Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 52-58.doi: 10.11978/2018119CSTR: 32234.14.2018119
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
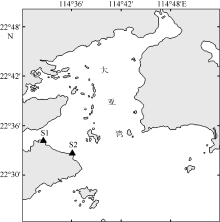
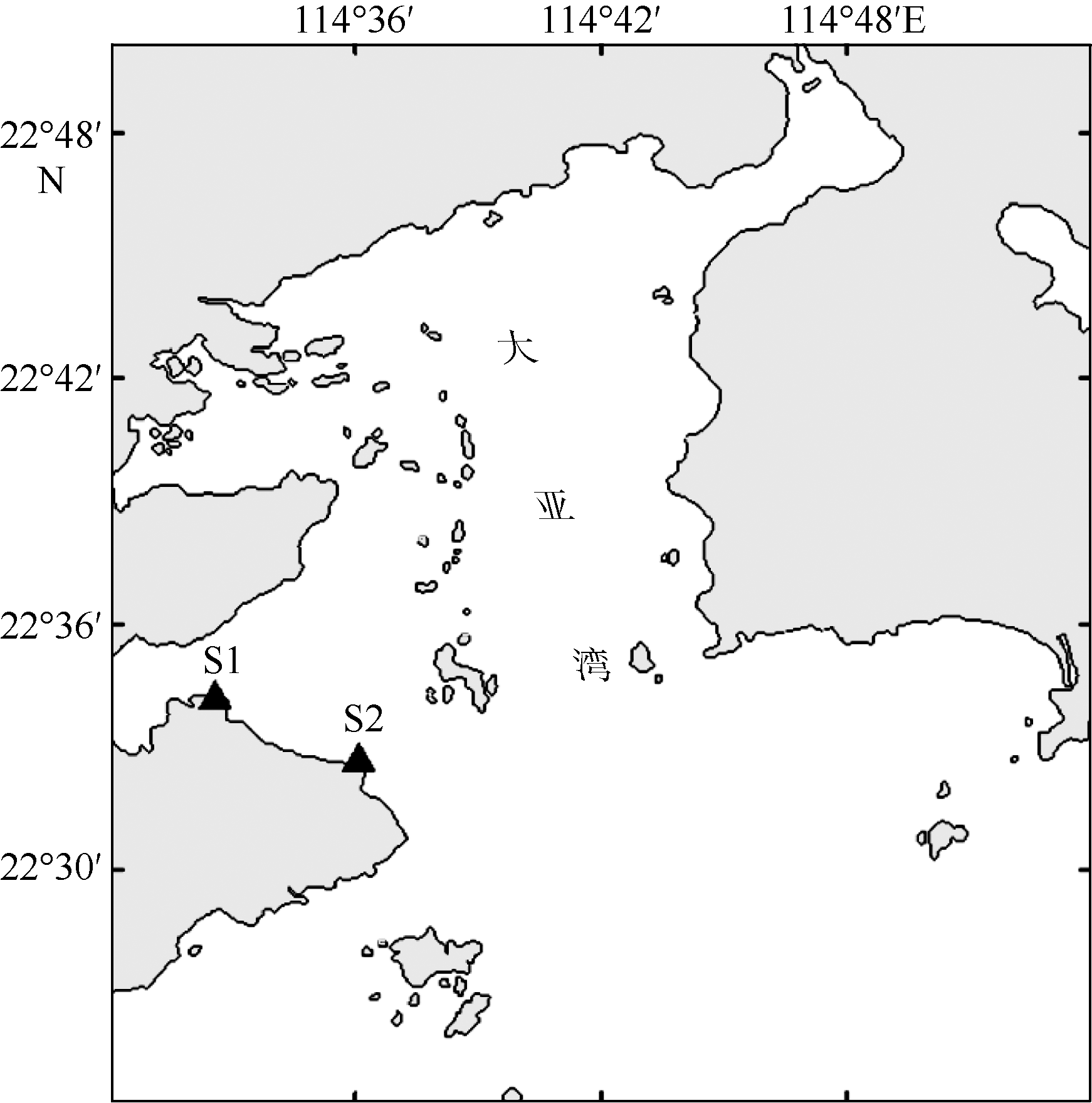
The population distribution of Hyale grandicornis in macroalgae canopies of Daya Bay
Hui WANG1,2,Hengxiang LI1,Lu LI1,Yan YAN1( )
)
- 1. South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2018-11-14Revised:2019-01-04Online:2019-07-20Published:2019-07-21 -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program (2017YFB0903703); Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2018A030313136); Guangzhou Science and Technology Planning Project (201707010163)
Cite this article
Hui WANG,Hengxiang LI,Lu LI,Yan YAN. The population distribution of Hyale grandicornis in macroalgae canopies of Daya Bay[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 52-58.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
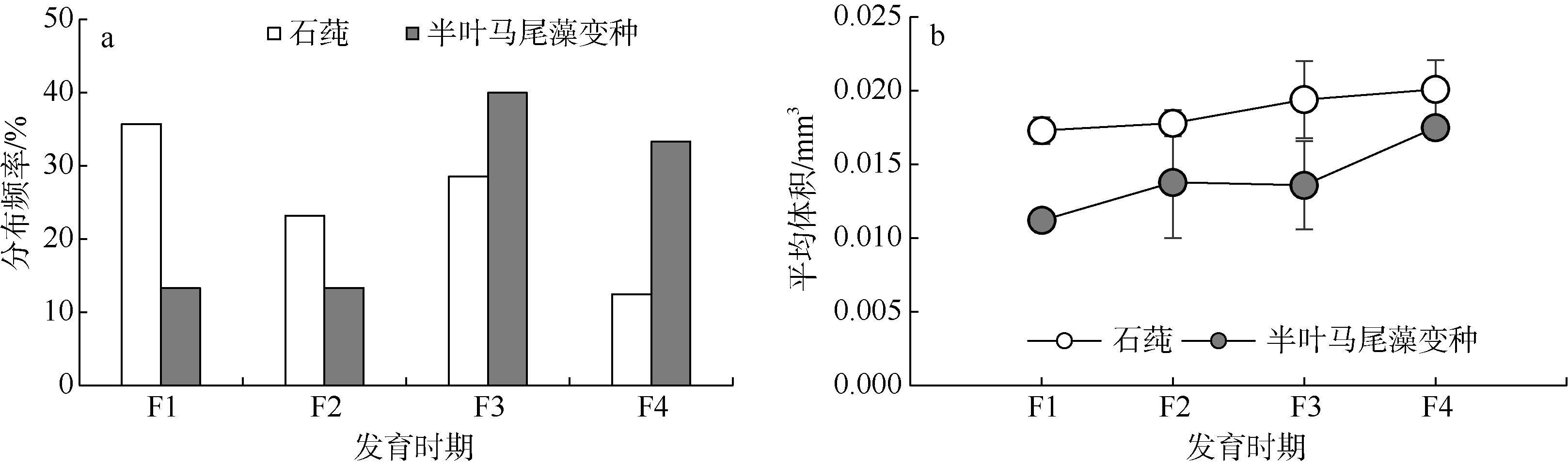
Tab. 2
The body sizes of Hyale grandicornis in two marine macroalgae"
| 石莼藻丛 | 半叶马尾藻变种藻丛 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体长范围/mm | 平均体长±标准误差/mm | 体长范围/mm | 平均体长±标准误差/mm | ||
| 成熟雄性 | 7.06~18.40 | 11.56±0.10a | 5.46~16.31 | 10.04±0.40a | |
| 成熟雌性 | 5.00~14.73 | 9.58±0.13b | 5.09~13.22 | 8.33±0.28b | |
| 抱卵雌性 | 7.09~14.39 | 10.71±0.22ab | 6.33~12.51 | 9.14±0.47ab | |
| 幼体 | 1.63~4.96 | 4.19±0.14c | 1.50~4.86 | 3.53±0.27c | |
Tab. 3
The body weight of Hyale grandicornis in two marine macroalgae"
| 石莼藻丛 | 半叶马尾藻变种藻丛 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 体重范围/mg | 平均体重±标准误差/mg | 体重范围/mg | 平均体重±标准误差/mg | |||
| 成熟雄性 | 5.4~26.0 | 12.3±0.6a | 2.8~24.8 | 11.5±0.9a | ||
