Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2017, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 41-47.doi: 10.11978/2016040CSTR: 32234.14.2016040
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
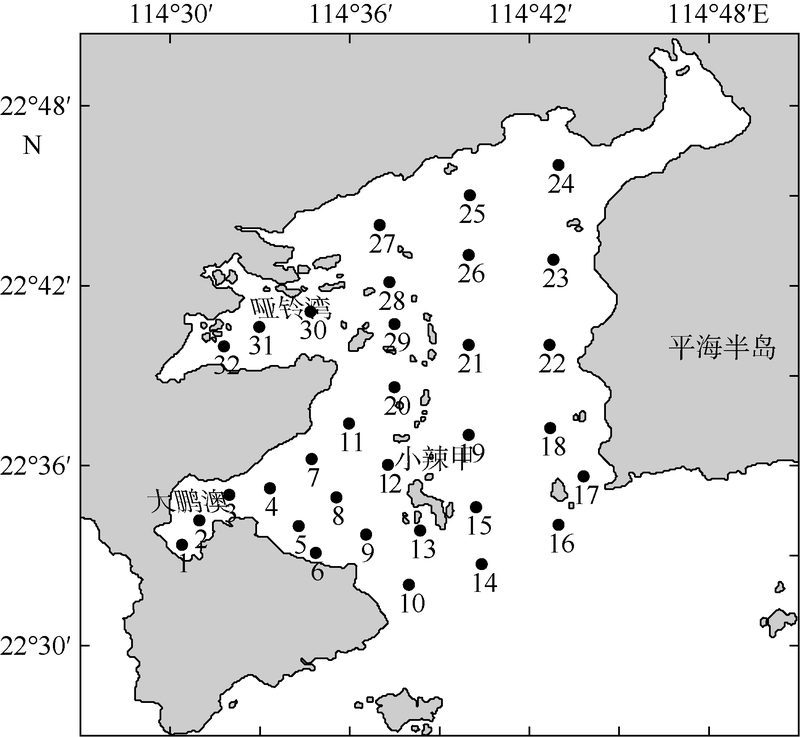
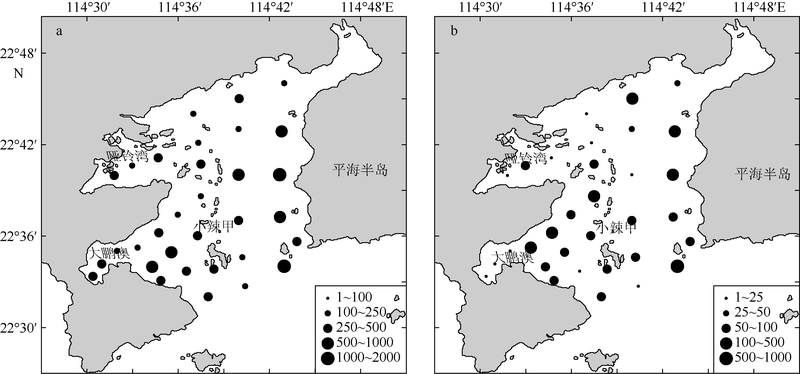
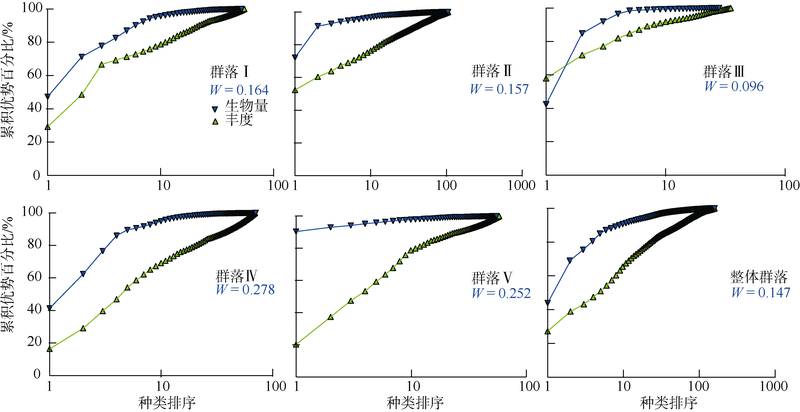
Community structure of macrobenthos in summer in Daya Bay
Taoping YUAN1,2( ), Hengxiang LI1, Lu LI1, Hui WANG1,2, Changping YANG3
), Hengxiang LI1, Lu LI1, Hui WANG1,2, Changping YANG3
- 1. Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Science, Guangzhou 510300, China
-
Received:2016-04-19Revised:2016-05-12Online:2017-01-18Published:2017-01-19 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (41206133)
Cite this article
Taoping YUAN, Hengxiang LI, Lu LI, Hui WANG, Changping YANG. Community structure of macrobenthos in summer in Daya Bay[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(1): 41-47.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
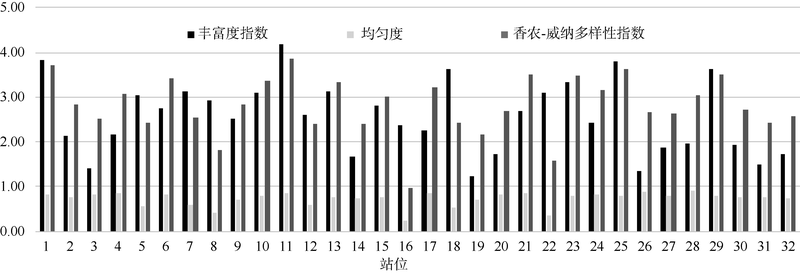
Tab. 2
Pearson correlations between community characteristics indices of macrobenthos and environmental factors"
| 环境因子 | 丰度 | 生物量 | 种类数 | 香浓-威纳指数H′ | 均匀度J | 丰富度指数D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黏土+粉砂 | -0.017 | 0.133 | 0.032 | 0.026 | -0.079 | -0.015 |
| 中值粒径 | -0.052 | 0.176 | 0.015 | 0.030 | -0.008 | 0.015 |
| 有机质 | -0.327 | -0.241 | -0.211 | -0.185 | 0.042 | -0.119 |
| 石油类 | -0.168 | -0.183 | -0.420* | -0.408* | 0.038 | -0.351* |
| 硫化物 | -0.041 | -0.092 | 0.176 | -0.224 | -0.171 | -0.217 |
| 铜(Cu) | -0.108 | -0.129 | -0.347 | -0.342 | -0.049 | -0.253 |
| 铅(Pb) | -0.252 | -0.219 | -0.242 | 0.220 | 0.045 | -0.105 |
| 锌(Zn) | 0.128 | 0.082 | 0.249 | 0.242 | 0.014 | 0.195 |
| 镉(Cd) | -0.020 | -0.183 | -0.170 | -0.173 | 0.009 | -0.103 |
| 铬(Cr) | -0.322 | -0.177 | -0.194 | -0.158 | 0.322 | 0.158 |
| 汞(Hg) | -0.128 | -0.080 | 0.055 | 0.114 | 0.106 | 0.159 |
| 砷(As) | -0.263 | -0.312 | -0.305 | -0.233 | 0.268 | 0.101 |
| [1] | 杜飞雁, 张汉华, 李纯厚, 等, 2008. 大亚湾大型底栖动物种类组成及物种多样性[J]. 中国水产科学, 15(2): 252-259. |
| DU FEIYAN, ZHANG HANHUA, LI CHUNHOU, et al, 2008. Species composition and diversity of macrobenthic fauna in Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 15(2): 252-259 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [2] | 杜飞雁, 王雪辉, 贾晓平, 等, 2011. 大亚湾海域大型底栖生物种类组成及特征种[J]. 中国水产科学, 18(4): 877-892. |
| DU FEIYAN, WANG XUEHUI, JIA XIAOPING, et al, 2011. Species composition and characteristics of macrobenthic fauna in Daya Bay, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 18(4): 877-892 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [3] | 范振刚, 1982. 胶州湾潮间带污染生态学的研究[J]. 海洋科学, (6): 39-41. |
