Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2017, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 72-80.doi: 10.11978/2016034CSTR: 32234.14.2016034
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
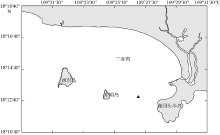
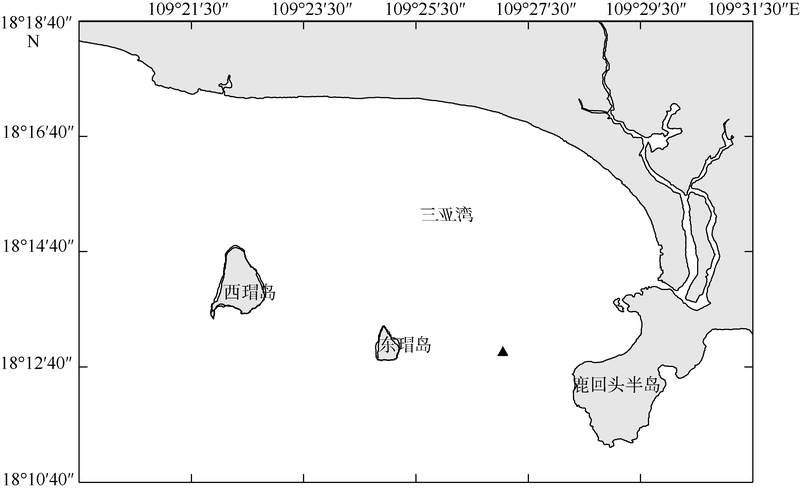
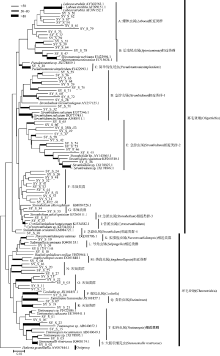
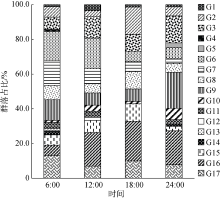
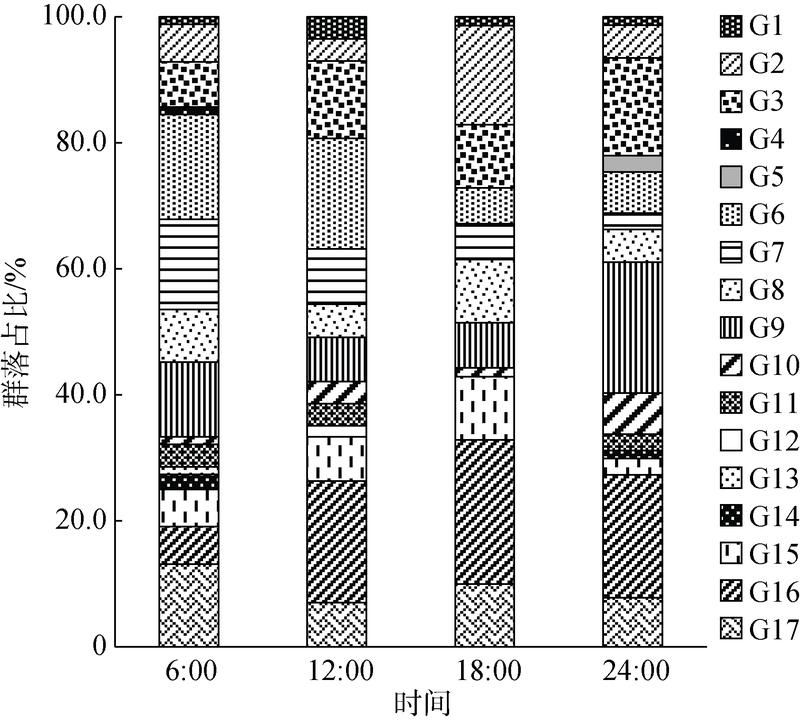
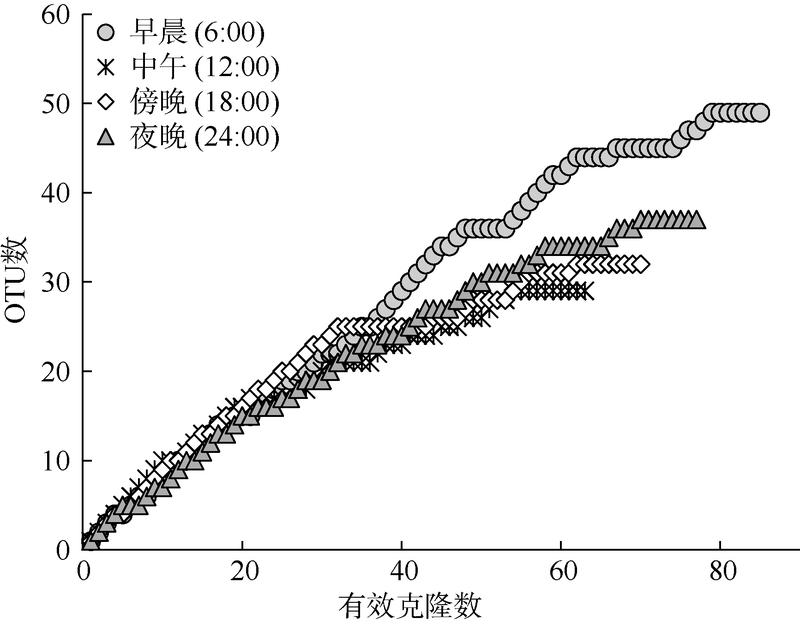
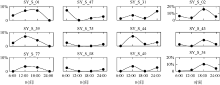
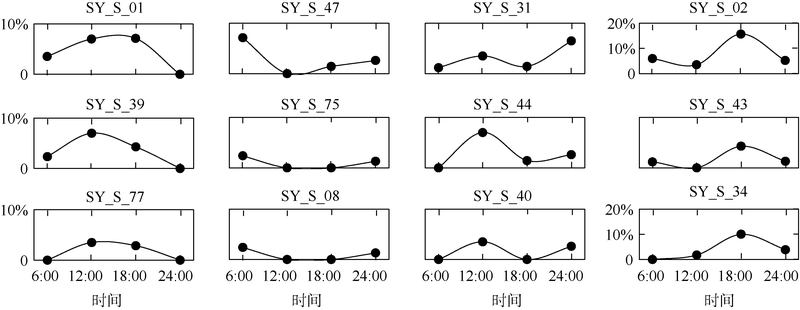
Diel variation of community structure of planktonic ciliates in coastal ecosystem of Sanya Bay
Youjun WANG1,2( ), Cuilian XU1,2, Simin HU1, Tao LI1,3, Sheng LIU1(
), Cuilian XU1,2, Simin HU1, Tao LI1,3, Sheng LIU1( )
)
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Tropical Marine Biological Research Station in Hainan, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Sanya 572000, China
-
Received:2016-04-05Revised:2016-05-13Online:2017-01-18Published:2017-01-19 -
Supported by:Strategic Priority Research Programof the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA13020102);National Natural Science Foundation of China (41276160);Science and Technology plan Projects of Guangdong Province (2015A020216013)
Cite this article
Youjun WANG, Cuilian XU, Simin HU, Tao LI, Sheng LIU. Diel variation of community structure of planktonic ciliates in coastal ecosystem of Sanya Bay[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(1): 72-80.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] | 苏强, 黄良民, 谭烨辉, 等, 2008. 三亚湾珊瑚礁海区微型浮游动物种群组成和摄食研究[J]. 海洋通报, 27(2): 28-36. |
| SU QIANG, HUANG LIANGMIN, TAN YEHUI, et al, 2008. Microzooplankton community composition and grazing pressure in coral reefs of Sanya Bay[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 27(2): 28-36 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 谭烨辉, 黄良民, 黄小平, 等, 2010. 三亚珊瑚礁水域纤毛虫种类组成和数量分布及与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学报, 30(24): 6835-6844. |
| TAN YEHUI, HUANG LIANGMIN, HUANG XIAOPING, et al, 2010. The relationships between ciliate composition, abundance, and environmental factors in Sanya Bay coral reef waters[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(24): 6835-6844 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 尹健强, 张谷贤, 黄良民, 等, 2004. 三亚湾浮游动物的昼夜垂直移动[J]. 热带海洋学报, 23(5): 25-33. |
| YIN JIANQINAG, ZHANG GUXIAN, HUANG LIANGMIN, et al, 2004. Diel vertical migration of zooplankton in Sanya bay, Hainan province, China[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 23(5): 25-33 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 张武昌, 张翠霞, 肖天, 2009. 海洋浮游生态系统中小型浮游动物的生态功能[J]. 地球科学进展, 24(11): 1195-1201. |
| ZHANG WUCHANG, ZHANG CUIXIA, XIAO TIAN, 2009. Role of microzooplankton in marine planktonic ecosystem[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 24(11): 1195-1201 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 郑重, 1986. 海洋浮游生物生态学文集[M]. 厦门: 厦门大学出版社: 86-95. |
| [6] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局,2008.GB/T 12763.6-2007 海洋调查规范第6部分:海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China(AQSIQ), 2008. GB/T 12763.6-2007 Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6:Marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: China Standard Publishing House (in Chinese). | |