| 成熟雌性 | 2.0~29.4 | 10.9±0.7b | 2.3~20.7 | 8.7±0.5b | ||
| 抱卵雌性 | 11.3~29.4 | 13.6±0.11a | 10.5~20.7 | 15.3±1.0c | ||
| 幼体 | 1.1~3.5 | 2.2±0.2c | 0.1~1.4 | 0.6±0.1d | ||
| [1] | 任先秋 , 2006. 中国动物志无脊椎动物第四十一卷甲壳动物亚门端足目钩虾亚目(一)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| REN XIANQIU , 2006. Fauna sinica Vol. 41 Invertebrata Crustacea Amphipoda Gammaridea[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 王友绍 , 2014. 大亚湾生态环境与生物资源[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| WANG YOUSHAO , 2014. Ecological environments and biological resources of Daya Bay[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese). | |
| [3] | 郑新庆, 黄凌风, 王蕾 , 等, 2011. 筼筜湖大型海藻群落的几种藻栖端足类的种群动态研究[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 50(5):928-933. |
| ZHENG XINQING, HUANG LINGFENG, WANG LEI , et al, 2011. Population dynamics of several species of amphipods in the macroalgae canopies in Yudang Lagoon[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 50(5):928-933 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] |
郑新庆, 黄凌风, 李元超 , 等, 2013. 啃食性端足类强壮藻钩虾对筼筜湖三种大型海藻的摄食选择性[J]. 生态学报, 33(22):7166-7172.
doi: 10.5846/stxb201207191030 |
|
ZHENG Xinqing, HUANG Lingfeng, LI Yuanchao , et al, 2013. The feeding selectivity of an herbivorous amphipod Ampithoe valida on three dominant macroalgal species of Yundang Lagoon[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(22):7166-7172 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.5846/stxb201207191030 |
|
| [5] |
ANDERSSON S, PERSSON M, MOKSNES P O , et al, 2009. The role of the amphipod Gammarus locusta as a grazer on macroalgae in Swedish seagrass meadows[J]. Marine Biology, 156(5):969-981.
doi: 10.1007/s00227-009-1141-1 |
