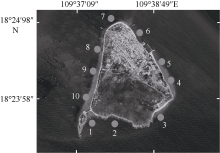
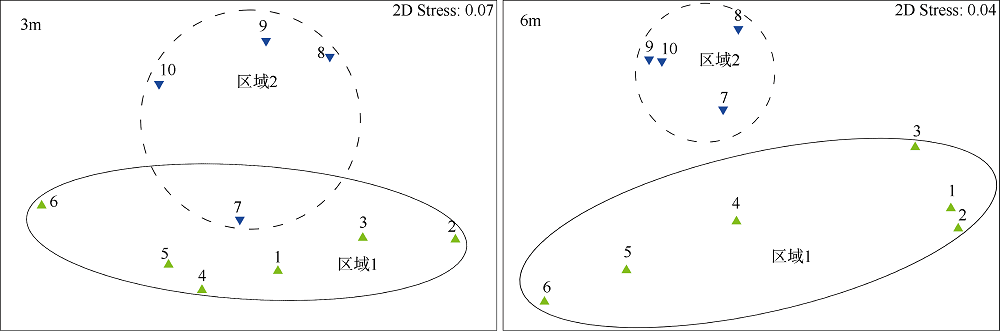
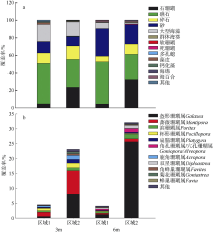
Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2020, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 103-113.doi: 10.11978/2020020CSTR: 32234.14.2020020
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
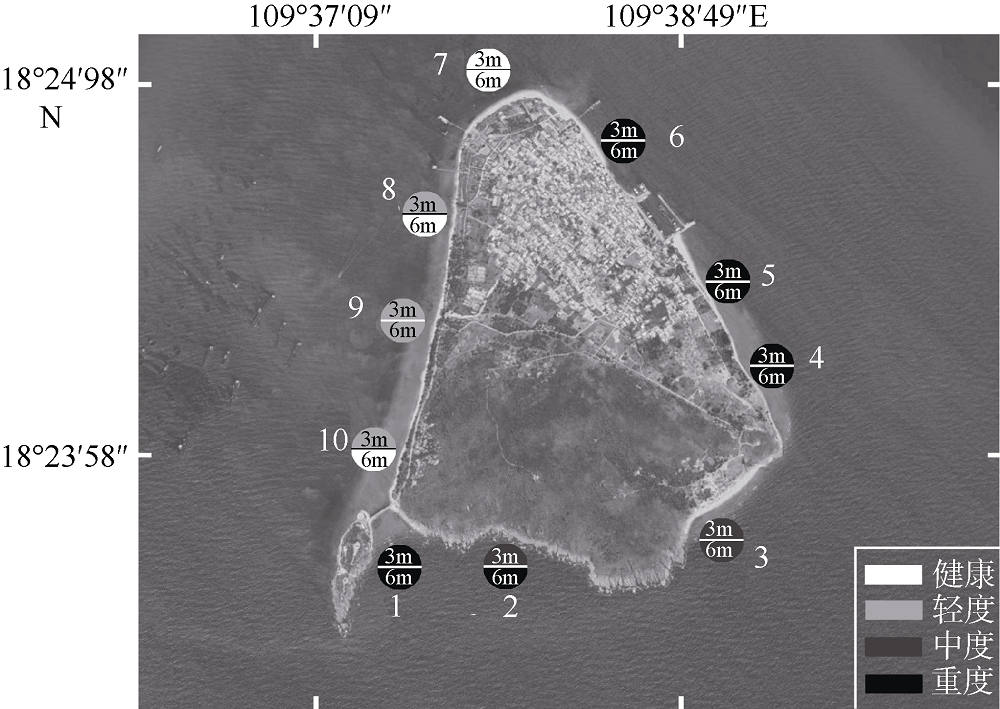
Coral community change and its influencing factors in Ximaozhou Island of Hainan
HUANG Jianzhong1,2( ), WEI Yuheng3, GU Zhifeng2,3, WU Chuanliang4, XU Qiang2,3, WANG Aiming2,3, LI Xiubao2,3(
), WEI Yuheng3, GU Zhifeng2,3, WU Chuanliang4, XU Qiang2,3, WANG Aiming2,3, LI Xiubao2,3( )
)
- 1. College of Ecology and Environment, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Marine Resource Utilization in South China Sea, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
3. Ocean College, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China
4. Institute of Coral Reef Ecology in Sanya, Sanya 572029, China
-
Received:2020-02-23Revised:2020-04-25Online:2020-10-10Published:2020-05-13 -
Contact:LI Xiubao E-mail:212828@163.com;xiubaoli@hainanu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Program of China(2019YFD0901304);Open Project of Guangdong Key Laboratory of Applied Marine Biology and Open Project of Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Biological Resources and Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences(2019011009);Foundation of Hainan University(KYQD(ZR)1805)
CLC Number:
- Q958.15
Cite this article
HUANG Jianzhong, WEI Yuheng, GU Zhifeng, WU Chuanliang, XU Qiang, WANG Aiming, LI Xiubao. Coral community change and its influencing factors in Ximaozhou Island of Hainan[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(6): 103-113.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
Tab. 1
List of scleractinian coral species in Ximaozhou Island"
| 科 | 属 | 种 | 1966年 | 2011年 | 本次调查 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 杯形珊瑚科 | 杯形珊瑚属 | 鹿角杯形珊瑚Pocillopora damicornis | + | + | + |