| FAN ZHEN'GANG, 1982. Studies on the pollution ecology of inter tidal zone of the Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Marine Sciences, (6): 39-41 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [4] | 方良, 李纯厚, 杜飞雁, 等, 2010. 大亚湾海域浮游动物生态特征[J]. 生态学报, 30(11): 2981-2991. |
| FANG LIANG, LI CHUNHOU, DU FEIYAN, et al, 2010. Ecological characteristics of zooplankton in Daya Bay[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 30(11): 2981-2991 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 韩庆喜, 李宝泉, 韩秋影, 等, 2011. 渔业捕捞对威海港附近海域底上大型底栖群落结构影响的初步研究[J]. 海洋通报, 30(2): 121-126. |
| HAN QINGXI, LI BAOQUAN, HAN QIUYING, et al, 2011. Preliminary study of the impact of fishery trawling on epifauna community in the coastal water of Weihai Port[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 30(2): 121-126 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [6] | 何明海, 蔡尔西, 吴启泉, 等, 1988. 厦门西港底栖生物的生态[J]. 台湾海峡, 7(2): 189-194. |
| HE MINGHAI, CAI ERXI, WU QIQUAN, et al, 1988. Ecology of benthos in west harbour of Xiamen[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 7(2): 189-194 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [7] | 贾晓平, 林钦, 蔡文贵, 2002. 大亚湾马鞭洲大型爆破对周围水域环境与海洋生物影响的评估[J]. 水产学报, 26(4): 313-320. |
| JIA XIAOPING, LIN QIN, CAI WENGUI, 2002. Evaluation for the impact of large explosion at Mabianzhou island on the neighboring aquatic environment and marine organisms in Daya Bay[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 26(4): 313-320 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] | 江锦祥, 蔡尔西, 吴启泉, 等, 1990. 大亚湾底栖生物的种类组成和数量分布[C]//国家海洋局第三海洋研究所. 大亚湾海洋生态文集(II). 北京: 海洋出版社, 237-247. |
| [9] | 李宝泉, 李新正, 于海燕, 等, 2005. 胶州湾底栖软体动物与环境因子的关系[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 36(3): 193-198. |
| LI BAOQUAN, LI XINZHENG, YU HAIYAN, et al, 2005. Macrobenthic Mollusca fauna and its relations to environmental factors in Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 36(3): 193-198 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [10] | 李新正, 李宝泉, 王洪法, 等, 2006. 胶州湾潮间带大型底栖动物的群落生态[J]. 动物学报, 52(3): 612-618. |
| LI XINZHENG, LI BAOQUAN, WANG HONGFA, et al, 2006. Macrobenthic community of the intertidal zone of Jiaozhou Bay[J]. Acta Zoologica Sinica, 52(3): 612-618 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] | 王肇鼎, 练健生, 胡建兴, 等, 2003. 大亚湾生态环境的退化现状与特征[J]. 生态科学, 22(4): 313-320. |
| WANG ZHAODING, LIAN JIANSHENG, HU JIANXING, et al, 2003. Characteristics of degraded ecosystem in Daya Bay China[J]. Ecologic Science, 22(4): 313-320 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [12] | 徐恭昭, 1989. 大亚湾环境与资源[M]. 合肥: 安徽科学技术出版社, 193-208. |
| XU GONGZHAO, 1989. Environments and resources of Daya Bay[M]. Hefei: Anhui Science & Technology Publishing House, 193-208 (in Chinese). | |
