Journal of Tropical Oceanography ›› 2019, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 67-77.doi: 10.11978/2018058CSTR: 32234.14.2018058
• Marine Biology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on the macrozoobenthic community structure in intertidal zone of Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China
Tinghe LAI1,2( ), Binyuan HE1,2(
), Binyuan HE1,2( ), Zhongjian HUANG2, Qiao TANG3, Luyan QIN2, Ting ZHU2, Zhenni MO2, Li LIU2, Yunxu ZHONG4
), Zhongjian HUANG2, Qiao TANG3, Luyan QIN2, Ting ZHU2, Zhenni MO2, Li LIU2, Yunxu ZHONG4
- 1. Qinzhou University, Qinzhou 535011, China
2. Guangxi Academy of Oceanography, Nanning 530022, China
3. Guangxi Beilun Estuary National Reserve, Fangchenggang 538100, China
4. Guangxi Mangrove Research Center, Beihai 536000, China
-
Received:2018-05-31Revised:2018-08-29Online:2019-03-20Published:2019-04-15 -
Supported by:Science and Technology Project of State Oceanic Administration (YLFCJ20164006-F);Science and Technology Project of Guangxi Oceanic Administration (GXHYJ100);National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFC0506100)
CLC Number:
- P735.542
Cite this article
Tinghe LAI, Binyuan HE, Zhongjian HUANG, Qiao TANG, Luyan QIN, Ting ZHU, Zhenni MO, Li LIU, Yunxu ZHONG. Study on the macrozoobenthic community structure in intertidal zone of Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(2): 67-77.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
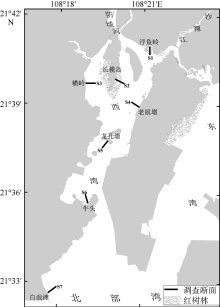
Tab. 1
Salinity, pH and habitat type at sampling stations for the intertidal macrozoobenthic community in Fangchenghe Estuary"
| 断面 | 渗出水盐度/‰ | 上覆水盐度/‰ | 渗出水pH | 上覆水pH | 生境特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 17.6~27.2 | 3.9~27.0 | 7.1~7.4 | 7.2~8.1 | 高、中潮带为桐花树林, 低潮带为沙泥质裸滩 |
| S2 | 21.0~27.8 | 6.5~28.1 | 7.1~7.4 | 7.3~8.2 | 高潮带为秋茄林, 中潮带为白骨壤林, 低潮带为沙泥质裸滩 |
| S3 | 23.4~28.8 | 11.5~29.3 | 7.2~7.6 | 7.4~8.2 | 3个潮带均为淤泥质裸滩 |
| S4 | 22.0~28.3 | 10.6~29.0 | 7.2~7.6 | 7.5~8.2 | 高、中潮带为人工沙质裸滩, 低潮带为沙泥质裸滩 |
| S5 | 27.0~31.0 | 17.6~30.2 | 7.4~7.7 | 7.5~8.3 | 3个潮带均为沙泥质的滩涂贝类养殖场 |
| S6 | 27.4~32.0 | 19.3~30.8 | 7.3~7.8 | 7.8~8.5 | 高潮带为白骨壤林, 中、低潮带为沙泥质的滩涂贝类养殖场 |
| S7 | 28.0~33.0 | 27.0~31.8 | 7.6~7.9 | 7.8~8.6 | 3个潮带均为天然沙质裸滩 |