| [7] | ALTSCHUL S F, MADDEN T L, SCHÄFFER A A, et al, 1997. Gapped blast and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 25(17): 3389-3402. |
| [8] | BOLLENS S M, FROST B W, 1991. Diel vertical migration in zooplankton: rapid individual response to predators[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 13(6): 1359-1365. |
| [9] | BULIT C, DÍAZ-AVALOS C, SIGNORET M, et al, 2003. Spatial structure of planktonic ciliate patches in a tropical coastal lagoon: an application of geostatistical methods[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 30(2): 185-196. |
| [10] | CALBET A, SAIZ E, 2005. The ciliate-copepod link in marine ecosystems[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 38(2): 157-167. |
| [11] | DOHERTY M, COSTAS B A, MCMANUS G B, et al, 2007. Culture-independent assessment of planktonic ciliate diversity in coastal northwest Atlantic waters[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 48(2): 141-154. |
| [12] | DOHERTY M, TAMURA M, COSTAS B A, et al, 2010. Ciliate diversity and distribution across an environmental and depth gradient in Long Island Sound, USA[J]. Environmental microbiology, 12(4): 886-898. |
| [13] | DOLAN J R, 1992. Mixotrophy in ciliates: a review of chlorella symbiosis and chloroplast retention[J]. Marine Microbial Food Webs, 6: 115-132. |
| [14] | FOISSNER W, 2008. Protist diversity and distribution: some basic considerations[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 17(2): 235-242. |
| [15] | FOISSNER W, CHAO A, KATZ L A, 2008. Diversity and geographic distribution of ciliates (Protista: Ciliophora)[J]. Biodiversity and Conservation, 17(2): 345-363. |
| [16] | GLIWICZ M Z, 1986. Predation and the evolution of vertical migration in zooplankton[J]. Nature, 320(6064): 746-748. |
| [17] | KAMIYAMA T, MATSUYAMA Y, 2005. Temporal changes in the ciliate assemblage and consecutive estimates of their grazing effect during the course of a Heterocapsa circularisquama bloom[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 27(4): 303-311. |
| [18] | KATZ L A, MCMANUS G B, SNOEYENBOS-WEST O L O, et al, 2005. Reframing the 'everything is everywhere' debate: evidence for high gene flow and diversity in ciliate morphospecies[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 41(1): 55-65. |
| [19] | MCLAREN I A, 1963. Effects of temperature on growth of zooplankton, and the adaptive value of vertical migration[J]. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada, 20(3): 685-727. |
| [20] | MODIGH M, CASTALDO S, 2005. Effects of fixatives on ciliates as related to cell size[J]. Journal of Plankton Research, 27(8): 845-849. |
| [21] | MONTAGNES D J S, LESSARD E J, 1999. Population dynamics of the marine planktonic ciliate Strombidinopsis multiauris: its potential to control phytoplankton blooms[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 20(2): 167-181. |
| [22] | OTA T, TANIGUCHI A, 2003. Standing crop of planktonic ciliates in the East China Sea and their potential grazing impact and contribution to nutrient regeneration[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 50(2): 423-442. |