| 多曲杯形珊瑚Pocillopora meandrina | + | ||||
| 疣状杯形珊瑚Pocillopora verrucosa | + | + | + | ||
| 舌状杯形珊瑚Pocillopora ligulata | + | ||||
| 达娜厄杯形珊瑚Pocillopora danae | + | ||||
| 短角杯形珊瑚Pocillopora brevicornis | + | ||||
| 鹿角珊瑚科 | 鹿角珊瑚属 | 花苔鹿角珊瑚Acropora anthocercis | + | ||
| 细枝鹿角珊瑚Acropora nana | + | ||||
| 芽枝鹿角珊瑚Acropora gemmifera | + | ||||
| 根枝鹿角珊瑚 Acropora surculosa | + | ||||
| 风信子鹿角珊瑚Acropora hyacinthus | + | ||||
| 巨锥鹿角珊瑚Acropora monticulosa | + | ||||
| 甲胄鹿角珊瑚 Acropora armata | + | ||||
| 钩状勃氏鹿角珊瑚Acropora brüggemanni | + | ||||
| 壮实鹿角珊瑚Acropora robusta | + | ||||
| 指形鹿角珊瑚Acropora digitifera | + | ||||
| 粗野鹿角珊瑚Acropora humilis | + | ||||
| 科 | 属 | 种 | 1966年 | 2011年 | 本次调查 |
| 美丽鹿角珊瑚Acropora muricata | + | ||||
| 锐角鹿角珊瑚Acropora decipiens | + | ||||
| 鼻形鹿角珊瑚Acropora nasuta | + | ||||
| 太平洋鹿角珊瑚 Acropora pacifica | + | ||||
| 伞房鹿角珊瑚Acropora corymbosa | + | ||||
| 佳丽鹿角珊瑚Acropora pulchra | + | ||||
| 蔷薇珊瑚属 | 瘿叶蔷薇珊瑚Montipora aequituberculata | + | |||
| 繁锦蔷薇珊瑚Montipora efflorescens | + | ||||
| 弯柔蔷薇珊瑚Montipora mollis | + | ||||
| 叶状蔷薇珊瑚Montipora foliosa | + | + | + | ||
| 指状蔷薇珊瑚Montipora digitata | + | ||||
| 翼形蔷薇珊瑚Montipora peltiformis | + | ||||
| 灌木蔷薇珊瑚Montipora fruticosa | + | ||||
| 多枝蔷薇珊瑚Montipora ramosa | + | ||||
| 鬃刺蔷薇珊瑚Montipora hispida | + | ||||
| 杯形蔷薇珊瑚Montipora caliculata | + | ||||
| 沙氏蔷薇珊瑚Montipora solunderi | + | ||||
| 索氏蔷薇珊瑚Montipora solanderi | + | ||||
| 中华蔷薇珊瑚Montipora sinensis | + | ||||
| 横条蔷薇珊瑚Montipora trabeculata | + | ||||
| 单星蔷薇珊瑚Montipora monasteriata | + | ||||
| 膨胀蔷薇珊瑚Montipora turgescens | + | + | |||
| 龟岛蔷薇珊瑚Montipora turtlensis | + | ||||
| 星孔珊瑚属 | 多星孔珊瑚Astreopora myriophthalma | + | |||
| 滨珊瑚科 | 滨珊瑚属 | 火焰滨珊瑚Porites rus | + | ||
| 亚氏滨珊瑚Porites aranetai | + | ||||
| 扁枝滨珊瑚Porites andrewsi | + | ||||
| 细柱滨珊瑚Porites cylindrica | + | ||||
| 马氏滨珊瑚Porites matthaii | + | ||||
| 澄黄滨珊瑚Porites lutea | + | + | + | ||
| 角孔珊瑚属 | 柱角孔珊瑚Goniopora columna | + | |||
| 角孔珊瑚Goniopora stokesi | + | ||||
| 大角孔珊瑚Goniopora djiboutiensis | + | ||||
| 团块角孔珊瑚Goniopora lobata | + | ||||