Tab. 2
Density and biomass of macrozoobenthic communities in the intertidal zone of Fangchenghe Estuary and the relative important values V (units: %) of dominant populations"
| 断面 | 潮带 | 年均密度/(个?m-2) | 年均生物量/(g?m-2) | 优势种群及其相对优势度/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 高潮带 | 244 | 252.59 | CEC 68.88, GEC 14.73, GLA 3.64, GLC 3.60, SER 2.08 |
| 中潮带 | 297 | 92.97 | MIL 70.09, CEC 15.42, SER 6.59, BAL 4.80 | |
| 低潮带 | 115 | 193.25 | PHS 57.5, CEC 15.2, LAT 5.5, LAN 4.4, CYS 3.7 | |
| 全断面 | 219 | 179.60 | CEC 54.86, MIL 17.15, GEC 7.72, SER 4.59, PHS 3.60 | |
| S2 | 高潮带 | 151 | 401.79 | CEC 61.29, GEC 32.30, CEM 3.86, ONV 1.17 |
| 中潮带 | 138 | 226.24 | CEC 66.30, MIL 11.95, LAT 11.24, UCV 4.53, GEC 4.21 | |
| 低潮带 | 264 | 295.18 | CEC 78.52, LAT 8.72, SER 3.01, UCV 2.16, BAL 2.09 | |
| 全断面 | 184 | 307.74 | CEC 77.95, GEC 10.29, LAT 5.14, MIL 1.68, UCV 1.49 | |
| S3 | 高潮带 | 68 | 201.29 | CYS 64.98, ANL 15.68, MSJ 8.30, CEC 8.22 |
| 中潮带 | 50 | 146.06 | ANL 43.16, TEG 24.02, PHS 13.57, TRS 9.09, PEV 6.01 | |
| 低潮带 | 47 | 119.54 | PHS 61.17, ANL 22.67, MSJ 8.54, PLD 2.40, MOP 1.26 | |
| 全断面 | 55 | 155.63 | ANL 39.14, PHS 22.77, CYS 19.73, MSJ 7.22, TEG 2.84 | |
| S4 | 高潮带 | 66 | 60.33 | MIL 85.66, DOW 12.35, MEM 1.74 |
| 中潮带 | 44 | 63.34 | MIL 90.34, DOW 3.88, CYS 2.94, LAT 2.17 | |
| 低潮带 | 138 | 108.82 | CEC 37.09, RUP 33.58, MEM 16.38, LAN 4.72, MIL 4.27 | |
| 全断面 | 83 | 77.50 | MIL 69.42, DOW 8.11, CEC 7.02, MEM 6.97, RUP 6.36 | |
| S5 | 高潮带 | 256 | 577.28 | CYS 65.01, CEC 24.26, BAZ 3.79, MEM 3.11, UCV 1.30 |
| 中潮带 | 229 | 380.61 | BAZ 37.11, CEC 34.30, BAC 9.95, CYS 7.41, SIN 7.29 | |
| 低潮带 | 560 | 1080.09 | RUP 91.78, LAN 7.04 | |
| 全断面 | 348 | 679.33 | RUP 75.80, CYS 5.98, LAN 5.90, CEC 4.96, BAZ 2.80 | |
| S6 | 高潮带 | 522 | 334.98 | CEC 75.82, BAZ 19.73, MIL 3.16 |
| 中潮带 | 325 | 380.64 | MOR 38.73, BAZ 23.90, CEC 15.17, MIL 12.23, MEM 6.36 | |
| 低潮带 | 242 | 277.66 | CEC 76.28, BAZ 21.56 | |
| 全断面 | 363 | 331.09 | CEC 66.17, BAZ 24.65, MIL 3.73, MOR 3.26 | |
| S7 | 高潮带 | 178 | 181.39 | CYC 60.96, MAV 24.72, MIL 8.27, MAA 5.86 |
| 中潮带 | 85 | 87.39 | CYC 41.93, MAA 41.29, CRP 8.81, DOW 5.91, MAV 1.05 | |