| [23] | PÉREZ M T, DOLAN J R, VIDUSSI F, et al, 2000. Diel vertical distribution of planktonic ciliates within the surface layer of the NW Mediterranean (May 1995)[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 47(3): 479-503. |
| [24] | PIERCE R W, TURNER J T, 1992. Ecology of planktonic ciliates in marine food webs[J]. Reviews in Aquatic Sciences, 6(2): 139-181. |
| [25] | RHODE S C, PAWLOWSKI M, TOLLRIAN R, 2001. The impact of ultraviolet radiation on the vertical distribution of zooplankton of the genus Daphnia[J]. Nature, 412(6842): 69-72. |
| [26] | ROSETTA C H, MCMANUS G B, 2003. Feeding by ciliates on two harmful algal bloom species, Prymnesium parvum and Prorocentrum minimum[J]. Harmful Algae, 2(2): 109-126. |
| [27] | SEIBACH M, HADER D-P, KUHLMANN H-W, 1999. Phototaxis in Chlamydodon mnemosyne: Determination of the illuminance-response curve and the action spectrum[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology, 49(1): 35-40. |
| [28] | SHERR E B, SHERR B F, FALLON R D, et al, 1986. Small, aloricate ciliates as a major component of the marine heterotrophic nanoplankton[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 31(1): 177-183. |
| [29] | STOECKER D K, 1991. Mixotrophy in marine planktonic ciliates: physiological and ecological aspects of plastid-retention by oligotrichs[M]//REID P C, TURLEY C M, BURKILL P H. Protozoa and Their Role in Marine Processes. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer: 161-179. |
| [30] | STOECKER D K, MICHAELS A E, DAVIS L H, 1987. Large proportion of marine planktonic ciliates found to contain functional chloroplasts[J]. Nature, 326(6115): 790-792. |
| [31] | TAMURA M, KATZ L A, MCMANUS G B, 2011. Distribution and diversity of oligotrich and choreotrich ciliates across an environmental gradient in a large temperate estuary[J]. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 64(1): 51-67. |
| [32] | WILLIAMSON C E, SANDERS R W, MOELLER R E, et al, 1996. Utilization of subsurface food resources for zooplankton reproduction: implications for diel vertical migration theory[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 41(2): 224-233. |
| [33] | ZARET T M, SUFFERN J S, 1976. Vertical migration in zooplankton as a predator avoidance mechanism[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 21(6): 804-813. |
| [34] | ZHANG W, WANG R, 2000. Summertime ciliate and copepod nauplii distributions and micro-zooplankton herbivorous activity in the Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 51(1): 103-114. |
| [35] | ZHANG H, LIN S, 2005. Development of a cob-18S rRNA Gene Real-Time PCR Assay for Quantifying Pfiesteria shumwayae in the Natural Environment[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71(11): 7053-7063. |
| [1] | RAO Yiyong, ZHAO Meirong, KUANG Zexing, HUANG Honghui, TAN Erhui. Influence of raft-string oyster culture on the functional structure of macrobenthic communities: a case study in the Dapeng Cove* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(5): 69-83. |