| [13] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2008a. GB/T 12763.6-2007 海洋调查规范第6部分: 海洋生物调查[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China,Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China,2008a.GB/T 12763.6-2007, Specifications for oceanographic survey—Part 6: marine biological survey[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press (in Chinese). | |
| [14] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2008b. GB 17378.5-2007 海洋监测规范第5部分: 沉积物分析[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2008b. GB 17378.5-2007, The specification for marine monitoring—Part 5: sediment analysis[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press (in Chinese). | |
| [15] | AMBROSE R F, ANDERSON T W, 1990. Influence of an artificial reef on the surrounding infaunal community[J]. Marine Biology, 107(1): 41-52. |
| [16] | CARVALHO S, PEREIRA P, PEREIRA F, et al, 2011. Factors structuring temporal and spatial dynamics of macrobenthic communities in a eutrophic coastal lagoon (Óbidos lagoon, Portugal)[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 71(2): 97-110. |
| [17] | CHEN KOUPING, TIAN SHENGYAN, JIAO J J, 2010. Macrobenthic community in Tolo Harbour, Hong Kong and its relations with heavy metals[J]. Estuaries and Coasts, 33(3): 600-608. |
| [18] | GRAY J S, 1974. Animal-sediment relationships[J]. Oceanography and Marine Biology Annual Review, 12(12): 223-261. |
| [19] | HOLLAND A F, 1985. Long-term variation of macrobenthos in a mesohaline region of Chesapeake Bay[J]. Estuaries, 8(2A): 93-113. |
| [20] | HOLLAND A F, MOUNTFORD N K, HIEGEL M H, et al, 1980. influence of predation on infaunal abundance in upper Chesapeake Bay, USA[J]. Marine Biology, 57(3): 221-235. |
| [21] | LU L, 2005. The relationship between soft-bottom macrobenthic communities and environmental variables in Singaporean waters[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 51(8-12): 1034-1040. |
| [22] | MUTLU E, ÇINAR M E, ERGEV M B, 2010. Distribution of soft-bottom polychaetes of the Levantine coast of Turkey, eastern Mediterranean Sea[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 79(1-2): 23-35. |
| [23] | RELINI G, ZAMBONI N, TIXI F, et al, 1994. Patterns of sessile macrobenthos community development on an artificial reef in the Gulf of Genoa (northwestern Mediterranean). Bulletin of Marine Science, 55(2-3): 745-771 |
| [24] | RUDLING L, 1976. Oil pollution in the Baltic Sea. A chemical analytical search for monitoring methods[J]. National Swedish Environmental Protection Board, SNV PM, 783: 1-80. |
| [25] | WILSON W H, 1991. Competition and predation in marine soft-sediment communities[J]. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 21: 221-241. |