| 低潮带 | 252 | 346.68 | CRP 32.88, CHS 22.92, MEM 22.80, MOR 8.16, PAV 7.86 | |
| 全断面 | 172 | 205.15 | CYC 41.95, MAV 17.81, CRP 11.14, MAA 9.76, CHS 4.70 |
Fig. 2
Indexes of species abundance (a), species diversity H′ (b), Richness d (c), and Evenness J (d) of macrozoobenthic communities seasonally sampled in the intertidal zone of Fangchenghe Estuary. Among the three letters in each legend, the first two letters are the abbreviation of sampling season: Sp = Spring, Su = Summer, Au = Autumn, and Wi = Winter; and the last letter is the abbreviation of tidal zone: H = high tidal zone, M = middle tidal zone and L = low tidal zone"
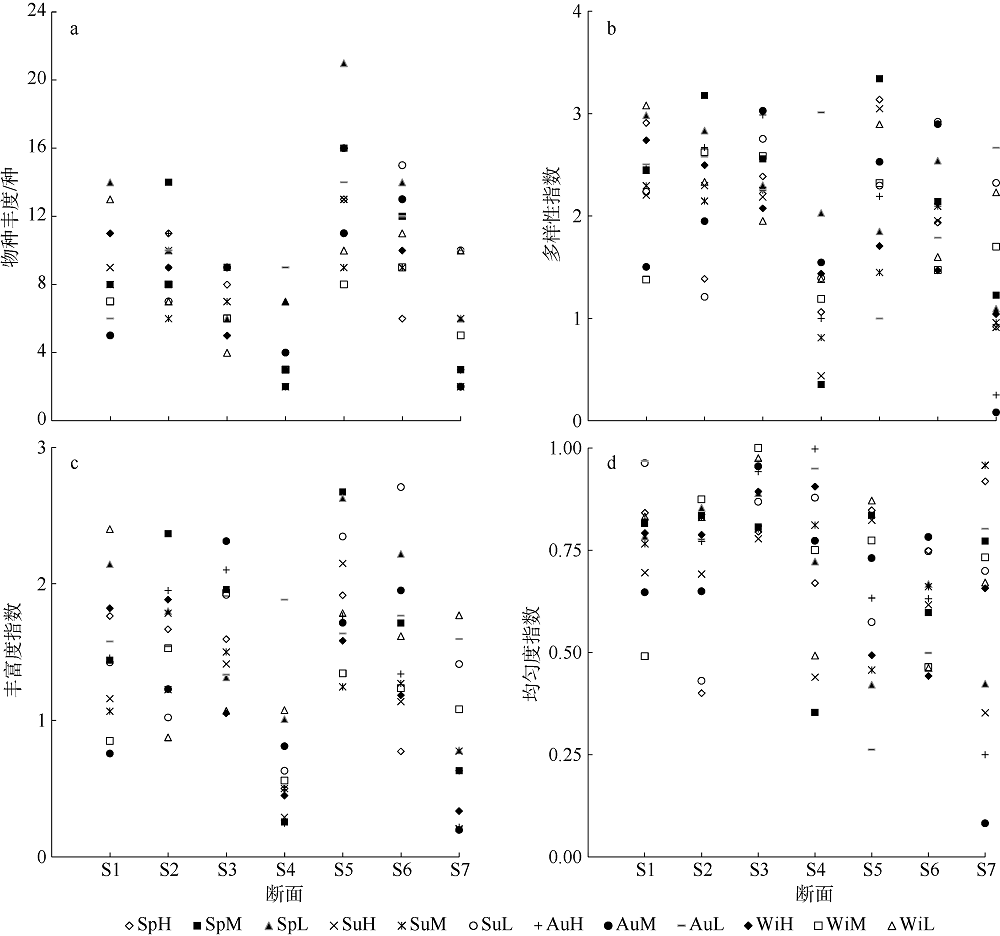
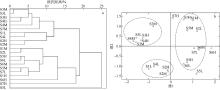
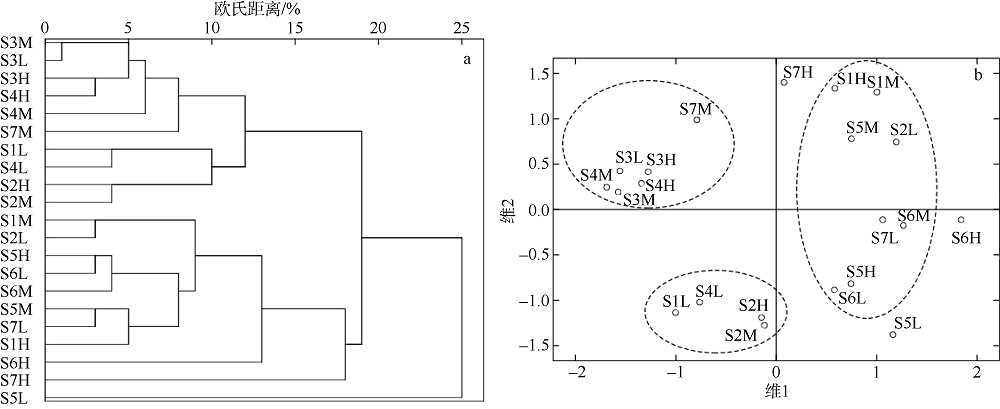
Fig. 3
The hierarchical cluster dendrogram (a) and 2-dimentional MDS ordinal configuration (b) of macrozoobenthic communities in the intertidal zone of Fangchenghe Estuary. H= high tidal zone, M= middle tidal zone and L= low tidal zone, Three dotted circles in figure b represent three major groups based on the MDS ordinal"
| [1] |
蔡立哲, 厉红梅, 林鹏, 等, 2001. 深圳河口潮间带泥滩多毛类的数量变化及环境影响[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 40(3): 741-750.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-0479.2001.03.016 |
|
CAI LIZHE, LI HONGMEI, LIN PENG, et al, 2001. Analysis of environmental effect and polychaete quantitative variations on intertidal mudflat in Shenzhen estuary[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 40(3): 741-750 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0438-0479.2001.03.016 |
|
| [2] |
蔡立哲, 林鹏, 厉红梅, 2007. 截污后深圳河落马洲段大型底栖动物群落的恢复过程[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 13(4): 497-500.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687x.2007.04.011 |
|
CAI LIZHE, LIN PENG, LI HONGMEI, 2007. Restoration process of macrofaunal community at Luomazhou section of the Shenzhen River after pollution interception[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied & Environmental Biology, 13(4): 497-500 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-687x.2007.04.011 |
|
| [3] |
崔磊, 吕颂辉, 董悦镭, 等, 2017. 围填海工程对淇澳岛附近水域环境因子与生物群落的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 36(2): 96-105.