| [6] |
BA-AKDAH M A, SATHEESH S, AL-SOFYANI A A , 2016. Habitat preference and seasonal variability of epifaunal assemblages associated with macroalgal beds on the Central Red Sea coast, Saudi Arabia[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 96(7):1457-1467.
doi: 10.1017/S0025315415001678 |
| [7] |
BERTHELSEN A K, TAYLOR R B , 2014. Arthropod mesograzers reduce epiphytic overgrowth of subtidal coralline turf[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 515:123-132.
doi: 10.3354/meps11025 |
| [8] |
BUENO M, DIAS G M, LEITE F P P , 2017. The importance of shore height and host identity for amphipod assemblages[J]. Marine Biology Research, 13(8):870-877.
doi: 10.1080/17451000.2017.1306650 |
| [9] |
BUSCHMANN A H , 1990. Intertidal macroalgae as refuge and food for amphipoda in Central Chile[J]. Aquatic Botany, 36(3):237-245.
doi: 10.1016/0304-3770(90)90037-L |
| [10] |
CARVALHO N F, GRANDE H, ROSA FILHO J S , et al, 2018. The structure of gammarid Amphipod (Crustacea, Peracarida) assemblages associated with Sargassum (Phaeophyta, Fucales) and their link with the structural complexity of algae[J]. Hydrobiologia, 820(1):245-254.
doi: 10.1007/s10750-018-3661-5 |
| [11] |
CONLAN K E , 1994. Amphipod crustaceans and environmental disturbance: a review[J]. Journal of Natural History, 28(3):519-554.
doi: 10.1080/00222939400770241 |
| [12] |
CRUZ-RIVERA E, FRIEDLANDER M , 2013. Effects of algal phenotype on mesograzer feeding[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 490:69-78.
doi: 10.3354/meps10429 |
| [13] |
CRUZ-RIVERA E, HAY M E , 2000. Can quantity replace quality? Food choice, compensatory feeding, and fitness of marine mesograzers[J]. Ecology, 81(1):201-219.