| 斯氏角孔珊瑚Goniopora stutchburyi | + | + | |||
| 穴孔珊瑚属 | 穴孔珊瑚Alveopore gigas | + | |||
| 海绵穴孔珊瑚Alveopora spongiosa | + | ||||
| 蜂巢珊瑚科 | 刺星珊瑚属 | 小叶刺星珊瑚Cyphastrea microphthalma | + | ||
| 锯齿刺星珊瑚Cyphastrea serrailia | + | + | + | ||
| 刺孔珊瑚属 | 宝石刺孔珊瑚Echinopora gemmacea | + | |||
| 双星珊瑚属 | 同双星珊瑚Diploastrea heliopora | + | + | ||
| 蜂巢珊瑚属 | 蜂巢珊瑚Favia truncates | + | |||
| 海洋蜂巢珊瑚Favia maritima | + | ||||
| 神龙岛蜂巢珊瑚Favia lizardensis | + | ||||
| 黄癣蜂巢珊瑚Favia favus | + | + | |||
| 标准蜂巢珊瑚Favia speciosa | + | + | + | ||
| 美龙氏蜂巢珊瑚Favia veroni | + | ||||
| 科 | 属 | 种 | 1966年 | 2011年 | 本次调查 |
| 角蜂巢珊瑚属 | 秘密角蜂巢珊瑚Favites abdita | + | + | + | |
| 尖丘角蜂巢珊瑚Favites acuticollis | + | ||||
| 板叶角蜂巢珊瑚Favites complanata | + | ||||
| 多弯角蜂巢珊瑚Favites flexuosa | + | ||||
| 中国角蜂巢珊瑚Favites chinensis | + | ||||
| 罗素角蜂巢珊瑚Favites russelli | + | ||||
| 肠珊瑚属 | 不规则肠珊瑚Leptoria irregularis | + | |||
| 弗利吉亚肠珊瑚Leptoria phrygia | + | ||||
| 扁脑珊瑚属 | 尖边扁脑珊瑚Platygyra acuta | + | |||
| 肉质扁脑珊瑚Platygyra carnosus | + | ||||
| 弗利吉亚扁脑珊瑚Platygyra phrygia | + | ||||
| 精巧扁脑珊瑚Platygyra daedalea | + | + | |||
| 交替扁脑珊瑚Platygyra crosslandi | + | ||||
| 琉球扁脑珊瑚Platygyra ryukyuensis | + | + | |||
| 中华扁脑珊瑚Platygyra sinensis | + | + | |||
| 朴素扁脑珊瑚Platygyra rustica | + | ||||
| 菊花珊瑚属 | 梳状菊花珊瑚Goniastrea pectinata | + | + | + | |
| 粗糙菊花珊瑚Goniastrea aspera | + | + | + | ||
| 网状菊花珊瑚Goniastrea retiformis | + | ||||
| 狭小片菊花珊瑚Goniastrea yamanarii | + | ||||
| 同星珊瑚属 | 多孔同星珊瑚Plesiastrea versipora | + | + | ||
| 小星珊瑚属 | 白斑小星珊瑚Leptastrea pruinosa | + | |||
| 枇杷珊瑚科 | 盔形珊瑚属 | 稀杯盔形珊瑚Galaxea astreata | + | + | |
| 丛生盔形珊瑚Galaxea fascicularis | + | + | + | ||
| 拉氏盔形珊瑚Galaxea lamarcki | + | ||||
| 粗糙盔形珊瑚Galaxea aspera | + | ||||
| 菌珊瑚科 | 牡丹珊瑚属 | 十字牡丹珊瑚Pavona decussata | + | + | |
| 叶状牡丹珊瑚Pavona frondifera | + | ||||
| 易变牡丹珊瑚Pavona varians | + | ||||
| 阔叶牡丹珊瑚Pavona lata | + | ||||
| 铁星珊瑚科 | 沙珊瑚属 | 毗邻沙珊瑚Psammocora contigua | + | + | |
| 裸肋珊瑚科 | 刺柄珊瑚属 | 腐蚀刺柄珊瑚Hydnophora exesa | + | ||
| 邻基刺柄珊瑚Hydnophora contignatio | + | ||||
| 小角刺柄珊瑚Hydnophora microconos | + | ||||