doi: 10.11978/2016065 |
|
CUI LEI, LÜ SONGHUI, DONG YUELEI, et al, 2017. Influence on the biological community and environmental factors around Qi’ao Island caused by reclamation project[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 36(2): 96-105 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11978/2016065 |
|
| [4] | 顾炎斌, 宋文豪, 姚韡远, 等, 2013. 东营市河口区潮间带大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 海洋环境科学, 32(5): 702-706. |
| GU YANBIN, SONG WENHAO, YAO WEIYUAN, et al, 2013. Intertidal macrobenthic community structural features in Hekou district[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 32(5): 702-706 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [5] | 何斌源, 范航清, 张振日, 1998. 珍珠港红树林大型底栖动物生态的初步研究[M]//何其锐. 南海资源开发研究. 广州: 广东经济出版社: 1036-1048. |
| HE BINYUAN, FAN HANGQING, ZHANG ZHENRI, 1998. Preliminary study on the ecology of mangrove macrobenthos in Pearl bay, Guangxi [M]//HE QIRUI. Resources development and research in South China Sea. Guangzhou: Guangdong Economy Press: 1036-1048 (in Chinese). | |
| [6] |
何斌源, 邓朝亮, 罗砚, 2004. 环境扰动对钦州港潮间带大型底栖动物群落的影响[J]. 广西科学, 11(2): 143-147.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2004.02.015 |
|
HE BINYUAN, DENG CHAOLIANG, LUO YAN, 2004. Effect of environmental fluctuation on macrobenthos community in the intertidal flats of Qinzhou Harbor[J]. Guangxi Sciences, 11(2): 143-147 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9164.2004.02.015 |
|
| [7] | 何斌源, 赖廷和, 王欣, 等, 2013. 廉州湾滨海湿地潮间带大型底栖动物群落次级生产力[J]. 生态学杂志, 32(8): 2104-2112. |
| HE BINYUAN, LAI TINGHE, WANG XIN, et al, 2013. Secondary productivity of benthic macrofaunal community in intertidal zone of Lianzhou Bay, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 32(8): 2104-2112 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [8] |
何祥英, 苏搏, 许廷波, 等, 2012. 广西北仑河口红树林湿地大型底栖动物多样性的初步研究[J]. 湿地科学与管理, 8(2): 44-48.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3290.2012.02.13 |
|
HE XIANGYING, SU BO, XU TINGBO, et al, 2012. Macrobenthic biodiversity in mangrove wetland at the estuary of Beilun River in Guangxi. Wetland Science & Management, 8(2): 44-48 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3290.2012.02.13 |
|
| [9] |
贺心然, 陈斌林, 高文婕, 等, 2015. 灌河口潮间带及其入海河段秋季大型底栖动物生态学研究[J]. 海洋科学, 39(5): 28-35.
