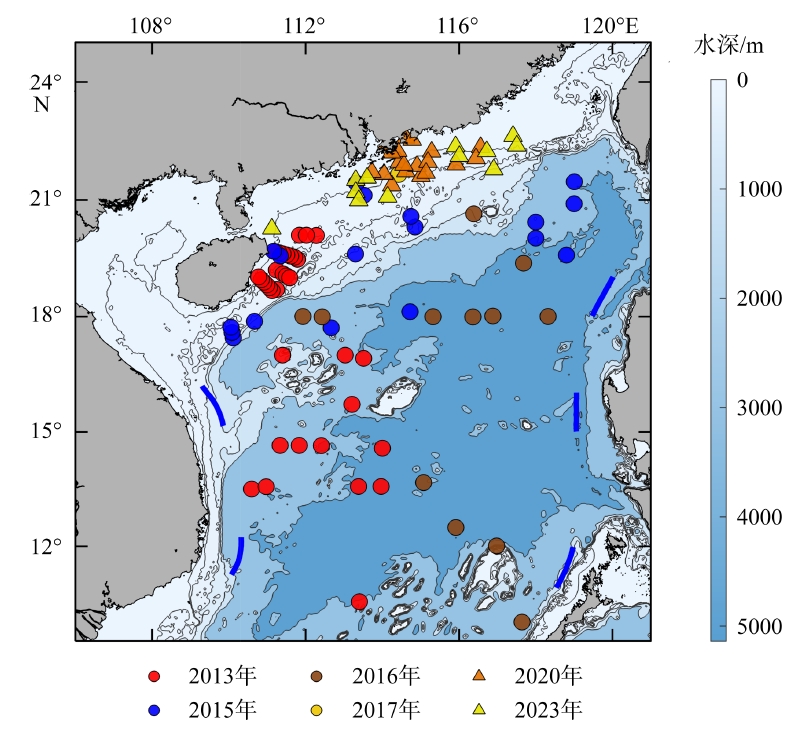
Tab. 1
A summary of the information collected from 2012 to 2023 on 12 cruises"
| 年份 | 数据采集时间 | 覆盖范围 | 站点数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 9月30日—10月25日 | 14°00′—22°12′N, 110°12′—119°00′E | 37 |
| 2013 | 8月9日—9月2日 | 10°00′—20°06′N, 110°30′—114°00′E | 61 |
| 2015 | 6月21日—7月17日 | 17°24′—22°30′N, 109°30′—119°00′E | 43 |
| 2016 | 9月3日—9月23日 | 10°00′—21°00′N, 111°30′—119°00′E | 23 |
| 2017 | 10月1日—10月23日 | 18°24′—21°54′N, 110°18′—114°54′E | 4 |
| 2018 | 6月12日—6月22日 | 21°30′—23°06′N, 113°12′—116°54′E | 7 |
| 8月18日—8月25日 | 17°54′—21°18′N, 110°36′—115°18′E | 1 | |
| 2019 | 9月27日—10月5日 | 17°42′—23°00′N, 110°30′—117°06′E | 3 |
| 2020 | 8月28日—9月4日 | 18°42′—22°00′N, 107°24′—117°00′E | 32 |
| 6月1日—6月29日 | 17°24′—23°06′N, 110°00′—117°36′E | 22 | |
| 2022 | 8月14日—6月22 日 | 14°00′—22°24′N, 110°12′—119°00′E | 27 |
| 2023 | 6月23日—7月20日 | 10°00′—20°06′N, 110°30′—114°00′E | 129 |
| [1] |
李建鸿, 黄昌春, 查勇, 等, 2021. 长江干流表层水体悬浮物的空间变化特征及遥感反演[J]. 环境科学, 42(11): 5239-5249.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
柳青青, 孟朔羽, 徐茗, 等, 2021. 随机森林反演卫星遥感海表面盐度研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 48(9): 1538-1545.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
王春玲, 史锴源, 明星, 等, 2022. 基于机器学习的水体化学需氧量高光谱反演模型对比研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 42(8): 2353-2358.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
张莹, 谢仕义, 邓伟彬, 等, 2019. 基于机器学习理论的海洋水质评价模型[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 41(6): 819-825.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
doi: 10.1007/s10661-023-11492-3 pmid: 37354319 |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39507-0 pmid: 37355684 |
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
doi: 10.1364/AO.33.002369 pmid: 20885588 |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
doi: 10.1007/s11707-016-0585-0 |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
doi: 10.1364/OE.503850 pmid: 38178466 |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [1] | LIU Jie, YAN Tong, JING Zhiyou. Observations of near-inertial waves generated by three successive typhoons in the northwestern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2025, 44(1): 66-81. |
| [2] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 3. data sharing service and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 158-165. |
| [3] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, HE Yunkai, YUAN Li, XU Xiaolu. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 1. data reorganization technology and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 143-149. |
| [4] | XU Chao, LONG Lijuan, LI Sha, XU Xiaolu, YUAN Li. Systematic reorganization of historical data of scientific investigation in the South China Sea and its affiliated islands and reefs 2. data curation and application [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 150-157. |
| [5] | QI Huandong, ZHU Cheng, LI Xuchun, JING Xindi, SONG Derui. Rule set and multilayer perceptron based quality control method for Argo temperature data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 190-202. |
| [6] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [7] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [8] | JIANG Lyumiao, CHEN Tianran, ZHAO Kuan, ZHANG Ting, XU Lijia. Experimental study on bioerosion of marginal reefs in the Weizhou Island, northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 155-165. |
| [9] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [10] | ZHAO Minghui, YUAN Ye, ZHANG Jiazheng, ZHANG Cuimei, GAO Jinwei, WANG Qiang, SUN Zhen, CHENG Jinhui. New developments on the rift-breakup of the continent-ocean transition zone in the northern margin of the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 173-183. |
| [11] | HUANG Yu, WANG Lin, MAI Zhimao, LI Jie, ZHANG Si. Isolation and characterization of sand fixation ability of bacteria in biological soil crusts of the tropical islands, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [12] | WANG Chenyan, SHI Jingwen, YAN Annan, KANG Yaru, WANG Yuxuan, QIN Suli, HAN Minwei, ZHANG Ruijie, YU Kefu. Bioaccumulation characteristics and source apportionment of organophosphate esters in Acanthaster planci from the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 30-37. |
| [13] | LI Niu, DI Pengfei, FENG Dong, CHEN Duofu. The impact of cold seepage on geochemical indices for redox conditions of marine sediments ―Site F active seep site in the northeastern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 144-153. |
| [14] | ZHANG Zhisheng, XIE Lingling, LI Junyi, LI Qiang. Comparative analysis of mesoscale eddy evolution during life cycle in marginal sea and open ocean: South China Sea and Kuroshio Extension [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 63-76. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xianqing, LI Cai, Zhou Wen, LIU Cong, XU Zhantang, CAO Wenxi, YANG Yuezhong. Studying on diffuse attenuation coefficient in the South China Sea based on volume scattering function and absorption coefficient* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 86-95. |
|
||