| 裸肋珊瑚属 | 狭裸肋珊瑚Merulina laxa | + | |||
| 阔裸肋珊瑚Merulina ampliata | + | ||||
| 褶叶珊瑚科 | 合叶珊瑚属 | 菌状合叶珊瑚Symphylia agaricia | + | + | |
| 合叶珊瑚Symphyllia recta | + | ||||
| 巨大合叶珊瑚Symphyllia gigantea | + | ||||
| 华贵合叶珊瑚Symphyllia nobilis | + | ||||
| 辐射合叶珊瑚Symphyllia radians | + | ||||
| 棘星珊瑚属 | 大棘星珊瑚Acanthastrea echinata | + | + | ||
| 联合棘星珊瑚Acanthastrea hemprichii | + | ||||
| 叶状珊瑚属 | 赫氏叶状珊瑚Lobophyllia hemprichii | + | |||
| 木珊瑚科 | 陀螺珊瑚属 | 皱褶陀螺珊瑚Turbinaria mesenterina | + | ||
| 盾形陀螺姗瑚Turbinaria peltata | + | + | |||
| 丁香珊瑚科 | 真叶珊瑚属 | 肾形真叶珊瑚Euphyllia ancora | + | ||
| 梳状珊瑚科 | 梳状珊瑚属 | 莴苣梳状珊瑚Pectinia lactuca | + | ||
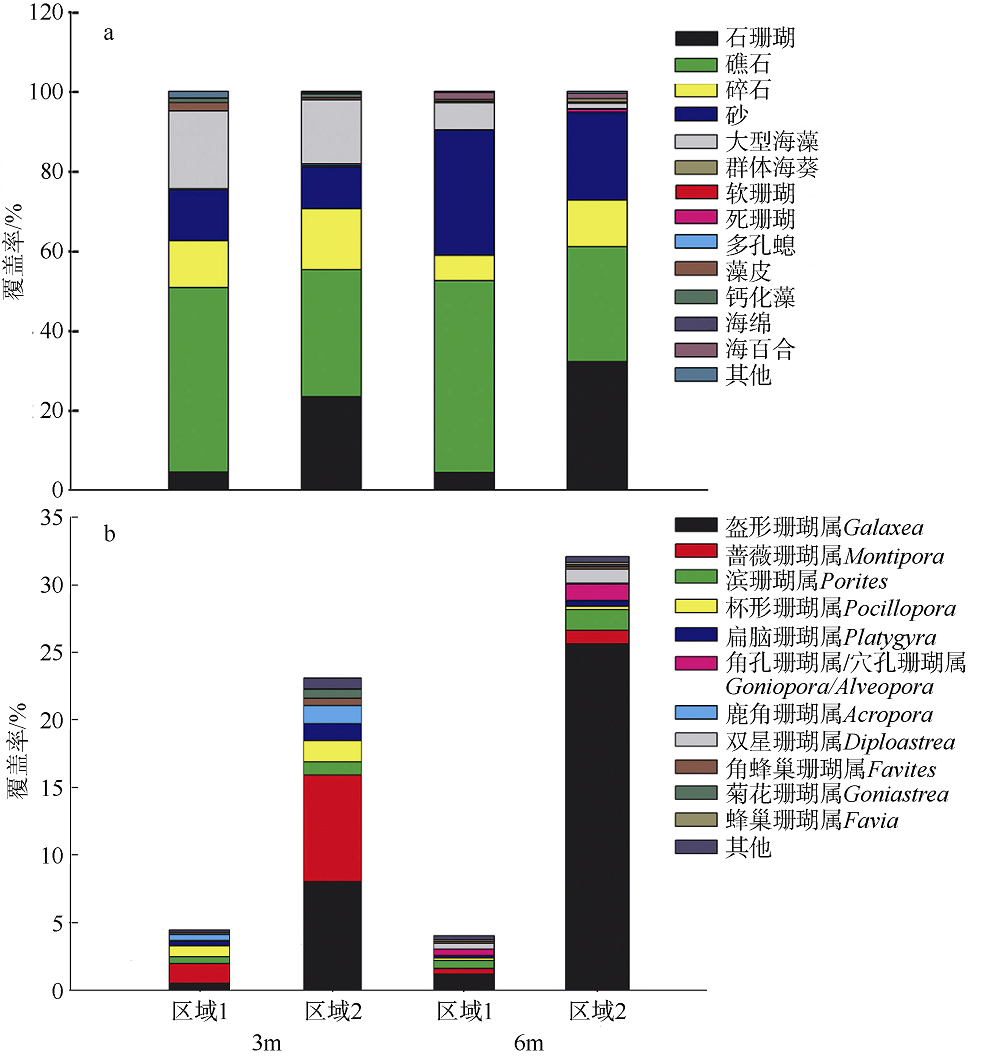
| 合计 | 52 | 26 | 68 |
Tab. 2
Temporal changes of dominant scleractinian coral species in Ximaozhou Island"
| 调查及时间 | 站位 | 覆盖率 | 优势种 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 东北侧离岸60~80m | - | 粗糙菊花珊瑚 | |
| 东北侧离岸80~93m | - | 多枝蔷薇珊瑚 | |
| 东北侧离岸93~110m | - | 佳丽鹿角珊瑚 | |
| 东北侧离岸110m以外 | - | 鼻形鹿角珊瑚 | |
| 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 2011 | 4 | 40.15% | 丛生盔形珊瑚和同双星珊瑚 |
| 5 9 | 39.80% 32.15% | 丛生盔形珊瑚和同双星珊瑚 丛生盔形珊瑚 | |
| 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 2013 | 4 9 | 0.15% 35.20% | 无 丛生盔形珊瑚 |
| 本次调查(2018) | 4 | 3.88% | 丛生盔形珊瑚 |
| 5 | 1.07% | 无 | |
| 9 | 30.07% | 丛生盔形珊瑚 |
| [1] | 戴昌凤, 洪圣雯 , 2009. 台湾珊瑚图鉴[M]. 台北, 中国: 猫头鹰出版社. |
| [2] | 黄晖, 张成龙, 杨剑辉, 等, 2012. 南沙群岛渚碧礁海域造礁石珊瑚群落特征[J]. 台湾海峡, 31(1):79-84. |
| HUANG HUI, ZHANG CHENGLONG, YANG JIANHUI, et al, 2012. Scleractinian coral community characteristics in Zhubi reef sea area of Nansha Islands[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 31(1):79-84 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 李秀保, 2011. 三亚造礁石珊瑚群落组成、时空分布及主要影响因子识别研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院: 1-107. |
| LI XIUBAO, 2011. Identification of major factors influencing the composition, spatial and temporal variation of scleractinian coral community in Sanya, China[D]. Beijing: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: 1-107 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 梁鑫, 彭在清, 2018. 广西涠洲岛珊瑚礁海域水质环境变化研究与评价[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 35(1):114-119. |