doi: 10.11759/hykx20140719001 |
|
HE XINRAN, CHEN BINLIN, GAO WENJIE, et al, 2015. Ecological studies of macrobenthos in the intertidal zone and near sea section of Guan River in autumn[J]. Marine Sciences, 39(5): 28-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.11759/hykx20140719001 |
|
| [10] | 侯森林, 余晓韵, 鲁长虎, 2011. 盐城自然保护区射阳河口潮间带大型底栖动物空间分布与季节变化[J]. 生态学杂志, 30(2): 297-303. |
| HOU SENLIN, YU XIAOYUN, LU CHANGHU, 2001. Spatial distribution and seasonal variation of macrobenthos in intertidal flat of Sheyang estuary, Yancheng Nature Reserve[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 30(2): 297-303 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [11] |
金亮, 蔡立哲, 周细平, 等, 2007. 深圳湾北岸泥滩大型底栖动物次级生产力研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 26(3): 415-421.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2007.03.016 |
|
JIN LIANG, CAI LIZHE, ZHOU XIPING, et al, 2007. Secondary production of macrobenthos on the mudflat of northern Shenzhen Bay[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 26(3): 415-421 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2007.03.016 |
|
| [12] | 李国强, 叶伟鹏, 余怀勇, 等, 2017. 平潭岛中国鲎保护区沙质潮间带的大型底栖动物群落[J]. 海洋环境科学, 36(2): 179-185. |
| LI GUOQIANG, YE WEIPENG, YU HUAIYONG, et al, 2017. Community of benthic macrofauna on sandy intertidal zone in Chinese horseshoe crab reserve in Pingtan Island, China[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 36(2): 179-185 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [13] | 厉红梅, 李适宇, 蔡立哲, 2003. 深圳湾潮间带底栖动物群落与环境因子的关系[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 42(5): 93-96. |
| LI HONGMEI, LI SHIYU, CAI LIZHE, 2003. Relationship between benthic community and environmental factors in Shenzhen Bay[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 42(5): 93-96 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [14] | 厉红梅, 孟海涛, 2004. 深圳湾底栖动物群落结构时空变化环境影响因素分析[J]. 海洋环境科学, 23(1): 37-40. |
| LI HONGMEI, MENG HAITAO, 2004. Analysis of environmental factors impacting spatio-temporal variation of benthic community structure in Shenzhen Bay[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 23(1): 37-40 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [15] | 黎清华, 万世明, 何军, 等, 2014. 近两百年来人类活动对北部湾潮间带环境的影响[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(1): 57-64. |
| LI QINGHUA, WAN SHIMING, HE JUN, et al, 2014. Human impact on the intertidal environment in Beibu Gulf over the last 200 years[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 34(1): 57-64 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [16] |
李晓静, 周政权, 陈琳琳, 等, 2016. 山东烟台大沽夹河河口及邻近海域大型底栖动物群落特征[J]. 生物多样性, 24(2): 157-165.
doi: 10.17520/biods.2015217 |
|
LI XIAOJING, ZHOU ZHENGQUAN, CHEN LINLIN, et al.Characteristics of macrobenthic communities in the estuary of Dagujia River and its adjacent water areas in Yantai, Shandong[J]. Biodiversity Science, 24(2): 157-165 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.17520/biods.2015217 |
|
| [17] |
刘修泽, 李轶平, 于旭光, 等, 2011. 旅顺南部基岩海岸潮间带大型底栖动物的群落结构研究[J]. 水产科学, 30(12): 777-780.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2011.12.012 |
|
LIU XIUZE, LI YIPING, YU XUGUANG, et al, 2011. The community structure of macrobenthos in intertidal zones in rocky shore in south Lvshun in Dalian[J]. Fisheries Science, 30(12): 777-780 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2011.12.012 |
|
| [18] | 陆健健, 2003. 河口生态学[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社. |
| LU JIANJIAN, 2003. Estuary ecology[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press (in Chinese). | |
| [19] | 许铭本, 赖俊翔, 张荣灿, 等, 2015. 北仑河口北岸潮间带大型底栖动物生态特征及潮间带环境质量评价[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 35(1): 57-61. |
| XU MINGBEN, LAI JUNXIANG, ZHANG RONGCAN, et al, 2015. Ecological characteristics of macrobenthic animals and environmental quality on the north shore intertidal zone of Beilun estuary[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 35(1): 57-61 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [20] |
叶属峰, 纪焕红, 曹恋, 等, 2004. 河口大型工程对长江河口底栖动物种类组成及生物量的影响研究[J]. 海洋通报, 23(4): 32-37.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2004.04.006 |
|
YE SHUFENG, JI HUANHONG, CAO LIAN, et al, 2004. Studies on the impacts of large-scale estuarine engineering on species composition and biomass of benthos in the Yangtze River estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 23(4): 32-37 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2004.04.006 |