doi: 10.1890/0012-9658(2000)081[0201:CQRQFC]2.0.CO;2 |
| [14] |
CRUZ-RIVERA E, HAY M E , 2001. Macroalgal traits and the feeding and fitness of an herbivorous amphipod: the roles of selectivity, mixing, and compensation[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 218:249-266.
doi: 10.3354/meps218249 |
| [15] |
DAS S, DESHMUKHE G, DWIVEDI A , 2014. Grazing of selected genera of green, red and brown macroalgae[J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 12(3):717-725.
doi: 10.15666/aeer |
| [16] |
DAUVIN J C, ANDRADE H, DE-LA-OSSA-CARRETERO J A , et al, 2016. Polychaete/amphipod ratios: an approach to validating simple benthic indicators[J]. Ecological Indicators, 63:89-99.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.11.055 |
| [17] |
DE PAULA D R, ALMEIDA A C, JACOBUCCI G B , 2016. Reproductive features of sympatric species of Caprella (Amphipoda) on the southeastern Brazilian coast: a comparative study[J]. Crustaceana, 89(8):933-947.
doi: 10.1163/15685403-00003566 |
| [18] |
DUFFY J E , 1990. Amphipods on seaweeds: partners or pests?[J]. Oecologia, 83(2):267-276.
doi: 10.1007/BF00317764 |
| [19] | FLYNN M N, PEREIRA W R L S, PIRES R C , et al, 2009. Population dynamics of Hyale nigra (Haswell, 1879) (Amphipoda, Hyalidae) associated to Bryocladia thyrsigera (J. Agardh) at Peruibe beach, Itanhaém (SP), southeastern Brazil[J]. Nauplius, 17(1):1-8. |
| [20] |
GESTOSO I, OLABARRIA C, TRONCOSO J S , 2014. Selection of habitat by a marine amphipod[J]. Marine Ecology, 35(1):103-110.
doi: 10.1111/maec.2014.35.issue-s1 |
| [21] |
GUIDONE M, THORNBER C S, VAN ALSTYNE K L , 2015. Herbivore impacts on two morphologically similar bloom- forming Ulva species in a eutrophic bay[J]. Hydrobiologia, 753(1):175-188.
doi: 10.1007/s10750-015-2204-6 |
| [22] |
KRAUFVELIN P, SALOVIUS S, CHRISTIE H , et al, 2006. Eutrophication-induced changes in benthic algae affect the behaviour and fitness of the marine amphipod Gammarus locusta[J]. Aquatic Botany, 84(3):199-209.
doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2005.08.008 |
| [23] |
LANCELLOTTI D A, TRUCCO R G , 1993. Distribution patterns and coexistence of six species of the amphipod genus Hyale[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 93:131-141.
doi: 10.3354/meps093131 |
| [24] |
LÖF M, SUNDELIN B, BANDH C , et al, 2016. Embryo aberrations in the amphipod Monoporeia affinis as indicators of toxic pollutants in sediments: a field evaluation[J]. Ecological Indicators, 60:18-30.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.05.058 |
| [25] |
OZGA A V, DA SILVA CASTIGLIONI D , 2017. Reproductive biology of two species of Hyalella Smith, 1874 (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Hyalellidae) from southern Brazil[J]. Journal of Natural History, 51(41-42):2509-2521.
doi: 10.1080/00222933.2017.1377777 |
| [26] |
PARDAL M A, MARQUES J C, METELO I , et al, 2000. Impact of eutrophication on the life cycle, population dynamics and production of Ampithoe valida (Amphipoda) along an estuarine spatial gradient (Mondego estuary, Portugal)[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 196:207-219.
doi: 10.3354/meps196207 |
| [27] |
POORE A G B, GALLAGHER K M , 2013. Strong consequences of diet choice in a talitrid amphipod consuming seagrass and algal wrack[J]. Hydrobiologia, 701(1):117-127.
doi: 10.1007/s10750-012-1263-1 |
| [28] |
SAINTE-MARIE B , 1991. A review of the reproductive bionomics of aquatic gammaridean amphipods: variation of life history traits with latitude, depth, salinity and superfamily[J]. Hydrobiologia, 223(1):189-227.