| LIANG XIN, PENG ZAIQING, 2018. Analysis and appraisal of seawater quality in coral reef water, Weizhou Island, Guangxi[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 35(1):114-119 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 钱军, 李洪武, 王晓航, 等, 2015. 大洲岛珊瑚礁海域水质状况分析与评价[J]. 生态科学, 34(6):22-29. |
| QIAN JUN, LI HONGWU, WANG XIAOHANG, et al, 2015. Analysis and appraisal of seawater quality in coral reef water, Dazhou Island[J]. Ecological Science, 34(6):22-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 孙有方, 雷新明, 练健生, 等, 2018. 三亚珊瑚礁保护区珊瑚礁生态系统现状及其健康状况评价[J]. 生物多样性, 26(3):258-265. |
| SUN YOUFANG, LEI XINMING, LIAN JIANSHENG, et al, 2018. Ecosystem status and health assessment of Sanya Coral Reef National Nature Reserve[J]. Biodiversity Science, 26(3):258-265 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 吴钟解, 王道儒, 叶翠信, 等, 2012. 三亚珊瑚变化趋势及原因分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 31(5):682-685. |
| WU ZHONGJIE, WANG DAORU, YE CUIXIN, et al, 2012. Variation tendency and analysis of cause of coral in Sanya[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 31(5):682-685 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 吴钟解, 张光星, 陈石泉, 等, 2015. 海南西瑁洲岛周边海域造礁石珊瑚空间分布及其生态系统健康评价[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 34(1):133-140. |
| WU ZHONGJIE, ZHANG GUANGXING, CHEN SHIQUAN, et al, 2015. Spatial distribution and ecosystem health assessment of hermatypic corals in surrounding waters of Ximaozhou Island, Hainan[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 34(1):133-140 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [9] | 赵美霞, 余克服, 张乔民, 等, 2010. 近50年来三亚鹿回头岸礁活珊瑚覆盖率的动态变化[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 41(3):440-447. |
| ZHAO MEIXIA, YU KEFU, ZHANG QIAOMIN, et al, 2010. Long-term change in coral cover in Luhuitou fringing reef, Sanya[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 41(3):440-447 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 邹仁林, 馬江虎, 宋善文, 1966. 海南岛珊瑚礁垂直分带的初步研究[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 8(2):153-162. |