|
| [21] |
袁兴中, 陆健健, 2002. 长江口潮滩湿地大型底栖动物群落的生态学特征[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 11(5): 414-420.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2002.05.005 |
|
YUAN XINGZHONG, LU JIANJIAN, 2002. Ecological characteristics of macrozoobenthic community of tidal flat wetland in the Changjiang estuary[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 11(5): 414-420 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2002.05.005 |
|
| [22] |
张敬怀, 2014. 珠江口及邻近海域大型底栖动物多样性随盐度、水深的变化趋势[J]. 生物多样性, 22(3): 302-310.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13141 |
|
ZHANG JINGHUAI, 2014. The variation of biodiversity of macrobenthic fauna with salinity and water depth near the Pearl Estuary of the northern South China Sea[J]. Biodiversity Science, 22(3): 302-310 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2014.13141 |
|
| [23] | 张莹, 吕振波, 徐宗法, 等, 2012. 环境污染对小清河口大型底栖动物多样性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志 |
| ZHANG YING, LV ZHENBO, XU ZONGFA, et al, 2012, Impacts of environmental pollution on macrobenthos diversity in Xiaoqing estuary of Shandong Province, East China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 31(2): 381-387 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [24] |
赵永强, 曾江宁, 高爱根, 等, 2009. 椒江口滩涂大型底栖动物群落格局与多样性[J]. 生物多样性, 17(3): 303-309.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.03.057 |
|
ZHAO YONGQIANG, ZENG JIANGNING, GAO AIGEN, et al, 2009. Community pattern and diversity of macrozoobenthos in an intertidal flat, Jiaojiang Estuary[J]. Biodiversity Science, 17(3): 303-309 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2009.03.057 |
|
| [25] | 周进, 纪炜炜, 2012. 三都澳大型底栖动物次级生产力[J]. 海洋渔业, 34(1): 32-38. |
| ZHOU JIN, JI WEIWEI, 2012. Secondary productivity of macrobenthos in Sandu Bay[J]. Marine Fisheries, 34(1): 32-38 (in Chinese with English abstract). | |
| [26] |
ARBI I, ZHANG JINGPING, LIU SONGLIN, et al, 2017. Benthic habitat health assessment using macrofauna communities of a sub-tropical semi-enclosed bay under excess nutrients[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 119(2): 39-49.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.03.042 |
| [27] |
BELAN T A, 2003. Marine environmental quality assessment using polychaete taxocene characteristics in Vancouver Harbour[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 57(1-2): 89-101.
doi: 10.1016/S0141-1136(03)00062-X pmid: 12962648 |
| [28] |
CARCEDO M C, FIORI S M, PICCOLO M C, et al, 2015. Variations in macrobenthic community structure in relation to changing environmental conditions in sandy beaches of Argentina[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 166: 56-64.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.03.005 |
| [29] |
CHAPMAN M G, TOLHURST T J, 2004. The relationship between invertebrate assemblages and bio-dependant properties of sediment in urbanized temperate mangrove forests[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 304(1): 51-73.
doi: 10.1016/j.jembe.2003.11.019 |
| [30] |
EDGAR G J, BARRETT N S, 2002. Benthic macrofauna in Tasmanian estuaries: Scales of distribution and relationships with environmental variables[J]. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology, 270(1): 1-24.
doi: 10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00014-X |
| [31] |
FUJII T, 2007. Spatial patterns of benthic macrofauna in relation to environmental variables in an intertidal habitat in the Humber estuary, UK: Developing a tool for estuarine shoreline management[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 75(1-2): 101-119.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2007.02.027 |
| [32] |
GESTEIRA J L G, DAUVIN J-C, 2000. Amphipods are good bioindicators of the impact of oil spills on soft-bottom macrobenthic communities[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40(11): 1017-1027.
doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00046-1 |
| [33] |
OCCHIPINTI-AMBROGI A, SAVINI D, FORNI G, 2005. Macrobenthos community structural changes off Cesenatico coast (Emilia Romagna, Northern Adriatic), a six-year monitoring programme[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 353(1-3): 317-328.