doi: 10.1007/BF00047641 |
| [29] |
SCHREIDER M J, GLASBY T M, UNDERWOOD A J , 2003. Effects of height on the shore and complexity of habitat on abundances of amphipods on rocky shores in New South Wales, Australia[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 293(1):57-71.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(03)00185-0 |
| [30] |
SOTKA E E , 2007. Restricted host use by the herbivorous amphipod Peramphithoe tea is motivated by food quality and abiotic refuge[J]. Marine Biology, 151(5):1831-1838.
doi: 10.1007/s00227-007-0612-5 |
| [31] | VALENTINE J F, DUFFY J E , 2006. The central role of grazing in seagrass ecology[M] //LARKUM A W D, ORTH R J, DUARTE C M. SEAGRASSES: biology, ecology and conservation. Dordrecht: Springer:463-501. |
| [1] | XI Chen, LIN Zongxuan, SA Rula, DENG Xi, LIU Qiang, NI Liang, LUO Laicai, MA Teng, XIE Zhijie, CHEN Siruo, CHEN Songze. Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [2] | SUN Cuici, YUE Weizhong, ZHAO Wenjie, WANG Youshao. Distribution of the microbial Carbohydrate-Active enzymes genes in the surface sediment of the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [3] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [4] | XING Jianwei, SONG Jinming. Atmospheric deposition and its eco-environmental effects on the South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 19-39. |
| [5] | ZHAO Hongwuyi, ZHOU Wen, ZENG Kai, DENG Lin, LIAO Jianzu, CAO Wenxi. A study of the regional size-fractionated primary production algorithm based on phytoplankton absorption coefficient and photosynthetically active radiation in the South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 43-55. |
| [6] | JIANG Xun, WU Wen, SONG Dehai. Identification and quantitative analysis of key controlling factors of water quality response to human activities in the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 182-191. |
| [7] | CHEN Jingfu, ZHONG Yu, WANG Lei, GUO Yupei, QIU Dajun. Noctiluca scintillans effects on eukaryotic plankton community structure using Environmental DNA analysis in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [8] | MENG Miaomiao, ZHENG Xiangyang, XING Qianguo, LIU Hailong. Remote sensing estimation of green macroalgae Ulva pertusa based on unmanned aerial vehicle and satellite image [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 46-53. |
| [9] | LI Gang, WAN Mingyue, SHI Xiaohan, QIN Geng, MAI Guangming, HUANG Liangmin, TAN Yehui, ZOU Dinghui. Comparative study on photophysiology of four macroalgae from the Zhongsha Atoll, with special reference to the effects of temperature rise* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 101-110. |
| [10] | ZHANG Wanru, LIU Qingxia, HUANG Honghui, QIN Xiaoqing, LI Jiajun, CHEN Jianhua. Study on stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen of main fishery organisms in the southwestern waters of Daya Bay, South China Sea in winter 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [11] | LI Yao, XIANG Chenhui, JIANG Zhijian, SONG Xingyu. Production and metabolism characteristics of planktonic community and their influencing factors in Daya Bay during summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(6): 83-92. |
| [12] | XIANG Chenhui, LIU Jiaxing, KE Zhixin, ZHOU Linbin, TAN Yehui. Phytoplankton responses to Dan’ao River estuary water enrichment in terms of size structure and community composition* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(2): 49-60. |
| [13] | DAI Xiaojuan, HU Ren, LUO Hongtian, WANG Qing, HU Xiaojuan, BAI Mindong, YANG Yufeng. Effects of the decomposition of Gracilaria lemaneiformis on seawater quality [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(1): 91-98. |
| [14] | ZHANG Liming, TAN Yehui, LI Jiajun, HUANG Xiaoping, LIU Jiaxing. Characteristics of the phytoplankton community and its response to Dan’ao River input in Daya Bay in summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [15] | ZHANG Caixue, ZHOU Weinan, SUN Xingli, SONG Zhiguang. Seasonal succession of macroalgae community in Naozhou Island [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(1): 74-84. |
|
||