| [2] | LIU Weiwei, WEN Shaowei, TAN Yehui. Progress in studies on diversity and ecological role of ciliates in mariculture [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 1-19. |
| [3] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [4] | XU Lijia, LIAO Zhiheng, CHEN Hui, WANG Yongzhi, HUANG Baiqiang, LIN Qiaoyun, GAN Jianfeng, YANG Jing. Community structure of scleractinian corals in the northern South China Sea and their responses to the marine heatwaves [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 58-71. |
| [5] | LI Cai, LIU Cong, ZHANG Xianqing, CHEN Fei, XIAO Zhihui, YANG Zeming, ZHENG Yuanning, ZHOU Wen, XU Zhantang. Development and Application of the Multiangle Volume Scattering and Attenuation Meter (VSAM)* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 1-11. |
| [6] | CHEN Junqiang, WANG Wenbo, WANG Qing, YANG Yufeng. Species diversity and habitat preference of bdelloid rotifers in the Weizhou island, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(2): 81-91. |
| [7] | HUANG Yu, WANG Lin, MAI Zhimao, LI Jie, ZHANG Si. Isolation and characterization of sand fixation ability of bacteria in biological soil crusts of the tropical islands, South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 101-110. |
| [8] | CHENG Xiawen, ZHANG Lanlan, QIU Zhuoya, XIANG Rong, CHANG Hu. Biodiversity, biogeography and seasonal variation of zooplankton Collodarians (Radiolaria) in surface waters from the northern Indian Ocean to the South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 97-112. |
| [9] | WANG Zihan, ZENG Cong, JIANG Ziyu, CAO Ling. Conservation gap analysis of threatened fish in the East China Sea and adjacent sea areas [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 66-86. |
| [10] | YE Jincheng, CHEN Yiqing, GAO Lin, ZHOU Xianjiao, ZHONG Cairong, ZHANG Ying, WANG Yun. Analysis of rhizosphere bacterial community characteristics of mangrove plant Sonneratia × gulngai and its parents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 75-89. |
| [11] | LI Cun, CUI Linqing, YANG Hongqiang, LONG Lijuan, TIAN Xinpeng. Diversity of cultured bacteria isolated from three coral reef sediments in South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 149-158. |
| [12] | LI Kaizhi, KE Zhixin, WANG Junxing, TAN Yehui. Preliminary study on the community structure of zooplankton in coral reef waters of Xisha Islands* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [13] | LU Chunju, LU Meilin, LIU Xinming, LIU Yonghong, GAO Chenghai, XU Xinya. Diversity and anti-bacteria activity of the gorgonian derived fungi from Weizhou Island of Guangxi Province* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 45-52. |
| [14] | ZOU Congcong, WANG Lijuan, WU Zhihao, YOU Feng. Population genetic structure of Japanese anchovy (Engraulis japonicus) in the Yellow Sea based on mitochondrial control region sequences* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 25-35. |
| [15] | REN Huimin, ZHANG Heng, XU Shasha, LI Shengfa, LI Jiansheng, LI Zhihong, HE Lijun. Population genetic structure and historical dynamics of Trachurus japonicus in the China seas based on mitochondrial control region [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 36-44. |
|
||