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.09.021 pmid: 16257433 |
| [34] |
OTANI S, KOZUKI Y, KURATA K, et al, 2008. Relationship between macrobenthos and physical habitat characters in tidal flat in eastern Seto Inland Sea, Japan[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 57(1-5): 142-148.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2007.10.010 pmid: 18405925 |
| [35] | PICANÇO T C, ALMEIDA C M R, ANTUNES C, et al, 2014. Influence of the abiotic characteristics of sediments on the macrobenthic community structure of the Minho estuary saltmarsh (Portugal)[J]. Limnetica, 33(1): 73-88. |
| [36] | REHITHA T V, ULLAS N, VINEETHA G, et al, 2017. Impact of maintenance dredging on macrobenthic community structure of a tropical estuary[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 144: 71-82. |
| [37] | SARKER J, TANMAY M H, RAHMAN F, et al, 2016. Assessment of coastal water pollution in Greater Noakhali-Bangladesh[J]. Journal of Coastal Zone Management, 19: 427. |
| [1] | LIU Yuan, KE Zhixin, LI Kaizhi, TAN Yehui, LIANG Junce, ZHOU Weihua. Zooplankton community in the coastal waters of eastern Guangdong under the influence of human activities and ocean currents [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 98-111. |
| [2] | LIU Didi, ZHANG Xiyang, SUN Fulin, WANG Mingzhuang, TAN Fei, SHI Qi, WANG Guan, YANG Hongqiang. Microbial communities and specific strains within beachrocks of the South China Sea: implications for the origin of beachrock* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(4): 112-122. |
| [3] | HU Simin, ZHOU Tiancheng, ZHANG Chen, LIU Sheng, LI Tao, HUANG Hui. Effect of suspended solids on zooplankton community and their feeding selectivity in the Sanya coral waters [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 122-130. |
| [4] | LUO Yong, HUANG Lintao, YANG Jianhui, LIAN Jiansheng, LIU Chengyue, JIANG Lei, LIANG Yuxian, CHEN Lunju, LEI Xinming, LIU Sheng, HUANG Hui. Community structure of reef-building corals and their environmental impact factors in the coastal waters of Hongpai-Maniao, Lingao, Hainan [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(3): 72-86. |
| [5] | GENG Wanlu, XING Yongze, ZHANG Qiufeng, GUAN Weibing. Structural characteristics of macrobenthic communities at intertidal zone for mangrove in Beihai, Guangxi [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [6] | ZHANG Lanlan, CHENG Xiawen, XIANG Rong, QIU Zhuoya, CHANG Hu. Changes of radiolarian community structure with depth in the central Bay of Bengal in spring 2019 [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(4): 166-175. |
| [7] | SONG Xingyu, LIN Yajun, ZHANG Liangkui, XIANG Chenhui, HUANG Yadong, ZHENG Chuanyang. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of meso- and micro-zooplankton communities in the offshore waters of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(3): 136-148. |
| [8] | CHEN Jingfu, ZHONG Yu, WANG Lei, GUO Yupei, QIU Dajun. Noctiluca scintillans effects on eukaryotic plankton community structure using Environmental DNA analysis in Daya Bay* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(5): 121-132. |
| [9] | MA Wengang, XIA Jingquan, WEI Yifan, YIN Hongyang, QIN Lezheng, LIU Xiangbo, HU Xueqing, XU Qiang, LI Xiubao, WANG Aimin. Community structure evaluation of epifaunal macrozoobenthos in the near-island waters of marine ranching in Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(3): 135-146. |
| [10] | ZHU Wentao, XIA Jingquan, LIU Xiangbo, YIN Hongyang, ZHU Ming, REN Yuxiao, XIE Minrui, HUANG Jianzhong, LI Xiubao. Analysis of photosynthetic physiology and symbiotic fungi community in Galaxea fascicularis [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2): 132-141. |
| [11] | ZHANG Liming, TAN Yehui, LI Jiajun, HUANG Xiaoping, LIU Jiaxing. Characteristics of the phytoplankton community and its response to Dan’ao River input in Daya Bay in summer* [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(5): 43-54. |
| [12] | Tongchen LIAO, Jianqiang YIN, Kaizhi LI, Yehui TAN. Distribution of planktonic ostracods and its influencing factors during summer and winter in the northwestern coastal waters of South China Sea [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 77-87. |
| [13] | Yuzheng REN, Zhixin KE, Yehui TAN, Kaizhi LI. Community structure of zooplankton and its influencing factors in the eastern waters of Nan’ao Island, Guangdong [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2020, 39(2): 65-76. |
| [14] | Sixuan HE,Binyuan HE. Study on fish community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in Fangchenghe Estuary of Guangxi, China [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2019, 38(5): 86-97. |
| [15] | Zhangfeng LUO, Zhanqiang FANG. A study on the community structure of macrobenthos during the period of artificial mangrove restoration in Mangzhou wetland of Hengqin Island, Zhuhai [J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(3): 61-72. |
|
||