| [26] | WU R S S, SHIN P K S, 1997. Sediment characteristics and colonization of soft-bottom benthos: A field manipulation experiment[J]. Marine Biology, 128(3): 475-487. |
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [3] | XI Chen, LIN Zongxuan, SA Rula, DENG Xi, LIU Qiang, NI Liang, LUO Laicai, MA Teng, XIE Zhijie, CHEN Siruo, CHEN Songze. Analysis of water environmental changes and influencing factors in the southwestern waters of the Daya Bay based on continuous monitoring data from dual buoys [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 153-164. |
| [4] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [5] | LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [6] | GENG Wanlu, XING Yongze, ZHANG Qiufeng, GUAN Weibing. Structural characteristics of macrobenthic communities at intertidal zone for mangrove in Beihai, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [7] | SUN Cuici, YUE Weizhong, ZHAO Wenjie, WANG Youshao. Distribution of the microbial Carbohydrate-Active enzymes genes in the surface sediment of the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [8] | ZHANG Lanlan, CHENG Xiawen, XIANG Rong, QIU Zhuoya, CHANG Hu. Changes of radiolarian community structure with depth in the central Bay of Bengal in spring 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [9] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [10] | JIANG Xun, WU Wen, SONG Dehai. Identification and quantitative analysis of key controlling factors of water quality response to human activities in the Daya Bay, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(1): 182-191. |
| [11] | INYANG Aniefiok Ini, ZHOU Yueyue, WANG Youshao. Characteristics of water quality and their eutrophication assessment on the mangrove ecosystems along the Guangdong coast [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(6): 1-11. |
| [12] | CHEN Jingfu, ZHONG Yu, WANG Lei, GUO Yupei, QIU Dajun. Noctiluca scintillans effects on eukaryotic plankton community structure using Environmental DNA analysis in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [13] | MA Wengang, XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang, LI Xiubao, WANG Aimin. Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [14] | ZHANG Wanru, LIU Qingxia, HUANG Honghui, QIN Xiaoqing, LI Jiajun, CHEN Jianhua. Study on stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen of main fishery organisms in the southwestern waters of Daya Bay, South China Sea in winter 2020 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 147-155. |
| [15] | ZHU Wentao, XIA Jingquan, LIU Xiangbo, YIN Hongyang, ZHU Ming, REN Yuxiao, XIE Minrui, HUANG Jianzhong, LI Xiubao. Analysis of photosynthetic physiology and symbiotic fungi community in Galaxea fascicularis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 132-141. |
|
||