| ZOU RENLIN, MA JIANGHU, SONG SHANWEN, 1966. A preliminary study on the vertical zonation of the coral reef of Hainan Island[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 8(2):153-162 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 邹仁林 , 2001. 中国动物志-腔肠动物门, 珊瑚虫纲, 石珊瑚目, 造礁石珊瑚[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-289. |
| [12] | BELLWOOD D R, HUGHES T P, FOLKE C , et al, 2004. Confronting the coral reef crisis[J]. Nature, 429(6994):827-833. |
| [13] | CONNELL J H , 1978. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs[J]. Science, 199(4335):1302-1310. |
| [14] | ENGLISH S, WILKINSON C, BAKER V , 1997. Survey manual for tropical marine resources[M]. 2nd ed. Townsville: Australian Institute of Marine Science. |
| [15] | ERFTEMEIJER P L A, RIEGL B, HOEKSEMA B W , et al, 2012. Environmental impacts of dredging and other sediment disturbances on corals: a review[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(9):1737-1765. |
| [16] |
GOMEZ E D, ALIÑO P M, YAP H T , et al, 1994. A review of the status of Philippine reefs[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 29(1-3):62-68.
doi: 10.1016/0025-326X(94)90427-8 |
| [17] | HALPERN B S, FRAZIER M, POTAPENKO J , et al, 2015. Spatial and temporal changes in cumulative human impacts on the world’s ocean[J]. Nature Communications, 6:7615. |
| [18] |
HUANG HUI, WEN C K C, LI XIUBAO , et al, 2017. Can private management compensate the ineffective marine reserves in China?[J]. Ambio, 46(1):73-87.
pmid: 27430996 |
| [19] |
HUGHES T P, BAIRD A H, BELLWOOD D R , et al, 2003. Climate change, human impacts, and the resilience of coral reefs[J]. Science, 301(5635):929-933.
doi: 10.1126/science.1085046 |
| [20] |
HUGHES T P, HUANG HUI, YOUNG M A L , 2013. The wicked problem of China's disappearing coral reefs[J]. Conservation Biology, 27(2):261-269.
doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2012.01957.x |
| [21] | LI XIUBAO, HUANG HUI, LIAN JIANSHENG , et al, 2013a. Spatial and temporal variations in sediment accumulation and their impacts on coral communities in the Sanya Coral Reef Reserve, Hainan, China[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 96:88-96. |
| [22] | LI XIUBAO, HUANG HUI, LIAN JIANSHENG , et al, 2013b. Coral community changes in response to a high sedimentation event: a case study in southern Hainan Island[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(9):1028-1037. |
| [23] | LIU P J, MENG PEIJIE, LIU LILIAN , et al, 2012. Impacts of human activities on coral reef ecosystems of southern Taiwan: a long-term study[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 64(6):1129-1135. |
| [24] | MCCOOK L J , 1999. Macroalgae, nutrients and phase shifts on coral reefs: scientific issues and management consequences for the Great Barrier Reef[J]. Coral Reefs, 18(4):357-367. |
| [25] | MOUSTAKA M, LANGLOIS T J, MCLEAN D , et al, 2018. The effects of suspended sediment on coral reef fish assemblages and feeding guilds of north-west Australia[J]. Coral Reefs, 37(3):659-673. |
| [26] | TEBBETT S B, GOATLEY C H R, BELLWOOD D R , 2017. Fine sediments suppress detritivory on coral reefs[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 114(2):934-940. |
| [27] | WEDDING L M, LECKY J, GOVE J M , et al, 2018. Advancing the integration of spatial data to map human and natural drivers on coral reefs[J]. PLoS One, 13(3):e0189792. |
| [28] | WILLIAMS G J, SMITH J E, CONKLIN E J , et al, 2013. Benthic communities at two remote Pacific coral reefs: effects of reef habitat, depth, and wave energy gradients on spatial patterns[J]. PeerJ, 1:e81. |
| [29] | ZHAO M X, YU K F, SHI Q , et al, 2013. Coral communities of the remote atoll reefs in the Nansha Islands, southern South China Sea[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(9):7381-7392. |
| [1] | XI Chen, LIN Zongxuan, SA Rula, DENG Xi, LIU Qiang, NI Liang, LUO Laicai, MA Teng, XIE Zhijie, CHEN Siruo, CHEN Songze. Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [2] | ZENG Weite, ZHANG Dongqiang, LIU Bing, YANG Yongpeng, ZHANG Hangfei, WU Duoyu, WANG Xiaolin. Distribution, main controlling factors and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface seawater of the Northern Bay of Hainan Island, south China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(6): 156-167. |
| [3] | WU Weizhi, ZHAO Zhixia, YANG Sheng, LIANG Licheng, Chen Qiuxia, LU Xiang, LIU Xing, ZHANG Xiaowei. The mangrove forest distribution and analysis of afforestation effect in Zhejiang Province [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 67-74. |
| [4] | LI Kaizhi, KE Zhixin, WANG Junxing, TAN Yehui. Preliminary study on the community structure of zooplankton in coral reef waters of Xisha Islands* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 121-131. |
| [5] | LI Ao, FENG Yang, WANG Yuntao, XUE Huijie. Spatiotemporal variation of water area with high chlorophyll a concentration in the South China Sea based on OC-CCI data* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 77-89. |
| [6] | MA Mengzhen, LI Qian, WU Zhengchao, CHEN Yinchao, YU Jiancheng. Underwater glider observation of oxygen minimum zone in the northern South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 131-142. |
| [7] | LI Huawei, XU Xiangrong. Pollution characteristics of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and alternative brominated flame retardants in sediments from typical mangrove wetlands of China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(1): 117-130. |
| [8] | WANG Jian, CHEN Chuqun, ZHOU Weihua, LI Xiangfu, WU Jie, YE Haibin, TANG Shilin. Estimating the spatial distribution of heterotrophic bacteria abundance in the Northern South China Sea using remote sensing* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 53-62. |
| [9] | FANG Zhou, TAN Fei, YANG Hongqiang, XU Huilong, XU Xiangrong, LI Hengxiang. Distribution characteristics of plastic debris and microplastics on the beaches of Ganquan Island and Quanfu Island in Xisha Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(5): 123-133. |
| [10] | WANG Yuanqi, YANG Yang, ZHOU Liang, WANG Yaping, GAO Shu. Interpreting the origin of coastal boulders on a coral reef flat at Xiaodonghai of Hainan Island based on storm wave energy analysis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(4): 110-121. |
| [11] | LI Kaizhi, REN Yuzheng, KE Zhixin, LI Gang, TAN Yehui. Vertical distributions of epipelagic and mesopelagic zooplankton in the continental slope of the northeastern South China Sea* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2021, 40(2): 61-73. |
| [12] | Yuzheng REN, Zhixin KE, Yehui TAN, Kaizhi LI. Community structure of zooplankton and its influencing factors in the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island, Guangdong [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 65-76. |
| [13] | LONG Lijuan, YANG Fangfang, WEI Zhangliang. A review on ecological restoration techniques of coral reefs [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(6): 1-8. |
| [14] | Xinming LEI,Hui HUANG,Jiansheng LIAN,Laurence J MCCOOK. The diversity and distribution of coralline algae in China: state of knowledge and research [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 30-40. |
| [15] | Hui WANG,Hengxiang LI,Lu LI,Yan YAN. The population distribution of Hyale grandicornis in macroalgae canopies of Daya Bay [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(4): 52-58. |
|
||